A new coronavirus strain has wreaked havoc on human lives so the WHO was declared as a pandemic since 20th March 2020. The Membrane glycoprotein MP spans the viral envelope and it has a highly conserved glycosylation sequence.
AimOur study goal was to find out the N-glycosylation, ligand binding sites, and antigenic variations between COVID-19 and other associated viruses.
MethodsWe performed In silico methodologies for serial analysis at both an operational and result/output level is assessed and compared study factors.
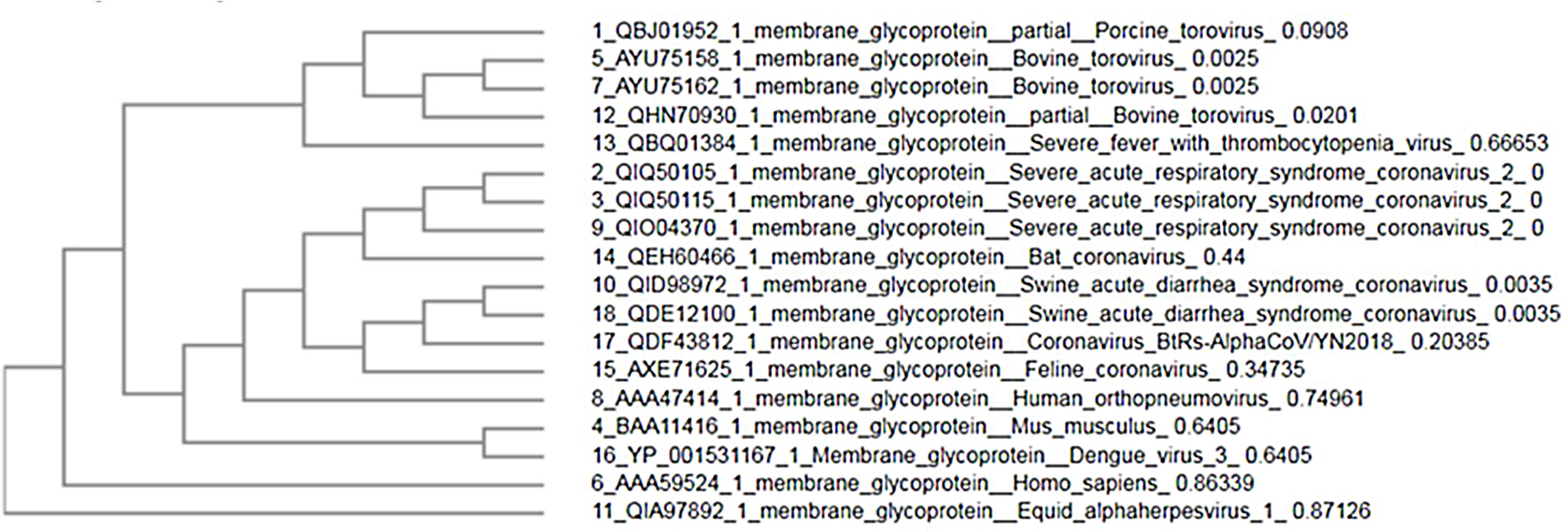
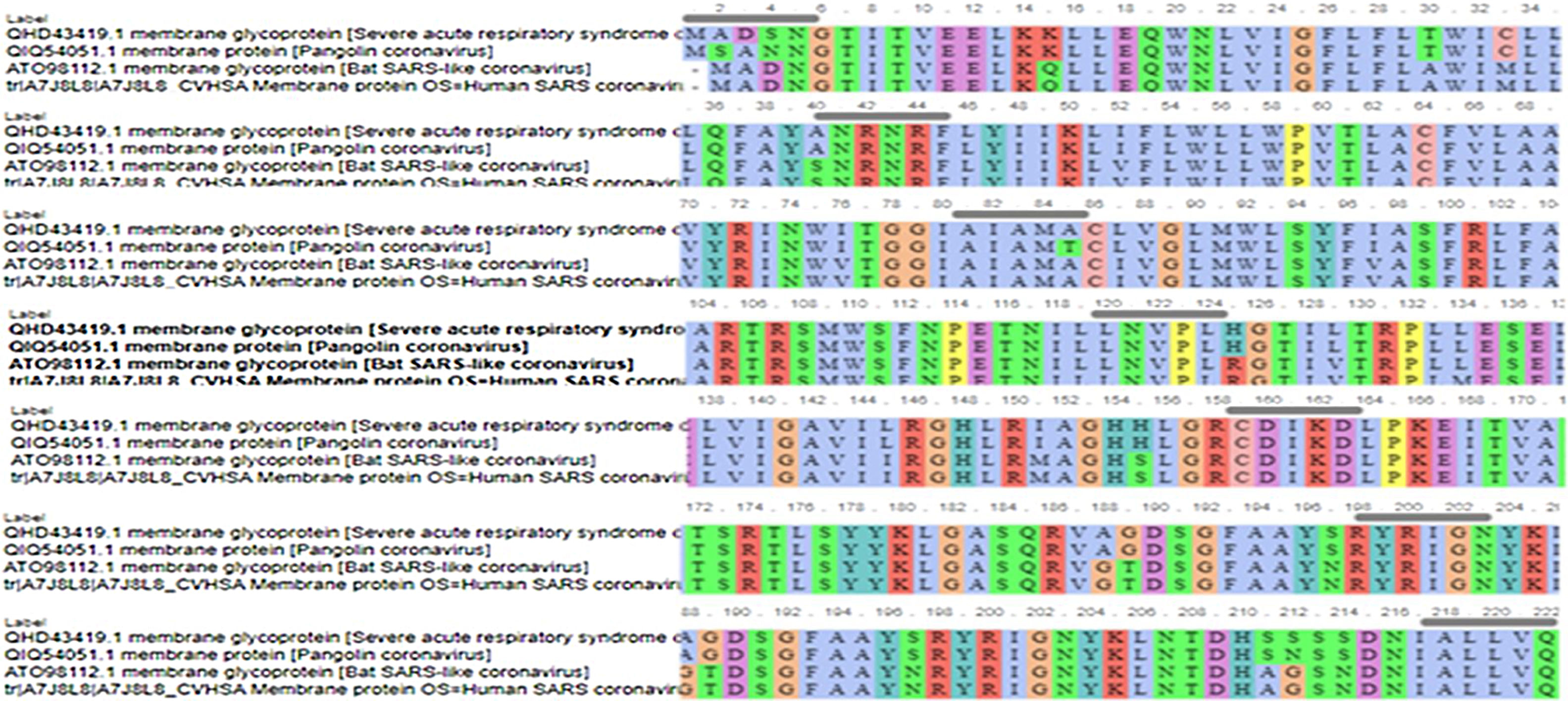
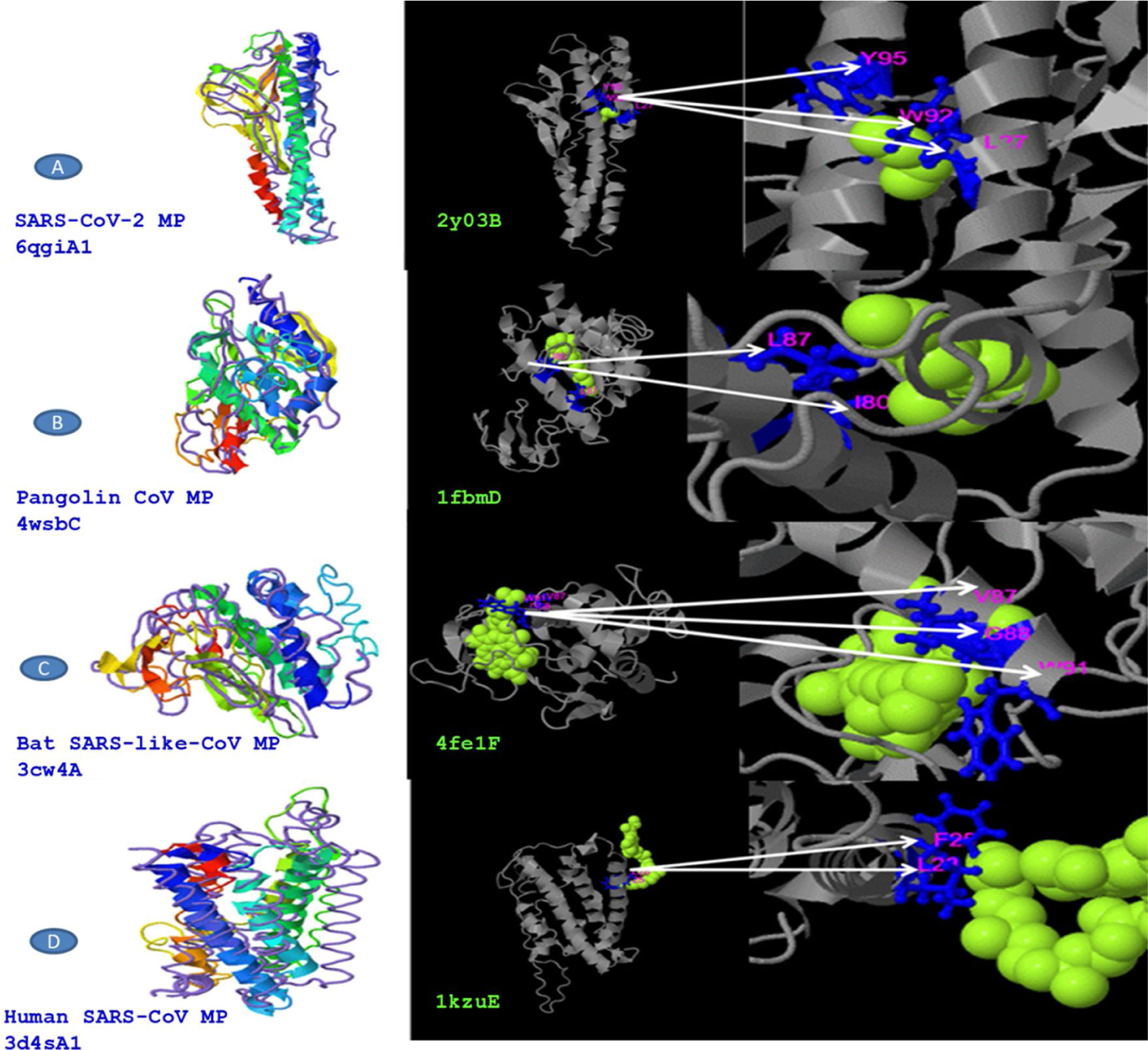
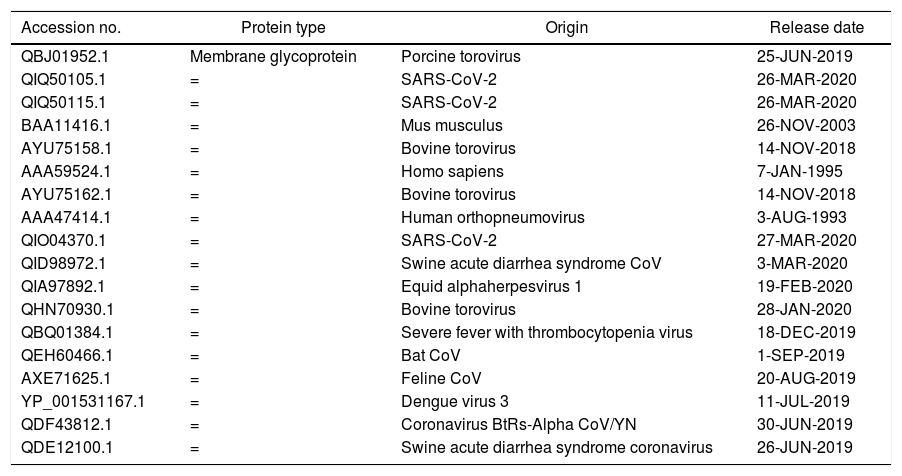
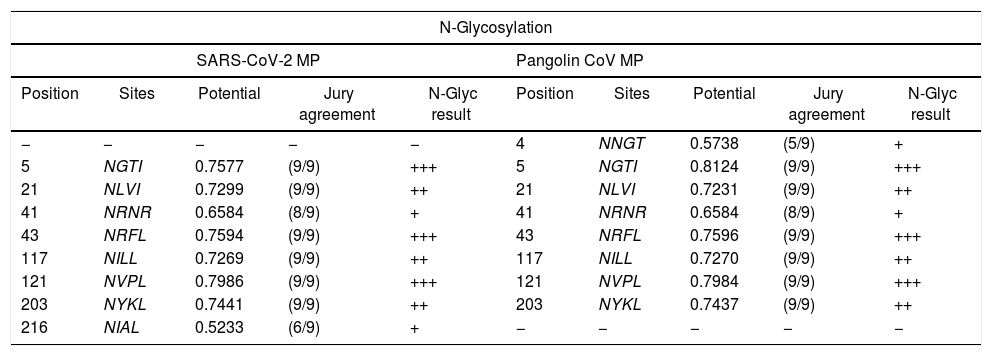
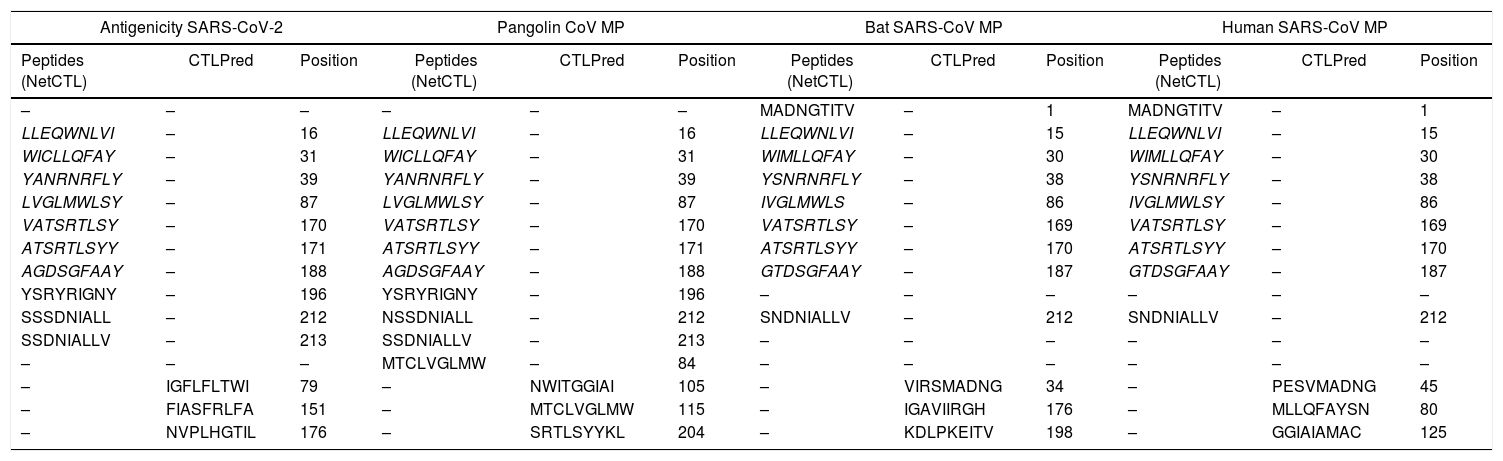
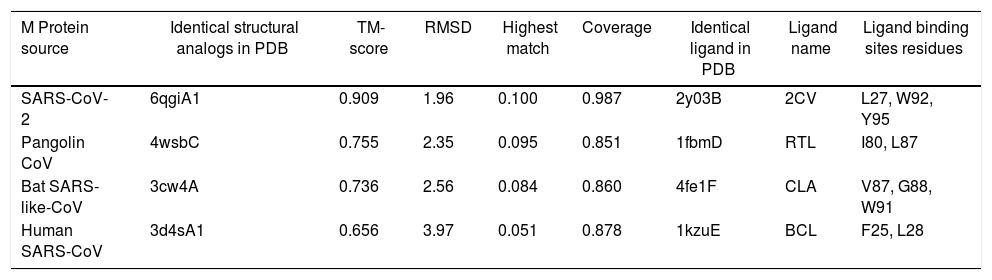
ResultsWe detected high similarity in sequence alignment for >89% between COVID-19 MP and other MP of CoVs. Prediction of N-glycosylation and cytotoxic T-cell epitopes, we identified precisely sites between SARS-CoV-2 MP and Pangolin CoV MP 100%. We also didn’t obtain any similarity in ligand binding site residues between MP sequences. Our study didn’t reveal any similarity in CTL epitope predication between coronaviruses under study using the CTLPred server.
ConclusionsOur results exhibit that the membrane glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 is closely associated with predecessor SARS-CoVs specifically Pngolin CoV. Prediction of novel CTL epitopes may substantial scopes for the expansion of a peptide-based vaccine for the inhibition virion assembly of SARS-CoV-2.
Una nueva cepa de coronavirus está causando estragos en la humanidad, por lo que la OMS declaró la situación de pandemia el 20 de marzo de 2020. La glicoproteína de membrana MP atraviesa la envoltura viral, y tiene una secuencia de glicosilación altamente conservada.
ObjetivoEl objetivo de nuestro estudio fue averiguar la N-glicosilación, los sitios de unión y las variaciones antigénicas entre COVID-19 y el resto de virus asociados.
MétodosRealizamos metodologías in silico para análisis de series, tanto a nivel operativo como de resultados, y valoramos y comparamos los factores de estudio.
ResultadosDetectamos una gran similitud en cuanto a la alineación de secuencia para > 89% entre la MP de COVID-19 y otras MP de CoV. Prediciendo la N-glicosilación y los epítopos de las células T citotóxicas identificamos con precisión del 100% los sitios entre MP de SARS-CoV-2 y MP de CoV de pangolín. No obtuvimos ninguna similitud en cuanto a los residuos del sitio de unión del ligando entre las secuencias de MP. Nuestro estudio no reveló ninguna similitud en la predicción del epítope CTL entre los coronavirus estudiados, utilizando el servidor CTLPred.
ConclusionesNuestros resultados muestran que la glicoproteína de membrana de SARS-CoV-2 está estrechamente asociada a los SARS-CoV anteriores, específicamente CoV de pangolín. La predicción de los nuevos epítopos CTL puede definir sustancialmente la expansión de una vacuna basada en péptidos para la inhibición del ensamblaje del virión de SARS-CoV-2.