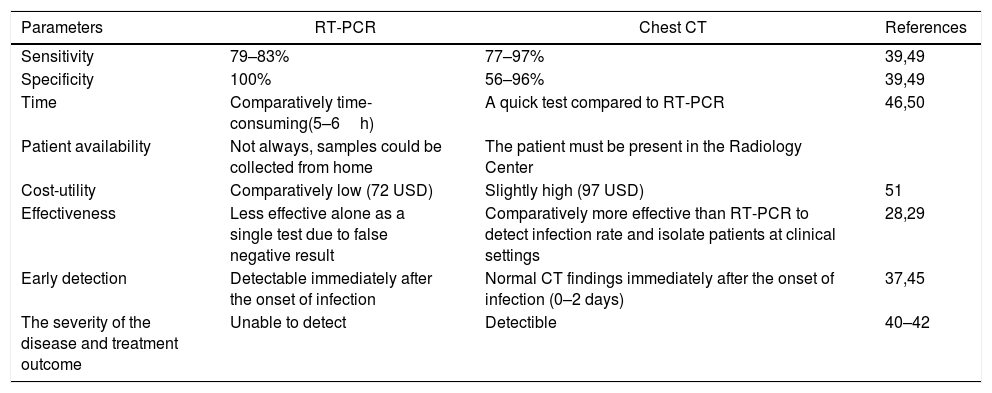
A group of pneumonia patients was detected in Hubei Province, in China in December 2019. The etiology of the disease was unknown. Later, the researchers diagnosed the novel Coronavirus as the causal agent of this respiratory disease. On February 12th 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) officially named this disease Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Consequently, the disease spread globally and became a pandemic. As there is no specific treatment for the symptomatic patients and several vaccines are approved by WHO, the efficacy and effectiveness of these vaccines are not fully understood yet and the availability of these vaccines are very limited. In addition, new variants and mutants of SARS-CoV-2 are thought to be able to evade the immune system of the host. So, diagnosis and isolation of infected individuals is advised. Currently, real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is considered the gold standard method to detect novel Coronavirus, however, there are few limitations associated with RT-PCR such as false-negative results. This demanded another diagnostic tool to detect and isolate COVID-19 early and accurately. Chest computed tomography (CT) became another option to diagnose COVID-19 patients accurately (about 98% sensitivity). However, it did not apply to the asymptomatic carriers and sometimes the results were misinterpreted as from other groups of Coronavirus infection. The combination of RT-PCR and chest CT might be the best option in detecting novel Coronavirus infection early and accurately thereby allowing adaptation of measures for the prevention and control of the COVID-19.
En diciembre de 2019 se detectó un grupo de pacientes con neumonía en la provincia de Hubei, China, desconociéndose la etiología de la enfermedad. Posteriormente, los investigadores señalaron al nuevo coronavirus como agente causal de esta enfermedad respiratoria. El 12 de febrero de 2020, la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) la designó oficialmente como enfermedad por coronavirus de 2019 (COVID-19). A continuación, dicha enfermedad se propagó a nivel global, y se convirtió en una pandemia. No existe tratamiento específico para los pacientes sintomáticos, y la OMS ha aprobado diversas vacunas. Sin embargo, la eficacia y la efectividad de las mismas no se comprende plenamente aún, siendo muy limitada su disponibilidad. Además, se piensa que las diferentes variantes y mutaciones del SARS-CoV-2 son capaces de evadir el sistema inmune del huésped. Por tanto, se recomienda el diagnóstico y aislamiento de las personas infectadas. Actualmente se considera la reacción en cadena de la polimerasa con transcriptasa inversa (RT-PCR) a tiempo real el método de referencia para detectar el nuevo coronavirus. Sin embargo, existen algunas limitaciones asociadas a RT-PCR tales como los resultados falso-negativos. En consecuencia, ello ha demandado otra herramienta diagnóstica para detectar y aislar la COVID-19 de manera temprana y precisa. La tomografía computarizada (TC) de tórax se ha convertido en otra opción para diagnosticar de manera precisa a los pacientes con COVID-19 (cerca del 98% de sensibilidad). Sin embargo no se aplica a los portadores asintomáticos, y a veces se han malinterpretado los resultados como en el caso de otros grupos de infección por coronavirus. La combinación de RT-PCR y TC de tórax podría ser la mejor opción para detectar la nueva infección por coronavirus de manera temprana y precisa, permitiendo, por tanto, la adaptación de las medidas para la prevención y el control de la COVID-19.