The Bosniak classification of cystic renal lesions was first published in 1986 based on computed tomography (CT). In the present study, we aimed to investigate the effect of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) on Bosniak category compared with CT, and to determine how this effect changed the treatment modality in the evaluation of complex renal cysts.
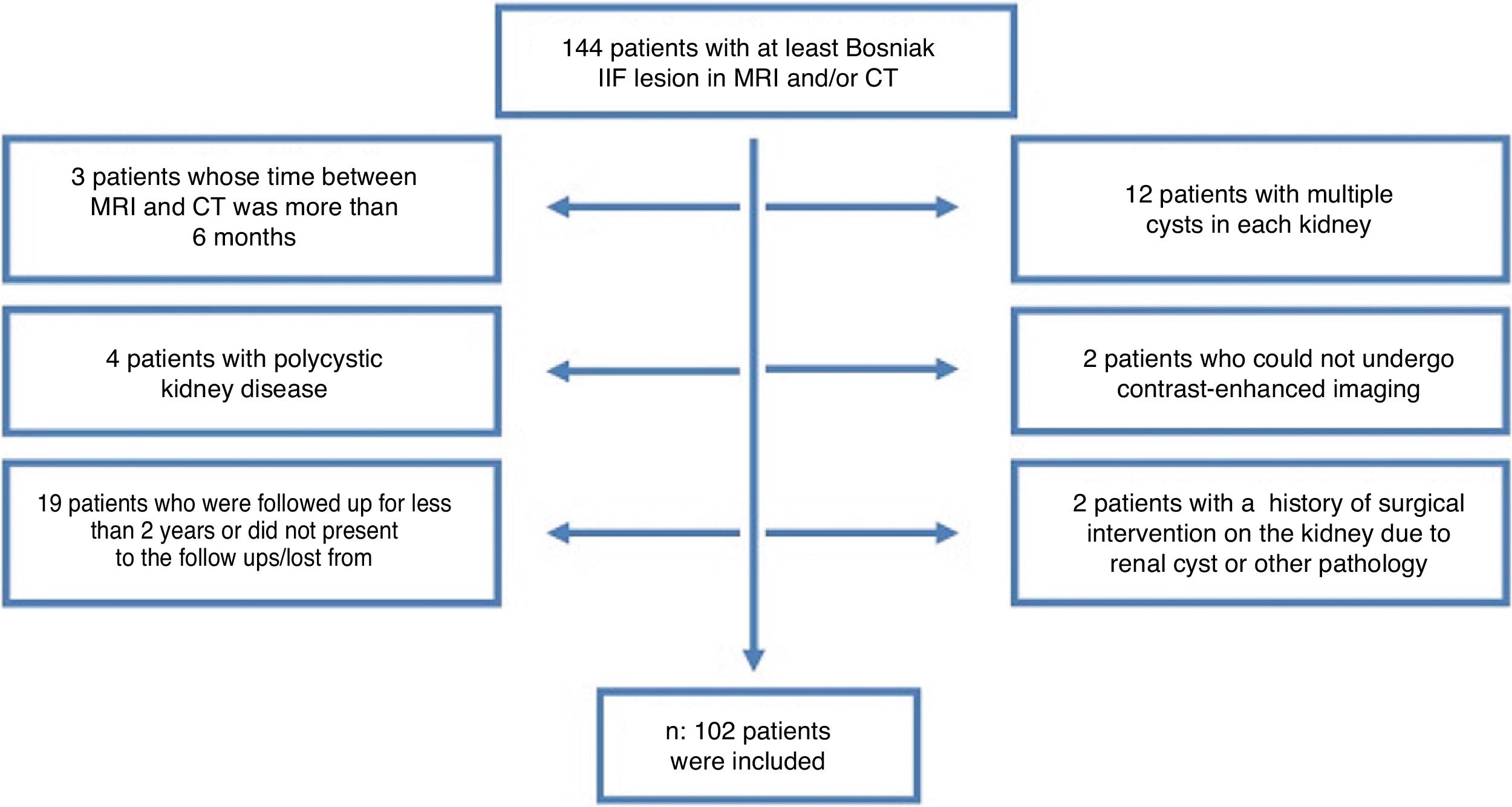
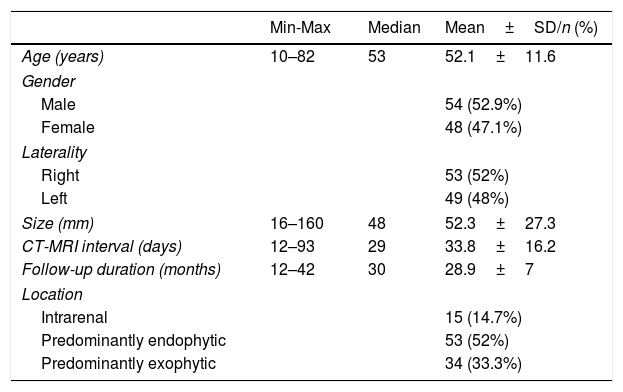
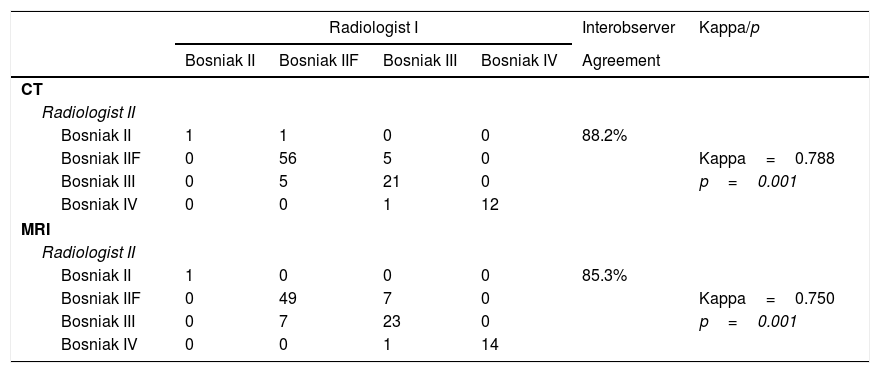
Material and methodsData of 144 patients were collected retrospectively. After exclusion criteria, 102 cystic renal lesions with a Bosniak category of at least IIF on CT or MRI between 2013 and 2016 were evaluated by 2 abdominal radiologists. The demographic data, Bosniak category, interobserver agreement, and pathologic data of patients who underwent surgery were recorded.
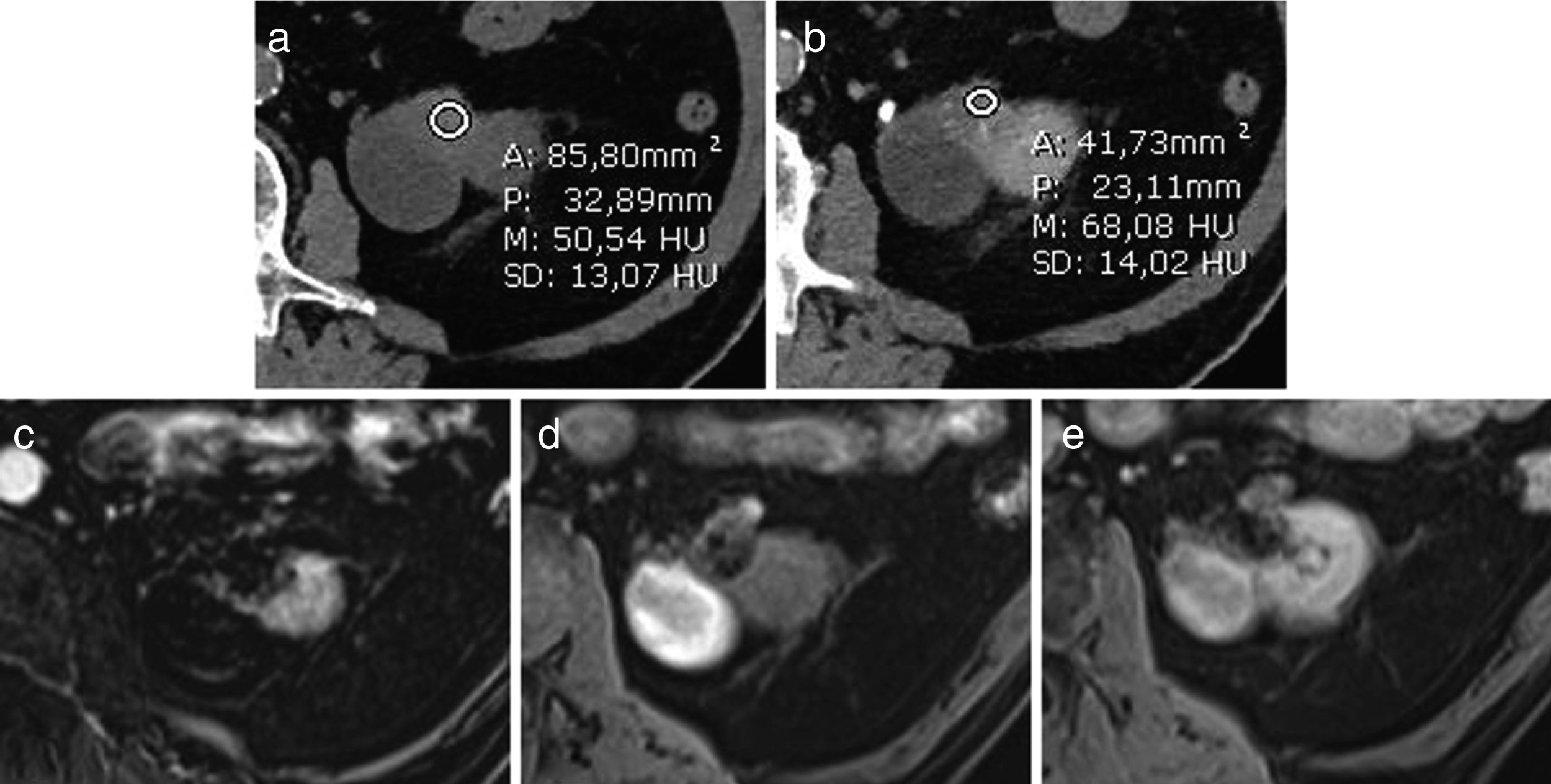
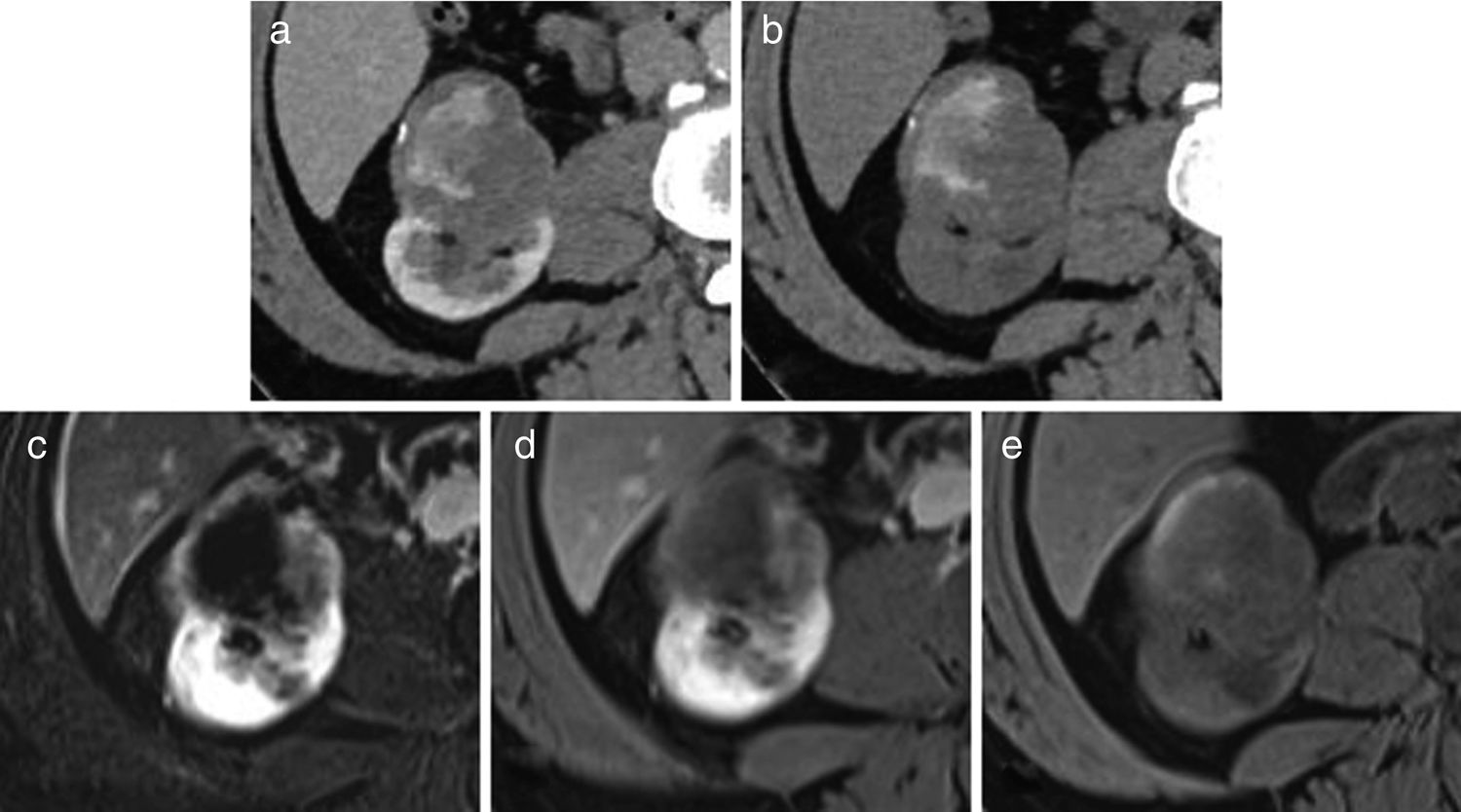
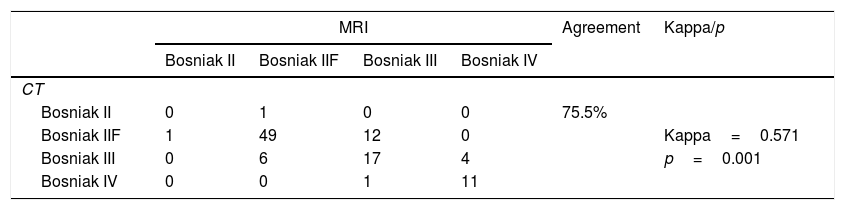
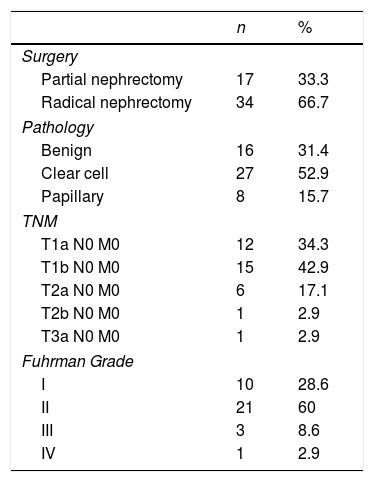
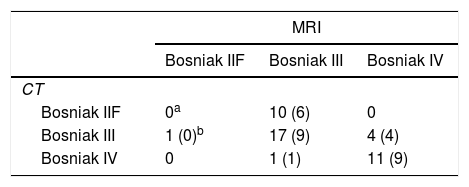
ResultsThe coherence between MRI and CT was 75.5%. The Bosniak classification of 17 patients was upgraded with MRI, and the treatment modality changed in 10 patients, and they underwent surgery. The Bosniak category was downgraded from III to IIF in 6 patients out of 8 whose Bosniak category was downgraded with MRI and the treatment modality changed. Surgery was performed in one patient out of these 6 patients, and the pathology was reported as benign. Progression was detected in the follow-up at month 18 of 1 patient out of 5, and surgery was performed. The pathology was reported as renal cell carcinoma. The pathology result was reported as RCC in 35 (68.6%) patients out of 51 who underwent surgery. Progression was detected in 7 patients out of 51 who were followed up (13.7%), and the pathology results were reported as RCC. The majority of the malignant tumors were low stage and grade.
ConclusionsMRI may be successfully used in the evaluation of renal cystic lesions. In particular, the challenging Bosniak IIF and all Bosniak III lesions must be evaluated using MRI before making the decision for surgery. The upgrading of Bosniak category with MRI is more possible compared with CT due to its high-contrast resolution, therefore further studies are required to identify whether it was the cause of overtreatment of Bosniak III lesions.
La clasificación de Bosniak para las lesiones renales quísticas se publicó por primera vez en 1986 con base en los hallazgos de tomografía computarizada (TC). El objetivo de nuestro estudio fue investigar el rol de la resonancia magnética (RM) y su impacto en la clasificación de Bosniak para compararla con la TC, y determinar cómo la RM puede alterar el tipo de tratamiento de los quistes renales complejos.
Material y métodosSe recogieron retrospectivamente los datos de 144 pacientes. Después de aplicar los criterios de exclusión, 2radiólogos especialistas en ecografía abdominal evaluaron 102 lesiones quísticas renales con una categoría Bosniak de al menos IIF en TC o RM entre 2013 y 2016. Se registraron los datos demográficos, la categoría de Bosniak, la concordancia interobservador y las enfermedades de los pacientes tratados con cirugía.
ResultadosLa concordancia entre la RM y la TC fue del 75,5%. La categoría Bosniak se vio incrementada tras la RM en 17 pacientes, y se cambió el tipo de tratamiento en 10 pacientes, que posteriormente fueron tratados quirúrgicamente. Tras la RM, la categoría Bosniak pasó de III a IIF en 6 pacientes de 8 y provocó un cambio en el tipo de tratamiento. Se realizó cirugía en un paciente de estos 6, y el informe de anatomía patológica se informó como benigno. Se detectó progresión durante el seguimiento al decimoctavo mes en un paciente de 5, y se practicó cirugía en este caso. La enfermedad se informó como carcinoma de células renales (CCR). De los 51 pacientes tratados mediante cirugía, 35 (68,6%) recibieron informe anatomopatológico de CCR. Se detectó progresión en 7 pacientes de 51 que recibieron seguimiento (13,7%), y los resultados de la enfermedad se informaron como CCR. La mayoría de los tumores malignos eran de grado y estadio bajo.
ConclusionesLa RM se puede emplear con éxito en la evaluación de lesiones quísticas renales. En particular, el manejo de las lesiones Bosniak IIF y de todas aquellas clasificadas como Bosniak III debe incluir evaluación mediante RM antes de optar por el tratamiento quirúrgico. El incremento en la categoría de Bosniak es más factible con RM que con TC, debido a su resolución de alto contraste. Por lo tanto, se requieren más estudios para identificar si esta fue la causa del sobretratamiento en pacientes con lesiones Bosniak III.