About 4.25% of people have lost their lives due to COVID-19 disease, among SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. In an unforeseen situation, approximately 25,000 frontline healthcare workers have also been infected by this disease while providing treatment to the infected patients. In this devastating scenario, without any drug or vaccine available for the treatment, frontline healthcare workers are highly prone to viral infection. However, some countries are drastically facing a shortage of healthcare workers in hospitals.
MethodsThe literature search was conducted in ScienceDirect and ResearchGate, using words “Medical Robots”, and “AI in Covid-19” as descriptors. To identify and evaluate the articles that create the impact of robots and artificial intelligence in pandemic diseases. Eligible articles were included publications and laboratory studies before and after covid-19 and also the prospective and retrospective of application of Robots and AI.
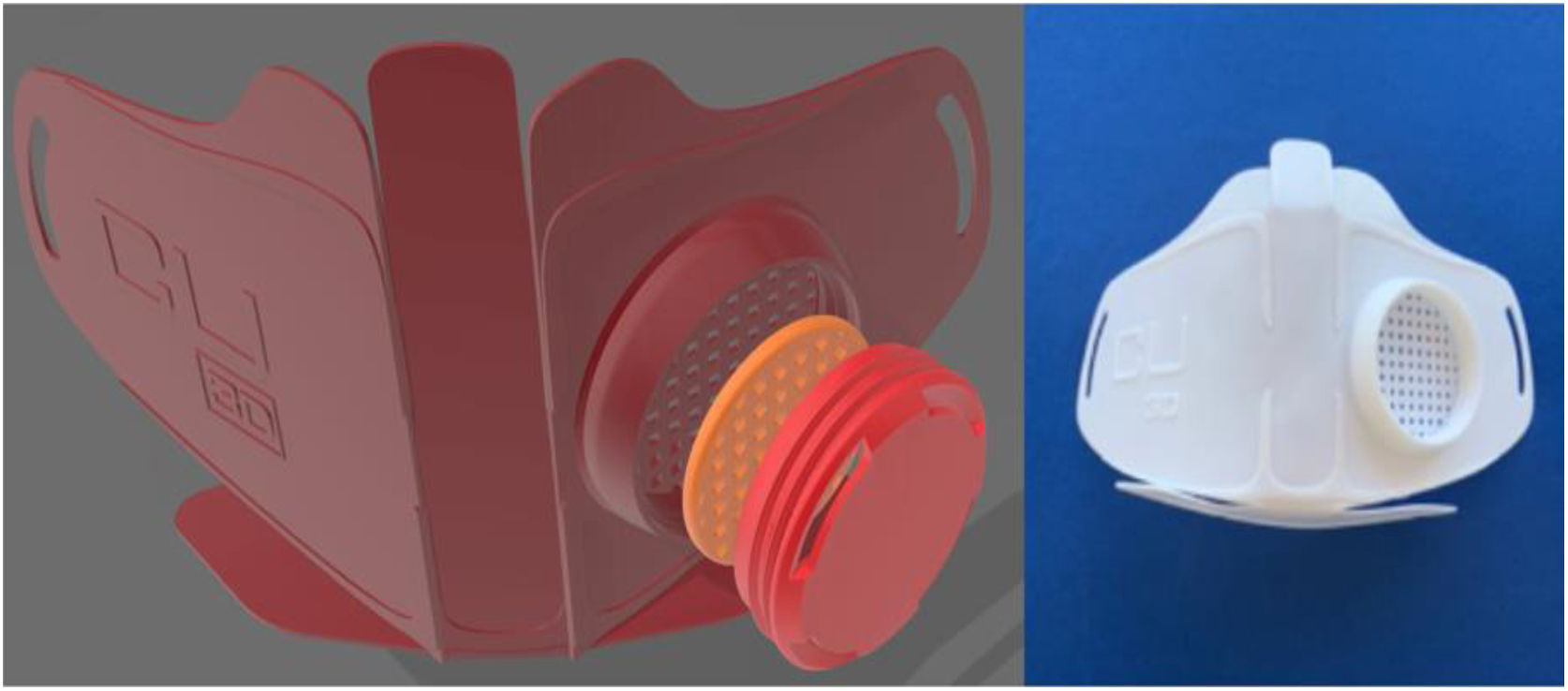
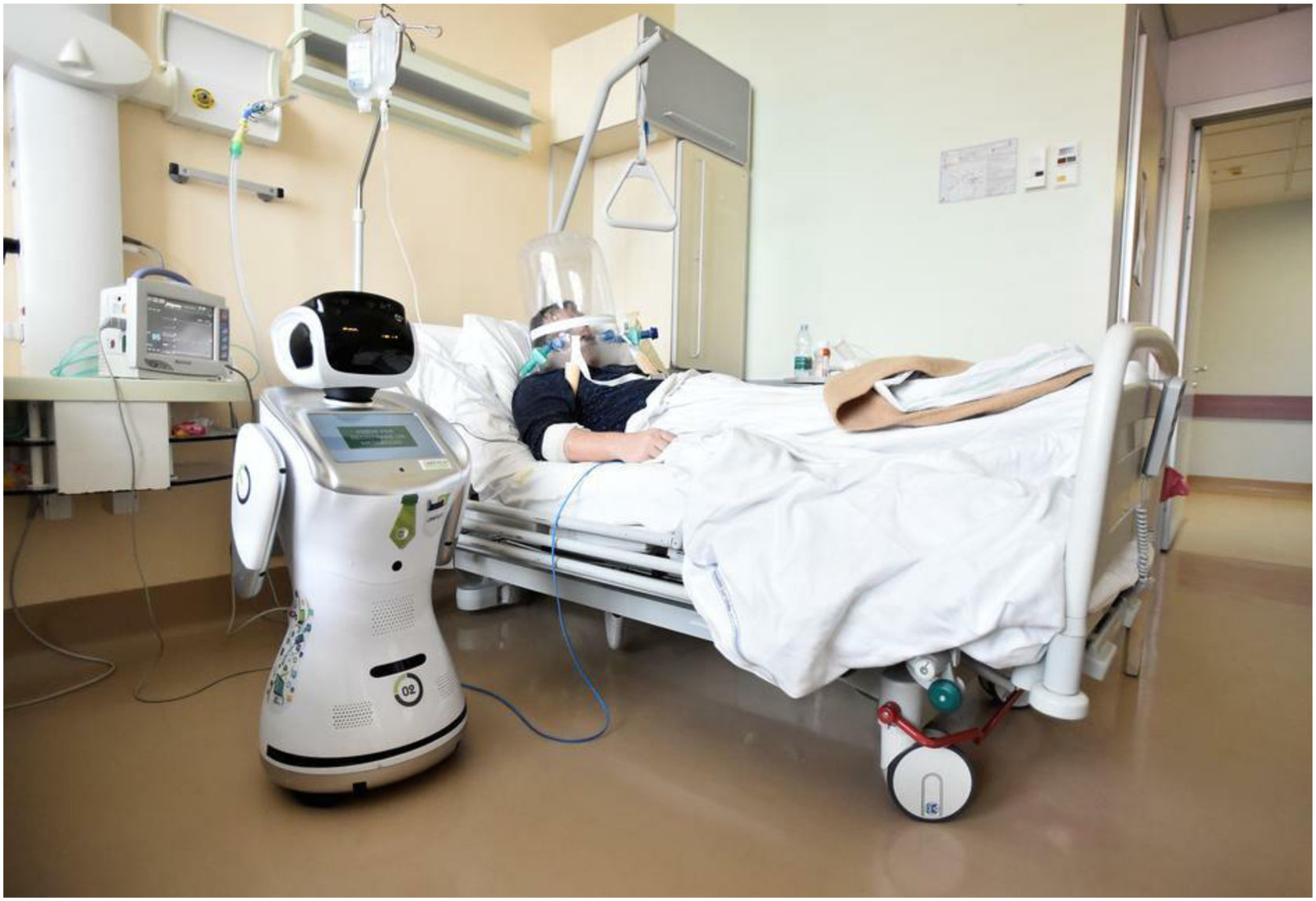
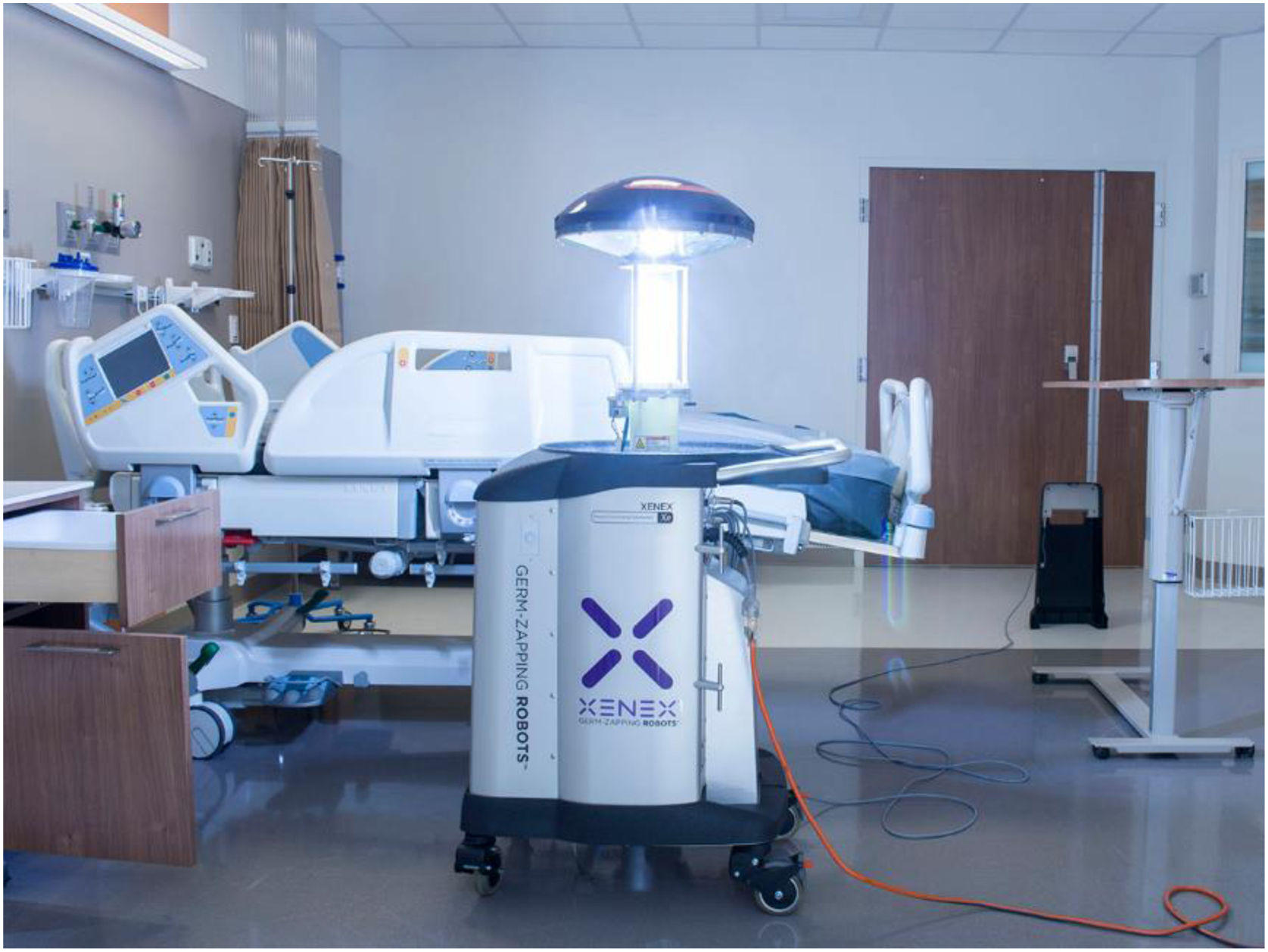
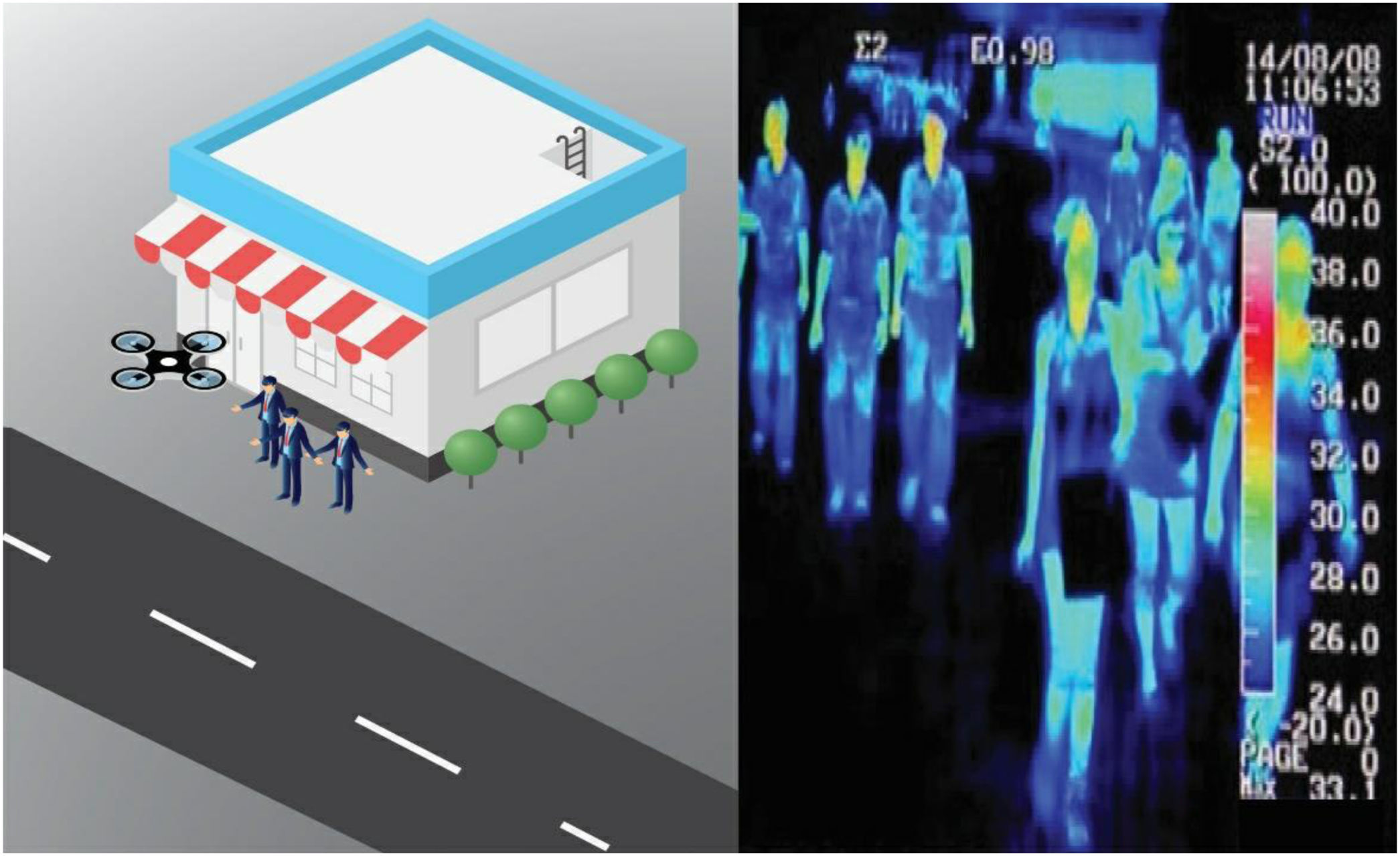
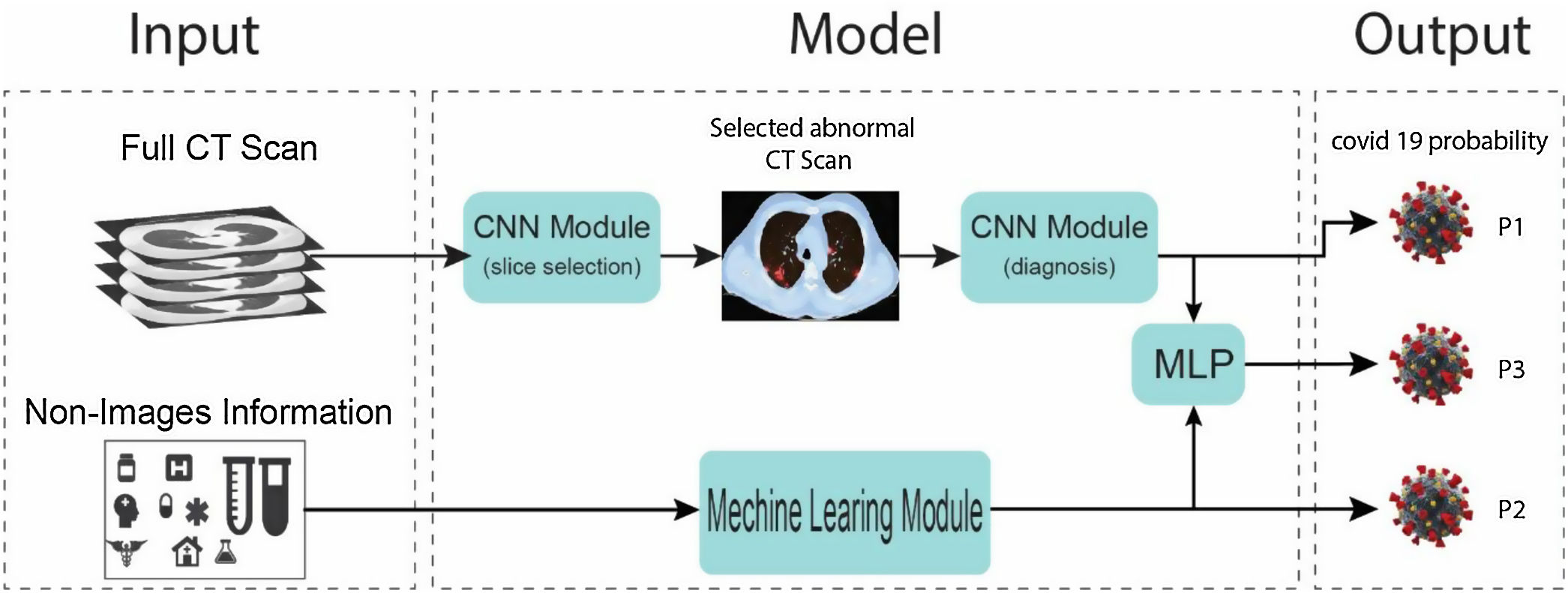
ConclusionIn this pandemic situation, robots were employed in some countries during the COVID-19 outbreak, which are medical robots, UV-disinfectant robots, social robots, drones, and COBOTS. Implementation of these robots was found effective in successful disease management, treatment, most importantly ensures the safety of healthcare workers. Mainly, the Disposal of deceased bodies and the location and transportation of infected patients to hospitals and hospitals were tough tasks and risk of infection. These tasks will be performed by employing mobile robots and automated guided robots respectively. Therefore, in the future, advanced automated robots would be a promising choice in hospitals and healthcare centers to minimize the risk of frontline healthcare workers.
Cerca de un 4,25% de personas han perdido la vida a causa de la COVID-19, entre los pacientes infectados por SARS-CoV-2. En esta situación imprevista, aproximadamente 25.000 trabajadores sanitarios de primera línea se han visto también infectados por esta enfermedad, al proporcionar tratamiento a los pacientes infectados. En este escenario devastador, en el que no se dispone de fármacos o vacunas para el tratamiento, el personal sanitario de primera línea está altamente expuesto a la infección vírica. Sin embargo, algunos países se están enfrentando a un recorte drástico de personal sanitario en sus hospitales.
MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda en la literatura en ScienceDirect y ResearchGate, utilizando los términos «medical robots» y «AI in COVID-19» como factores descriptivos, para identificar y evaluar los artículos que crean el impacto de los robots y la inteligencia artificial (AI) en las pandemias. Los artículos elegibles incluyeron publicaciones y estudios de laboratorio, antes y después de la COVID-19, y también la aplicación prospectiva y retrospectiva de robots e AI.
ConclusiónEn esta situación de pandemia, algunos países utilizaron robots durante el brote de COVID-19, es decir, robots médicos, robots desinfectantes de rayos UV, robots sociales, drones, y cobots. Se encontró que la implementación de estos robots era eficaz para la gestión y tratamiento de la enfermedad y, más importantemente, la garantía de la seguridad del personal sanitario. En particular, la eliminación de cadáveres y la localización y transporte de pacientes infectados a los hospitales eran tareas duras que suponían un riesgo de infección. Dichas tareas podrán realizarse utilizando robots móviles y robots automatizados, respectivamente. Por tanto, en el futuro, los robots automatizados avanzados constituirán una elección prometedora en hospitales y centros sanitarios, para minimizar el riesgo del personal sanitario de primera línea.