The involvement of the pregnant woman during the epidemic caused by the Zika virus is one of the main reasons for the development of preventive measures. Vaccination of children or pre-fertile female may be the best approach to this epidemic infection.
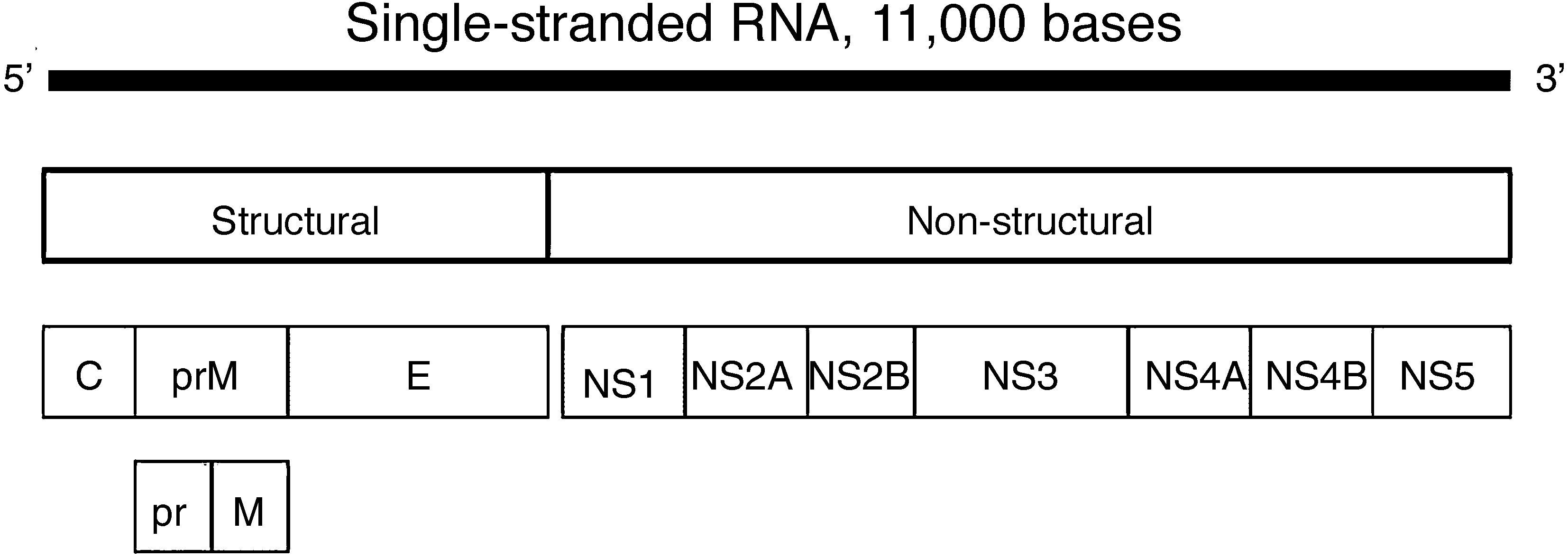
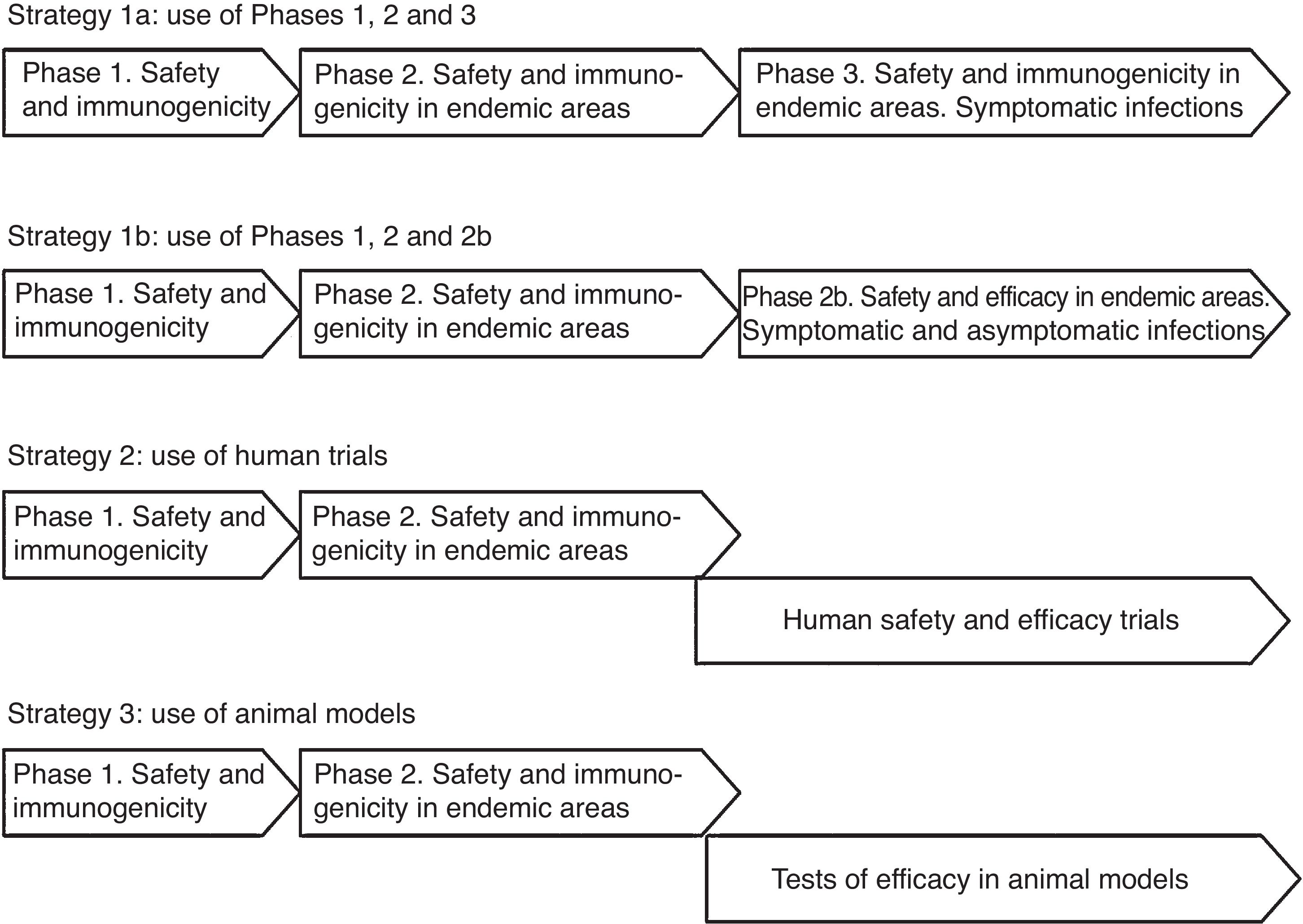
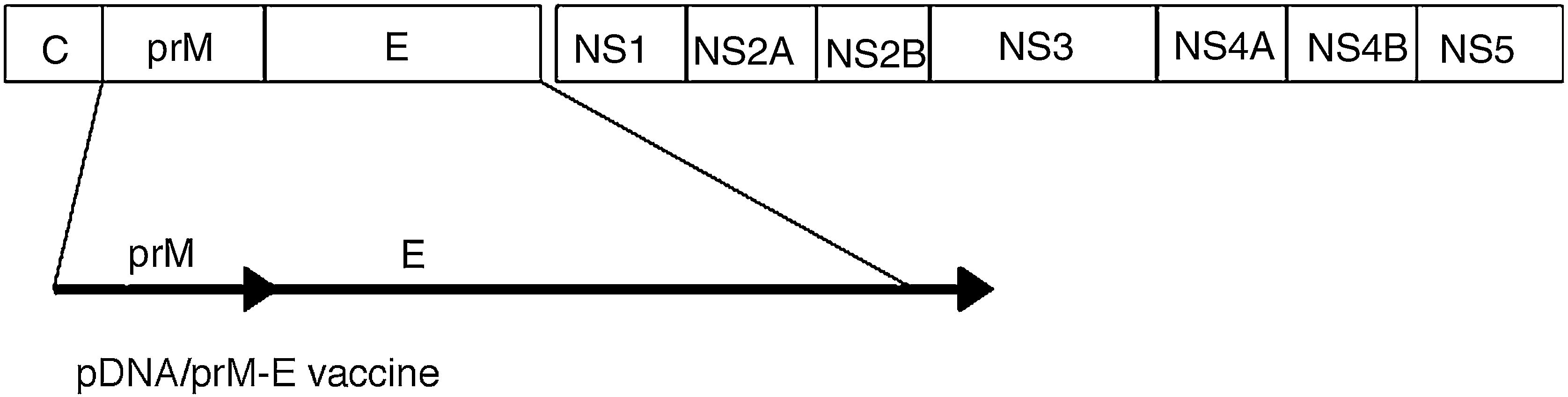
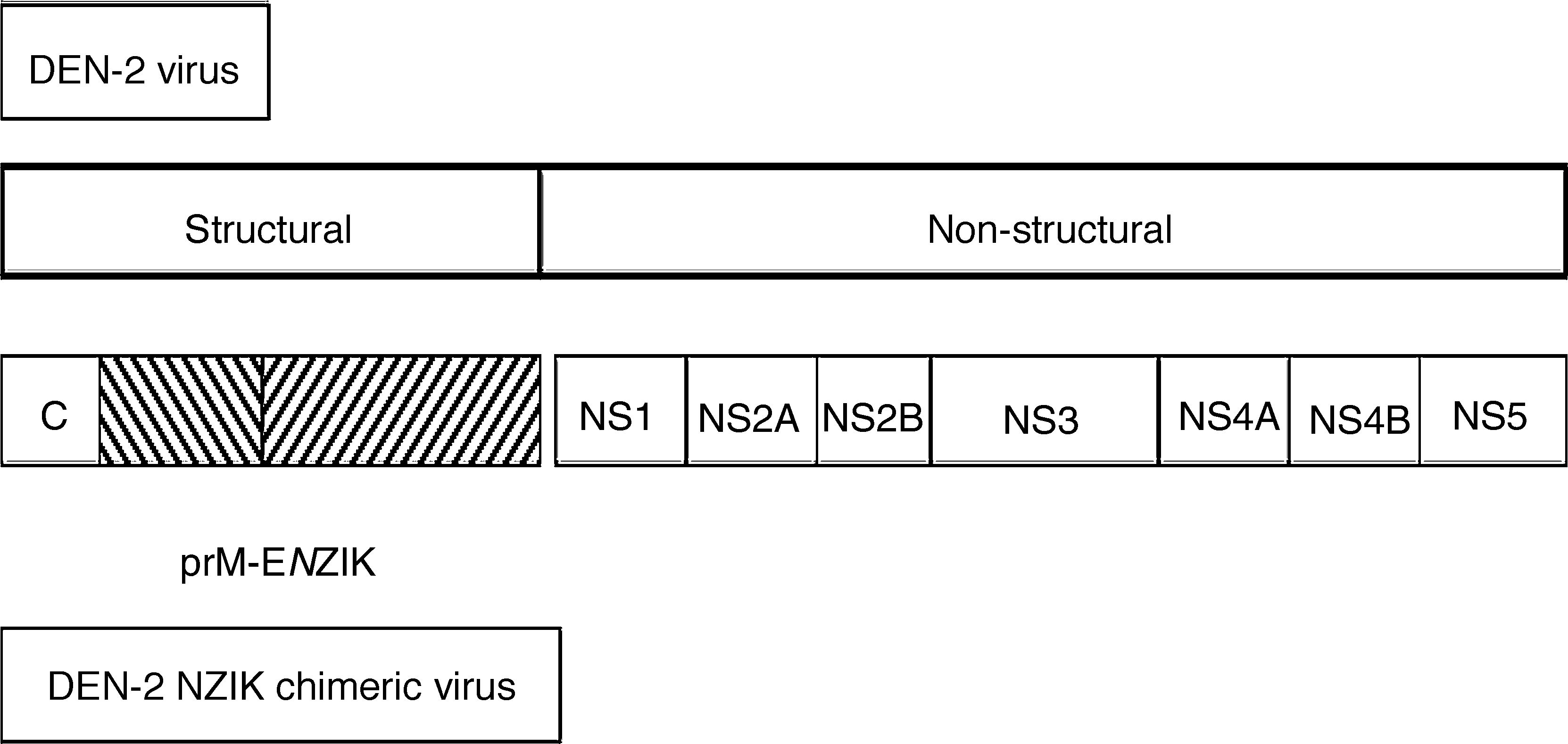
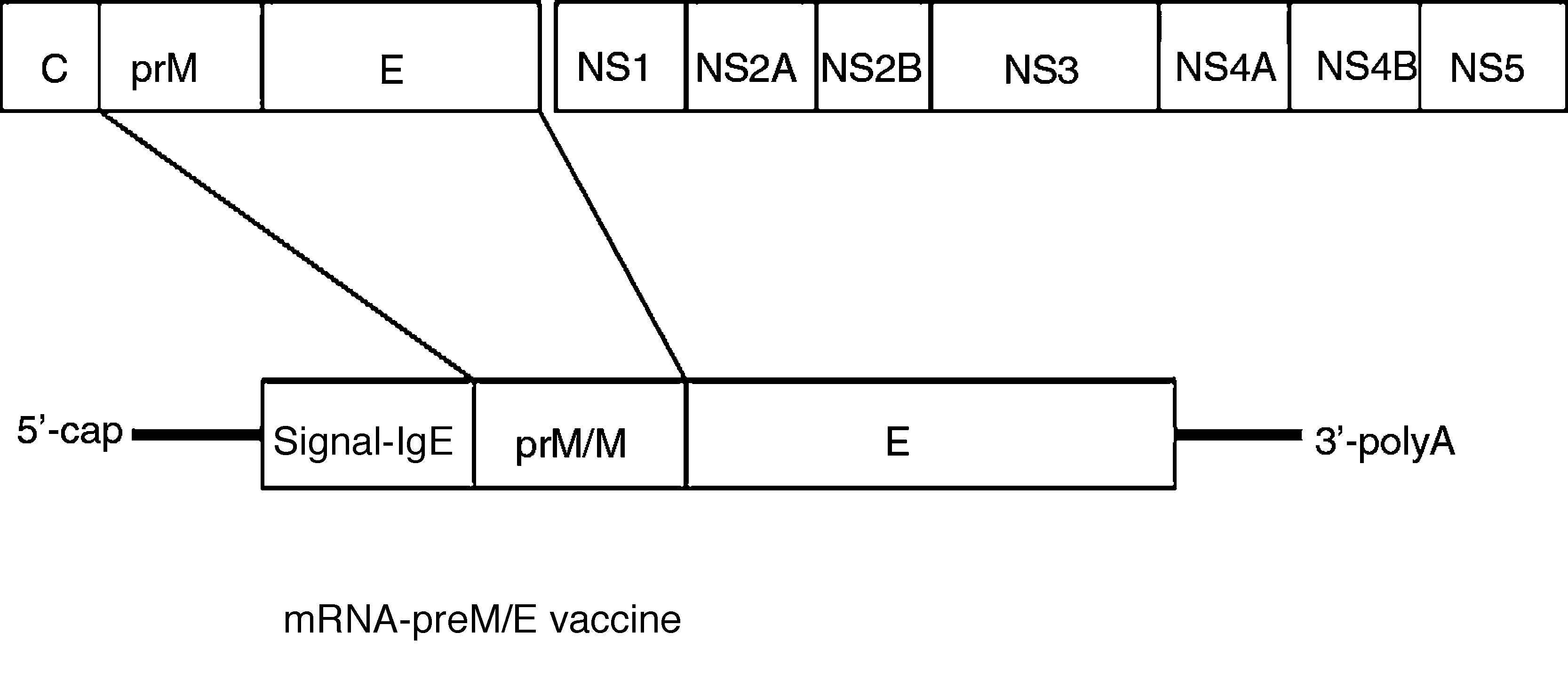
Different vaccine platforms are being developed based on the use of plasmid DNA including the prM/M and E structural proteins of the virus. They have shown in animal models, both mice and non-human primates, a 100% protection against exogenous infection. The main immune response is a humoral neutralising type. Some of these have already passed Phase 1 clinical trials. Chimeric vaccines are also being evaluated using the dengue virus genome, an adenoviral insertion vector and other attenuated and inactivated particle vectors. The results in animals are generally satisfactory.
When validating any of these vaccines it is very important to establish their ability to respond, immunity and role of the previous antibodies against dengue or other flaviviruses. As well as the possible induction of autoimmune phenomena such as Guillain–Barre syndrome and other neurological affections.
In spite of all this is progressing in a deeper knowledge not only of the virology of the Zika virus but of the development of new genetic vaccine platforms.
La afectación de la embarazada durante la epidemia causada por el virus Zika es una de las principales razones para el desarrollo de medidas preventivas. La vacunación de la población infantil o de las niñas en edad prefértil podría ser el mejor abordaje de esta infección epidémica.
Se están desarrollado diferentes plataformas vacunales basadas en la utilización de ADN plasmídico que incluyen las proteínas estructurales prM/M y E del virus. Estas han demostrado en modelos animales, tanto ratones como primates no humanos, un 100% de protección frente a la infección exógena. La principal respuesta inmune es de tipo humoral neutralizante. Algunas de ellas ya han pasado a los ensayos clínicos en fase 1. También se están evaluando vacunas quiméricas utilizando el genoma del virus dengue, un vector adenoviral de inserción y otras atenuadas y de partículas inactivadas. Los resultados en animales son generalmente satisfactorios.
A la hora de validar cualquiera de estas vacunas es muy importante establecer su capacidad de respuesta, inmunidad y papel de los anticuerpos previos frente al dengue u otros flavivirus. Así como la posible inducción de fenómenos autoinmunes como el síndrome de Guillain-Barre y otras afectaciones neurológicas.
A pesar de todo ello se está avanzando en un conocimiento más profundo no solo de la virología del virus Zika sino del desarrollo de nuevas plataformas vacunales de tipo genético.