To compare the oncological outcomes between two open surgical techniques and two endoscopic approaches for the management of the distal ureter during laparoscopic radical nephroureterectomy (LRNU).
Material and methodsRetrospective review of 152 patients submitted to LRNU for the management of upper urinary tract tumors between 2007 and 2014. We analyzed the potential impact of two different open surgical (extravesical vs intravesical) and two endoscopic (resection of ureteral orifice and fragment removal vs endoscopic bladder cuff) techniques on the development of bladder recurrence, distant/local recurrence and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
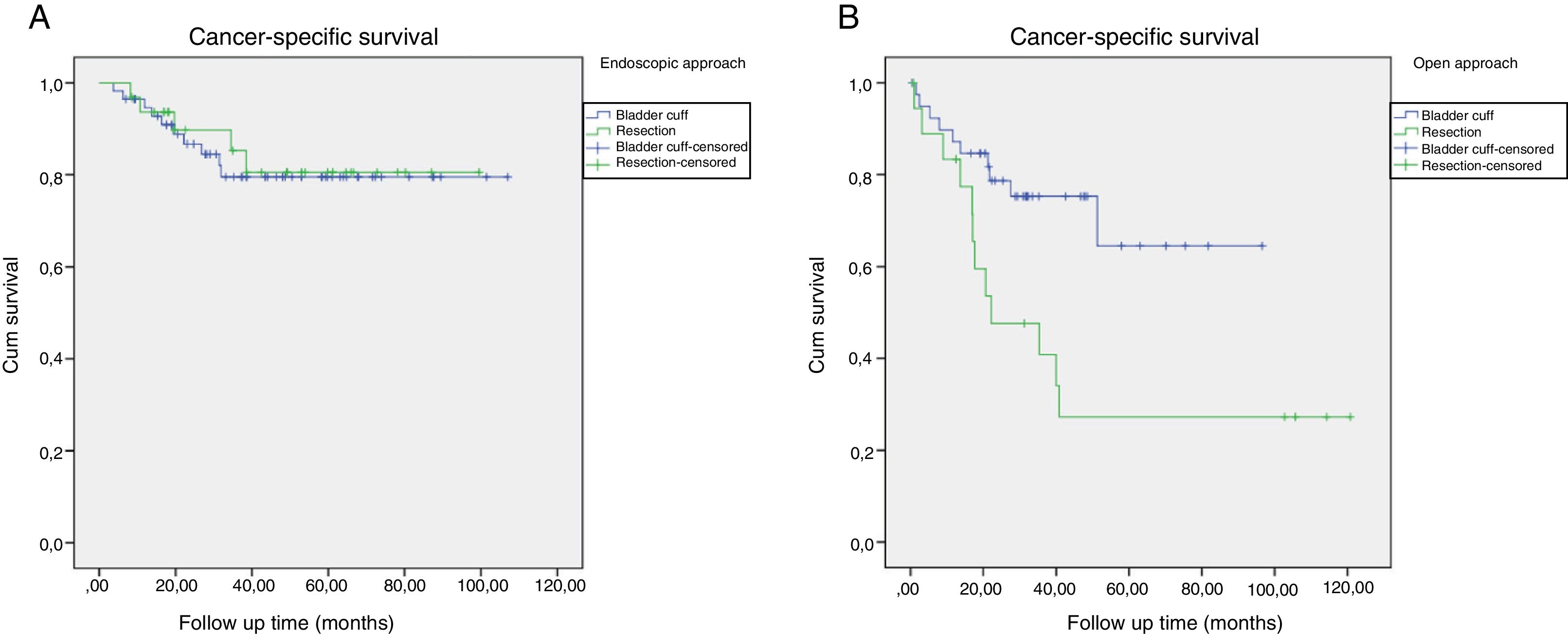
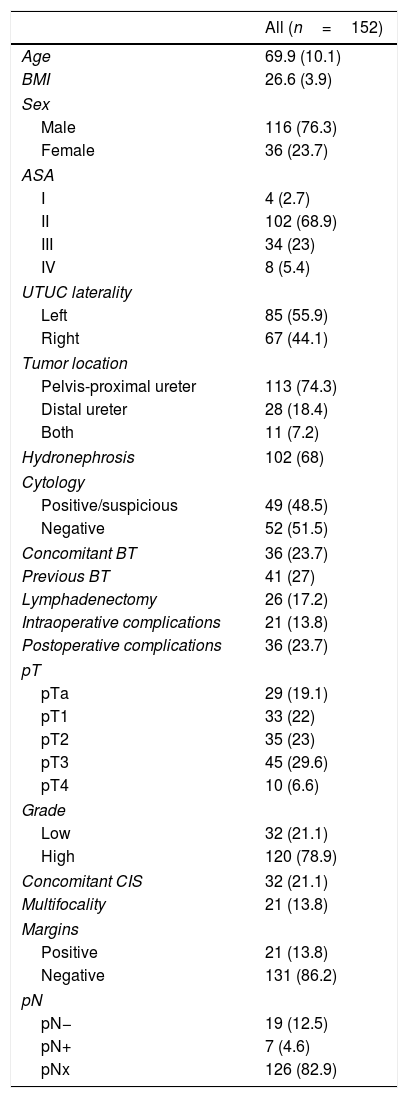
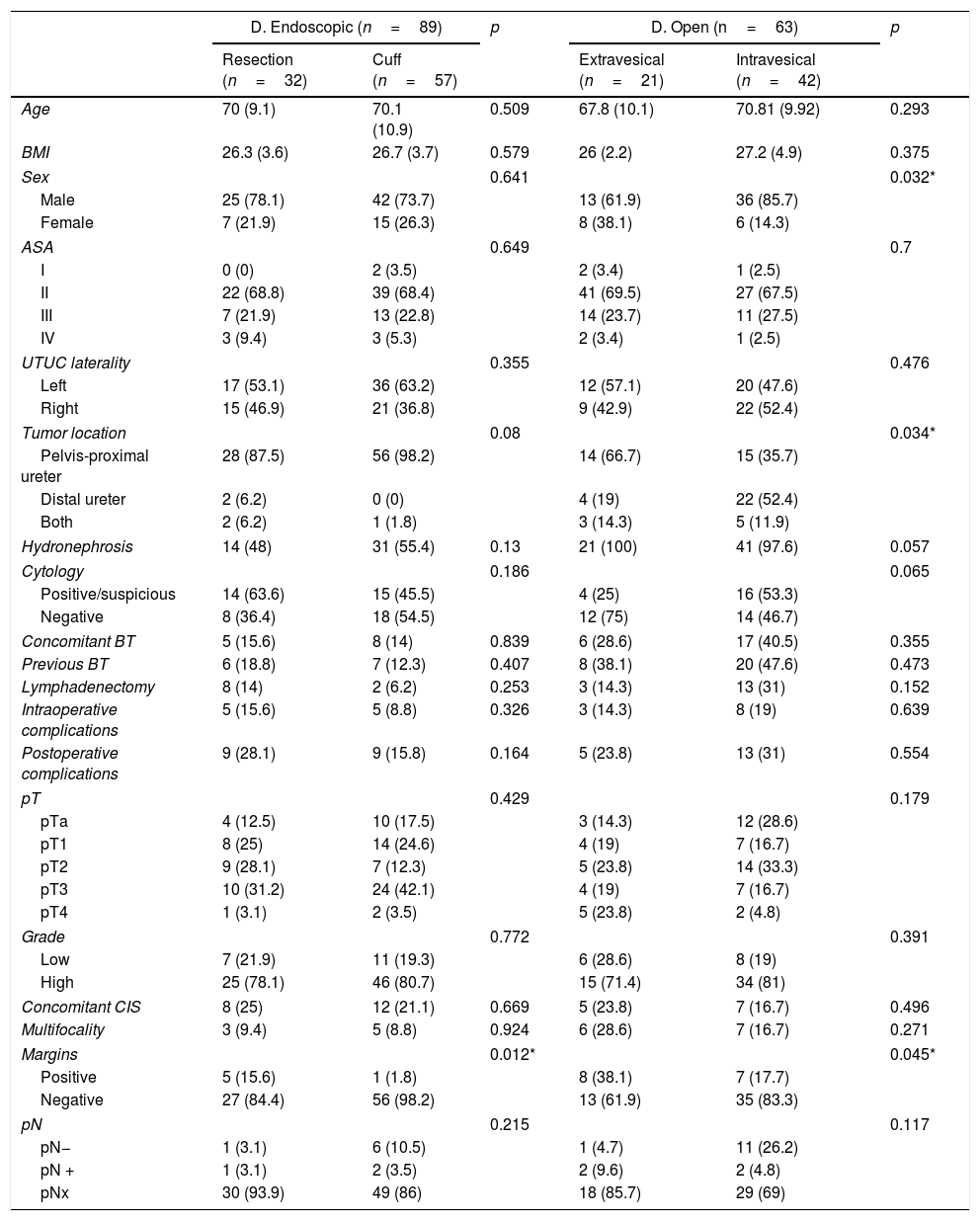
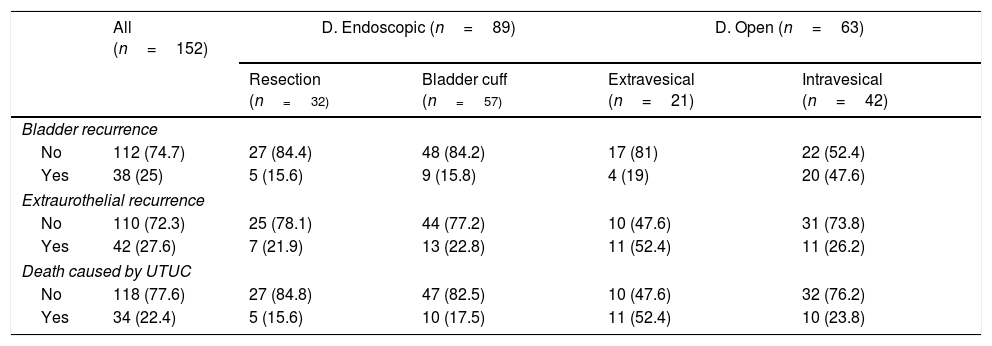
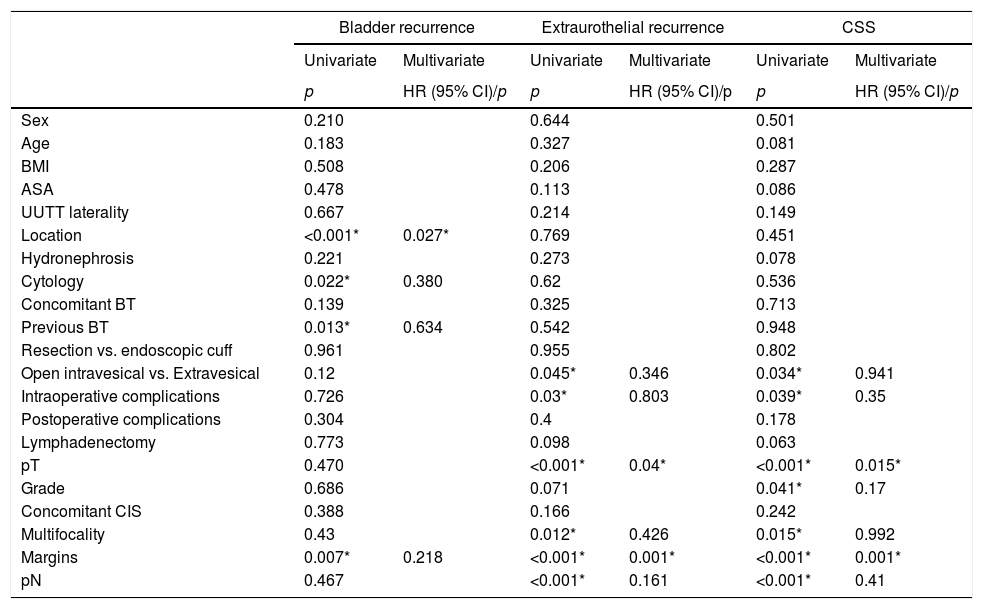
ResultsA total of 152 patients with a mean age of 69.9 years (±10.1) underwent LRNU. We reported 62 pTa-T1 (41%), 35 pT2 (23%) and 55 pT3-4 (36%). Thirty-two were low grade (21.1%) and 120 high grade (78.9%). An endoscopic approach was performed in 89 cases (58.5%), 32 with resection (36%) and 57 with bladder cuff (64%), and open approach in 63 (41.5%), 42 intravesical (66.7%) and 21 extravesical (33.3%). Within a median follow-up of 32 months (3–120), 38 patients (25%) developed bladder recurrence, 42 distant/local recurrence (27.6%) and 34 died of tumor (22.4%). In the univariate analysis, the type of endoscopic technique was not related to bladder recurrence (p=0.961), distant/local recurrence (p=0.955) nor CSS (p=0.802). The open extravesical approach was not related to bladder recurrence (p=0.12) but increased distant/local recurrence (p=0.045) and decreased CSS (p=0.034) compared to intravesical approach.
ConclusionsLRNU outcomes are not dependant on the type of endoscopic approach performed. The open extravesical approach is a more difficult technique and could worsen the oncological outcomes when compared to the intravesical.
Comparar los resultados oncológicos de dos técnicas quirúrgicas abiertas y dos endoscópicas para el manejo del uréter distal durante nefroureterectomía laparoscópica (NUL).
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de 152 pacientes sometidos a NUL por tumor del tramo urinario superior entre 2007 y 2014. Se analizó el potencial impacto de distintas técnicas de desinserción abierta (extravesical vs. intravesical) y endoscópica (resección meato con evacuación de fragmentos vs. rodete perimeático) sobre el desarrollo de recidiva vesical, extraurotelial y supervivencia cáncer-específica (SCE).
ResultadosUn total de 152 pacientes con edad media de 69,9 años (±10,1) fueron sometidos a NUL. Se reportaron 62 pTa-T1 (41%), 35 pT2 (23%) y 55 pT3-4 (36%). Treinta y dos fueron bajo grado (21,1%) y 120 alto grado (78,9%). Se realizó desinserción endoscópica en 89 casos (58,5%), 32 con resección (36%) y 57 con rodete (64%), y abierta en 63 (41,5%), 42 intravesical (66,7%) y 21 extravesical (33,3%). Con mediana de seguimiento de 32 meses (3-120), 38 pacientes (25%) desarrollaron recidiva vesical, 42 extraurotelial (27,6%) y 34 murieron por tumor (22,4%). En el análisis univariante, el tipo de técnica endoscópica no se relacionó con recidiva vesical (p=0,961), extraurotelial (p=0,955) ni SCE (p=0,802). El abordaje abierto extravesical no se relacionó con recidiva vesical (p=0,12) pero sí con aumento de recidiva extraurotelial (p=0,045) y menor SCE (p=0,034) respecto al intravesical.
ConclusionesEl subtipo de desinserción endoscópica no influye en los resultados de la NUL. La desinserción abierta extravesical es una técnica más compleja que la intravesical y podría empeorar los resultados oncológicos.