Pemphigus herpetiformis is an autoimmune bullous disease considered an infrequent variant of pemphigus. It is characterized by clinical findings of dermatitis herpetiformis with immunopathological features of pemphigus. We report the case of a 33-year-old woman with dermatosis on the scalp, trunk and upper and lower extremities presenting as circular plaques with vesicles in a herpetiform pattern, white scale and yellowish crusts. Histopathological and direct immunofluorescence findings were compatible with pemphigus. The patient was treated with dapsone and prednisone, with significant improvement. This presentation is uncommon, and the clinical course differs from that of pemphigus vulgaris.
El pénfigo herpetiforme es una enfermedad ampollosa, autoinmune, considerada una variante clínica infrecuente. Se caracteriza por hallazgos clínicos de la dermatitis herpetiforme en combinación con aspectos patológicos e inmunológicos específicos. Se presenta el caso de una paciente femenina de 33 años de edad, con una dermatosis diseminada a cabeza en piel cabelluda, tronco por ambas caras y en extremidades superiores e inferiores con lesiones aisladas. Estaba constituida por placas circulares con vesículas agrupadas en racimos, escama blanquecina y costras melicéricas. Los estudios histopatológico y de inmunofluorescencia directa, fueron sugestivos de pénfigo. Se estableció tratamiento sistémico con dapsona y prednisona con mejoría significativa. Esta forma de presentación poco común tiene un curso clínico diferente a la del pénfigo vulgar.
Pemphigus herpetiformis (PH) is an uncommon variant of pemphigus that combines the clinical features of dermatitis herpetiformis with the immunopathologic features of pemphigus vulgaris. As far back as 1955, Floden and Gentele described certain clinical features they dubbed “acantholytic dermatitis herpetiformis”, and the diagnostic criteria for this entity were proposed by Jablonska et al.1 By 2014, around 100 cases had been reported in the literature.2
Incidence of the herpetiformis variant among pemphigus patients ranges from 6% to 7.3%. Mean age at onset is 65 years (range 30–80 years), and only four cases have been reported in the paediatric population.3 The disease has no predilection for either sex or race.2
Clinically, the disorder is characterised by the presence of erythematous, vesicular and/or bullous lesions forming the typical annular or bunched “herpetiform” pattern. Lesions usually occur on the trunk and the upper portion of the limbs. Mucous involvement is uncommon. Pruritus is a typical symptom of this disease. Peripheral eosinophilia is found in 40% of cases on average.4
PH histology varies with respect to the evolution of the topical lesions. Some findings characteristic of the early of late stages of the disease include: eosinophilic spongiosis and intraepidermal or subcorneal neutrophilic and eosinophilic microabscesses. Inflammatory cell infiltration, predominantly eosinophils (20%), neutrophils (20%), or both (60%), is also a feature. Unlike pemphigus vulgaris, acantholysis is an uncommon finding, but can present in the later stages of the disease.5
Direct immunofluorescence on perilesional skin samples shows IgG and C3 deposition around the cell surfaces of keratinocytes in the upper epidermis. There have also been reports of elevated interleukin 8 levels that stimulate neutrophil chemotaxis in this layer. Indirect immunofluorescence shows the presence of circulating IgG antibodies that bind to epidermal cell surfaces. In both techniques, IgG subclass 4 antibodies predominate. The target antigen for these antibodies is desmoglein 1, a desmosomal protein predominantly located in the upper epidermis, and to a lesser extent desmoglein 3, found in the lower epidermis.6,7 Several authors have also reported the presence of antibodies to desmoglein 1 and 3.4,8–10
The clinical presentation of PH is non-specific, and the features are often confused with those of other blistering diseases such as dermatitis herpetiformis, pemphigus foliaceus, bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA dermatosis and pemphigus vulgaris. Intense pruritus is a common feature of PH, and this, together with a finding of IgG antibodies, narrows down the differential diagnosis with other variants of pemphigus. Diagnosis is based on the correlation between clinical and histopathology findings. However, given the variability of the latter, immunopathology findings are considered the most reliable basis for confirmation.2
The treatment of choice for PH is dapsone, at a dose of between 100 and 300mg/day.2 It can be used in monotherapy, but should ideally be combined with steroids and/or systemic immunosuppressants, and has been associated with remission in some cases. Systemic steroid dosage varies from 10 to 120mg/day as a loading dose. The most commonly used immunosuppressants are: azathioprine, at a dose of 100–200mg/day, and cyclophosphamide, at 50–100mg/day, combined with systemic steroids. Good results have been reported with this therapy, above all in patients whose initial symptoms ultimately evolve into the classic variants of pemphigus.2,4,11 Leflunomide at a dose of 15mg/day in combination with steroids achieved remission in a patient previously refractory to azathioprine and sulfasalazine.12 The combination of mycophenolate mofetil or methotrexate and systemic steroids has shown poor results and has led to recurrence in some cases.8,13 Some biological drugs have also been disappointing: although initial treatment with rituximab infusion was promising in two patients, the disease reappeared during follow-up.14 Rapid remission was achieved in a patient treated with plasmapheresis in combination with systemic steroids and cyclophosphamide, although the patient later relapsed.15 Remission has been reported in two cases following administration of 1g/kg parenteral immunoglobulin for 4 weeks followed by a monthly maintenance dose combined with systemic steroids or sulfasalazine.10,12
PH is a benign disease that responds well to conventional dapsone+steroid therapy. It is rarely associated with cancer: only seven such cases have been reported in the literature, four associated with lung cancer, one with oesophageal cancer, one with prostate cancer, and one with cutaneous angiosarcoma.16
We present the case of a patient with a clinical, histological and immunopathological diagnosis of PH who responded favourably to dapsone+systemic steroids.
Case studyThe patient is a 33-year-old women living in her native city of Mexico, with no personal or familial medical history relevant to her current complaint.
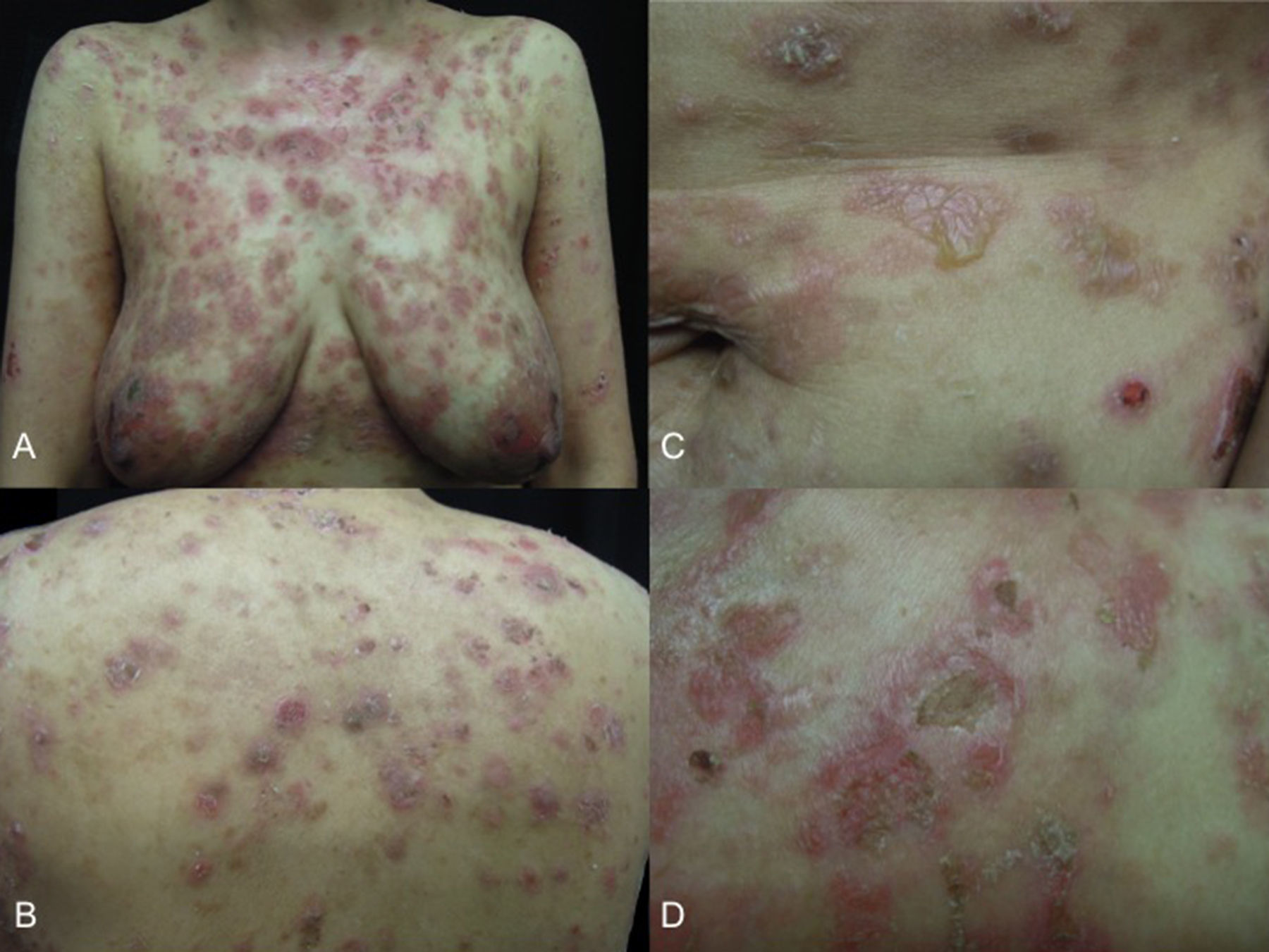
She presented with dermatosis affecting the scalp, the anterior and posterior skin of the trunk and the upper and lower limbs. The lesions consisted of circular plaques with vesicles, occurring either alone or in a herpetiform pattern, with whitish scale and yellow or haemorrhagic crusts (Fig. 1). The first signs, in the form of scales on the scalp, had appeared 18 months previously, and were followed 3 months later by urticarial plaques and eventually intensely pruritic vesicles on the trunk. These rapidly spread to the scalp and the upper and lower limbs. She had received topical therapies from other specialists (calcipotriol and clobetasol), with transient improvement followed shortly by relapse, which is why she consulted our department.
Based on our clinical suspicion, we took a biopsy for light microscopy, which showed laminated hyperkeratosis with areas of parakeratosis and crusting. Moderate, irregular spongiotic epidermal acanthosis and formation of intraepidermal spongiotic spaces, with isolated dyskeratotic cells, basal layer oedema and isolated lymphocytic exocytosis. The upper and mid-epidermis presented mild lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrates.
Direct immunofluorescence showed IgG deposits in keratinocyte junctions. Routine laboratory studies were unremarkable. We also ordered an endoscopic examination, as the patient reported recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms. The finding was erosive gastritis.
On the basis of these findings, we decided to start treatment with 1mg/kg/day oral prednisone on a tapering regimen, combined with 100mg/day dapsone until resolution.
DiscussionWe present a case of PH presenting with a series of different manifestations ranging from scales, urticarial plaques, and the classic herpetiform vesicle pattern. This clinical variability, together with the histopathological findings consisting mainly of spongiosis, spongiotic intraepidermal spaces and lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrates in the superficial and mid-epidermis, could be explained by the presence of antibodies against desmoglein 1. Antibodies against desmoglein 3 are also found in some patients, but never a combination of both. This suggests that the disease may overlap the vulgar or foliaceus forms of pemphigus, although the finding of acantholysis would depend on the particular antibody expressed. One possible explanation for this is that the antibodies expressed in PH are relatively less virulent than those expressed in pemphigus foliaceus or vulgaris. Another theory suggests that antibodies target different epitopes on the autoantigen, and only cause inflammation by cytokine and complement activation, leading to intercellular oedema and eosinophilic spongiosis with no acantholysis. Bearing this in mind, changes in the epitopes targeted by antibodies would cause some cases of pemphigus herpetiformis to evolve into pemphigus vulgaris or pemphigus foliaceus.6,17
The foregoing, together with the presence of IgG deposits on the surface of epidermal keratinocytes, confirmed the diagnosis of PH in our patient. We decided to start combination therapy with oral dapsone and steroids, based on the findings of other authors who reported good outcome and few recurrences with this approach. Moreover, evidence has shown that patients with few or no antibodies and with evident eosinophilic spongiosis, as in our case, respond better to dapsone.4
Therapeutic response was favourable, an outcome consistent with the benign course of this disease, in which complete remission of dermatosis is usually achieved, followed by a low maintenance dose of steroids.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.