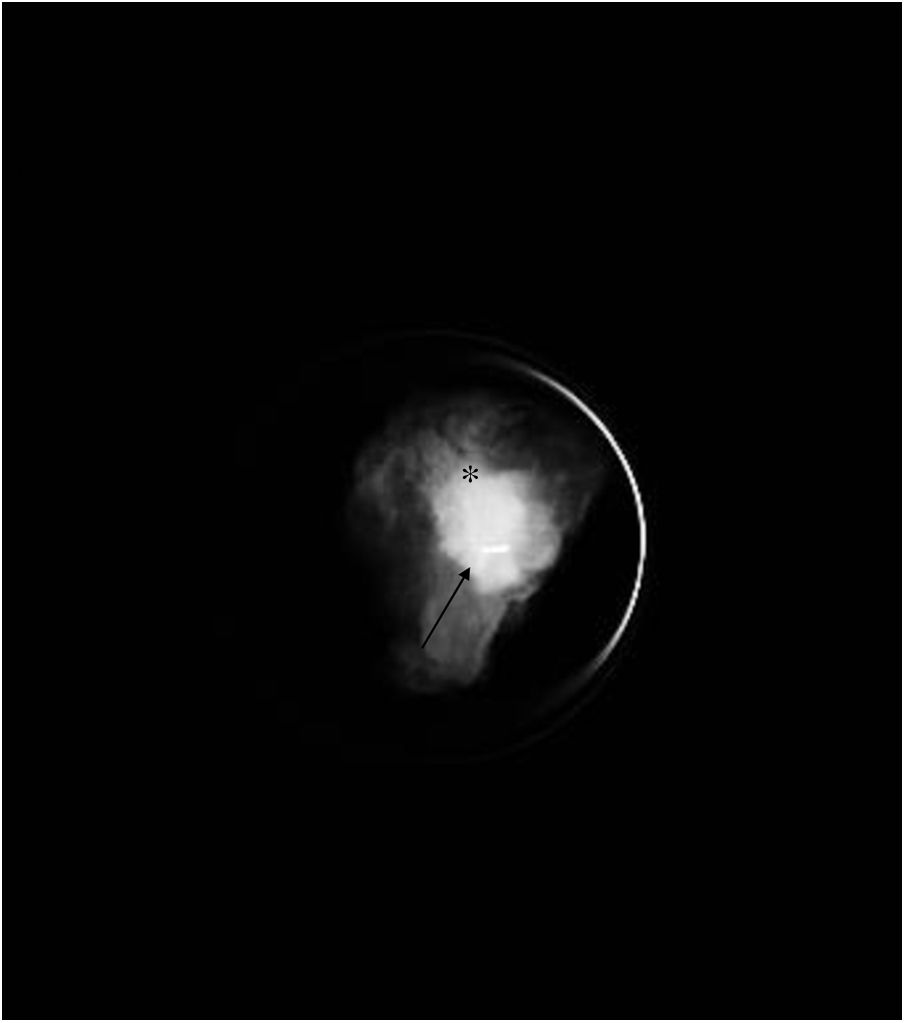
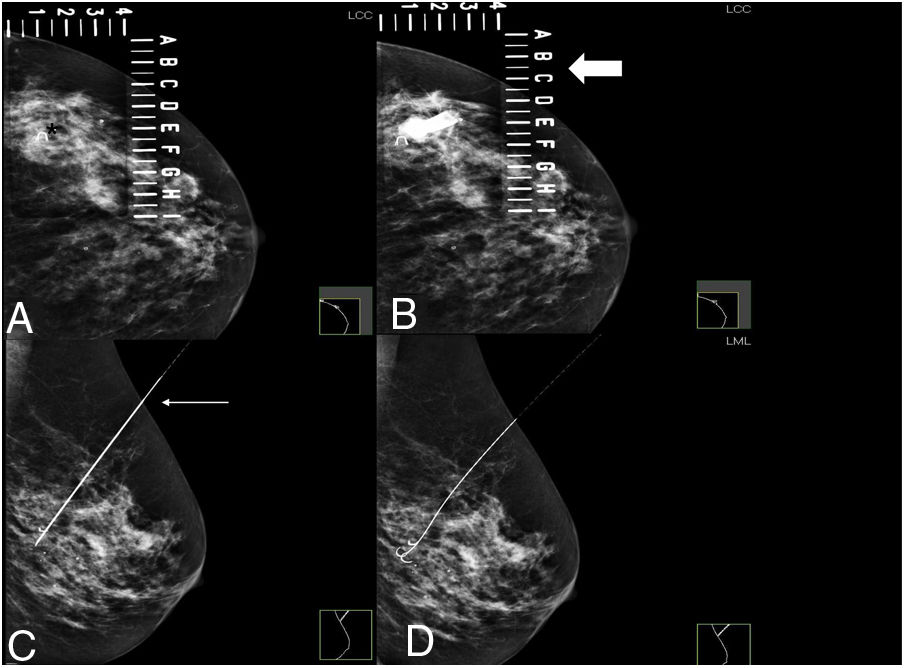
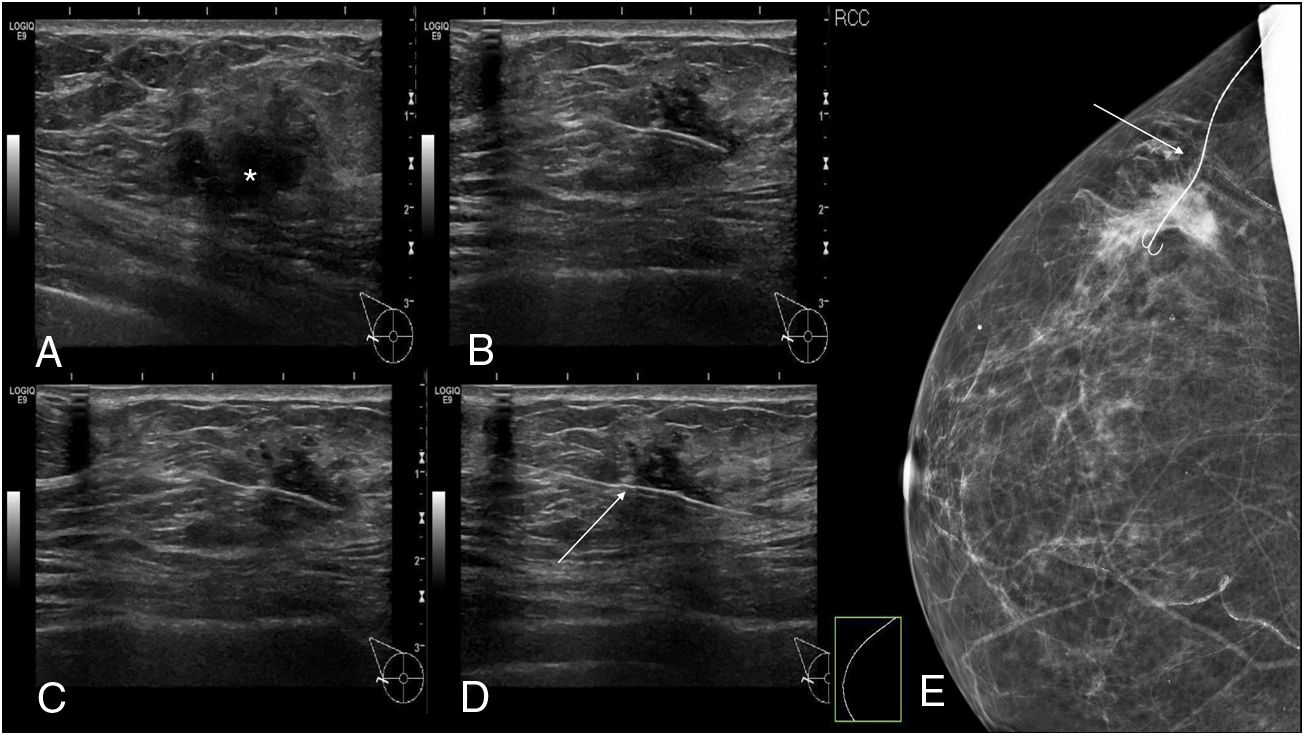
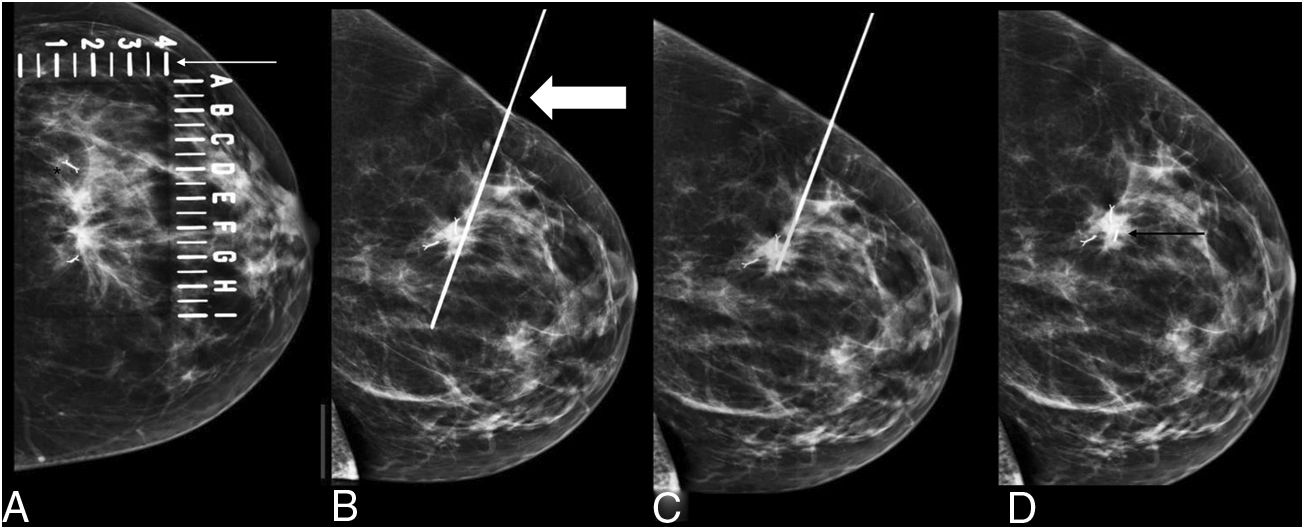
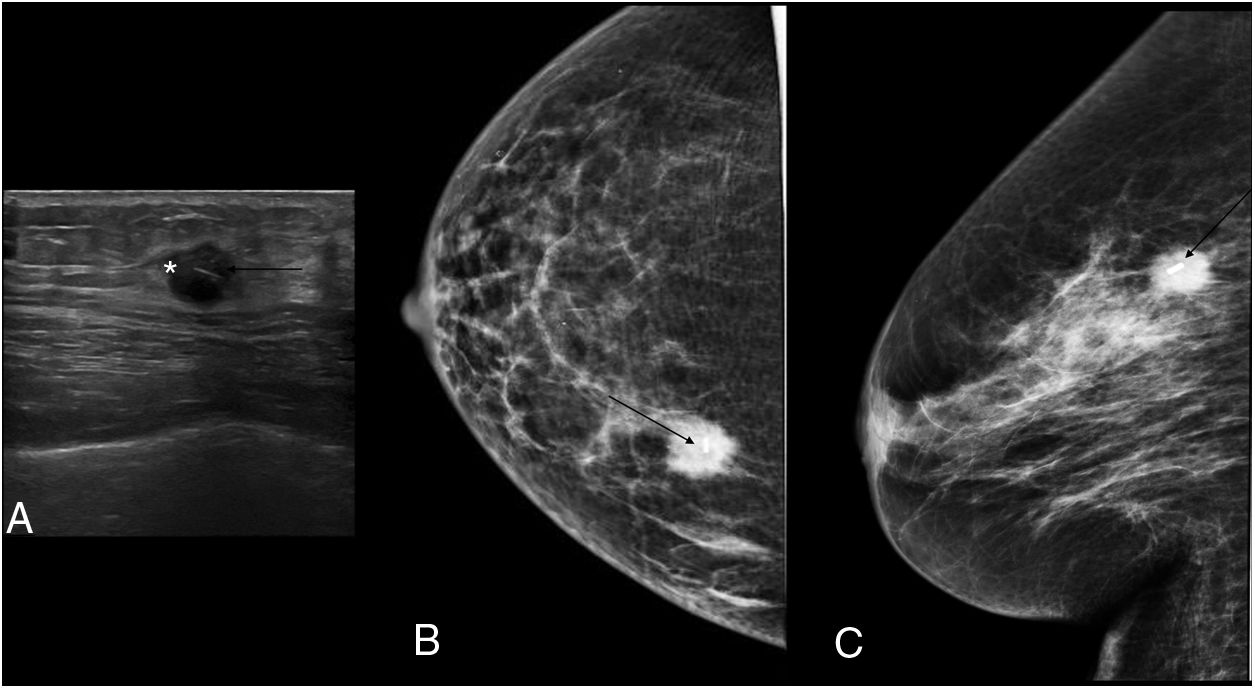
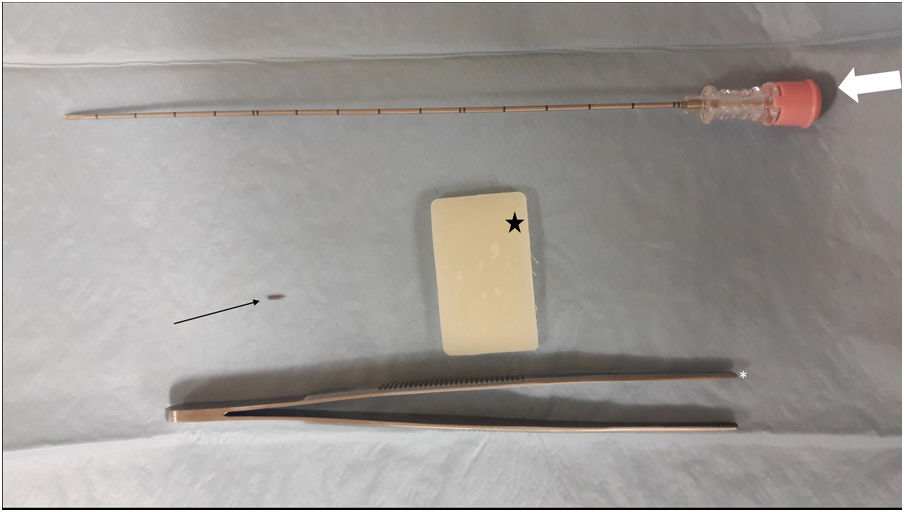
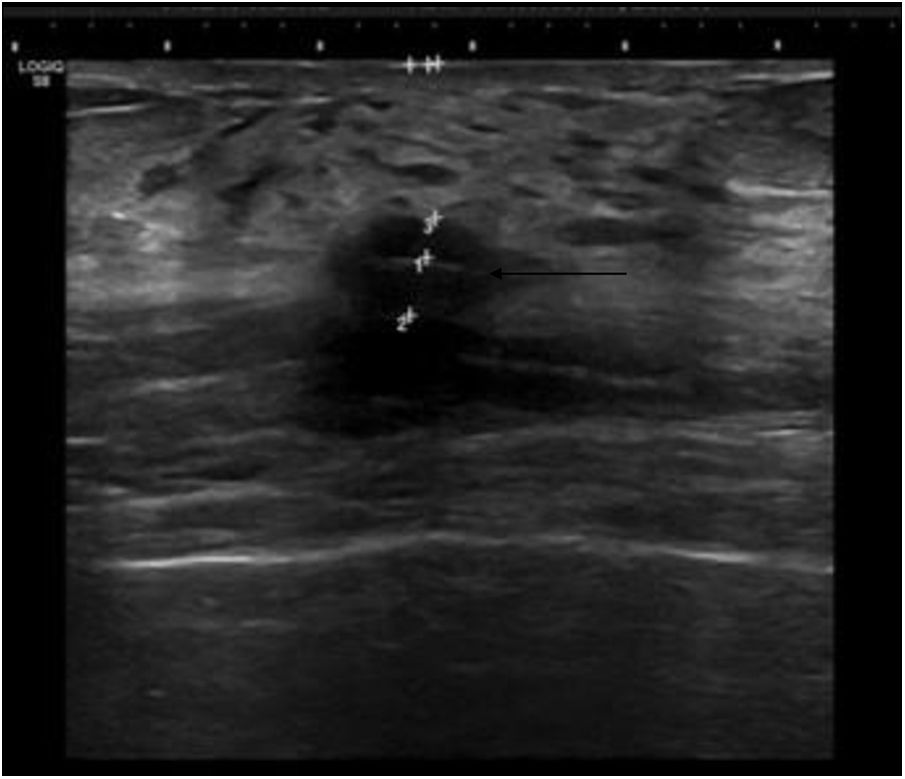
To assess the usefulness of iodine-125 (125I) seeds as an alternative to surgical clips for marking the location of nonpalpable malignant breast lesions for surgery.
Material and methodsWe included patients with histologically confirmed nonpalpable malignant lesions treated by surgery in 2015 or 2016. Patients were randomly assigned to presurgical marking with metallic clips (Group A) or with 125I seeds (Group B). In both groups, marking was guided by ultrasound and/or mammography depending on the radiologic characteristics of the lesion. During surgery, a gamma probe was used and afterward the presence of seeds in the surgical specimen was checked radiologically. In the histological analysis, the absence of tumour in the stain was considered free margins. We analysed the following variables: age, lesion characteristics (laterality, mean size on MRI and in the surgical specimen, radiological type), and presence/absence of free margins.
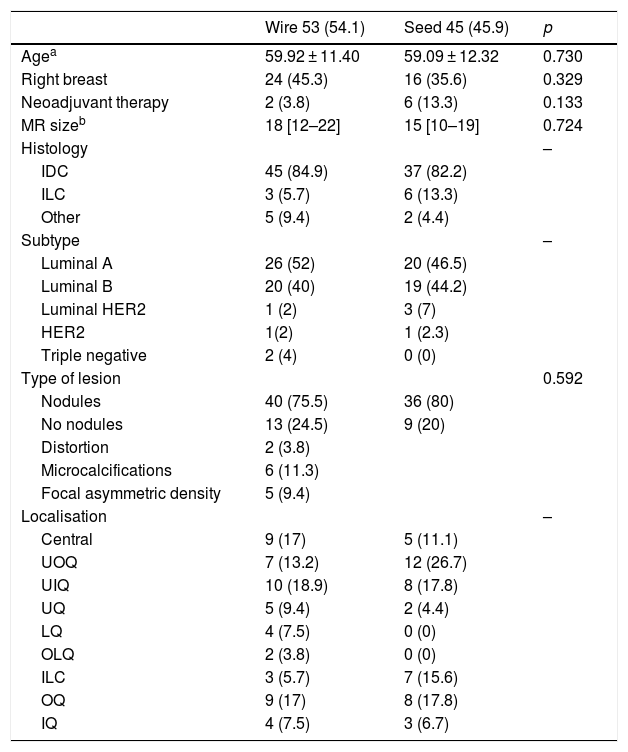
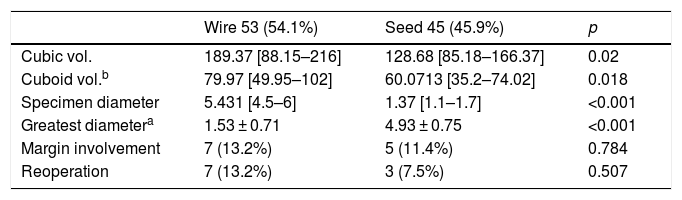
ResultsIn Group A (n = 53), the most common histologic subtypes were infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC, 84.9%) and luminal A (LA, 49.1%); the mean size of the lesions was 1.8 cm. In Group B (n = 45), the most common histologic subtypes were IDC (82.2%) and LA (46.5%); the mean size of the lesions was 1.5 cm.
In Group A, 13.2% had involved margins and 13.2% underwent a second surgical intervention. In Group, B 11.4% had involved margins and 7.5% underwent a second surgical intervention. The differences between groups were not significant (p = 0.7 for involved margins and p = 0.5 for reintervention). The volume of the surgical specimens was significantly lower in Group B than in Group A (128.68 cm3 vs. 189.37 cm3; p < 0.05).
ConclusionsUsing 125I seeds was feasible and enabled significantly smaller surgical specimens than using metallic clips.
Evaluar los resultados de la cirugía radioguiada mediante semillas de 125I como alternativa al arpón quirúrgico en pacientes con lesiones no palpables malignas de mama.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron pacientes con diagnóstico anatomopatológico de cáncer de mama, con lesiones no palpables, candidatas a tratamiento quirúrgico durante 2015–2016. Las pacientes fueron asignadas de manera aleatoria al marcaje prequirúrgico con arpón metálico (grupo A) o con semilla (grupo B). En ambos grupos, el procedimiento fue guiado mediante ecografía y/o mamografía en función de las características de la lesión radiológica. Durante la cirugía se utilizó una sonda gammadetectora y, posteriormente, se comprobó mediante radiología la presencia de las semillas en las piezas quirúrgicas. Se realizó el análisis histológico de las piezas, considerando márgenes libres la ausencia de tumour en la tinta. Las variables analizadas fueron la edad de las pacientes y varias características de la lesión (lateralidad, tamaño medido por resonancia magnética y en la pieza quirúrgica, tipo radiológico y presencia de márgenes quirúrgicos libres).
ResultadosEn el grupo A (n = 53), los subtipos histológicos más frecuentes fueron el carcinoma ductal infiltrante (CDI, 84,9%) y el luminal A (LA, 49,1%); el tamaño medio lesional (TML = 1,8 cm). En el grupo B (n = 45), los resultados fueron CDI = 82,2%, LA = 46,5%, TML = 1,5 cm. En el grupo A, la tasa de márgenes afectados fue del 13,2% y la tasa de reintervenciones, de un 13,2% (p = 0,7), y en el grupo B, la tasa de márgenes afectados fue 11,4% y la tasa de reintervenciones, del 7,5% (p = 0,5). Los volúmenes de las piezas quirúrgicas fueron significativamente menores en el grupo B (V = 128,68 cm3) que en el grupo A (V = 189,37 cm3) (p < 0,05).
ConclusionesLa utilización de semillas de 125I se ha mostrado como una técnica factible en la localización de lesiones no palpables de mama, mostrando diferencias significativas en el tamaño de las piezas quirúrgicas respecto al arpón.