Although cerebral angiography is the reference technique for the diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases, it is not without complications.
ObjectivesTo determine the incidence and risk factors of complications derived from therapeutic cerebral angiography (TCA), as well as to assess the risk factors associated with the appearance of local and intracranial complications.
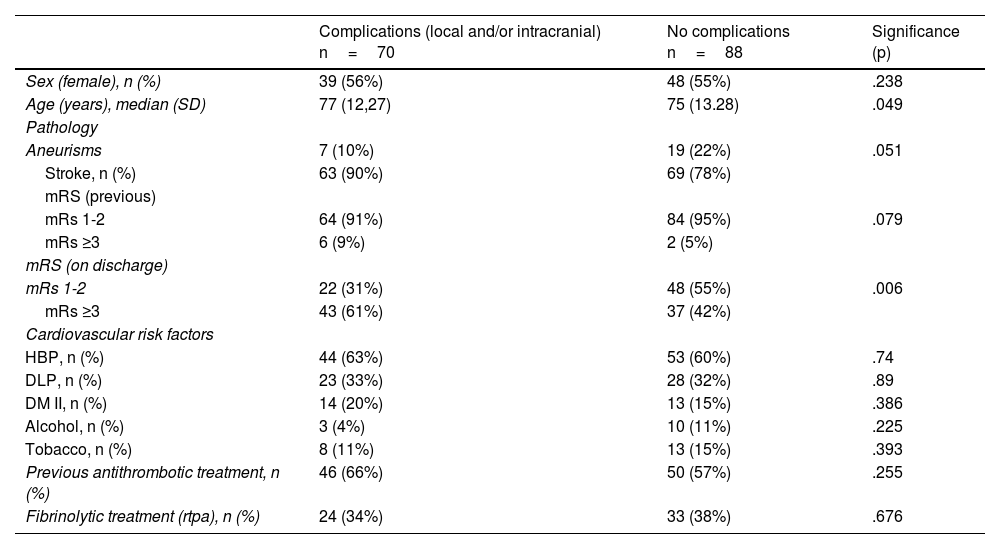
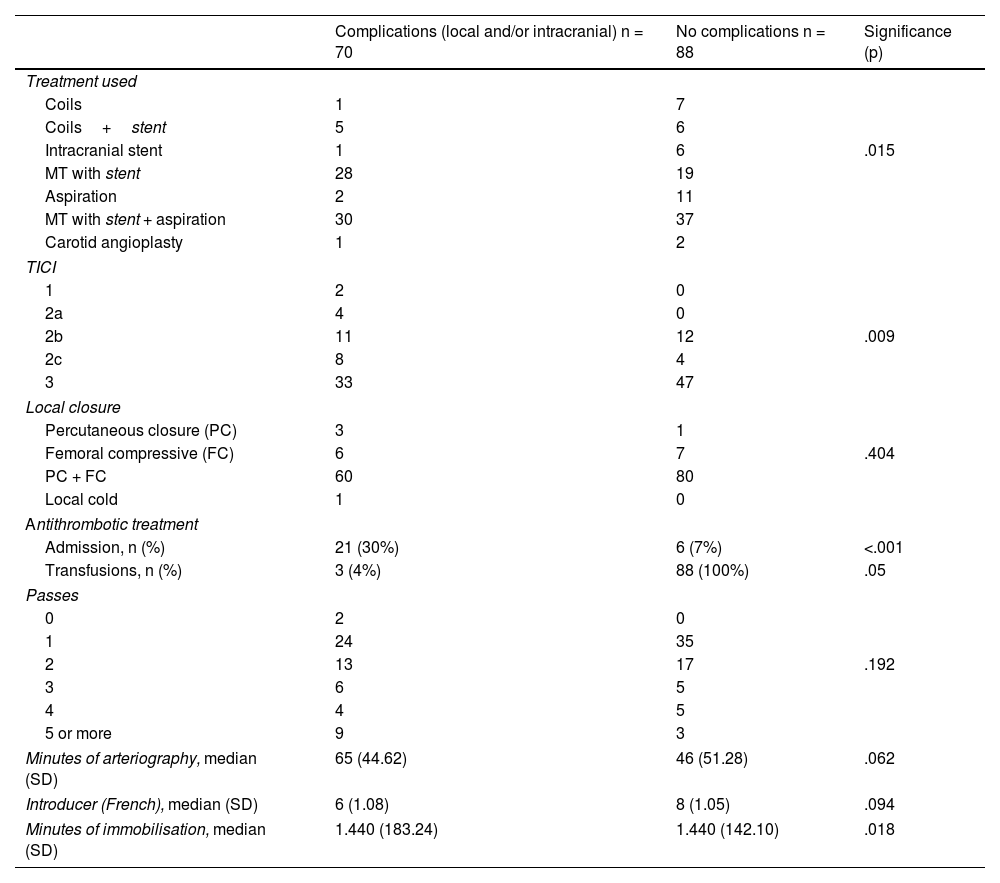
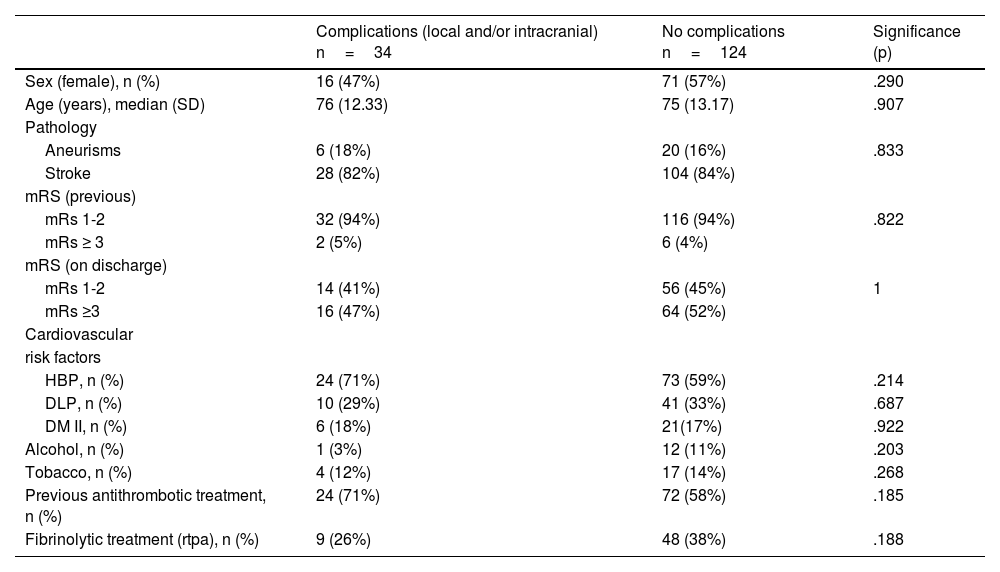
MethodologyRetrospective cross-sectional study on TCAs carried out in 2018 on admission to the Stroke Unit of the Hospital Clínic de Barcelona. The study was approved by the centre’s ethics committee. Demographic, clinical, analytical, and procedure-derived variables were collected. All patients older than 18 years undergoing TCA were included. Patients undergoing diagnostic cerebral arteriography and/or with a hospital stay less than 24h were excluded. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for the comparison of quantitative variables and Pearson’s Chi-squared test for the qualitative variables.
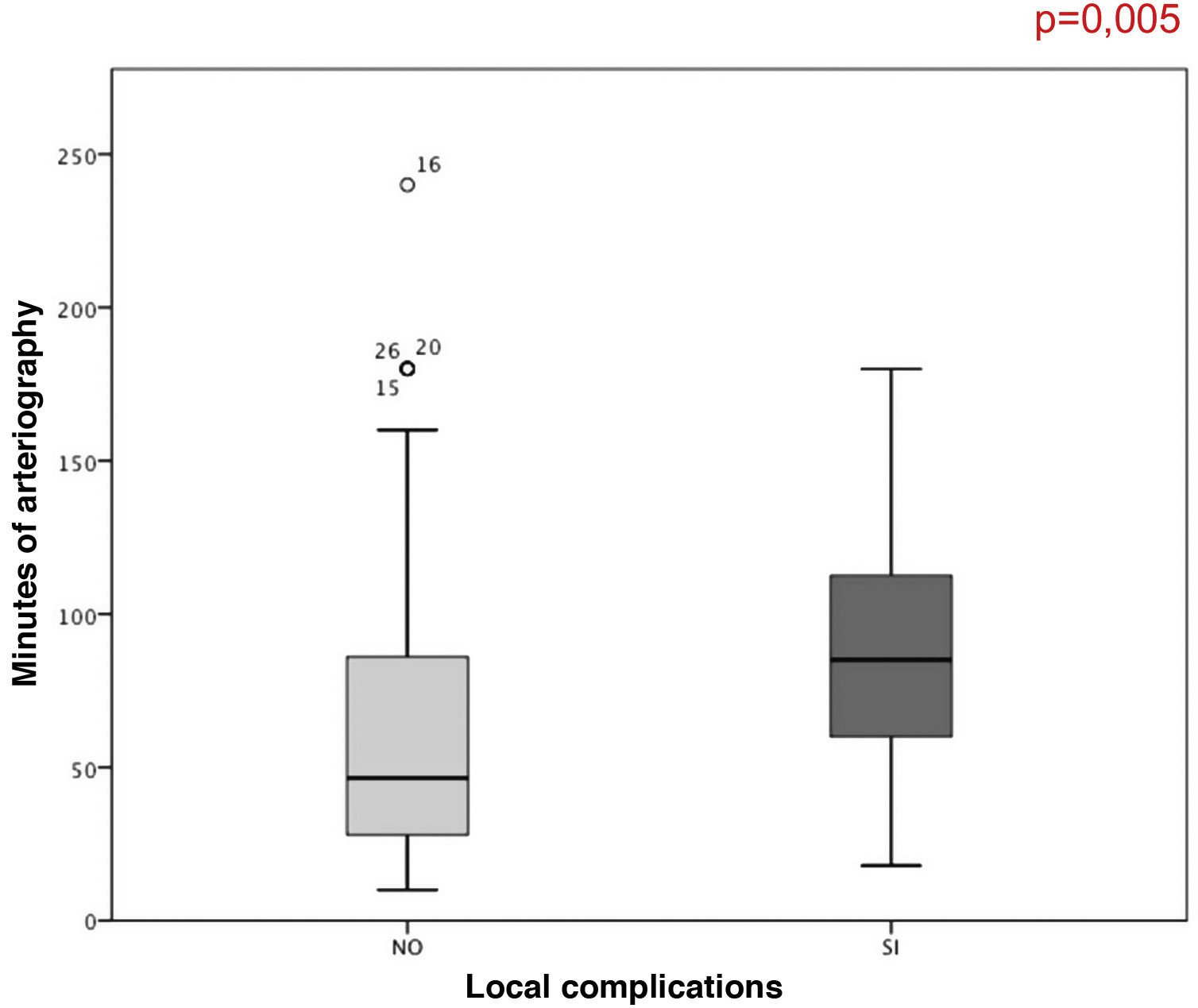
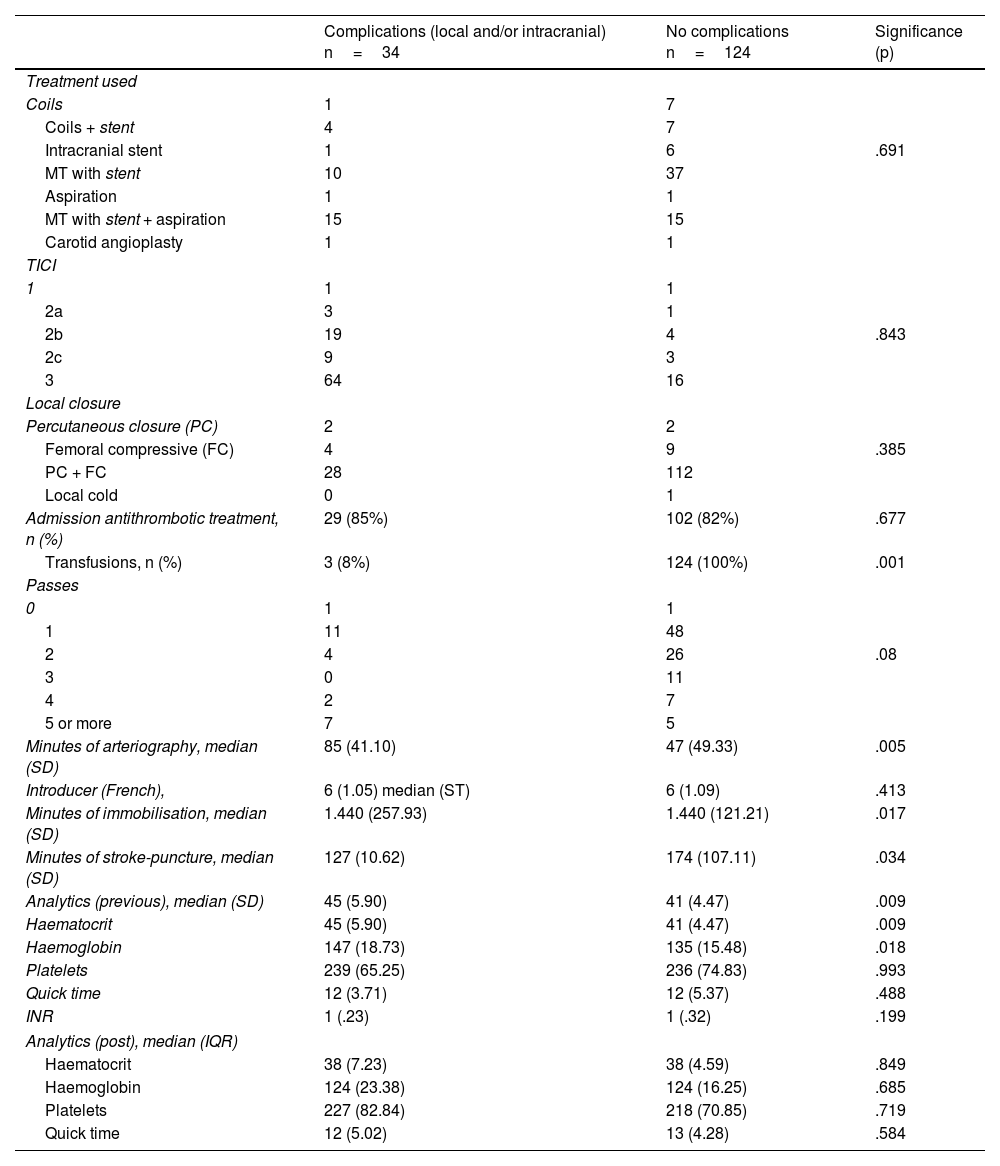
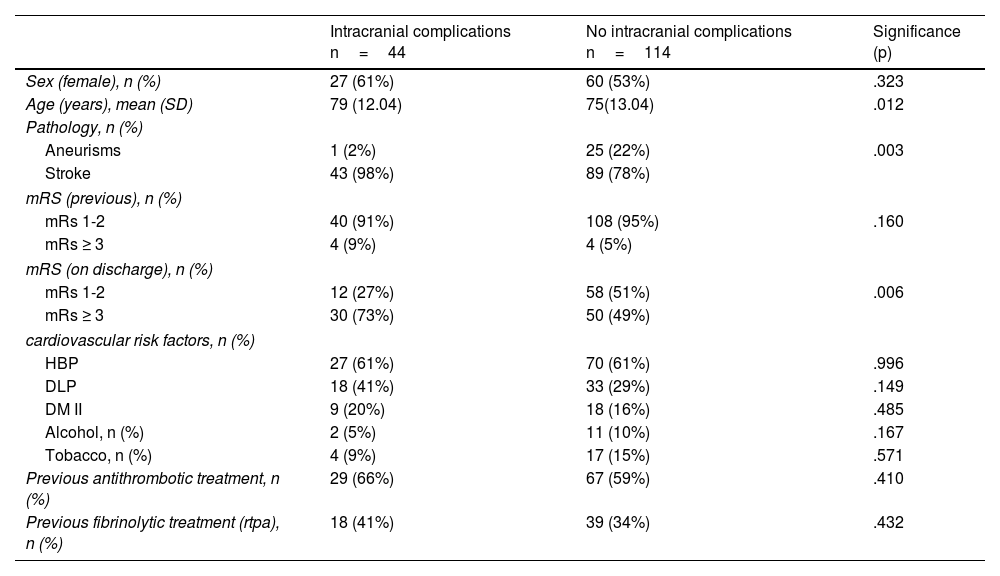
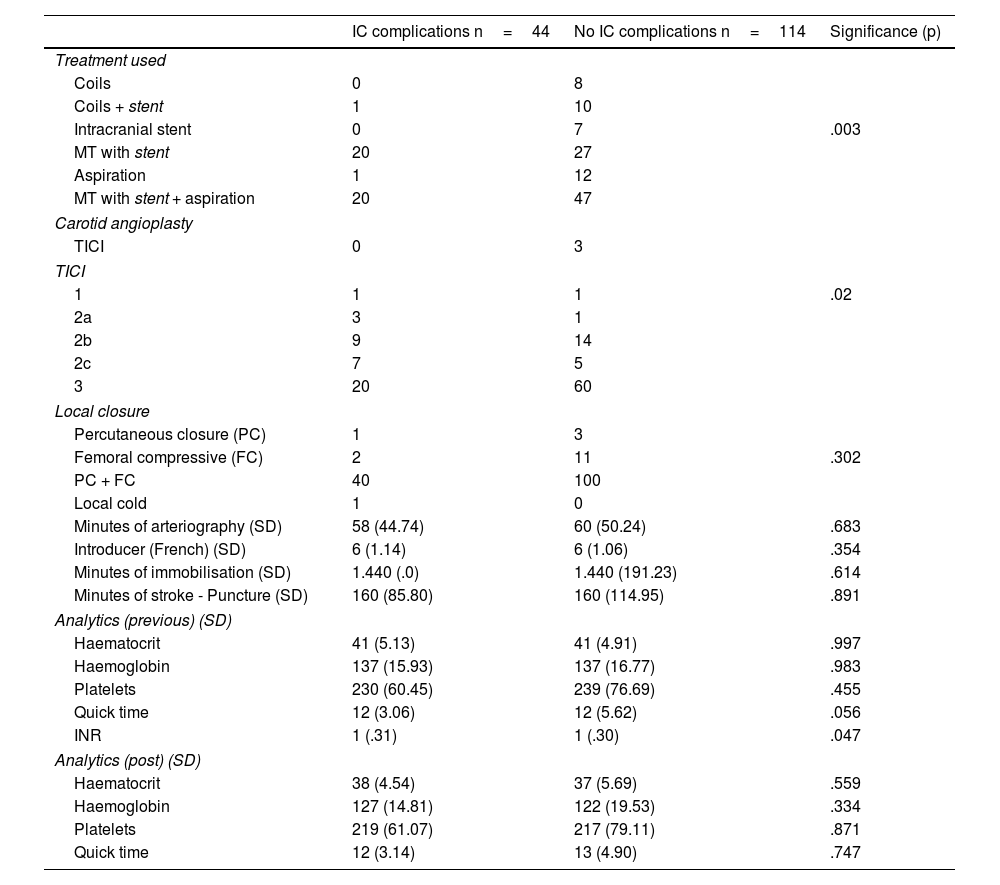
ResultsComplications were frequent, occurring in almost half of the sample (44%). A longer duration of arteriography was associated with an increase in local complications (p=.005). Intracranial complications occurred in 33% of the patients who underwent mechanical thrombectomy and were associated with older age (p=.012), stent use (associated or not with aspiration) (p=.003), and complete recanalization (p=.02), as well as having a worse functional status at discharge (p=.006).
ConclusionsComplications derived from ACT are frequent. Their importance and incidence must be known to detect those subjects at higher risk for developing them due to their functional implications and increased hospital stay.
La arteriografía cerebral es la técnica de referencia para el diagnóstico y tratamiento de enfermedades cerebrovasculares. No obstante, no está exenta de complicaciones.
ObjetivoDeterminar la incidencia de las complicaciones derivadas de la arteriografía cerebral terapéutica (ACT) y evaluar cuáles son los factores de riesgo asociados a la aparición de complicaciones tanto locales como intracraneales.
MetodologíaEstudio retrospectivo transversal sobre las ACT realizadas en el año 2018 que ingresaban en la Unidad de Ictus del Hospital Clínic de Barcelona. El estudio fue aprobado por el comité ético del centro. Se recopilaron variables demográficas, clínicas, analíticas y derivadas del procedimiento. Se incluyeron todos los pacientes mayores de 18 años sometidos a una ACT durante el 2018. Se excluyeron los pacientes sometidos a arteriografías cerebrales diagnósticas y con una estancia hospitalaria menor a 24horas. Se utilizó el test U de Mann Whitney para la comparación de variables cuantitativas y el test Chi cuadrado de Pearson para las cualitativas.
ResultadosLas complicaciones han sido frecuentes, llegándose a producir casi en la mitad de la muestra (44%). Se ha asociado la mayor duración de la arteriografía con un aumento de las complicaciones locales (p=0,005). Las complicaciones intracraneales ocurrieron en un 33% de los pacientes sometidos a trombectomía mecánica y se asociaron con presentar una edad más avanzada (p=0,012), el uso del stent (asociado o no a aspiración) (p=0,003) y una recanalización completa (p=0,02) así como el comportar un peor estado funcional al alta (p=0,006).
ConclusionesLas complicaciones derivadas de la ACT son frecuentes. Se debe conocer su importancia e incidencia para poder detectar a aquellos sujetos con mayor riesgo a su desarrollo por sus implicaciones funcionales y de aumento de estancia hospitalaria.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.