Stroke has increased in incidence worldwide. Although its mortality has reduced, it is the disease with the highest percentage of disability. For this reason, it is necessary to find new methods of rehabilitation and recovery from sequalae after a stroke, such as virtual reality (VR) therapy.
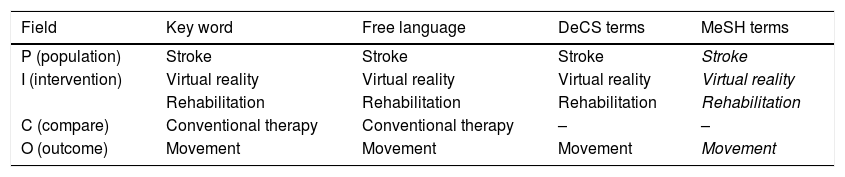
ObjectiveTo analyse the effectiveness of VR as a rehabilitation therapy for movement improvement in adults after suffering a stroke.
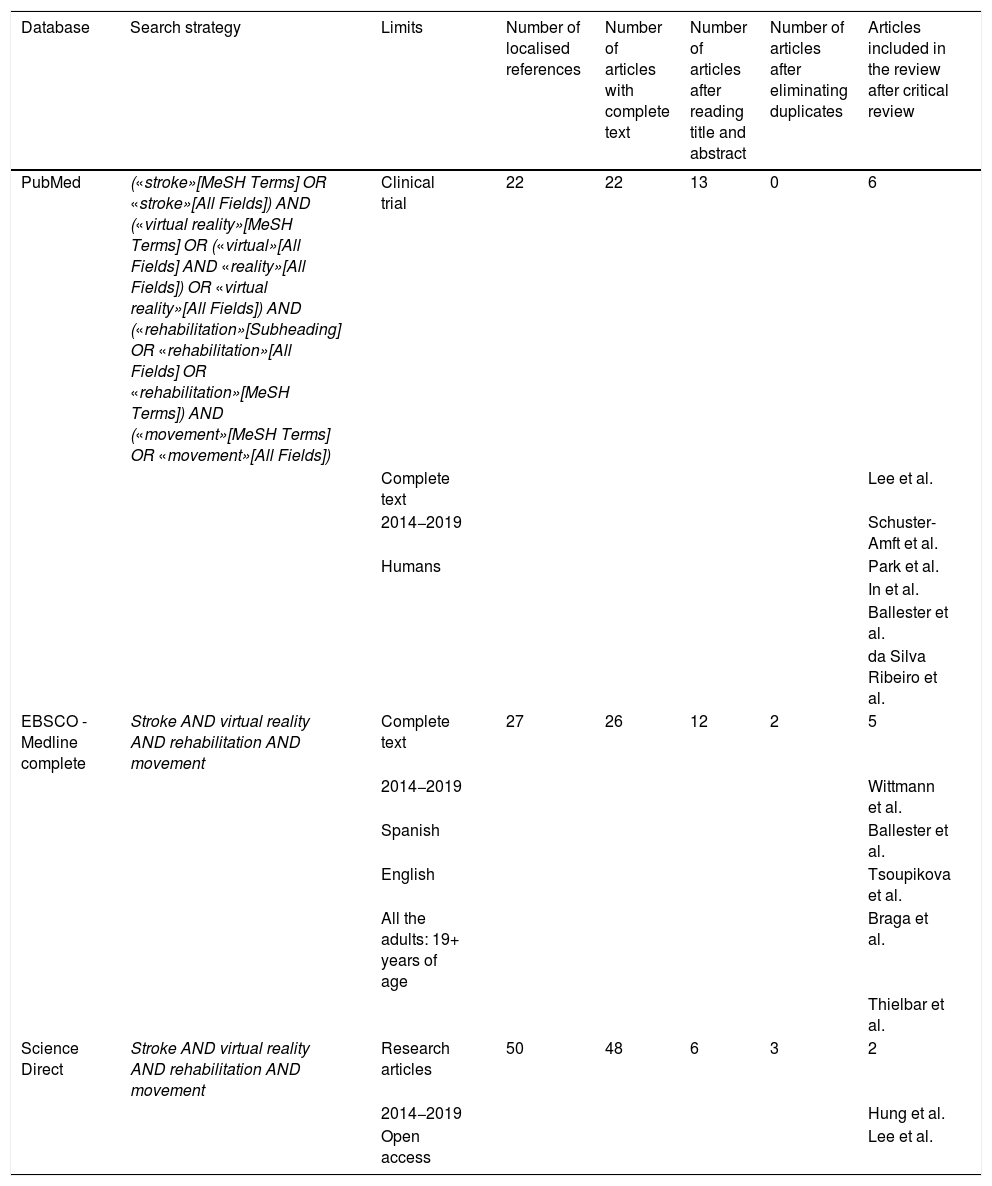
MethodA literature review was carried out through a systematic search in the PubMed, ScienceDirect and EBSCO databases (Medline Complete, Academic Search Complete, Academic Search Ultimate and E-Journal). A date restriction of the last five years and a language restriction in English and Spanish were applied.
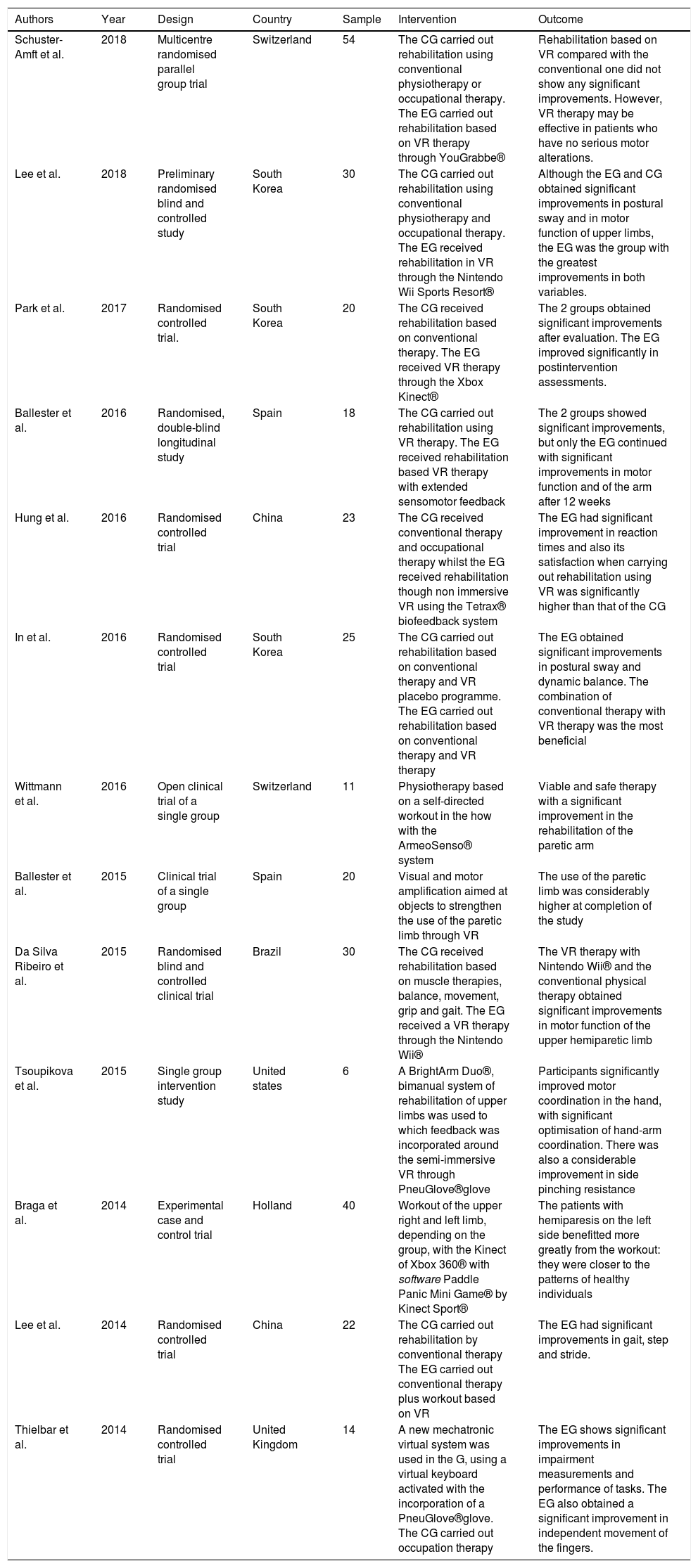
ResultsA total of 13 studies met the inclusion/exclusion criteria and the objectives of this review. The selected studies compared conventional therapy (CT) with VR therapy, or CT with the combination of CT+VR, and other studies assessed VR effectiveness in isolation.
ConclusionsVR therapy would be effective for improving movement in post-stroke patients, either in isolation or as a complement to conventional therapy. The type of VR most used for stroke rehabilitation is the semi-immersive of second person that is generally applied six months after suffering a stroke. Unfortunately, it has not yet been possible to determine the efficacy of VR according to the brain region affected.
El accidente cerebrovascular (ACV) ha aumentado su incidencia en todo el mundo. Aunque su mortalidad se ha reducido, es la enfermedad con mayor porcentaje de discapacidad. Por todo ello, es necesario encontrar nuevos métodos de rehabilitación y recuperación de las secuelas tras un ACV, como la terapia de realidad virtual (RV).
ObjetivoAnalizar la eficacia de la RV como terapia de rehabilitación para la mejora del movimiento en adultos tras sufrir un ACV.
MétodoSe llevó a cabo una revisión bibliográfica mediante una búsqueda sistemática en las bases de datos PubMed, ScienceDirect y EBSCO (Medline Complete, Academic Search Complete, Academic Search Ultimate y E-Journal). Se aplicó una restricción de fecha de los últimos cinco años y en los idiomas inglés y español.
ResultadosUn total de 13 estudios cumplieron los criterios de inclusión/exclusión y los objetivos de la revisión. Los estudios seleccionados comparaban la terapia convencional (TC) frente a la terapia de RV o la TC frente a la combinación de TC+RV y otros estudios evaluaron la eficacia de la RV aisladamente.
ConclusionesLa terapia basada en RV puede ser eficaz para mejorar el movimiento en pacientes post-ACV, tanto de manera aislada o como complemento de la terapia convencional. El tipo de RV más utilizada en la rehabilitación del ACV es la semi-inmersiva de segunda persona, siendo aplicada generalmente a los seis meses de haber sufrido un ACV. Desafortunadamente, todavía no se ha podido determinar la eficacia de la RV en función de la región cerebral afectada.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.