COVID-19 pandemic has posed mental health challenges for people from all walks of life, including the elders in Indonesia. Due to the wide-ranging effects of this pandemic due to various phases of smart, partial, or full lockdown, people worldwide have faced serious problems particularly with their mental health.
MethodsThis quantitative study analyses the experiences of the general public particularly focused on elders, those who are in isolation due to the COVID-19 protocols and limited social or physical interaction within the society. For investigating the social support mechanism among respondents, we have gathered a sample of respondents who are elders and using social media. The data reflect the opinion of respondents on elders during this pandemic. A survey was designed to gather data from elders facing mental health issues and using social media platforms to seek information in Indonesia. An online social support scale, self-awareness and insight scale were deployed to measure responses to the issue at hand.
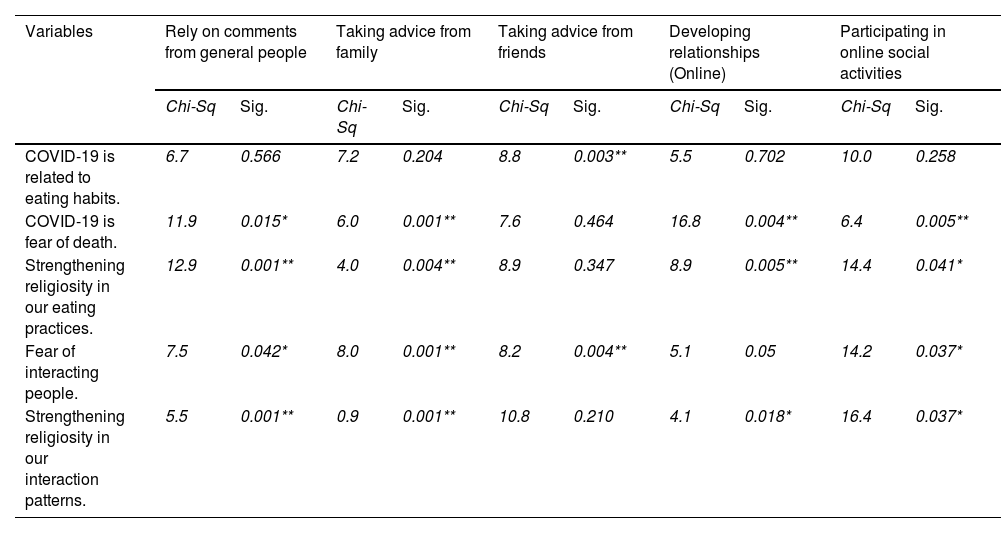
ResultsThe data show that the elders had varied conceptualisations about COVID-19 relating to the pandemic, i.e., eating habits, fear of death, strengthening religiosity in eating practices, fear of interacting with people, and interaction patterns. Elders were restricted to their places and had limited physical social interactions, thus social media platforms have played a significant role in developing online interaction among elders, to speak and discuss their matters for coping with the issues of isolation and mental health.
ConclusionThe online media platform is considered a great support for elders to stay connected with families, friends, as well as with other communities. The study concludes that despite declaring the non-emergency status of COVID-19, elders have still suffered with long-term repercussions of this pandemic affecting their mental health.
La pandemia de COVID-19 ha planteado múltiples desafíos de salud mental para personas de todos los ámbitos de la vida, incluidos los ancianos en Indonesia. Debido a los amplios efectos de esta pandemia debido a las diversas fases de confinamiento inteligente, parcial o total, personas en todo el mundo se han enfrentado a graves problemas, especialmente con su salud mental.
MétodosEste estudio cuantitativo analiza las experiencias del público en general, particularmente enfocado en las personas mayores, aquellos que se encuentran aislados debido a los protocolos COVID-19 y la interacción social o física limitada dentro de la sociedad. Para investigar el mecanismo de apoyo social entre los encuestados, hemos reunido una muestra de encuestados que son personas mayores y utilizan las redes sociales. Los datos reflejan la opinión de los encuestados sobre las personas mayores durante esta pandemia. Se diseñó una encuesta para recopilar datos de personas mayores que enfrentan problemas de salud mental y que utilizan plataformas de redes sociales para buscar información en Indonesia. Se implementaron una Escala de apoyo social en línea (OSS) y una Escala de autoconciencia e percepción (SRIS) para medir las respuestas al problema en cuestión.
ResultadosLos datos muestran que los ancianos tenían diversas conceptualizaciones sobre el COVID-19 en relación con la pandemia, es decir, hábitos alimentarios, miedo a la muerte, fortalecimiento de la religiosidad en las prácticas alimentarias, miedo a interactuar con las personas y patrones de interacción. Los ancianos estaban restringidos a sus lugares y tenían interacciones sociales físicas limitadas, por lo que las plataformas de redes sociales han desempeñado un papel importante en el desarrollo de la interacción en línea entre los ancianos, para hablar y discutir sus asuntos para hacer frente a los problemas de aislamiento y salud mental.
ConclusiónLa plataforma de medios en línea se considera un gran apoyo para que las personas mayores se mantengan conectadas con sus familias, amigos y otras comunidades. El estudio concluye que a pesar de declarar el estado de no emergencia del COVID-19, las personas mayores todavía han sufrido las repercusiones a largo plazo de esta pandemia que afectan su salud mental.