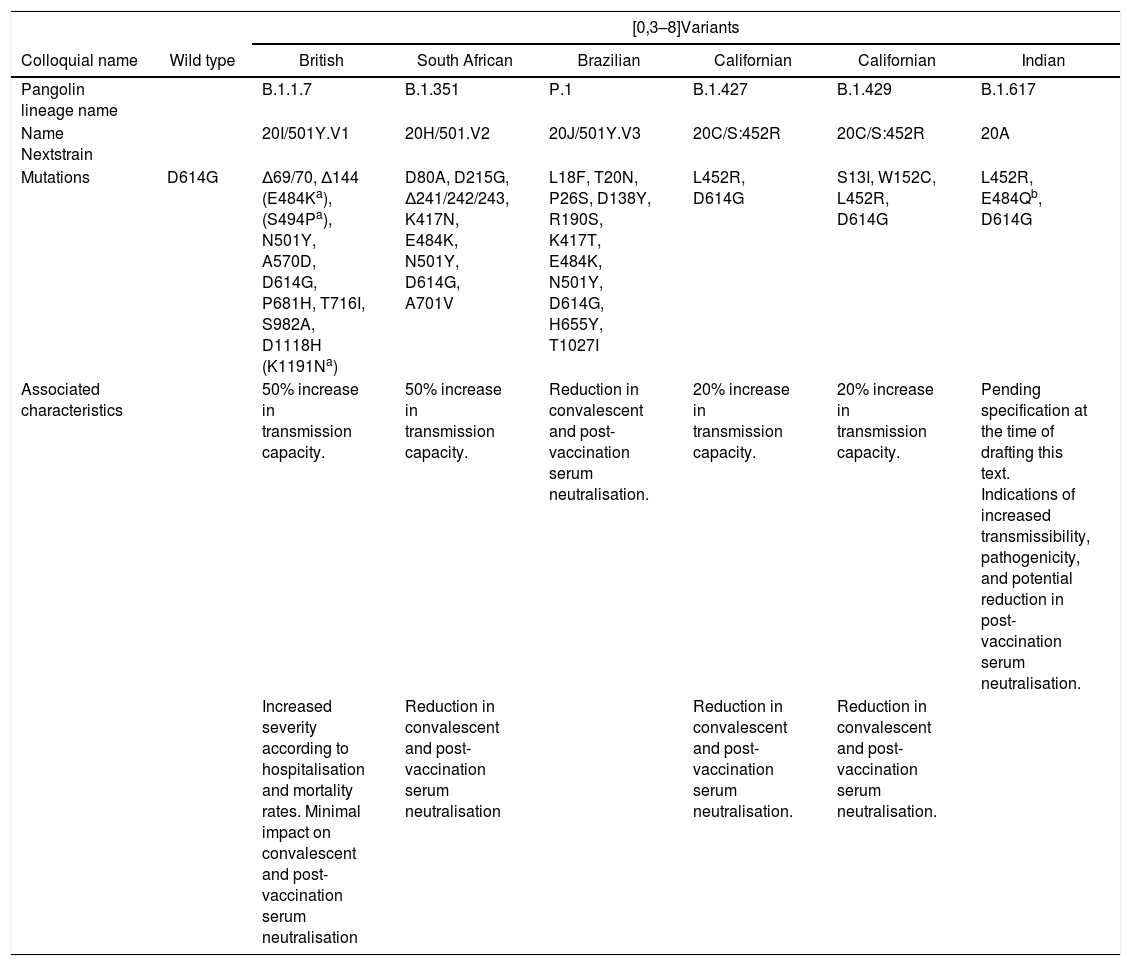
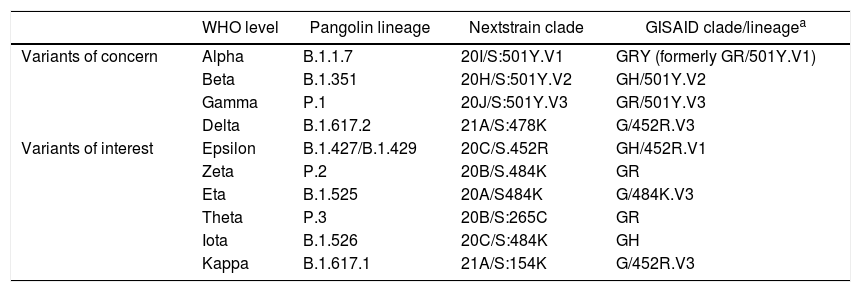
Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 genome can affect the gene encoding the Spike (S) antigen, which interacts with the host cell specific receptor, selecting mutant variants with changes in their infective capacity, pathogenic potential and resistance to neutralizing antibodies. The nomenclature to design the variants uses a colloquial form referred to the country or place of detection, a code from the “Pangolin” database and one from the “Nextstrain” page. New variants that have spread include the British B.1.1.7 (20I/501Y.V1), the South African B.1.351 (20H/501.V2), the Brazilian P.1 (20J/501Y.V3), the Californians B.1.427 B.1.429 (20C/S:452R) and the most recent, the Indian B.1.617 (VUI-21APR-01).
The gold standard for the identification of the variants is whole genome sequencing. However, real-time PCR techniques have already been developed for the detection of specific mutations that can facilitate their presumptive identification.
The impact of these variants on global vaccination programs has raised concern. It is generally thought that, since the response evoked by the vaccine against the S antigen is directed at the entire protein and the mutations only affect specific regions, the escape effect of the vaccine antibodies will be limited. Among the future strategies proposed for immuno-protection, the increase in the number of doses, the alternation of vaccines and the development of specific vaccines against different variants has been suggested.
Las mutaciones en el genoma de SARS-CoV-2 pueden afectar al gen que codifica el antígeno espicular (S), que interactúa con el receptor específico de la célula huésped, seleccionando variantes mutantes con alteraciones en su capacidad infectiva, potencial patógeno y resistencia a los anticuerpos neutralizantes. En la nomenclatura de las variantes se utiliza una forma “coloquial” que suele hacer referencia al país o lugar de detección, un código de la base de datos “Pangolín” y uno de la página “Nextstrain”. Entre las nuevas variantes que se han ido propagando se incluyen la Británica B.1.1.7 (20I/501Y.V1), la Sudafricana B.1.351 (20H/501.V2), la Brasileña P.1 (20J/501Y.V3), las Californianas B.1.427 y B.1.429 (20C/S:452R) y la más reciente, la India B.1.617 (VUI-21APR-01).
El método de referencia para la identificación de las variantes es la secuenciación del genoma completo. Sin embargo, ya se han desarrollado técnicas de PCR en tiempo real para la detección de mutaciones específicas que pueden facilitar su identificación presuntiva.
El impacto de estas variantes en los programas globales de vacunación ha suscitado inquietud. En general se piensa que, dado que la respuesta evocada por la vacuna frente al antígeno S se dirige a la totalidad de la proteína y las mutaciones sólo afectan a regiones concretas, el efecto de escape a los anticuerpos vacunales será sólo limitado. Entre las estrategias futuras propuestas para la inmuno-protección se ha sugerido el incremento del número de dosis, la alternancia vacunal y el desarrollo de vacunas específicas frente a diferentes variantes.