After the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination campaign, we observed alterations in post-vaccination international normalised ratio (INR) in patients treated with acenocoumarol. The aim of the study was to investigate whether there is an association between the observed blood coagulation alterations and SARS-CoV2 vaccination.
Materials and methodsA retrospective, longitudinal, observational study of patients over 60 years of age vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 and treated with acenocoumarol was conducted. The main variable measured was the INR before and after vaccination, and secondary variables were date of vaccination, age, sex, type of vaccine, and dose of acenocoumarol. Paired means were compared using non-parametric Friedman and Wilcoxon tests with Benjamini–Hochberg correction, and a linear regression analysis between age and differences between pre- and post-vaccination INR measurements. The analysis was performed on the total sample and by subgroups. Statistical significance was set at p-value <.05.
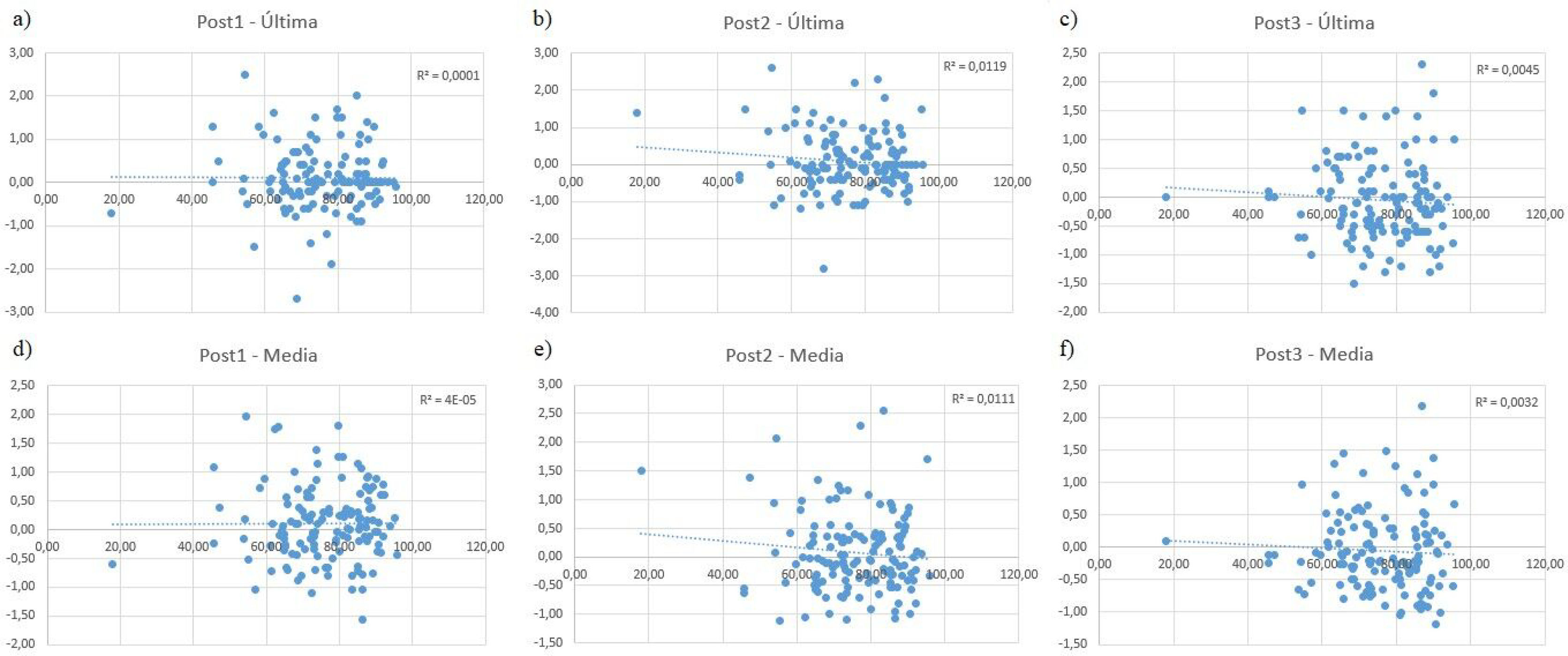
ResultsOverall, statistically significant differences (Friedman, p-value <.05) were found between INR measurements in the total sample, women, Comirnaty® vaccine, and Sintrom® 1 g dose, although the differences found are weak (W-Kendall <0.01). No statistically significant differences were found between specific pairs in INR measurements (Wilcoxon, p-value >.05). The goodness-of-fit of all linear regressions was R2<0.1.
ConclusionsThe alteration of coagulation due to vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 is not a population or generalised effect, but a possible side effect, and reinforces the safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in this type of patients.
En 2020, hubo una campaña de vacunación en España para combatir el SARS-CoV-2 con las vacunas Comirnaty®, Moderna®, Vaxzeviria® y Janssen®. Observamos alteraciones en el International Normalised Ratio (INR) post vacunación, en pacientes tratados con acenocumarol. El objetivo del estudio era averiguar si existe una asociación entre dichas alteraciones del INR y la vacunación frente a SARS-CoV-2.
Materiales y métodosSe llevó a cabo un estudio observacional, longitudinal retrospectivo en 137 pacientes mayores de 60 años vacunados contra el SARS-CoV-2 y a su vez tratados con acenocumarol. Como variable principal se consideró INR antes y después de la vacunación, y como variables secundarias se tomaron la fecha de vacunación, la edad, el sexo, el tipo de vacuna y la dosis de acenocumarol que tomaba cada paciente. Se compararon las medias pareadas mediante pruebas no paramétricas de Friedman y Wilcoxon con corrección Benjamini-Hochberg, y se llevó a cabo un análisis de regresión lineal entre la edad y las diferencias entre las mediciones del INR pre y post vacunación. El análisis se realizó sobre la muestra total y por subgrupos. Se consideró un nivel de significación estadístico en p-valour<0.05.
ResultadosSe hallaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas globales (Friedman, p-valour<0,05) entre mediciones INR en la muestra total, mujeres, vacuna Comirnaty® y dosis Sintrom® 1 g, aunque las diferencias encontradas son débiles (W-Kendall<0.01). No se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre pares concretos en las mediciones de INR (Wilcoxon, p-valour>0.05). La bondad de ajuste de todas las regresiones lineales fue de R2 < 0,1.
ConclusionesLas alteraciones de la coagulación a causa de la vacunación frente al SARS-CoV-2 es un posible efecto secundario, aunque no generalizado en las personas mayores de 60 años tratados con acenocumarol. Este hecho refuerza la evidencia de la seguridad de la vacunación frente a SARS-CoV-2 en este tipo de pacientes.