The social networks like Twitter®, Facebook® and YouTube® have become interaction media with visualisation scientific information. Alternative metrics (altmetrics) have emerged that assess the dissemination and the impact of the scientific journals in the social networks. However, it is unknown if there is a correlation between the journal and the traditional measurements of impact based on the number of citations for the journal of rheumatology.
MethodsThe journals of rheumatology included in Scimago Country and Journal Ranking were identified, and the results of their metrics were collected based on the number of citations. The presence in social networks was determined using metrics, such as the number of followers and tweets. The correlation between them was evaluated using the Spearman correlation coefficient, adjusted for the time elapsed since the account was created.
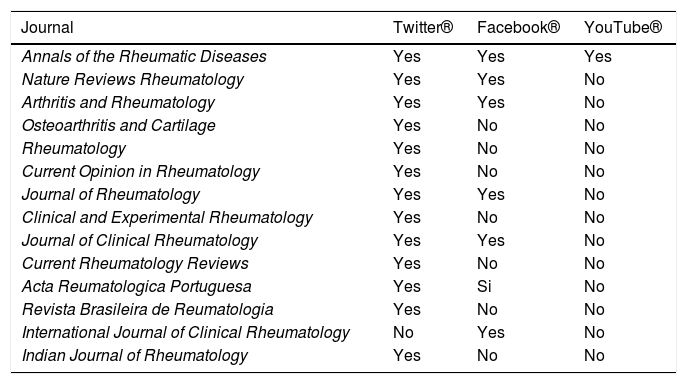
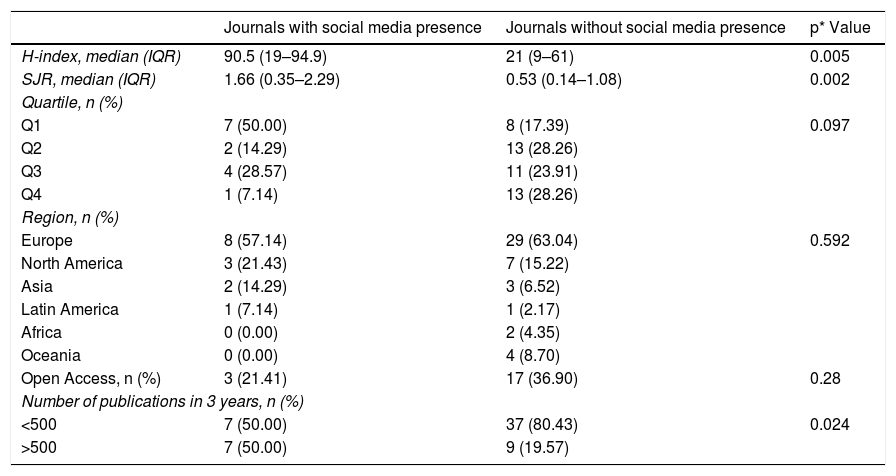
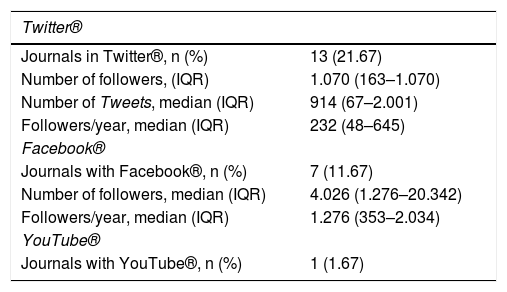
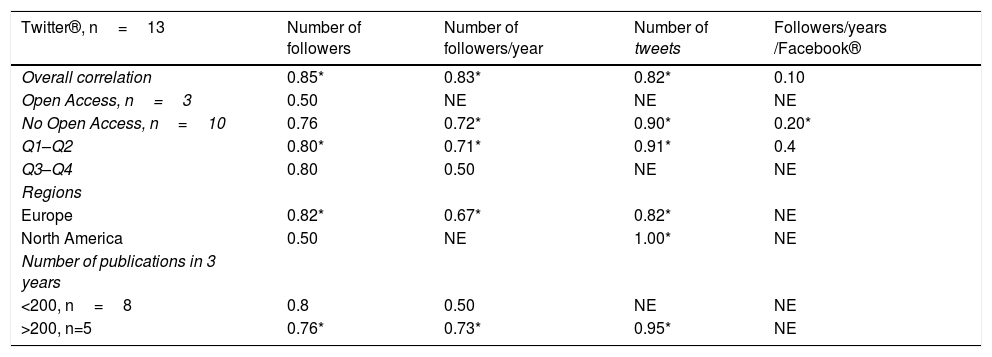
ResultsOut of a total of 60 rheumatology journals, 14 had a presence in social networks. The Scimago journal ranking indicator (SJR) was higher in journals with a social network (90.5 vs. 21; p<0.05). The correlation between the SJR and Twitter® activity metrics was excellent: with the number of followers (r=0.85), followers/year (r=0.83), and number of tweets (r=0.82).
ConclusionThis study suggests that traditional impact metrics based on the number of citations correlate very well with the social network presence metrics of rheumatology journals, especially on Twitter®.
Las redes sociales como Twitter®, Facebook® y YouTube® se han convertido en medios de interacción y visualización de información científica. Han surgido medidas alternativas (almetrics) que evalúan la diseminación y el impacto de las revistas científicas en las redes sociales; sin embargo, se desconoce si existe correlación entre la actividad de las revistas de reumatología en redes sociales y las métricas tradicionales de impacto basadas en número de citaciones.
MétodosSe identificaron las revistas de reumatología a partir de la base de datos de SCImago de Scopus® y se extrajo la información de las métricas tradicionales basadas en el número de citaciones. Se determinaron métricas alternativas de actividad de las revistas en Facebook®, Twitter®, YouTube® e Instagram®. Se evaluó la correlación entre ellas usando el coeficiente de correlación de Spearman, ajustado por el tiempo transcurrido desde la creación de la cuenta.
ResultadosDe un total de 60 revistas de reumatología, 14 contaban con la presencia en las redes sociales evaluadas. El SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) fue más alto en revistas con red social (90,5 vs. 21; p<0,05). La correlación entre el SJR y las métricas de actividad del Twitter® fue excelente: con el número de seguidores (r=0,85), seguidores/año (r=0,83) y número de tweets (r=0,82).
ConclusiónNuestro estudio sugiere que las métricas tradicionales de impacto basadas en el número de citaciones, se correlacionan muy bien con las métricas de presencia en redes sociales de las revistas de reumatología, en especial en Twitter®.