Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is one of the most frequent endocrine diseases. Most of the patients with PHPT are asymptomatic, and only 20% of them become symptomatic with increasing levels of calcium. It has been reported that normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism (NPHPT) may be the incipient period of PHPT where calcium (Ca) levels are in normal range, and it may advance to overt PHPT. Early diagnosis of PHPT is important in order to prevent its complications. In this retrospective study, we aimed to evaluate the role of 99mTc-MIBI parathyroid scintigraphy on lesion detection in patients with NPHPT.
Material and methodsThe parathyroid scintigraphy database was reviewed retrospectively in patients with PHPT. 117 patients who underwent 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy were recruited to the study. Serum calcium level above 10.5mg/dl was considered as hypercalcemia.
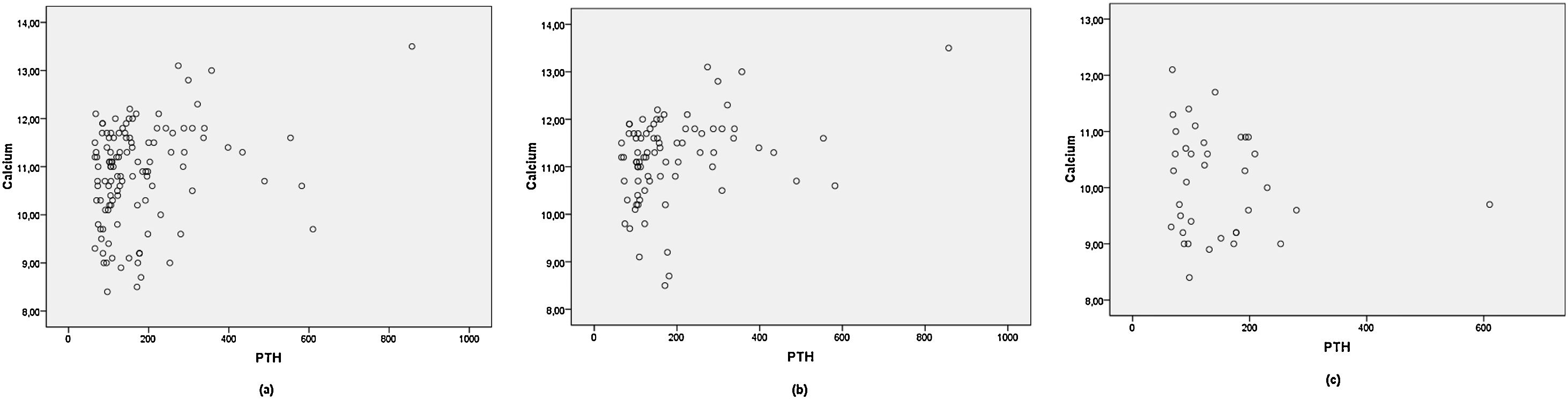
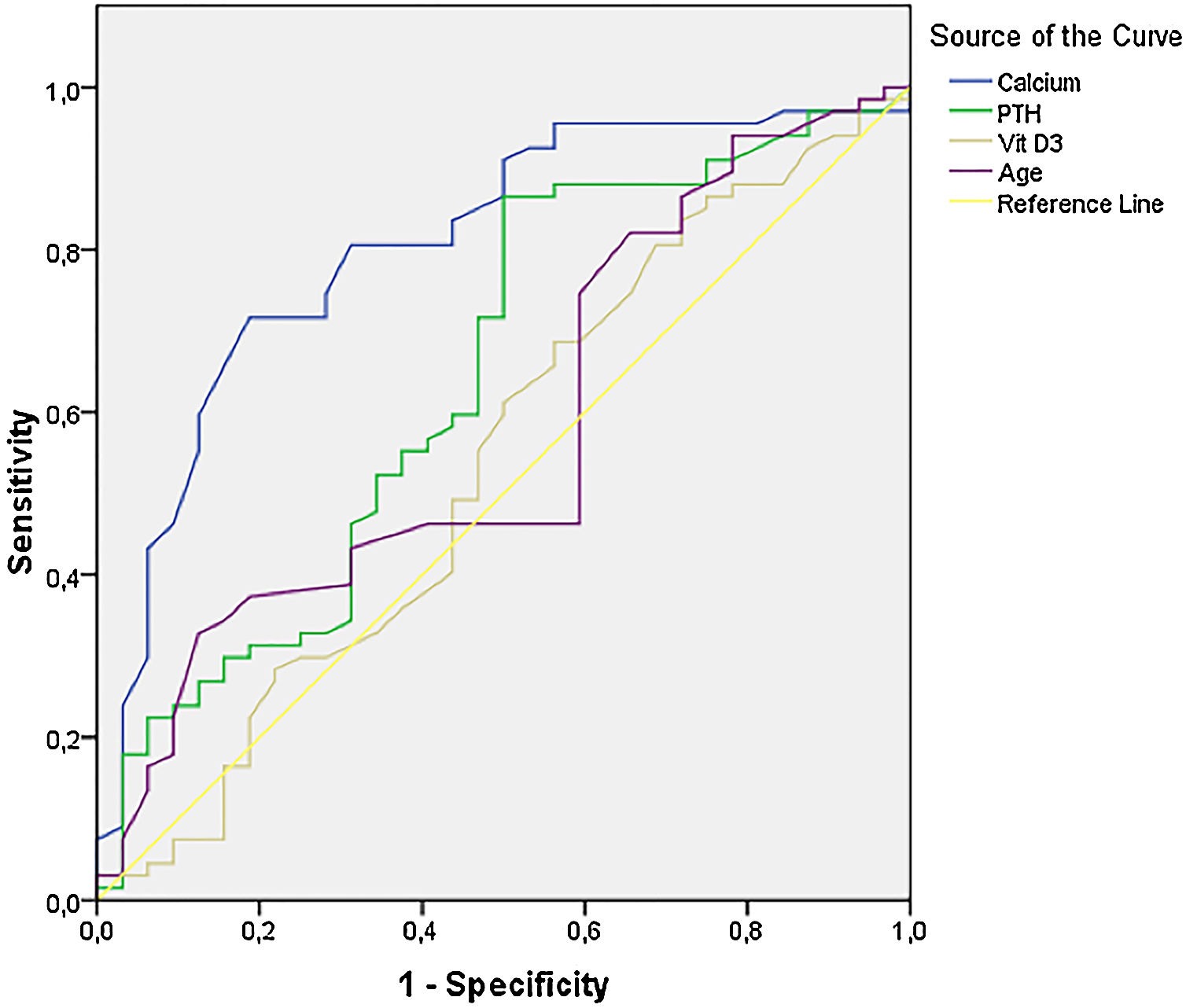
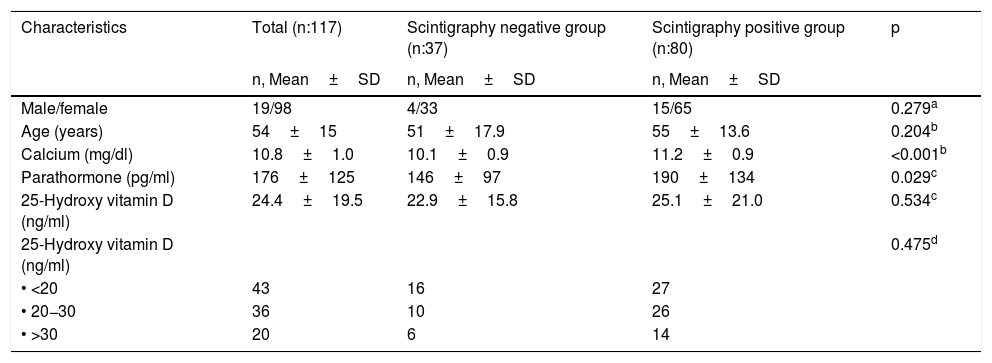
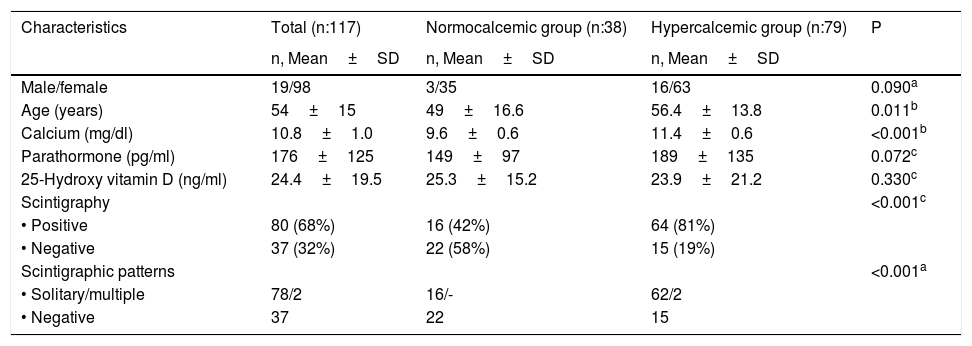
ResultsA total of 117 patients (female/male:98/19) mean serum PTH levels (mean±SD) were 149±97pg/ml in normocalcemic group (Ca:9.6±0.6mg/dl, n:38) and 189±135pg/ml in hypercalcemic group (Ca:11.4±0.6mg/dl, n:79) (p:0.072). The sex and ages were not different between the scintigraphy positive and negative groups, but the lesion detection rates with parathyroid scintigraphy were 42% in normocalcemic group and 81% in hypercalcemic group (p<0.0001).
ConclusionsSeveral factors including serum Ca, the imaging protocol, existence of multiglandular disease, the size and MIBI biokinetics of the adenoma may influence lesion detectability in parathyroid scintigraphy. Although high serum Ca level is an important parameter in predicting its success, parathyroid scintigraphy remains a valuable diagnostic method even in patients with NPHPT.
El hiperparatiroidismo primario (PHPT) es una de las enfermedades endocrinas más frecuentes. La mayoría de los pacientes con PHPT son asintomáticos, y sólo el 20% de ellos se vuelven sintomáticos con niveles crecientes de calcio. Se ha informado que el hiperparatiroidismo primario normocalcémico (NPHPT) puede ser el período incipiente de PHPT en el que los niveles de calcio (Ca) están en un rango normal, y puede avanzar a PHPT establecido. El diagnóstico temprano de la PHPT es importante para prevenir sus complicaciones. En este estudio retrospectivo, nos propusimos evaluar el papel de la gammagrafía paratiroidea 99mTc-MIBI en la detección de lesiones en pacientes con NPHPT.
Material y métodosLa base de datos de gammagrafía paratiroidea fue revisada retrospectivamente en pacientes con PHPT. Fueron reclutados 117 pacientes que se sometieron a la gammagrafía 99mTc-MIBI para estudio. El nivel de calcio sérico superior a 10,5mg/dl se consideró como hipercalcemia.
ResultadosLos niveles medios de HPT sérica (media±SD) de un total de 117 pacientes (mujeres/mujeres:98/19) fueron de 149±97pg/ml en el grupo normocalcémico (Ca:9,6±0,6mg/dl, n:38) y de 189±135pg/ml en el grupo hipercalcémico (Ca:11,4±0,6mg/dl, n:79) (p:0,072). El sexo y la edad no fueron diferentes entre los grupos de gammagrafía positiva y negativa, pero las tasas de detección de lesiones con gammagrafía paratiroidea fueron del 42% en el grupo normocalcémico y del 81% en el grupo hipercalcémico (p<0,0001).
ConclusionesVarios factores, entre los que se incluyen el Ca sérico, el protocolo de imágenes, la existencia de enfermedad multiglandular, el tamaño y la biocinética MIBI del adenoma pueden influir en la detectabilidad de la lesión en la gammagrafía paratiroidea. Aunque un alto nivel de Ca en suero es un parámetro importante para predecir su éxito, la gammagrafía paratiroidea sigue siendo un método de diagnóstico valioso incluso en pacientes con NPHPT.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)