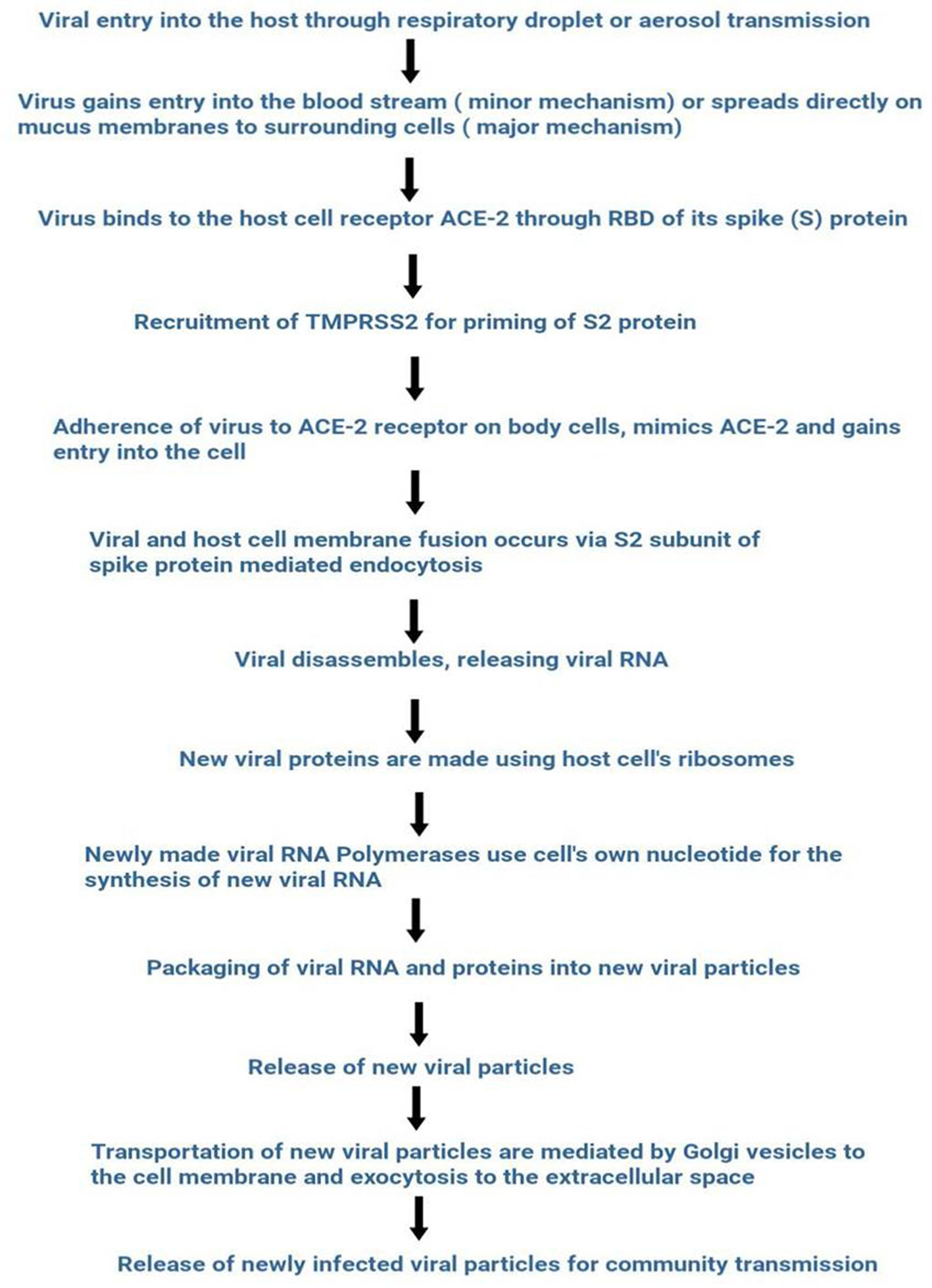
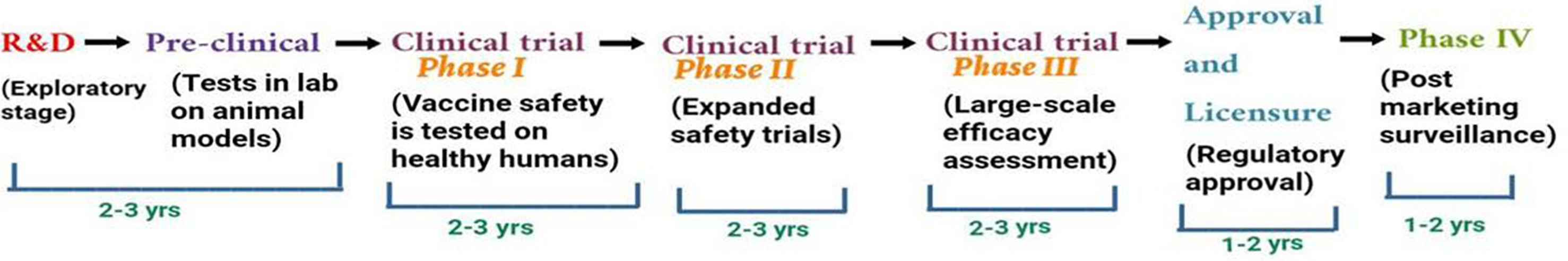
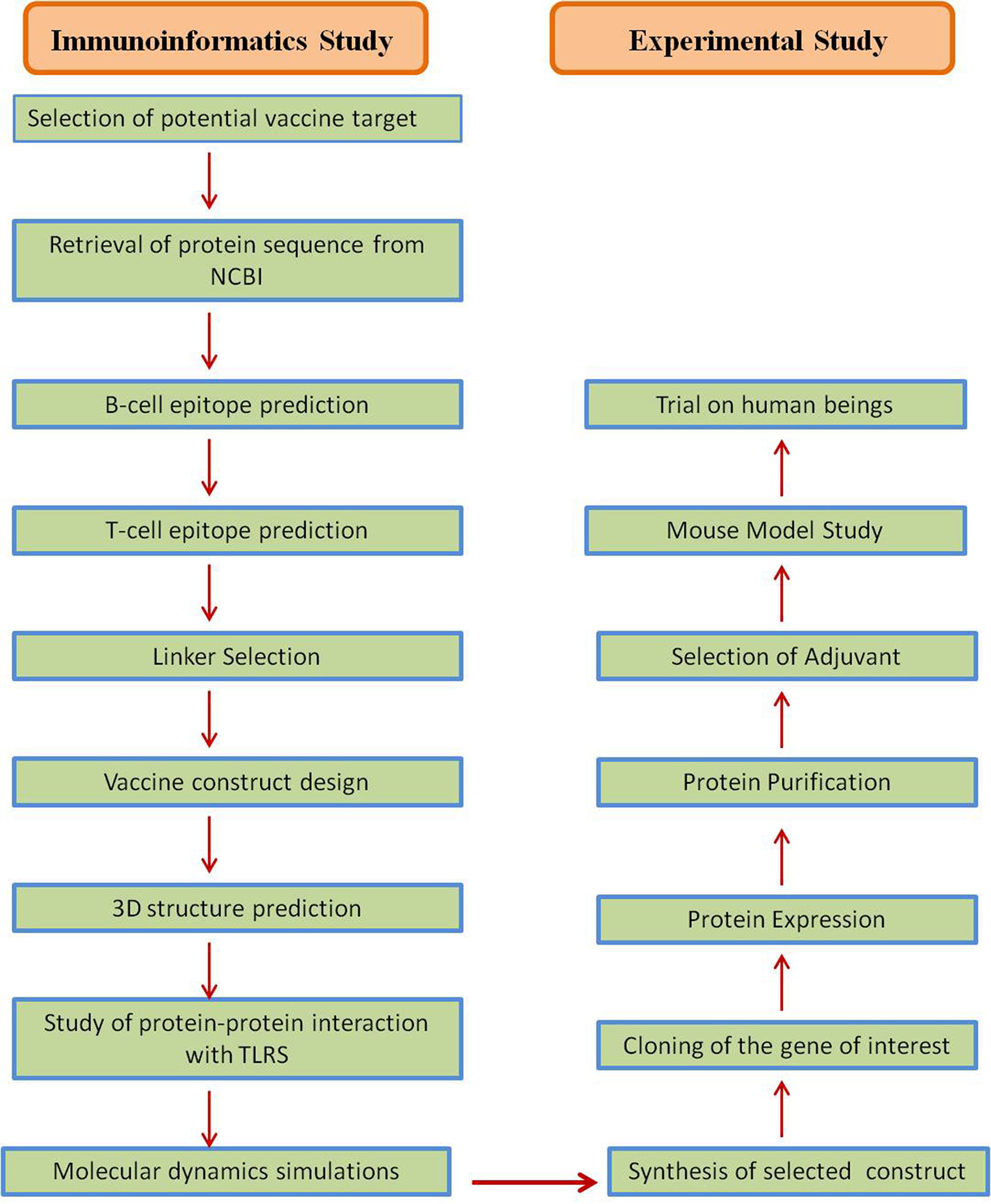
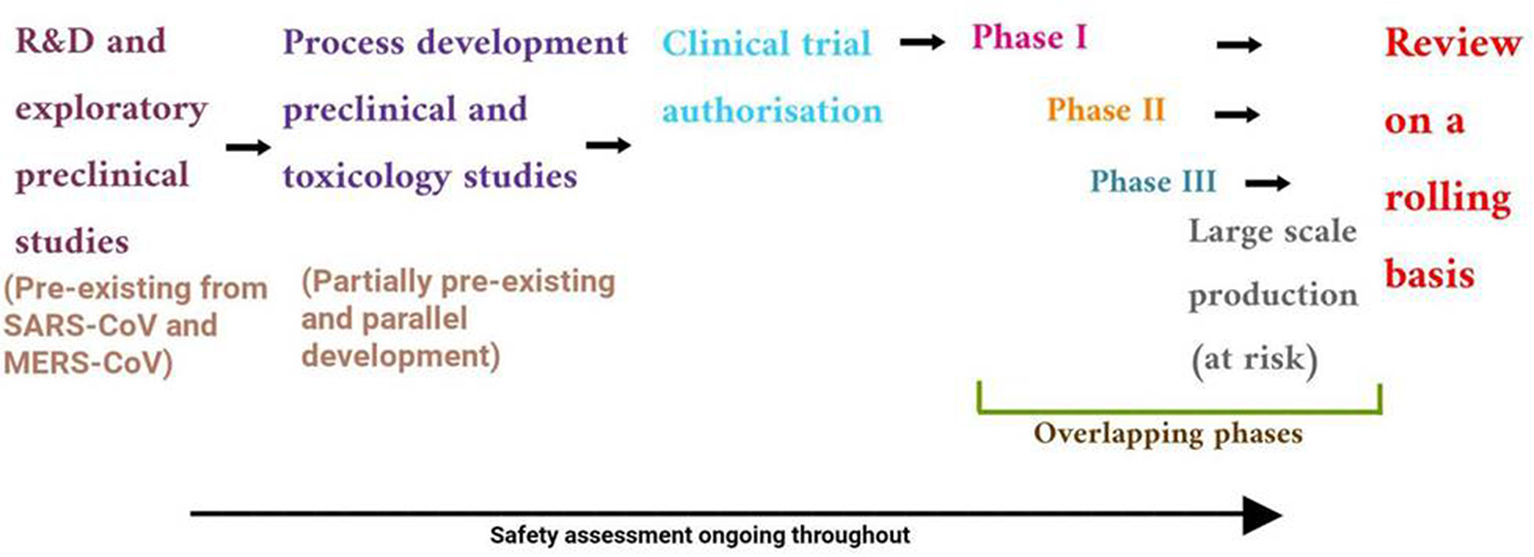
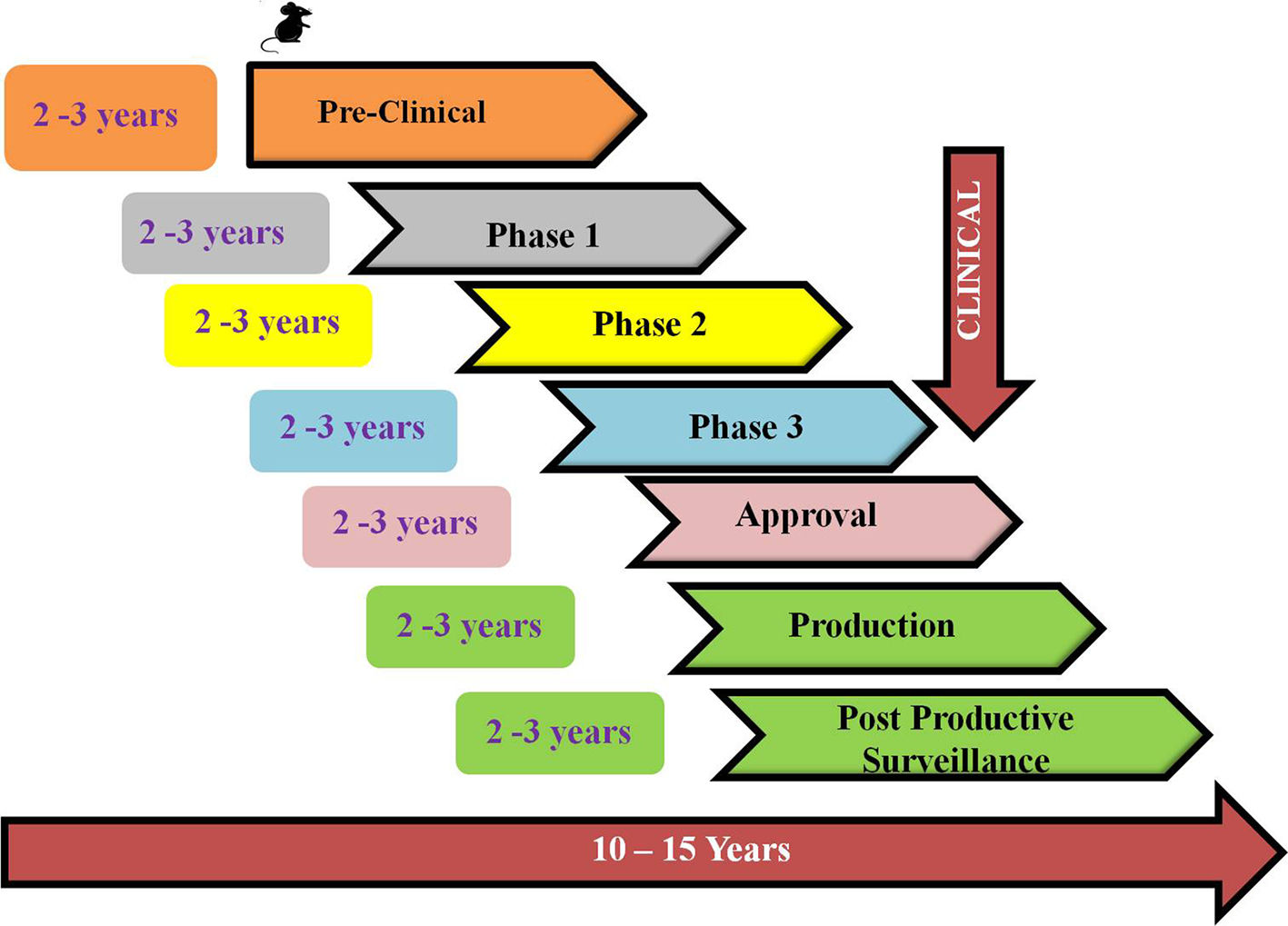
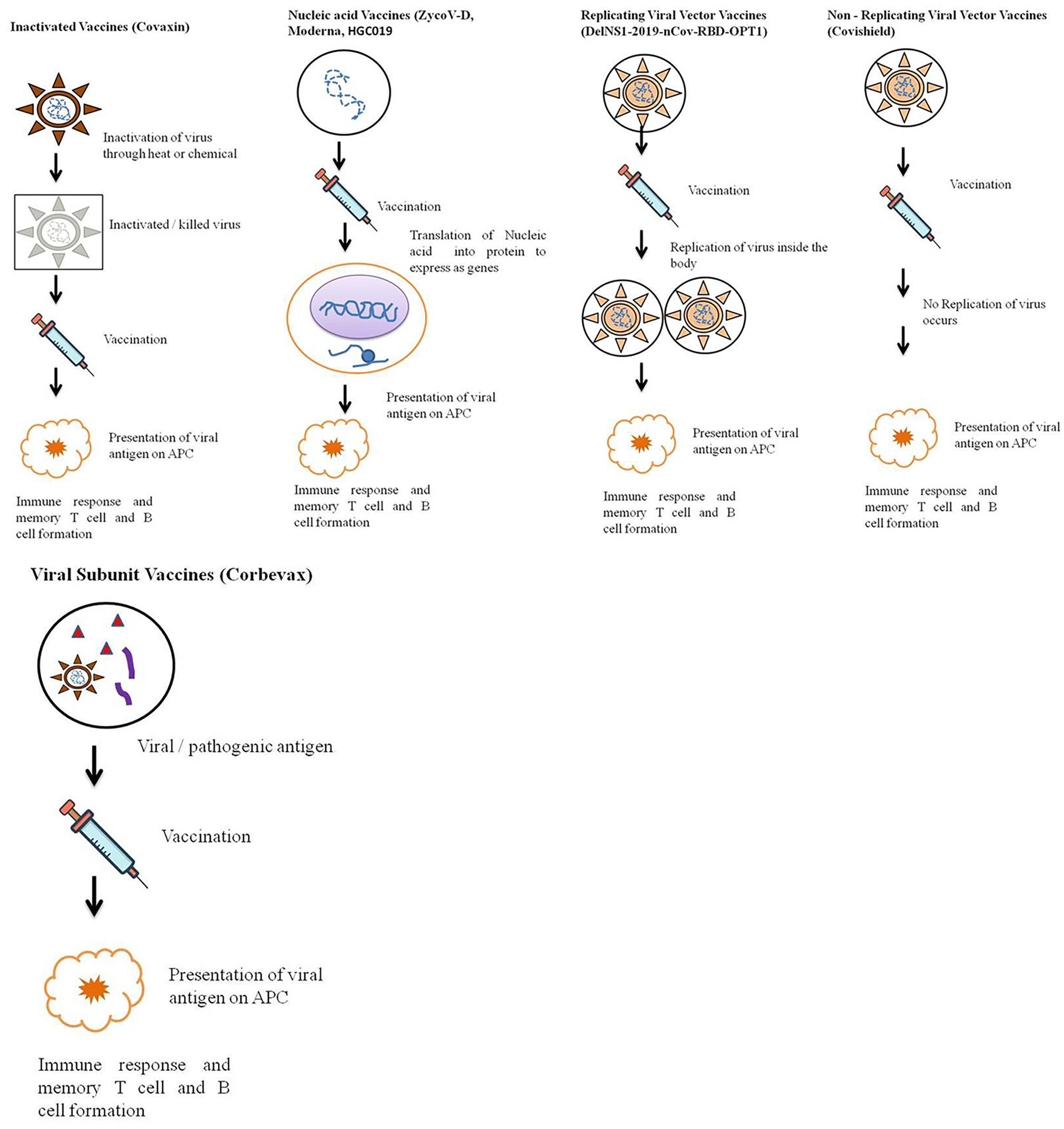
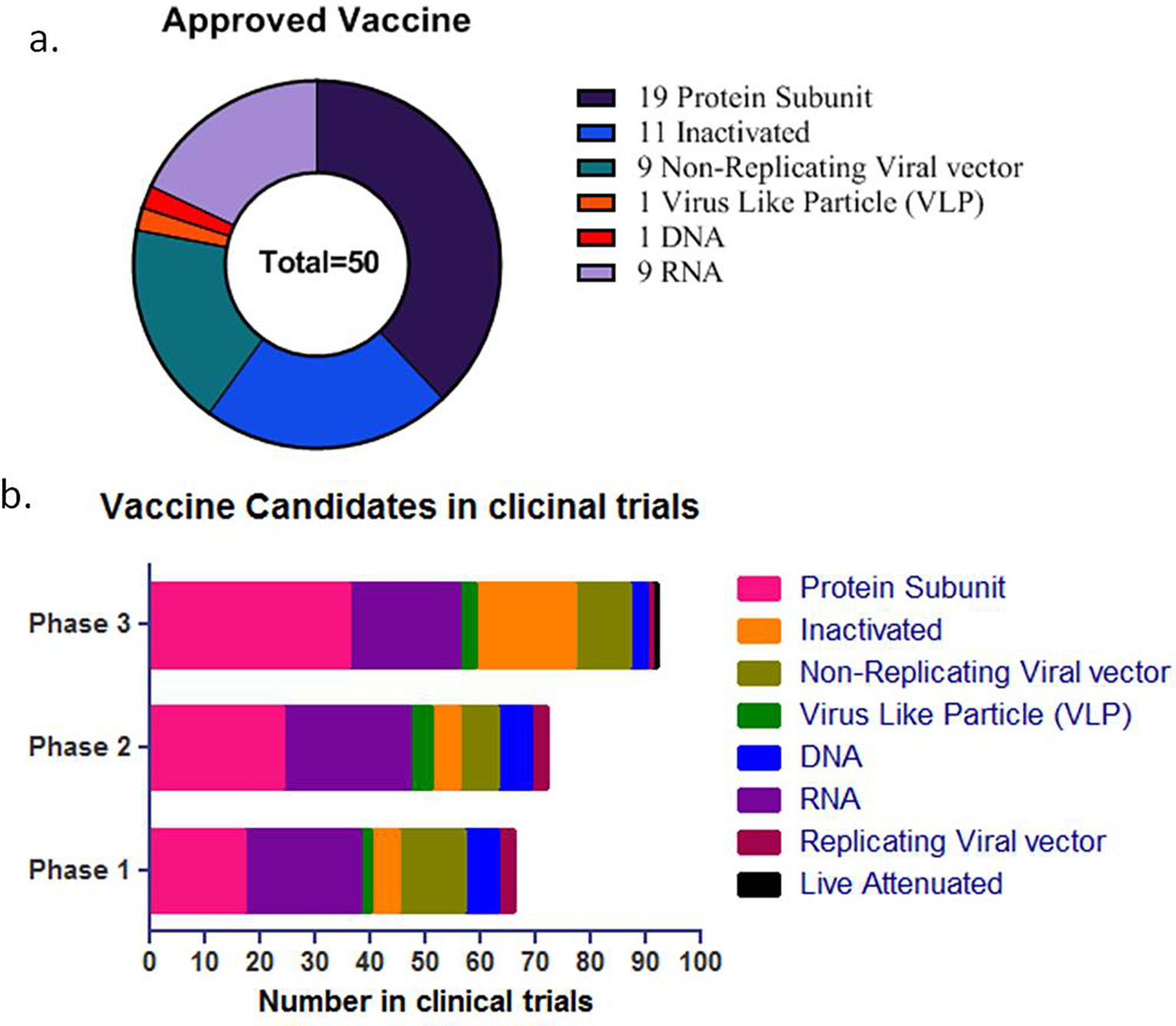
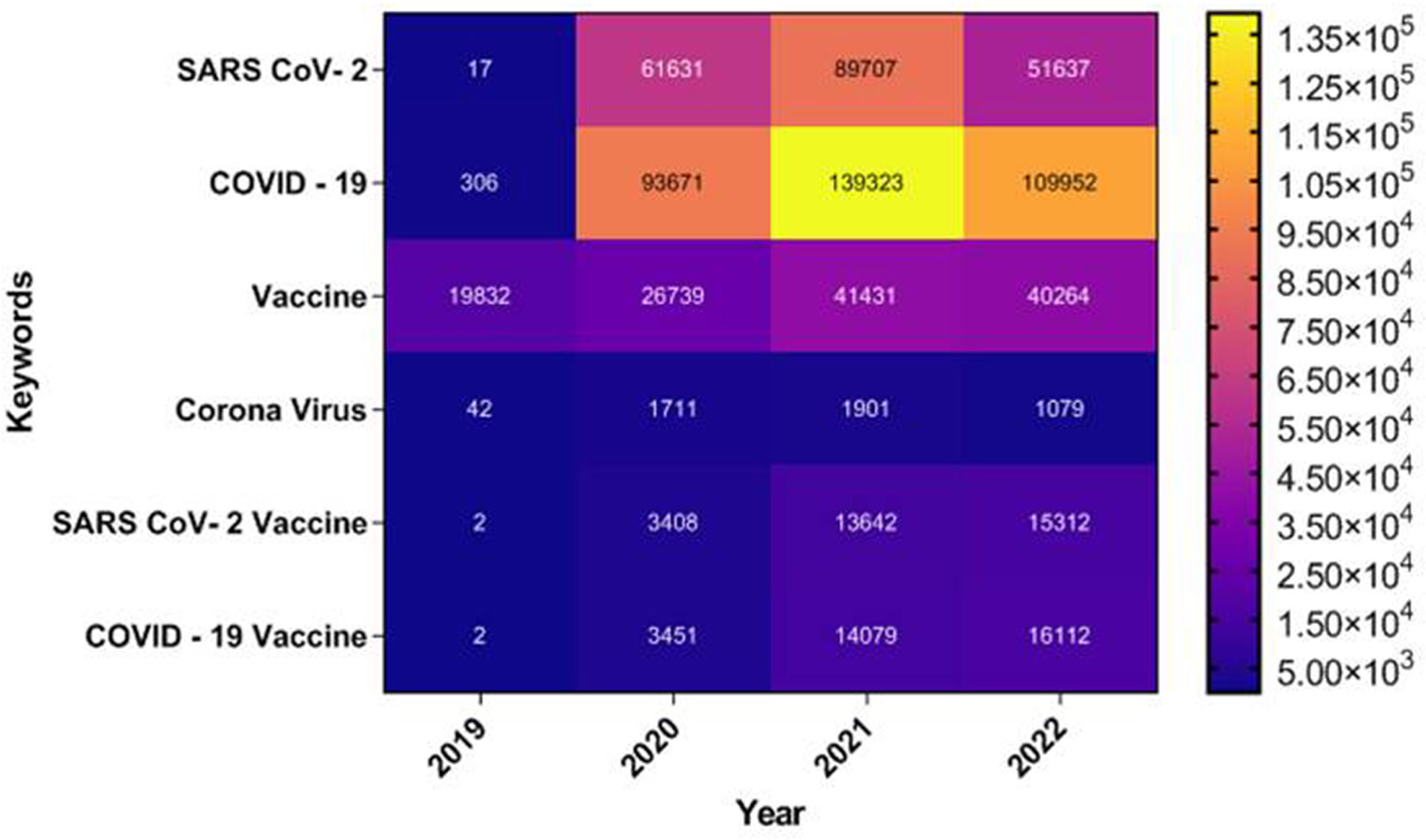
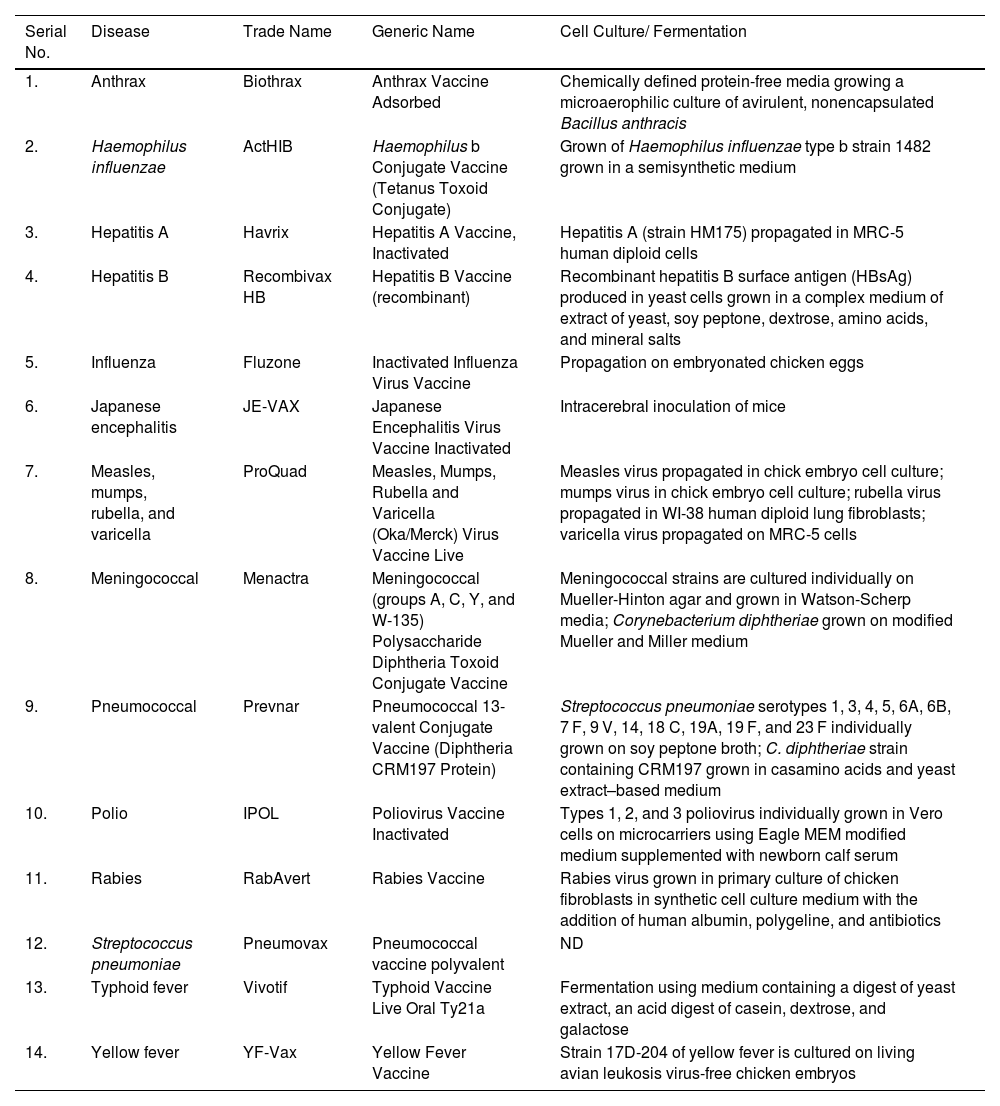
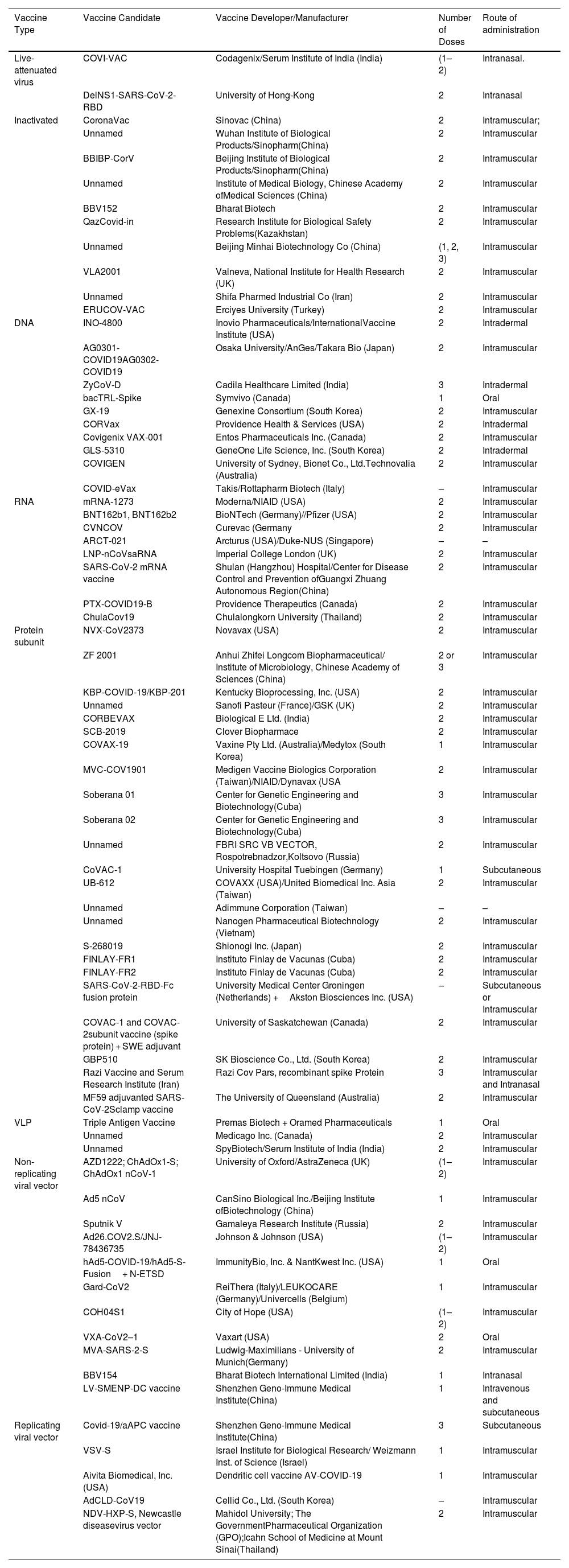
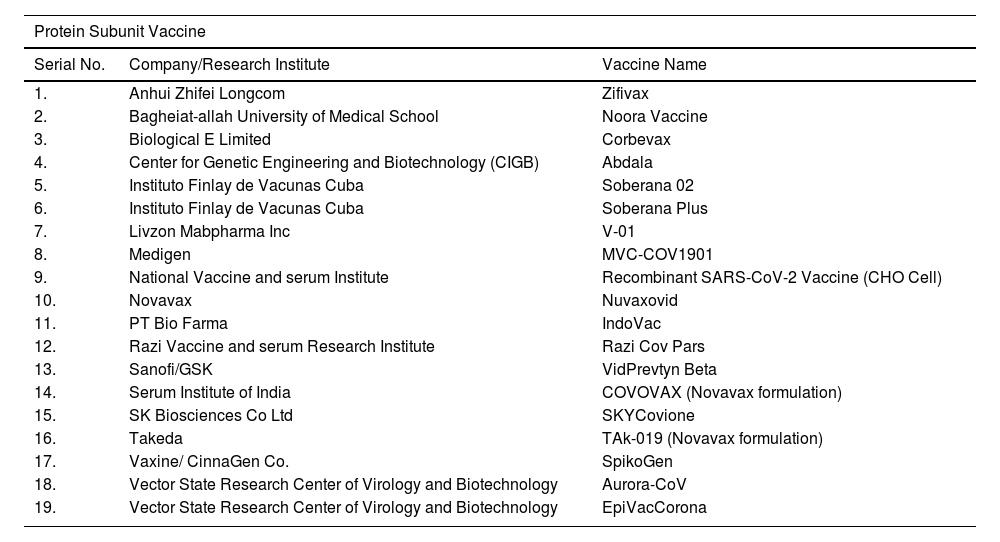
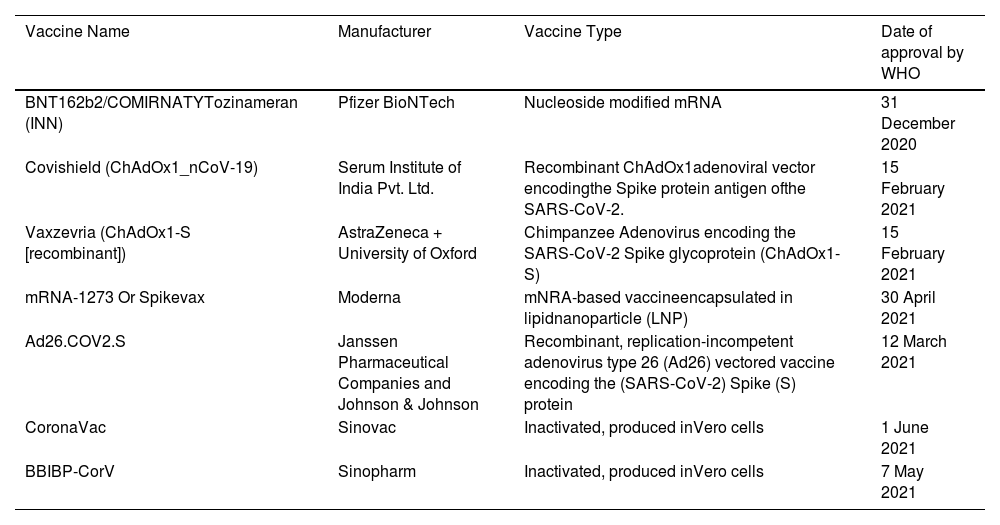
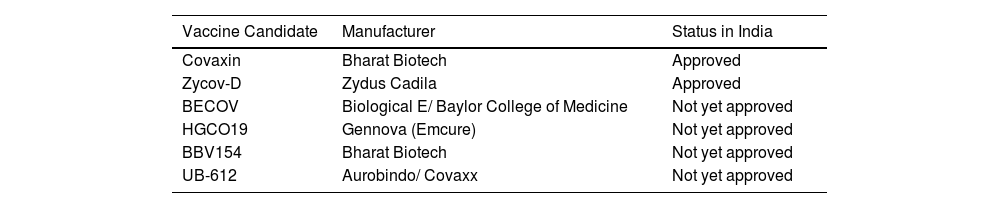
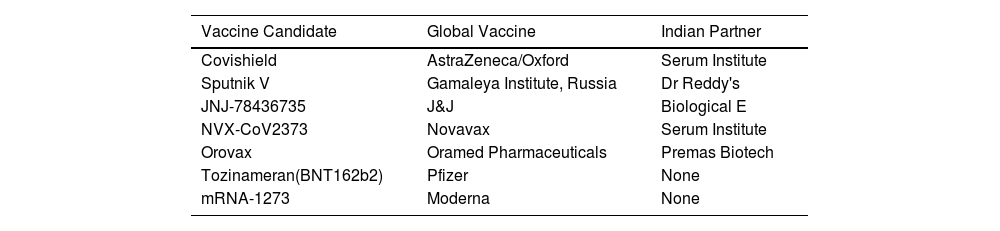
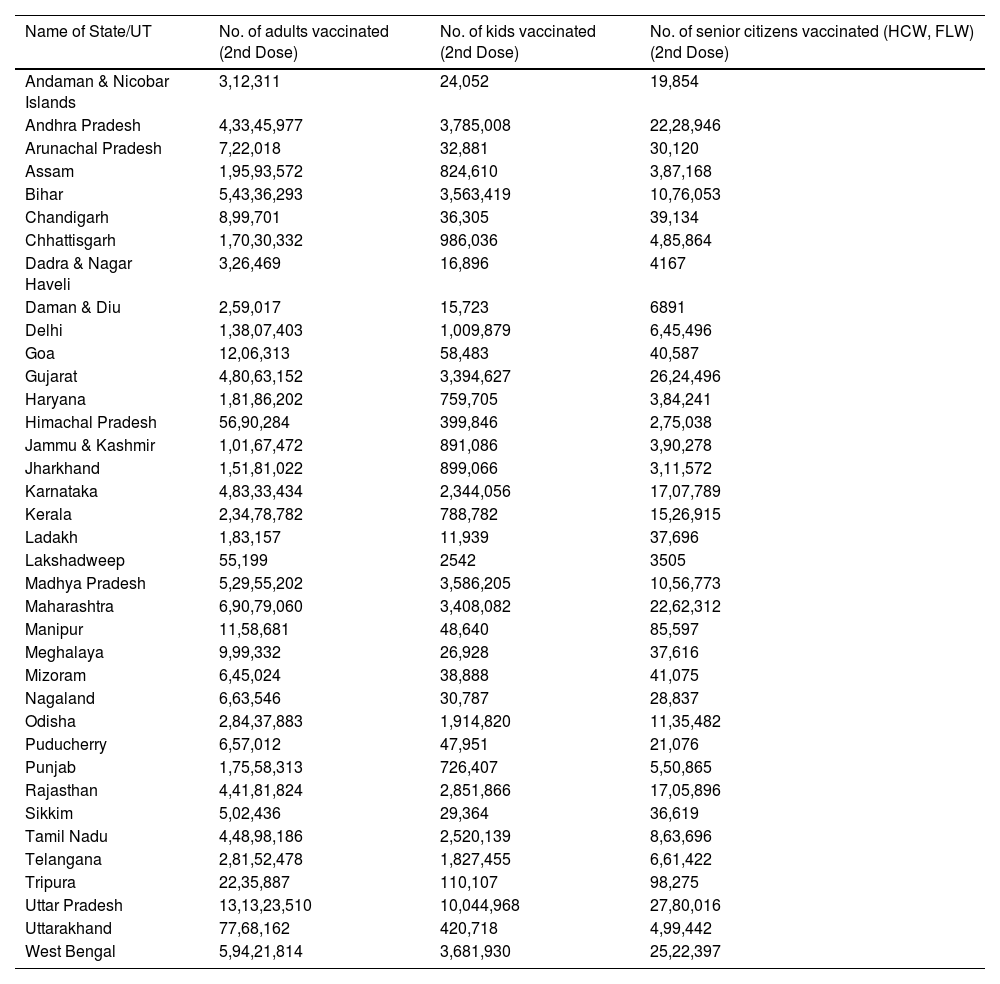
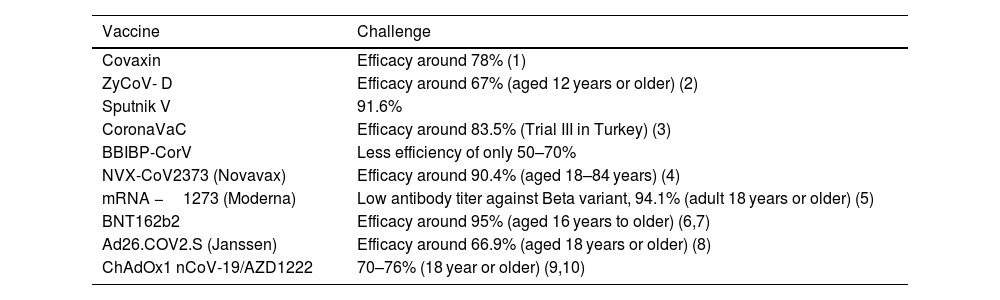
The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2, an etiologic agent of the COVID-19 pandemic disease in late December 2019 has left the whole world aghast with huge health and economic losses. Due to a lack of specific knowledge and understanding at the initial stages, an unprecedented rise in COVID-19 cases has been recorded globally. Various preventive measures and strategies were implemented, however, for the radical control of SARS-CoV-2 infections; it seems that the only effective way to control the ongoing infections is large-scale vaccination. So far, WHO has approved 11 vaccines for emergency use namely Pfizer/BioNTech, Oxford/Astra Zeneca, Johnson and Johnson, Moderna, Covilo, Novavax, Covovax, Spikevax, Can Sino, Comirnaty, and Coronavac while five other needs approval. The worldwide vaccination dataset reveals that 65.7% of the world population has received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. As a consequence of the proactive implementation of India's vaccination program, a historical milestone of administering over 1.9 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines have been achieved on 19th May 2022. This review summarizes the different types of traditional and modern vaccine designing strategies with an emphasis on COVID-19. Moreover, the review highlights the status of vaccines for COVID-19 approved in India which includes both indigenous and non-indigenous vaccines. The present article also encompasses vaccine designing and developmental strategies, efficacy, safety profile and usage among the population, and the efficacy of modern vaccines over traditional ones.
El brote de SARS-CoV-2, un agente etiológico de la enfermedad pandémica COVID-19, a fines de diciembre de 2019, ha dejado al mundo entero horrorizado con enormes pérdidas económicas y de salud. Debido a la falta de conocimiento y comprensión específicos en las etapas iniciales, se ha registrado un aumento sin precedentes en los casos de COVID-19 a nivel mundial. Sin embargo, se implementaron diversas medidas y estrategias preventivas para el control radical de las infecciones por SARS-CoV-2; parece que la única forma eficaz de controlar las infecciones en curso es la vacunación a gran escala. Hasta el momento, la OMS ha aprobado 11 vacunas para uso de urgencia Pfizer/BioNTech, Oxford/Astra Zeneca, Johnson and Johnson, Moderna, Covilo, Novavax, Covovax, Spikevax, Can Sino, Comirnaty y Coronavac, mientras que otras cinco necesitan aprobación. El conjunto de datos de vacunación mundial revela que el 65,7% de la población mundial ha recibido su primera dosis de la vacuna COVID-19. Como consecuencia de la implementación proactiva del programa de vacunación de la India, el 19 de mayo de 2022 se logró un hito histórico de administrar más de 1900 millones de dosis de vacunas contra el COVID-19. Esta revisión resume los diferentes tipos de estrategias de diseño de vacunas tradicionales y modernas con énfasis sobre COVID-19. Además, la revisión destaca el estado de las vacunas para COVID-19 aprobadas en India, que incluye vacunas tanto indígenas como no indígenas. El presente artículo también abarca estrategias de diseño y desarrollo de vacunas, eficacia, perfil de seguridad y uso entre la población, y la eficacia de las vacunas modernas sobre las tradicionales.