Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by damage to the myelin sheath that covers neurons, and which shows differences between men and women in terms of susceptibility and disease progression related in turn to functional ability and quality of life.
ObjectivesTo know the differences based on gender, assessing the functional capacity, muscle strength and fine motor skills of the upper extremities of patients with MS.
Material and methodsA quantitativede, scriptive, cross-sectional study was conducted with a sample of 51 MS patients, that were assessed for functional capacity (DASH scale); static and dynamic balance (Berg scale), perceived balance (ABC); strenght (Jamar and dynamometer); and fine motor skills (NHPT).
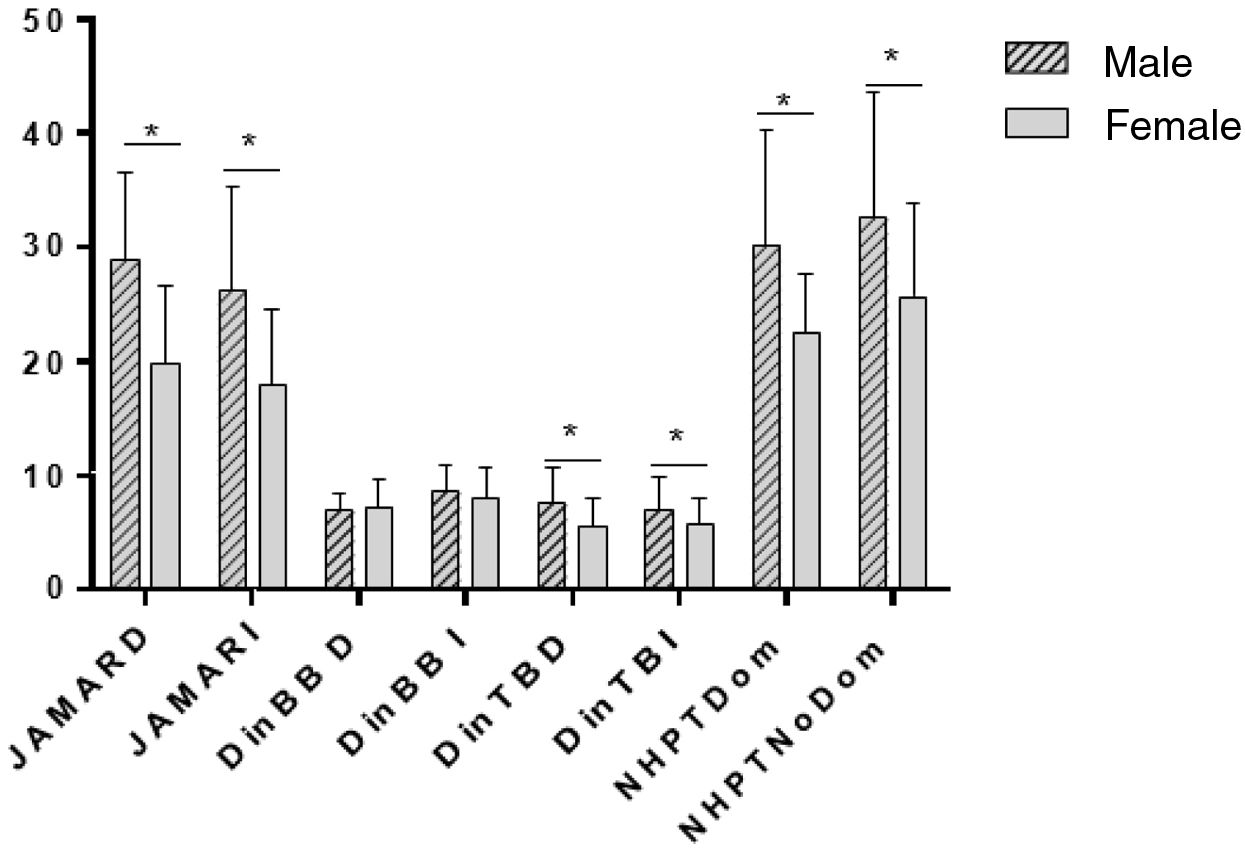
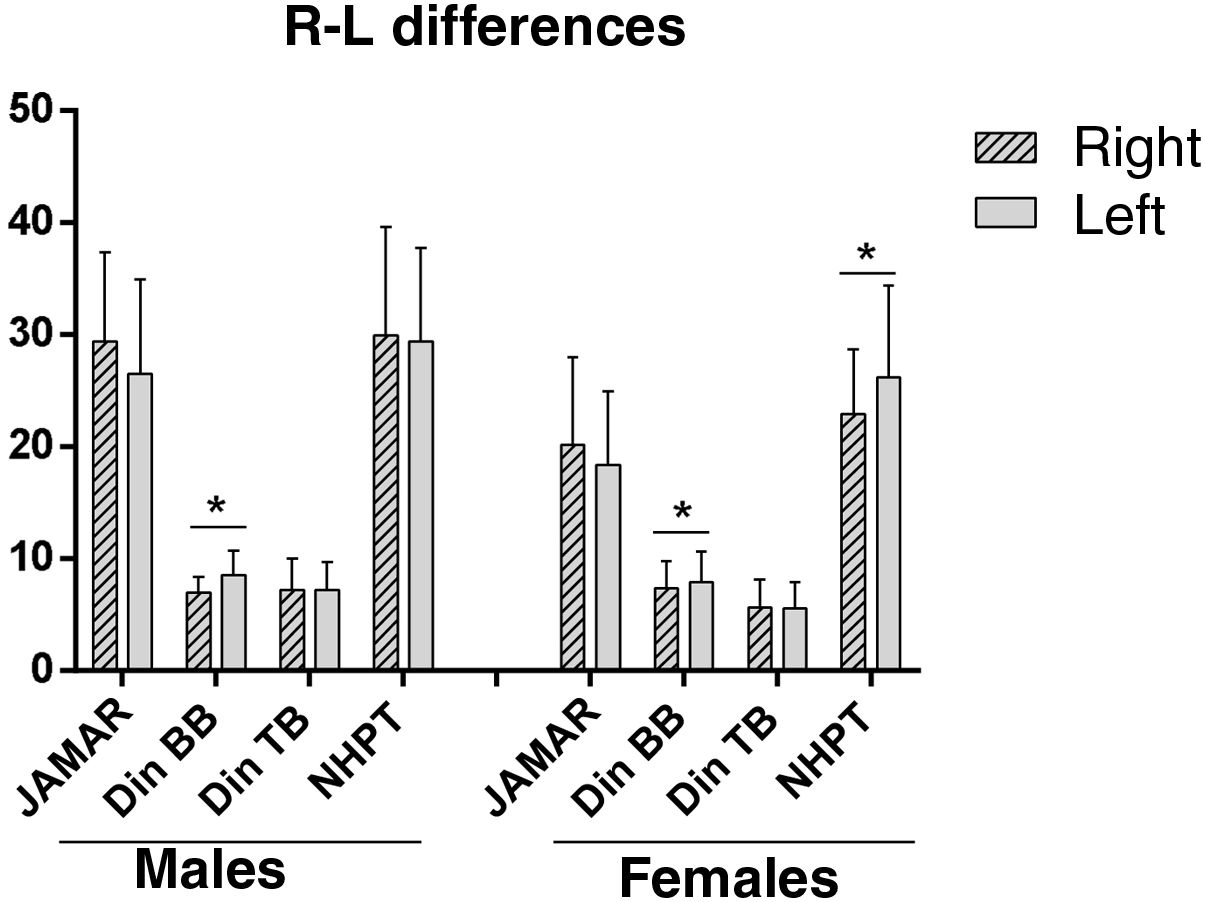
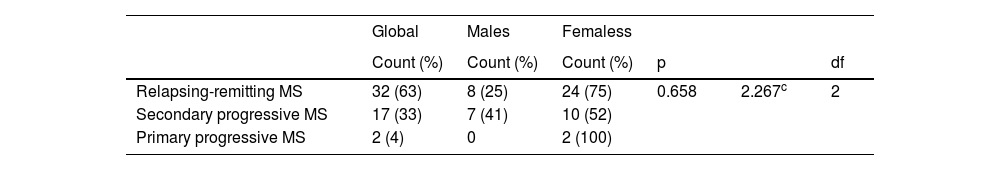
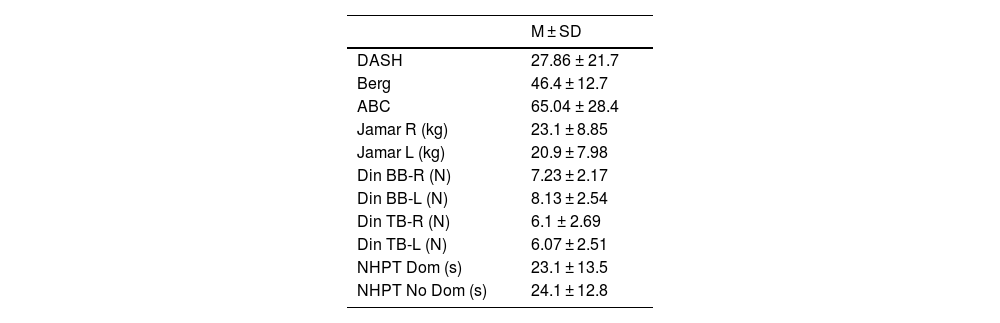
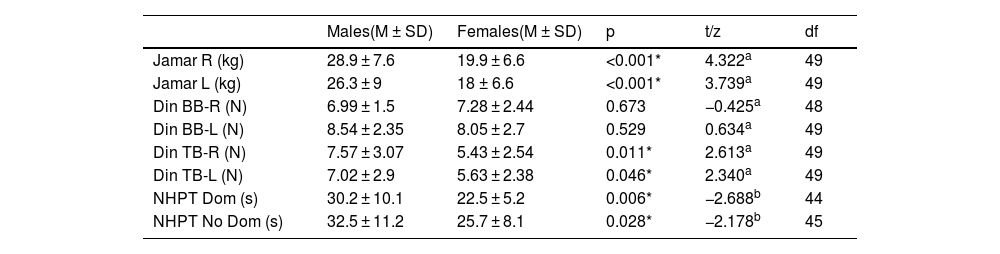
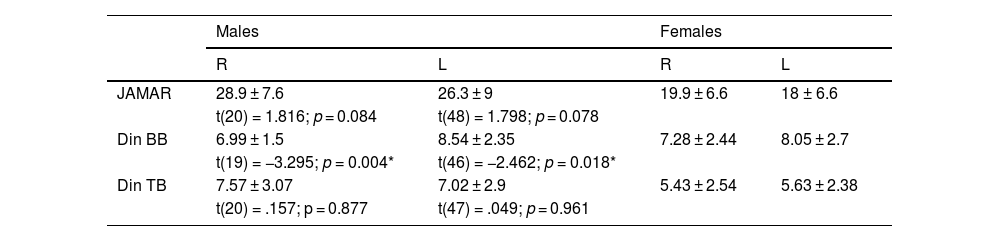
ResultsThe sample consisted of 15 men and 36 women, with a mean age of 47 ± 12 años. No differences were observed in functional capacity DASH (p = 0.616). In addition, men showed greater pincer strength (p < 0.001) and greater triceps strength (p < 0.05) in both arms. Regarding fine motor skills, it was better in women in both the dominant and non-dominant hands (p < 0.05).
ConclusionsDespite not observing functional differences by sex, there are differences in the parameters of pincer and triceps strength, which is higher in men; and in manual dexterity of both hands, which is better in women.
La esclerosis múltiple (EM) es una enfermedad neurodegenerativa caracterizada por daños en la vaina de mielina que recubre las neuronas, y que muestra diferencias entre hombres y mujeres en cuanto a la susceptibilidad y progresión de la enfermedad relacionada a su vez con la capacidad funcional y calidad de vida.
ObjetivosConocerlas diferencias en función del género, valorando la capacidad funcional, y fuerza muscular y motricidad fina de las extremidades superiores de pacientes con EM.
Material y métodosEstudio cuantitativo, descriptivo de carácter transversal que contó con una muestra poblacional de 51 pacientes diagnosticados de EM, a los que se valoró la capacidad funcional (escala DASH), el equilibrio estático, dinámico (escala Berg) y percibido (escala ABC); fuerza (Jamar y dinamómetro); y la motricidad fina de las manos (NHPT).
ResultadosLa muestra consistió en 15 hombres y 36 mujeres, con una edad media de 47 ± 12 años. no se observan diferencias en la capacidad funcional DASH (p = .616), Además, se observó en los hombres mayor fuerza en pinza (p < .001) y mayor fuerza en tríceps (p < .05), de ambos brazos. En cuanto a la motricidad fina, esta fue mejor en las mujeres tanto en la mano dominante como no dominante (p < .05).
ConclusionesA pesar de no observarse diferencias funcionales por sexo, si existen diferencias en los parámetros de fuerza en pinza y fuerza en el tríceps, que es mayor en hombres; y en destreza manual de ambas manos, que es mejor en las mujeres.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.