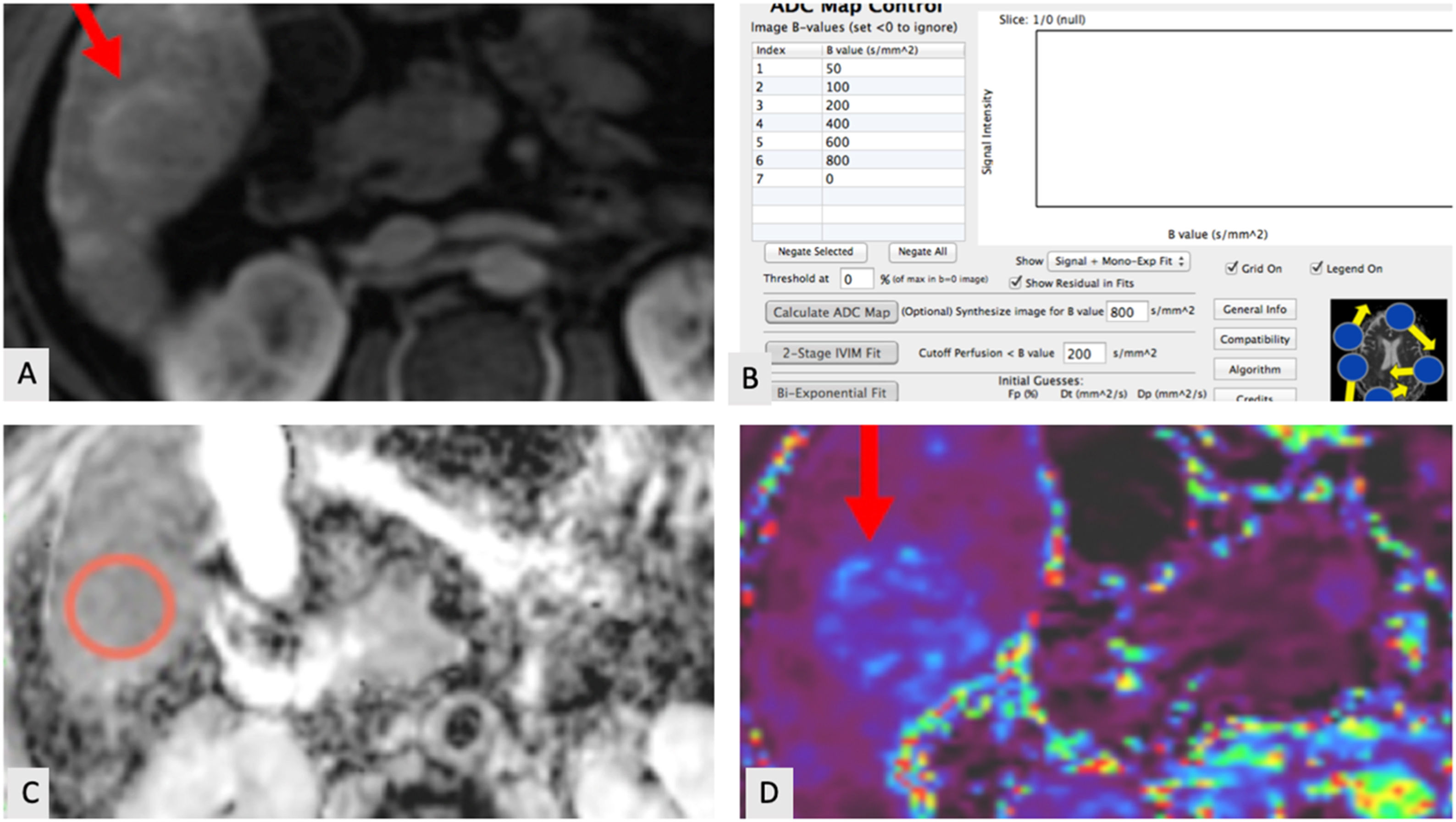
Response evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) currently is based on arterial phase enhancement which doesn’t take into microstructural changes in the tumor after trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE).
AimThis prospective study was conducted to assess the feasibility and efficacy of intravascular incoherent motion imaging (IVIM) in response evaluation of HCC after TACE.
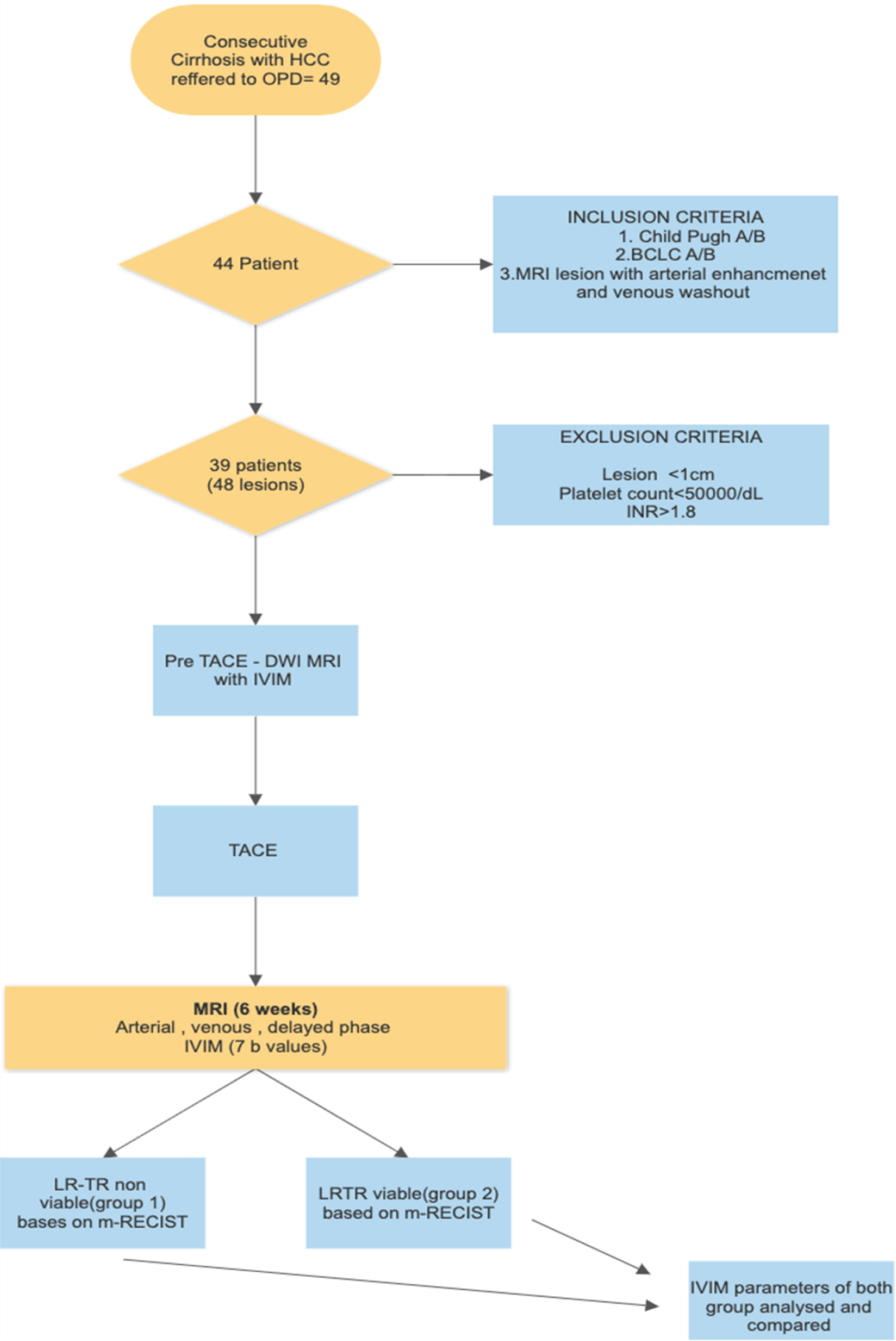
39 cirrhotic patients with 48 HCC underwent MR imaging 1 week within and 6weeks after TACE. IVIM parameters like Dslow (true diffusion), Dfast (pseudodiffusion), perfusion fraction and ADC were measured prior to and postTACE. The pre and post TACE values in LR-TR (LIRADS – treatment response) nonviable and viable lesions were compared using paired t-tests. ROC curve analysis was done to calculate sensitivity and specificity and propose cut-off values.
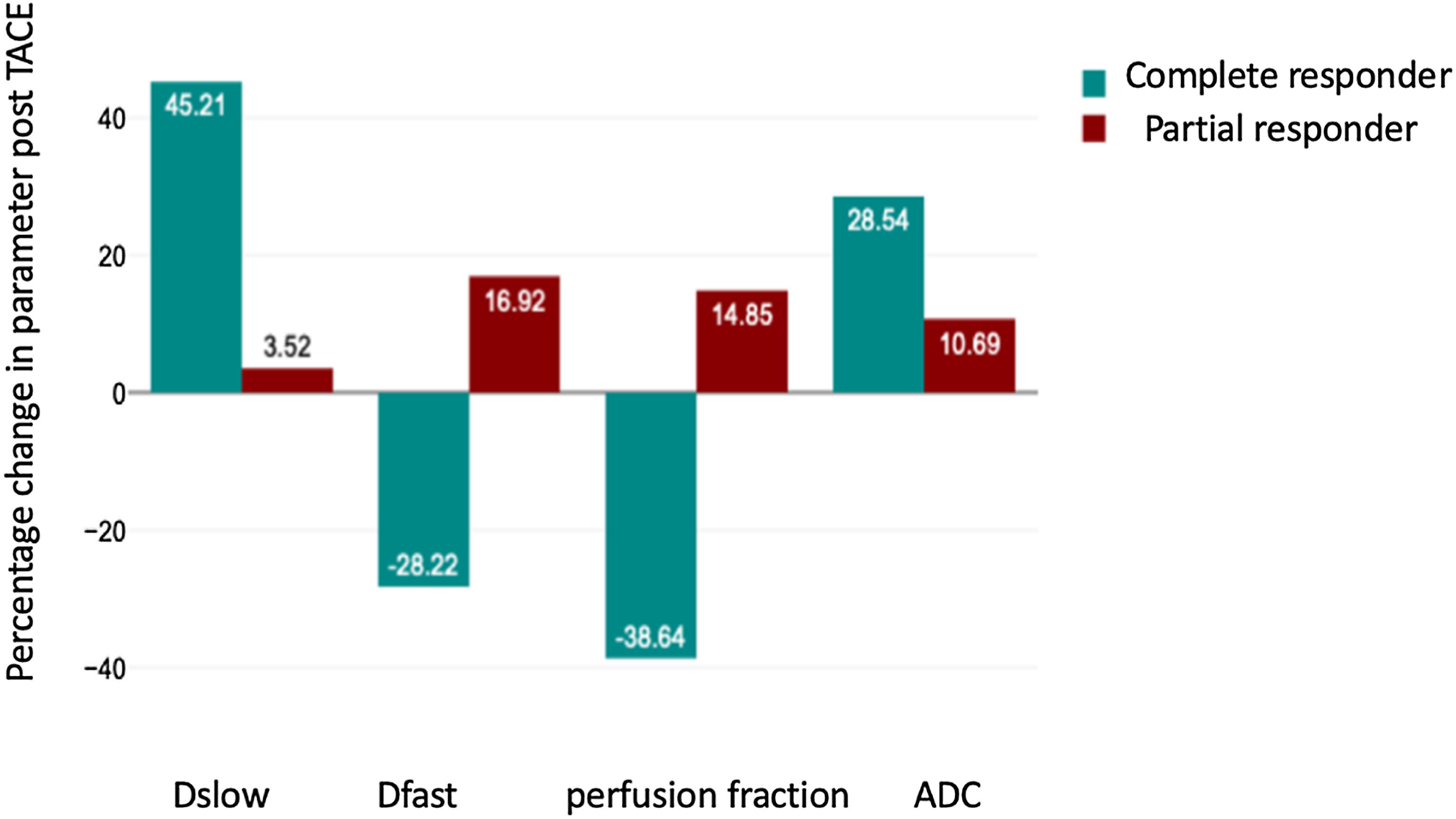
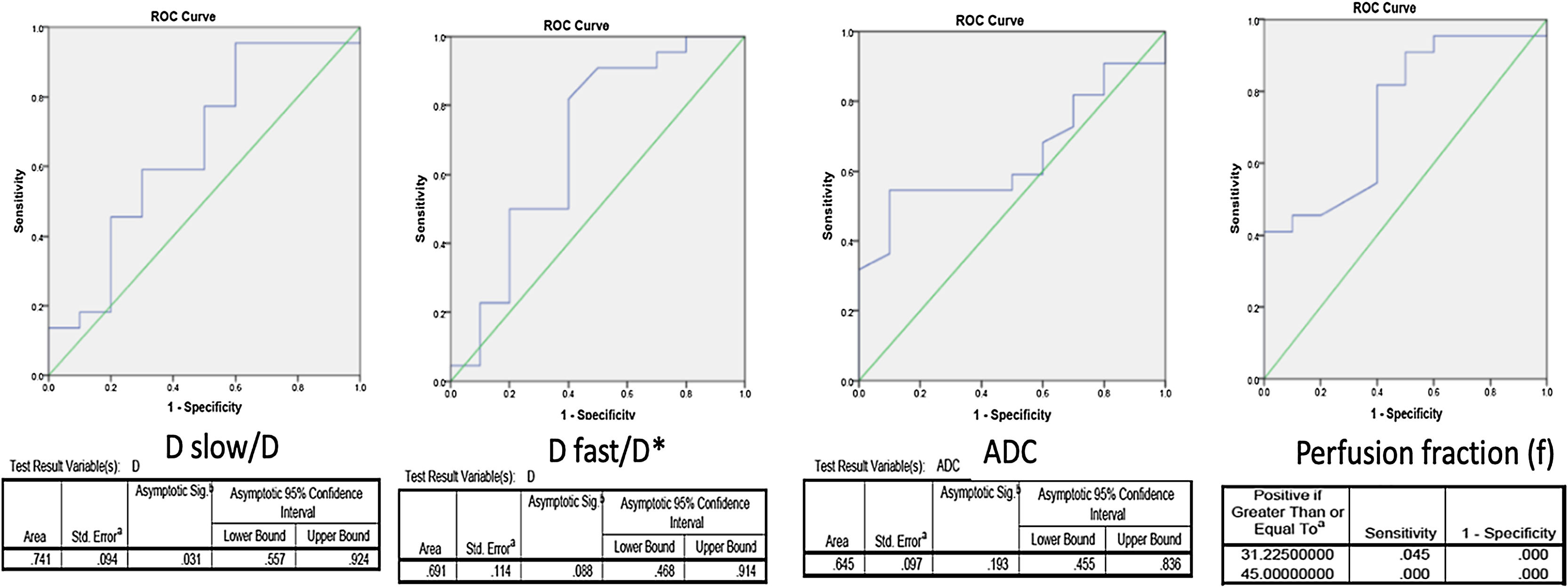
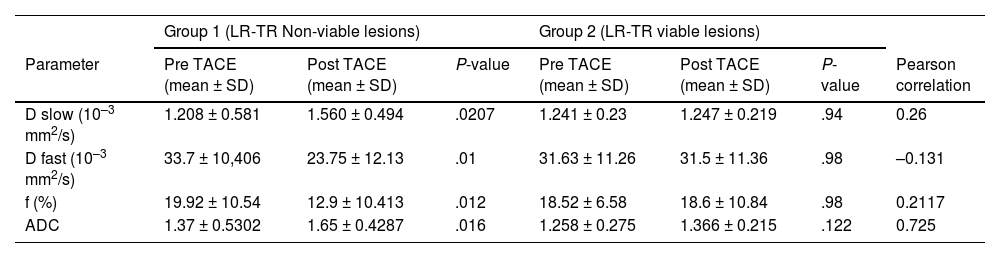
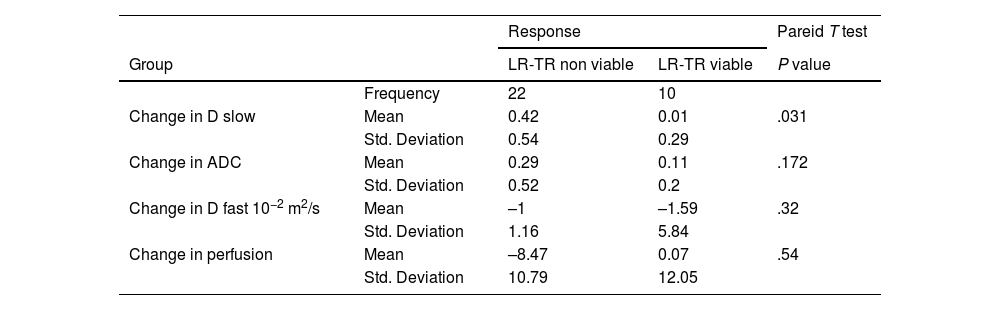
ResultNon-viable lesions showed a significant increase in Dslow (1.208 ± 0.581 vs 1.560 ± 0.494, P-value −.0207) and ADC (1.37 ± 0.53 vs 1.65 ± 0.4287, P value .016) after TACE. There was also significant decrease in Dfast (33.7 ± 10.4 vs 23.75 ± 12.13, P value .0005) and f (19.92 ± 10.54 vs 12.9 ± 10.41, P value .012) values after TACE in non-viable lesions compared to viable lesions. The change in true diffusion had the highest AUC (0.741) among IVIM parameters with greater than 0.075 increase between preTACE and postTACE values having a sensitivity and specificity of 81.8% and 60% respectively for complete response.
ConclusionIVIM imaging is feasible to assess the response in HCC after TACE. True diffusion is more sensitive and specific than apparent diffusion in evaluating the response.
La evaluación de la respuesta del carcinoma hepatocelular (CHC) se basa actualmente en el realce de la fase arterial, que no tiene en cuenta los cambios microestructurales en el tumor después de la quimioembolización transarterial (TACE).
ObjetivoEste estudio prospectivo se llevó a cabo para evaluar la viabilidad y la eficacia de la imagen de movimiento incoherente intravascular (IVIM) en la evaluación de la respuesta de CHC después de TACE.
A 39 pacientes cirróticos con 48 CHC se les realizó una resonancia magnética (RM) 1 semana antes y 6 semanas después de la TACE. Se midieron parámetros IVIM como Dslow (difusión verdadera), Dfast (seudodifusión), fracción de perfusión y ADC antes y después de la TACE. Los valores antes y después de la TACE en las lesiones no viables y viables de LR-TR (LIRADS [respuesta al tratamiento]) se compararon mediante pruebas t emparejadas. Se realizó un análisis de la curva ROC para calcular la sensibilidad y la especificidad y proponer valores de corte.
ResultadoLas lesiones no viables mostraron un aumento significativo de la Dslow (1,208 ± 0,581 frente a 1,560 ± 0,494, valor de P = –,0207) y de ADC (1,37 ± 0,53 frente a 1,65 ± 0,4287, valor de P = –,016) después de la TACE. También se observó una disminución significativa de los valores de Dfast (33,7 ± 10,4 frente a 23,75 ± 12,13, valor de P = ,0005) y f (19,92 ± 10,54 frente a 12,9 ± 10,41, valor de P = ,012) después de la TACE en las lesiones no viables en comparación con las viables. El cambio en la difusión verdadera tuvo el mayor AUC (0,741) entre los parámetros IVIM, con un aumento superior a 0,075 entre los valores previos y posteriores a la TACE, con una sensibilidad y especificidad del 81,8 y el 60%, respectivamente, para la respuesta completa.
ConclusiónLa IVIM es factible para evaluar la respuesta en el CHC después de la TACE. La difusión verdadera es más sensible y específica que la difusión aparente para evaluar la respuesta.