There is a higher risk of embolic complications in immobile stroke patients. Venous thromboembolism is a serious condition in which small clots form in the deep veins of the legs, called deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and these clots are carried through the blood circulation to the lungs, leading to pulmonary embolism. Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) has been proven to prevent deep vein thrombosis in 29.9% of stroke patients.
Objectives1. Discover the effects of intermittent pneumatic compression protocol implementation in patients with severe stroke in relation to comfort and safety, and determine how long implementation would take and the work load of this new protocol. 2. Compare functional evolution after 3 months in patients on whom an IPC system was applied with the previous sample at the beginning of the system application.
MethodObservational, transversal and descriptive study which evaluated the viability and safety of the IPC system in acute stroke patients in the Stroke Unit of the Hospital Vall d’Hebron. IPC was applied for 24h on patients with ischaemic stroke treated with reperfusion and on patients with intracranial haemorrhage during 72h.
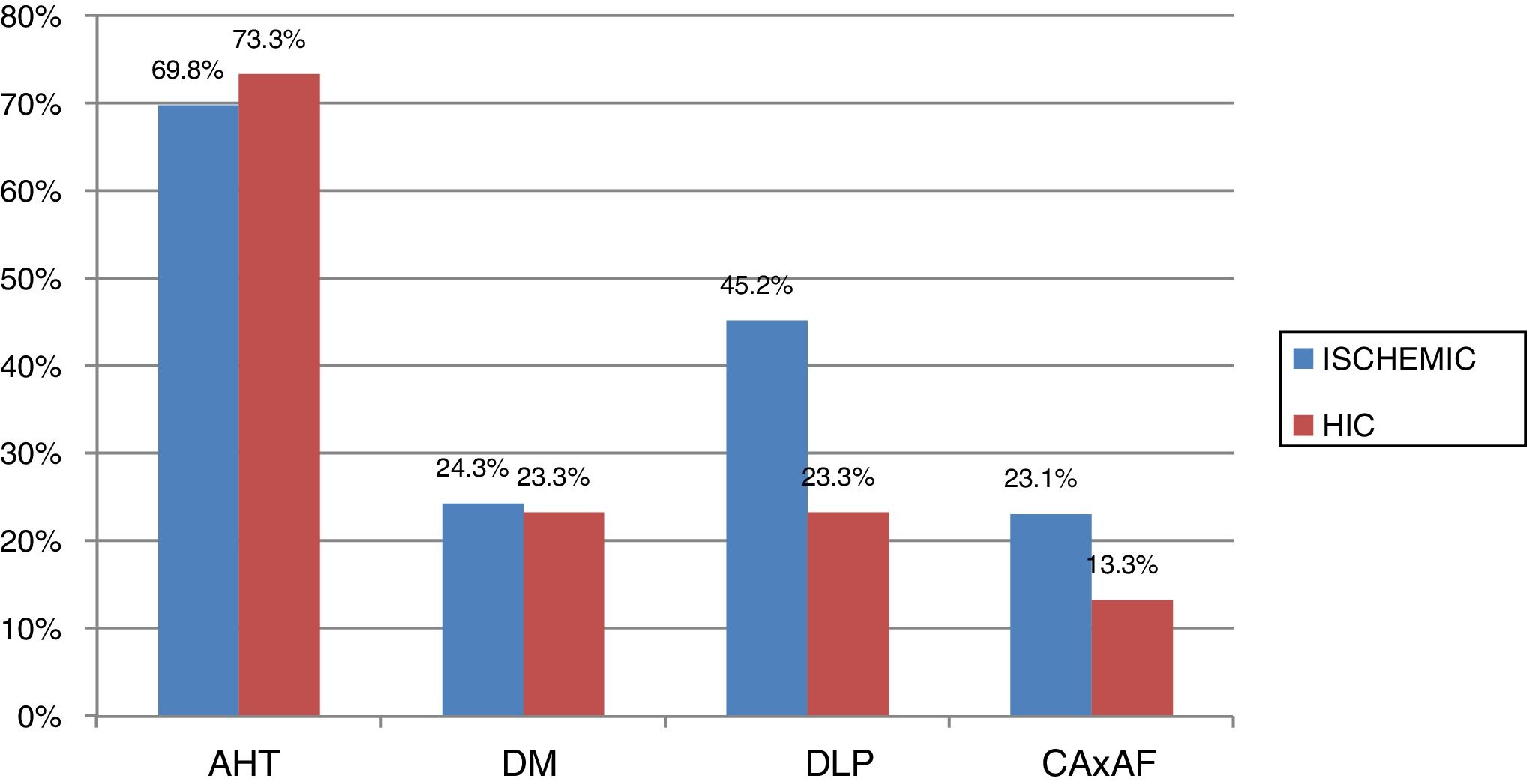
Results172 patients were included in the sample. The mean age was 71±14 years. 48% were women. 79.2% were diagnosed with ischaemic stroke. In the application phase the nurses reported that prior to training they had taken 15±2.3min to use the system and that after training application only took 6±1.5min. Practically all patients (98.8%) who were given IPC suffered no discomfort and did not present with any complications derived from its use. During this period no cases of DVT were detected.
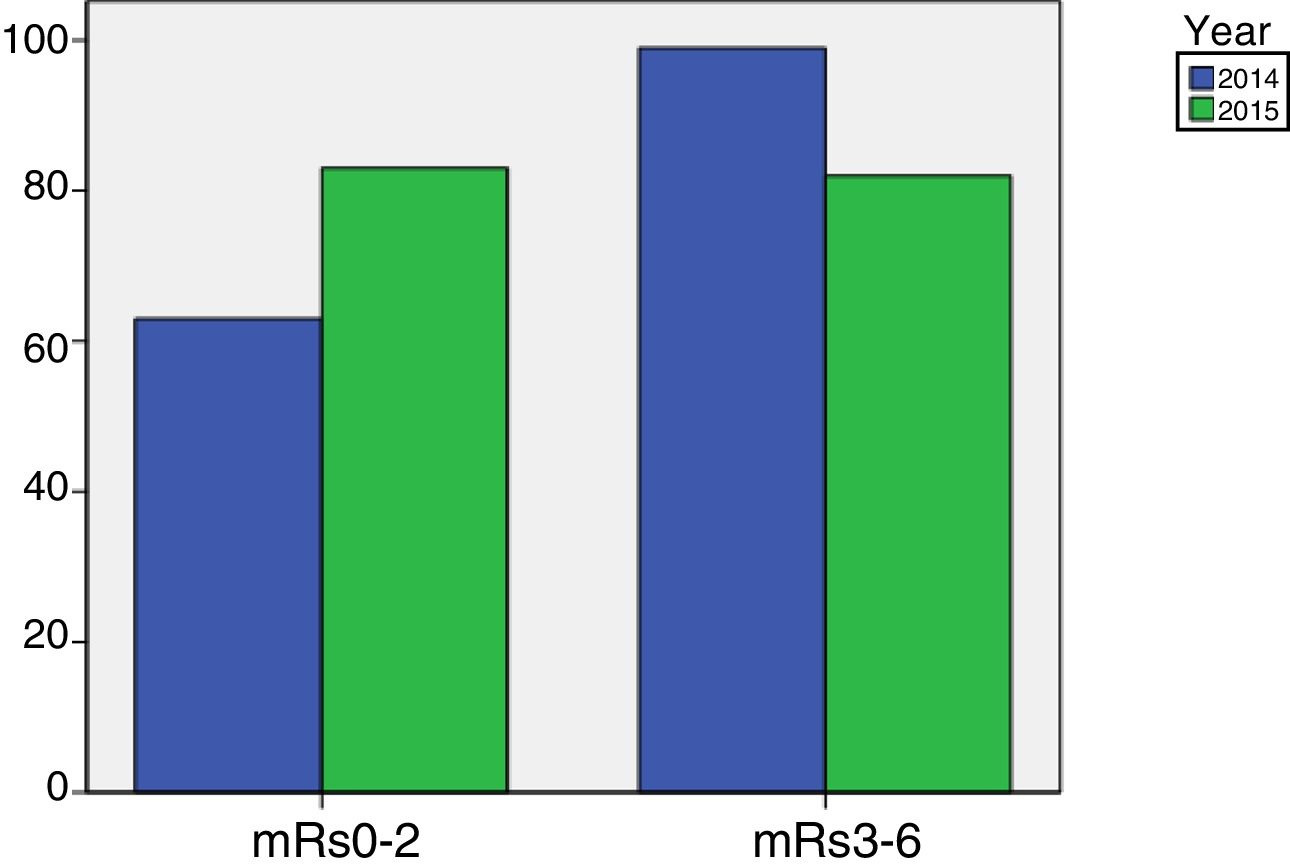
ConclusionsImplementation of the IPC systems protocol has been proven to have a preventative and efficient effect in the reduction of embolic complications, which is safe for the patient and with no discomfort in its use. The nurses’ work load is not increased with appropriate training. Following the introduction of the protocol a functional optimisation in patients 3 months post stroke was observed.
Los pacientes con ictus inmóviles presentan un riesgo incrementado de complicaciones embólicas. El tromboembolismo venoso es una afectación grave en la que se forman pequeños coágulos en las venas profundas de las piernas, conocido como trombosis venosa profunda (TVP), que viajan hacia la circulación sanguínea alojándose en los pulmones y provocando una embolia pulmonar. Las medias de compresión neumática intermitente (CNI) han demostrado prevenir la TVP en el 29,9% de los pacientes con ictus.
Objetivos1) Conocer los efectos de la implementación del protocolo de CNI en pacientes con ictus agudo en relación con la comodidad y seguridad, y determinar el tiempo de implementación y carga de trabajo de este nuevo protocolo; y 2) comparar la evolución funcional a los 3 meses de los pacientes a los que se les ha aplicado el sistema de medias de CNI con la muestra anterior al inicio de la aplicación del sistema.
MétodoEstudio observacional, transversal y descriptivo que evalúa la viabilidad y la seguridad de la implantación del protocolo de medias de CNI en pacientes con ictus agudo en la Unidad de Ictus del Hospital Vall d’Hebron. Las medias de CNI se aplicaron durante 24horas a pacientes con ictus isquémico tratados con terapias de reperfusión, y en pacientes con hemorragia intracraneal durante 72horas.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 172 pacientes. La edad media de la muestra fue de 71±14años, siendo un 48% mujeres. El 79,2% fue diagnosticado de ictus isquémico. En la fase de aplicación las enfermeras reportaron que antes del entrenamiento tardaban 15±2,3minutos en colocarlas, mientras que después del entrenamiento solo se tardaba 6±1,5minutos. Prácticamente todos los pacientes (98,8%) que llevaron las medias de CNI no presentaron incomodidad y ninguno tuvo complicaciones derivadas de su uso. En este período no se ha detectado ningún caso de TVP.
ConclusionesLa implementación del protocolo de medias de CNI ha demostrado un efecto preventivo y eficaz de reducción de complicaciones embólicas, de forma segura para el paciente y sin mostrar incomodidad en su utilización. Con una formación adecuada no incrementa las cargas de trabajo de enfermería. Tras la implementación del protocolo se ha observado una mejora funcional de los pacientes a los 3 meses postictus.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.