To study the relationship between malnutrition and dysphagia in stroke patients.
MethodAn observational, descriptive, longitudinal and prospective study that included 183 patients admitted to the neurological department of the University Hospital of Burgos with a diagnosis of stroke. Sociodemographic and clinical variables were collected using body mass index (BMI), CONUT index, Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA), Barthel's index, Rankin scale, volume-viscosity clinical examination method, on admission, on discharge, and at 3 months.
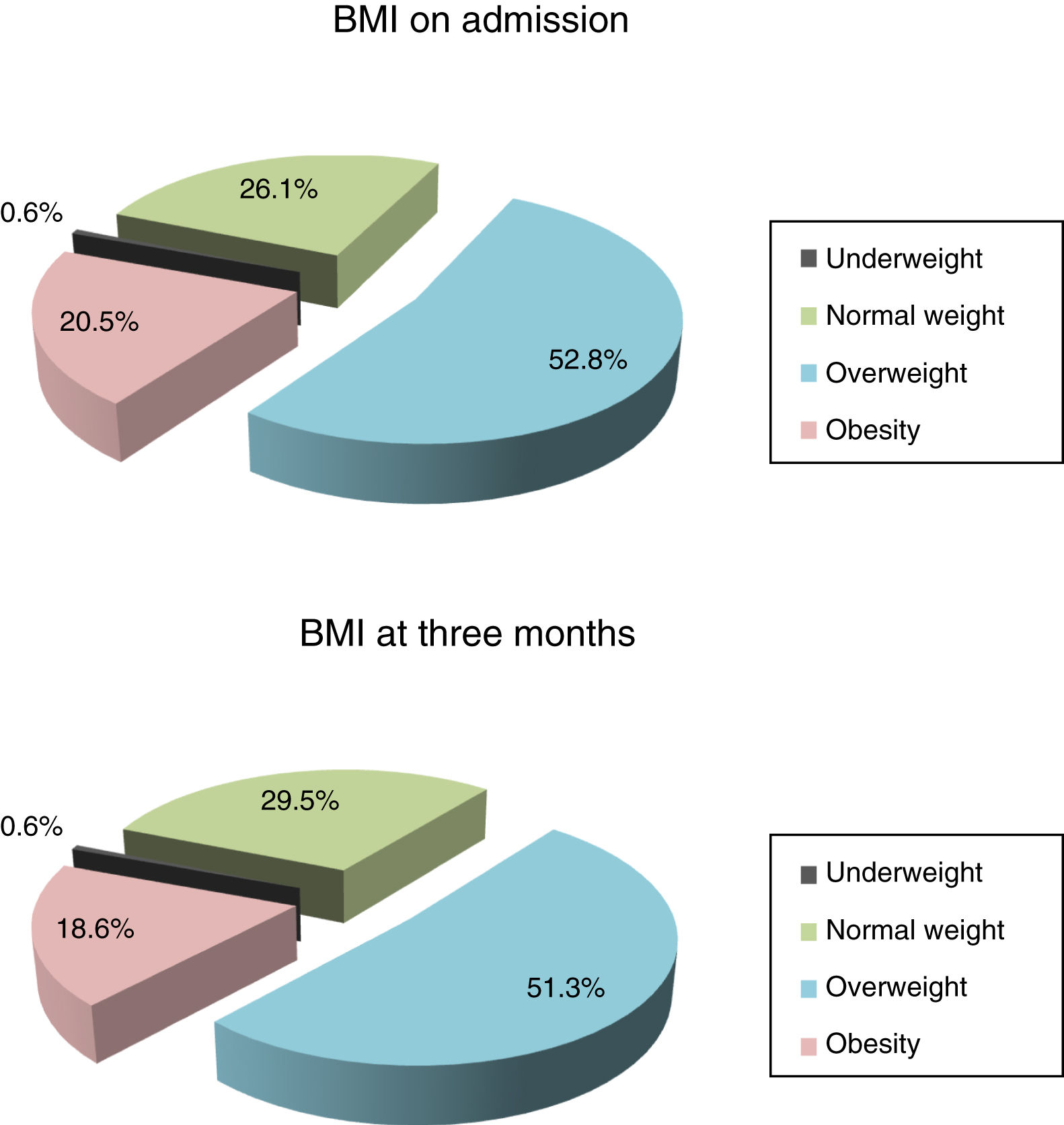
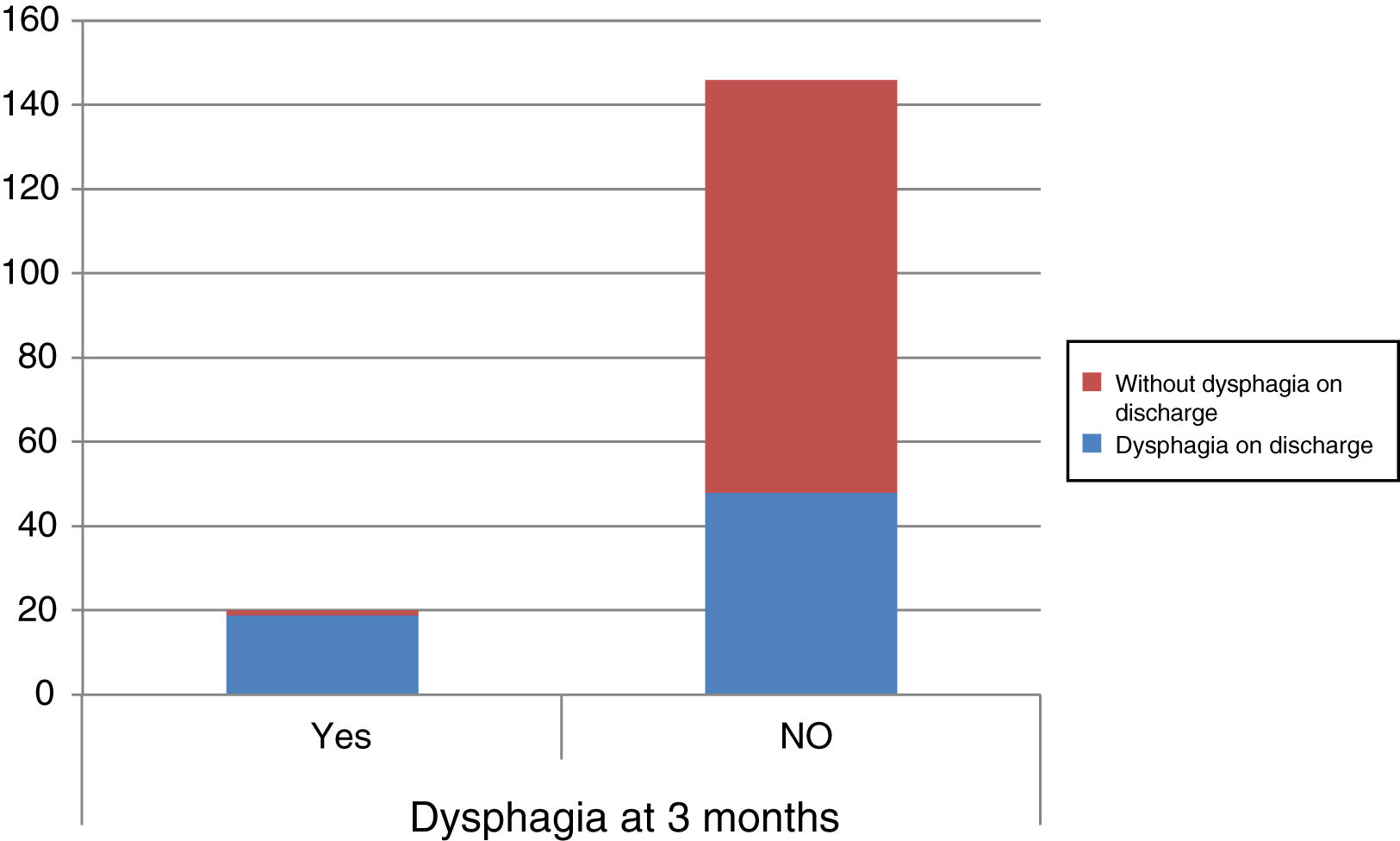
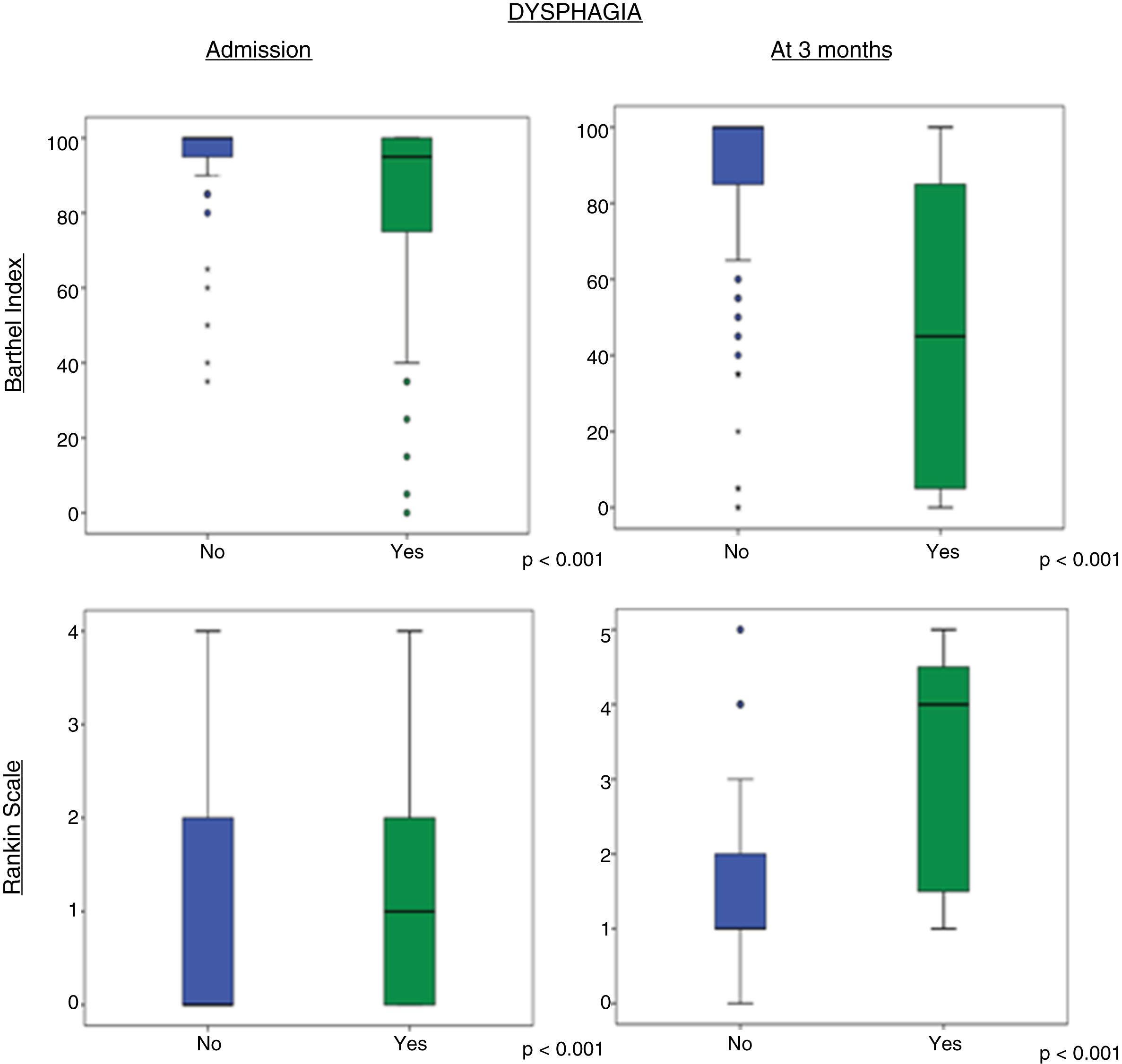
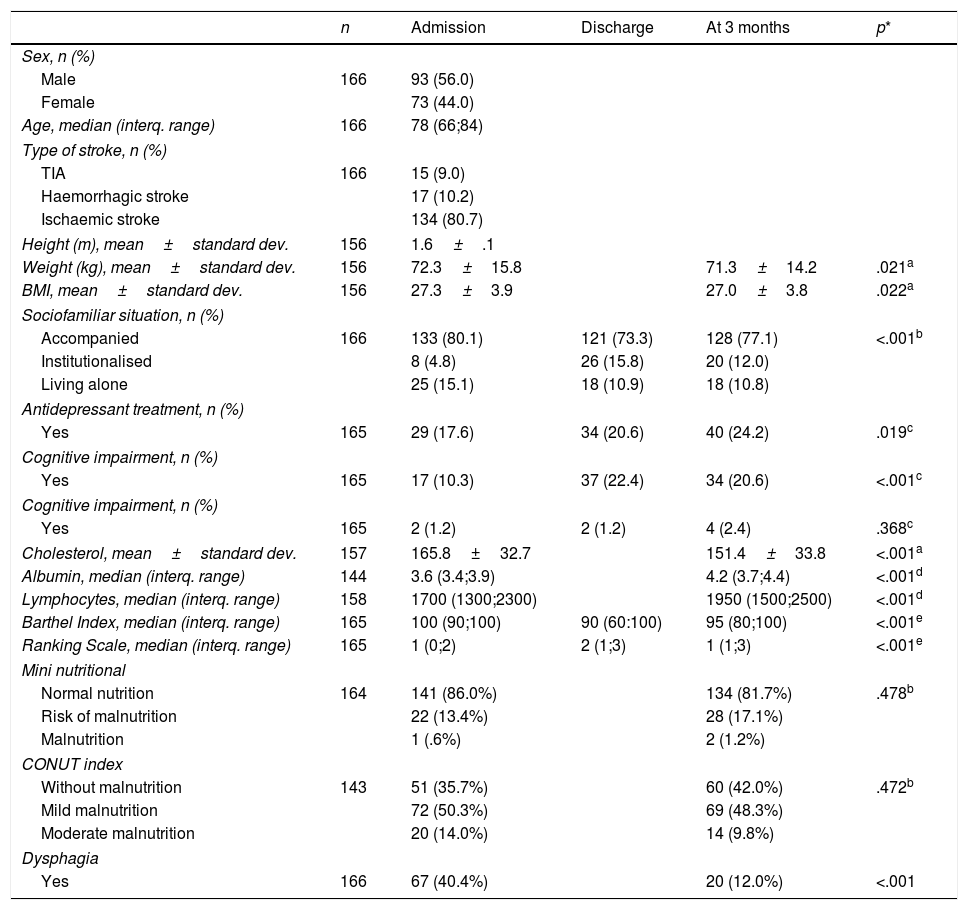
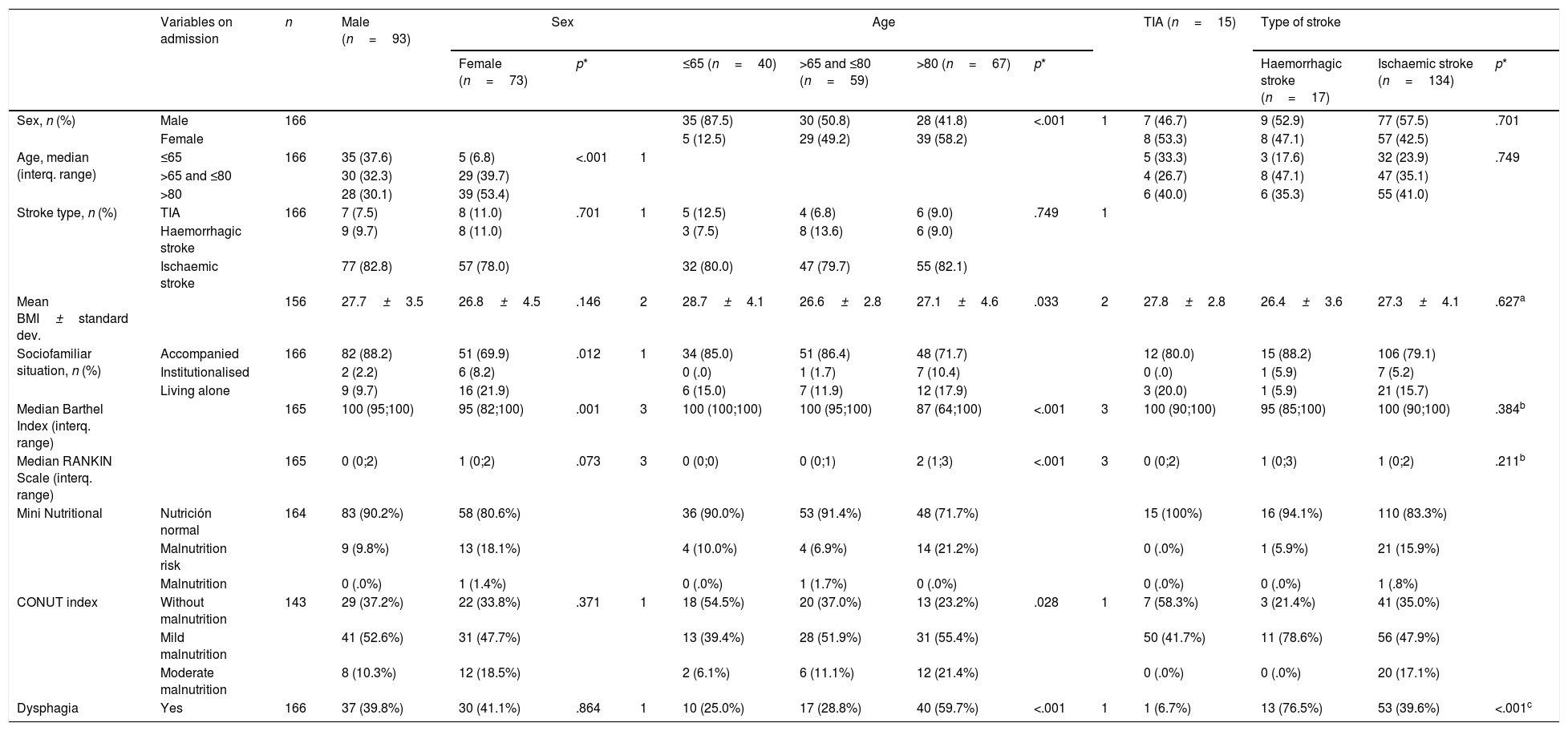
ResultsOn admission to hospital, 64.3% (92) of the patients had some degree of malnutrition according to the CONUT index, and 13.4% (22) were at risk of malnutrition according to the MNA. The median (interquartile range) of dependency was 100 (90;100). The median disability was 1 (0;2). Forty point four percent (67) of the patients had dysphagia.
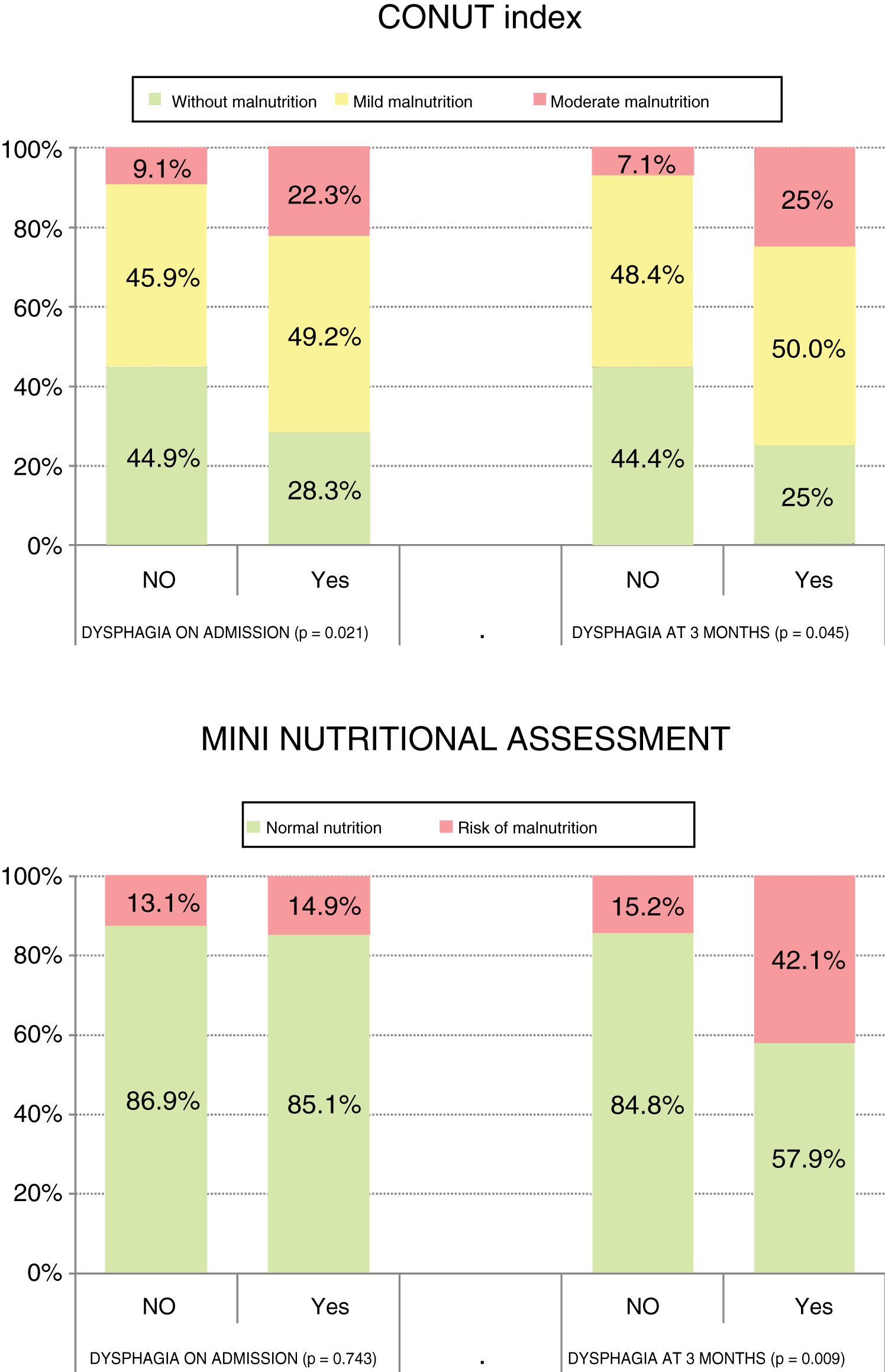
At 3 months, using the abovementioned scales, 58.2% of the patients had some degree of malnutrition, and 17.1% (28) were at risk of malnutrition. The median dependency was 95 (80;100). The median disability was 1 (1;3). Twelve percent (20) had dysphagia. There was a statistically significant relationship between dysphagia and level of malnutrition according to the CONUT index on admission (p=.021) and at 3 months (p=.045), and according to the MNA at 3 months (p=.009).
ConclusionIn stroke patients, there is an association between dysphagia and malnutrition, both on admission to hospital and at three months. After initial worsening, an improvement was observed at 3 months with regard to the degree of dependency and disability but pre-stroke levels were not achieved.
Estudiar la relación entre desnutrición y disfagia en pacientes con ictus.
MétodoEstudio observacional, descriptivo, longitudinal y prospectivo que incluyó 183 pacientes ingresados en Neurología del Hospital Universitario de Burgos, diagnosticados de ictus. Se recogieron variables sociodemográficas y clínicas utilizando el índice de masa corporal (IMC), el índice CONUT, el Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA), el índice de Barthel, la escala de Rankin y el método de exploración clínica volumen-viscosidad al ingreso, al alta hospitalaria y a los 3 meses.
ResultadosAl ingreso el 64,3% (92) de los pacientes presentaban algún grado de desnutrición según CONUT y el 13,4% (22) tenían riesgo de malnutrición según el MNA. La mediana (rango intercuartílico) de la dependencia fue 100 (90;100). La mediana de la discapacidad fue 1 (0;2). El 40,4% (67) de los pacientes presentaban disfagia.
A los 3 meses, utilizando las escalas anteriores, el 58,2% (83) de los pacientes presentaban algún grado de desnutrición y el 17,1% (28) tenían riesgo de malnutrición. La mediana de la dependencia fue 95 (80;100). La mediana de la discapacidad fue 1(1;3). El 12% (20) tenían disfagia. Existe una relación estadísticamente significativa entre disfagia y grado de desnutrición según CONUT al ingreso (p=0,021) y a los 3meses (p=0,045), y según el MNA a los 3meses (p=0,009).
ConclusiónEn los pacientes con ictus existe una asociación entre disfagia y desnutrición tanto al ingreso como a los 3 meses. Tras el empeoramiento inicial, se objetiva mejoría a los 3meses en relación con el grado de dependencia y discapacidad, sin llegar a alcanzar los valores previos al ictus.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.