Even after the enforcement of the lockdown, the government was unable to control the spread of the COVID-19 infection. Vaccination is the only remaining hope for preventing and controlling COVID-19 infections. The knowledge and attitude of the recipients can influence vaccine acceptance. In this study, we aim to assess the knowledge and attitude toward the COVID-19 vaccine among the general rural population of India.
MethodologyA community-based, prospective, cross-sectional study was conducted from May 2021 to October 2021 in the rural part of the Mandya district of Karnataka, India. Individuals over the age of 18 who met the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare's vaccination eligibility criteria were included in the study. Demographic details of participants and assessment of knowledge and attitude towards the COVID-19 vaccine were done in a designed and validated data collection form.
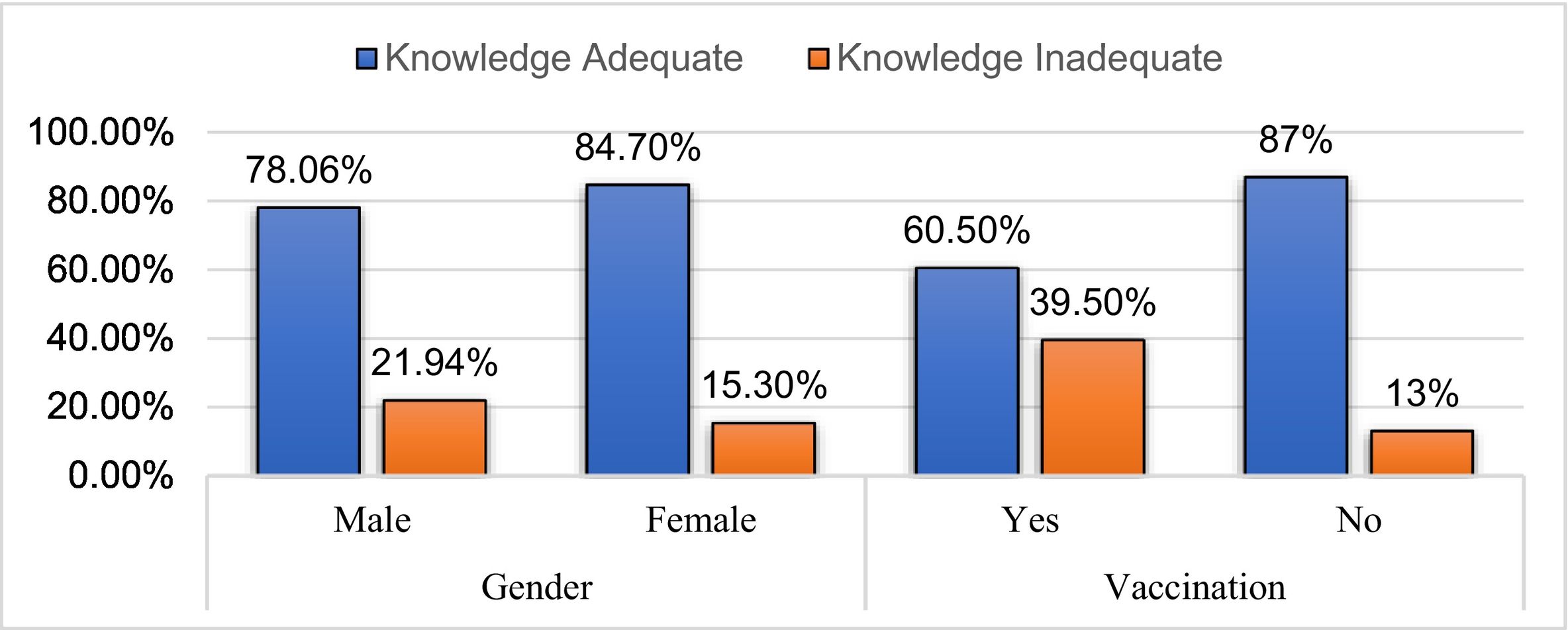
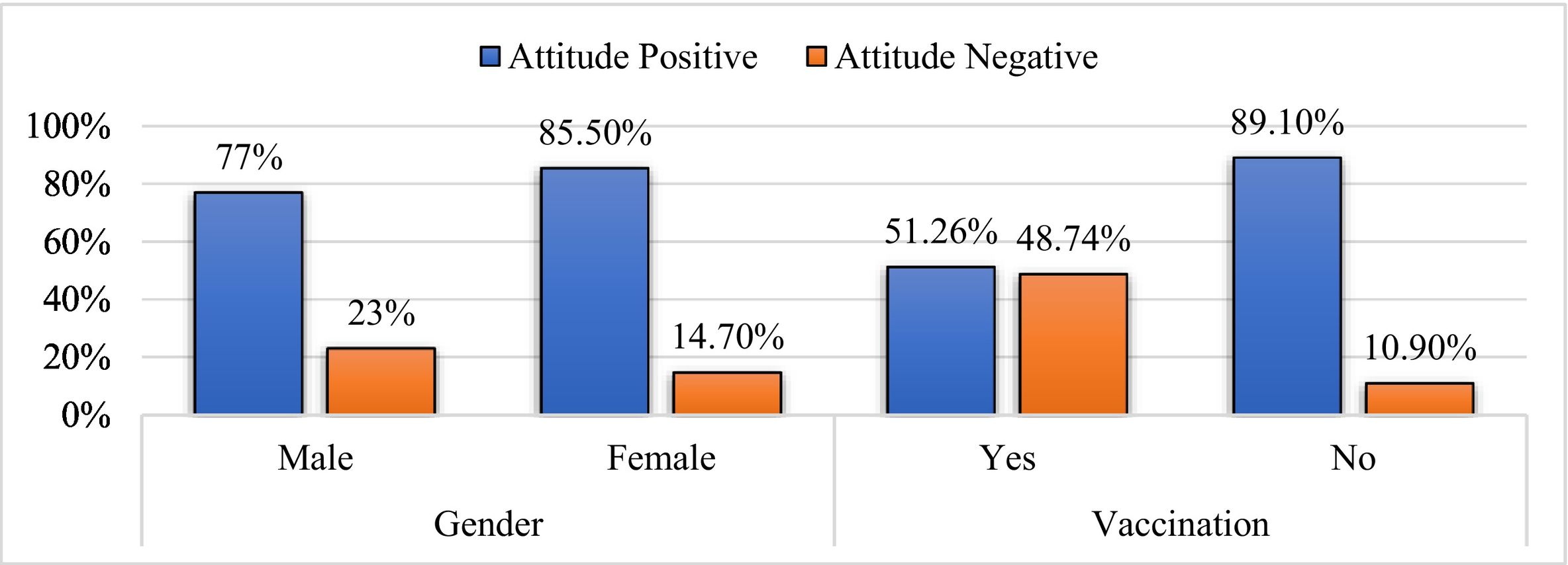
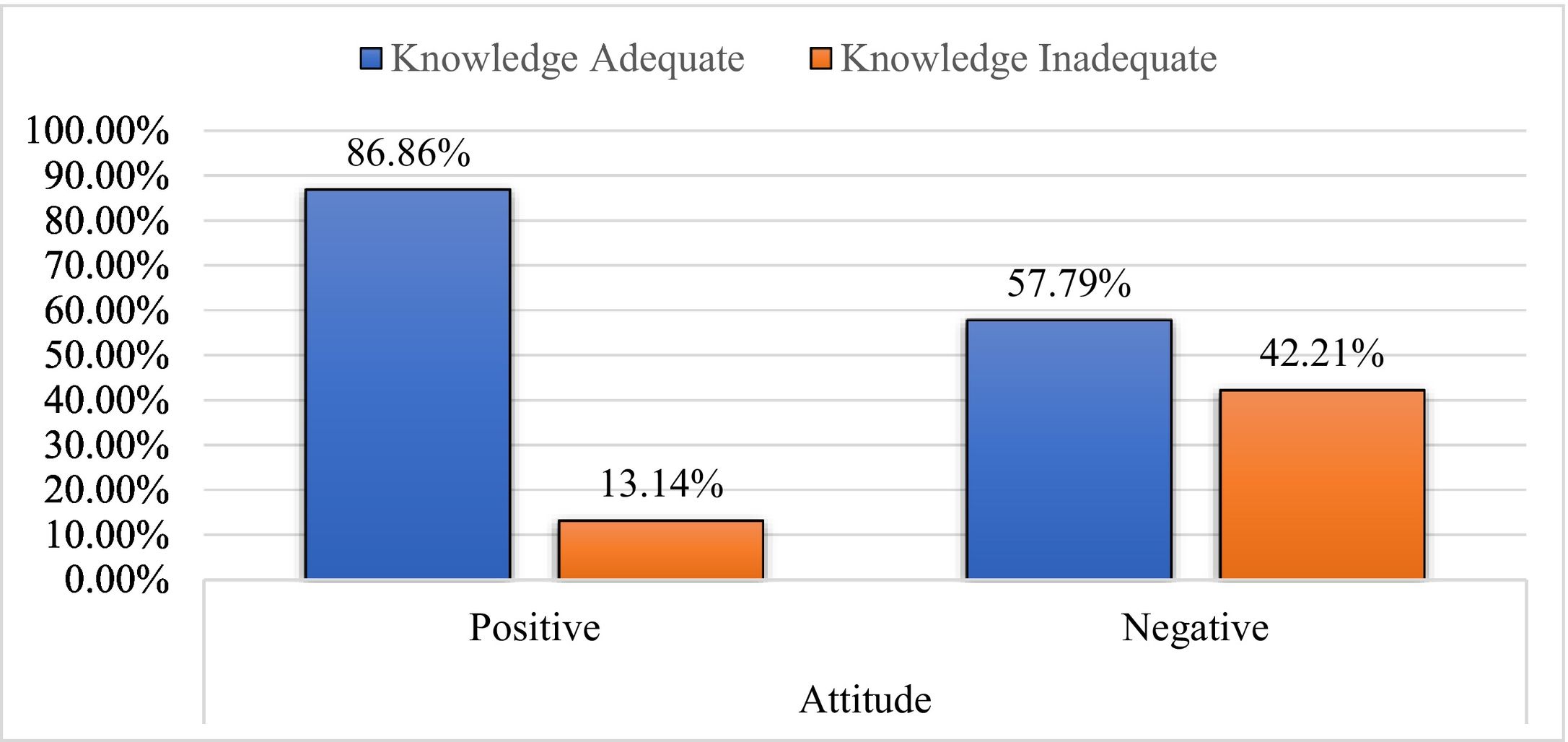
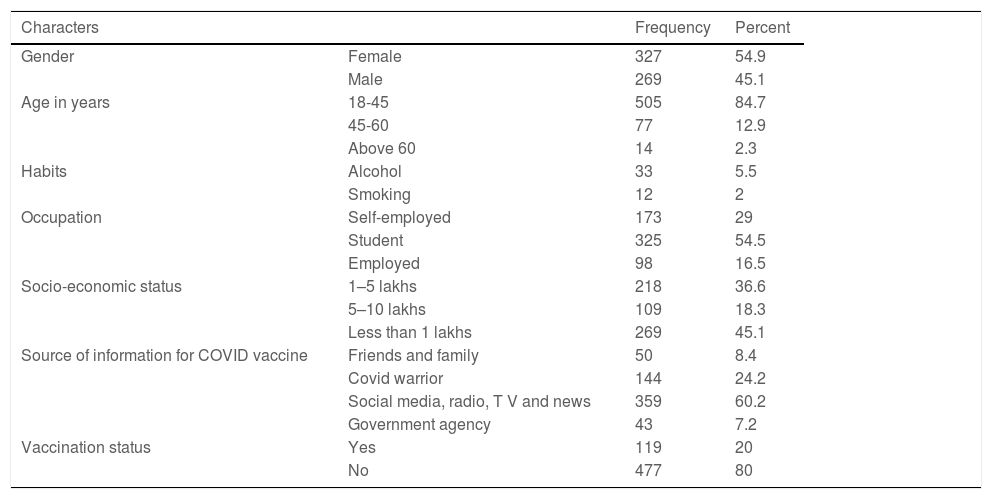
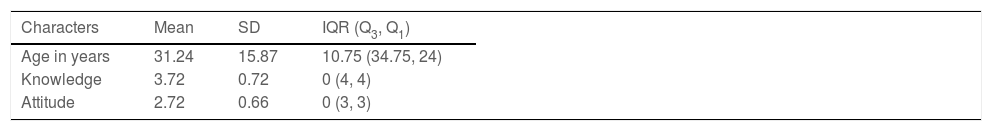
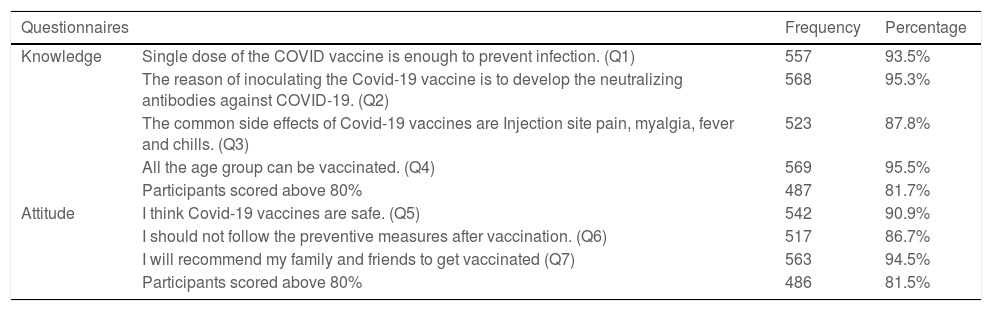
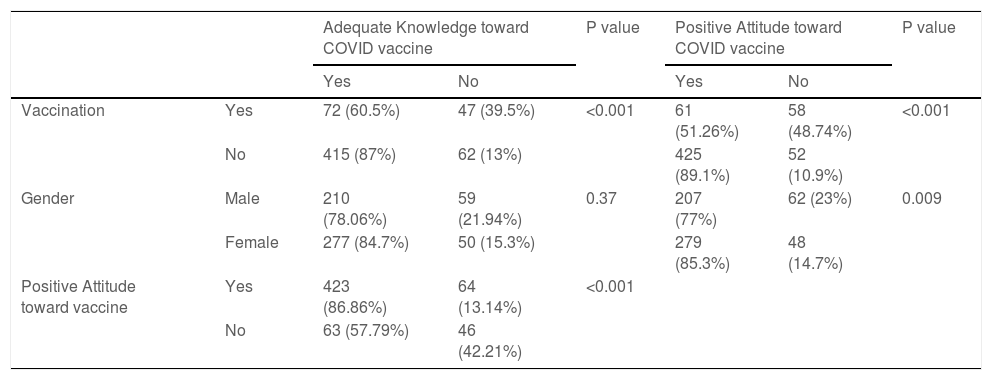
ResultsThe study included 596 participants, with females dominating males by 54.9 % (327). The average age of the participants was 31 years. Among them, 81.71% (487) had adequate knowledge, and 81.5% (486) had a positive attitude towards the COVID-19 vaccine. Females (85.3%, 279) tend to have a more positive attitude than males (77%, 207). Positive attitude participants (86.86 %, 423) have a higher level of knowledge about the COVID-19 vaccine than negative attitude participants (57.79 %, 63).
ConclusionIn the study, we found that 81.71% had adequate knowledge and 81.5% had a positive attitude toward the COVID-19 vaccine.
Incluso tras la obligatoriedad del confinamiento el gobierno fue incapaz de controlar la propagación de la infección por COVID-19. La vacuna es la única esperanza que queda para prevenir y controlar las infecciones por COVID-19. El conocimiento y la actitud de los receptores pueden influir en la aceptación de la vacuna. En este estudio, nuestro objetivo fue evaluar el conocimiento y la actitud hacia la vacuna contra la COVID-19 entre la población rural general de India.
MetodologíaSe realizó un estudio transversal, prospectivo y con base comunitaria de mayo a octubre de 2021 en la zona rural del distrito Mandya de Karnataka, India. Se incluyó en el estudio a los individuos mayores de 18 años que cumplieron los criterios de elegibilidad del Ministerio de Sanidad y Bienestar Familiar. Los datos demográficos de los participantes y la evaluación del conocimiento y la actitud hacia la vacuna contra la COVID-19 se incluyeron en un formulario de recopilación de datos diseñado y validado.
ResultadosEl estudio incluyó a 596 participantes, siendo más numerosas las mujeres que los hombres en un 54,9 % (327). La edad media de los participantes fue de 31 años. Entre ellos, el 81,71% (487) tenía un conocimiento adecuado, y el 81,5% (486) una actitud positiva hacia la vacuna contra la COVID-19. Las mujeres (85,3%, 279) tendieron a tener una actitud más positiva que los hombres (77%, 207). Los participantes con actitud positiva (86,86 %, 423) tuvieron un mayor nivel de conocimiento sobre la vacuna contra la COVID-19 que los participantes con actitud negativa (57,79 %, 63).
ConclusiónEn el estudio, encontramos que el 81,71% tuvo un conocimiento adecuado, y el 81,5% una actitud positiva hacia la vacuna contra la COVID-19.