In December 2019, cases of pneumonia were reported in Wuhan, China, caused by a new coronavirus called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and the resulting disease was named COVID-19.1
The first patient with coronavirus reported in Spain was identified on 31st January 2020. Since then, the number of infections has progressively increased, already bordering on 110,000 positives.
COVID-19 is characterized by the presence of common symptoms and signs, among which are: Fever, dry or productive cough, sore throat, dyspnoea, and gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhoea and vomiting).2
Other symptoms such as taste loss and anosmia have also been described.3
Laboratory results often show an increase in the levels of C-reactive protein. Coagulation disorders, especially D-dimer and prothrombin time, were more common in patients with greater severity.4,5 About a third of the cases showed hepatic cytolysis data. Severe lymphopenia was the most common haematological finding in critically ill patients.4,5
The most common radiological pattern in all series was alveolar infiltrate.4,5
Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal exudate, which allows virus isolation, confirms the diagnosis.
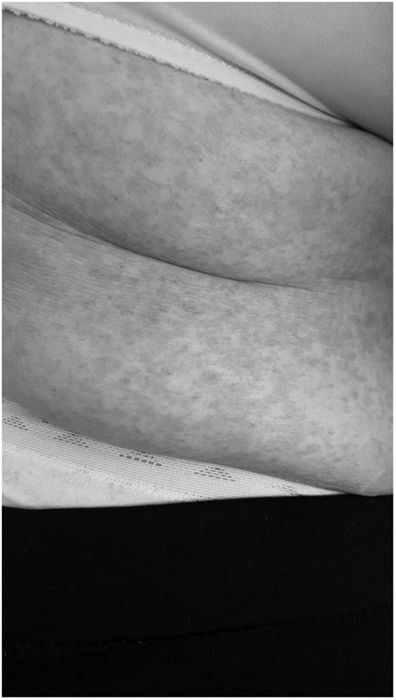
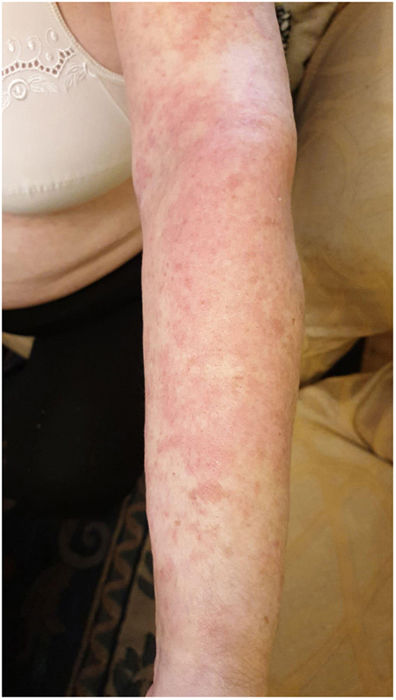
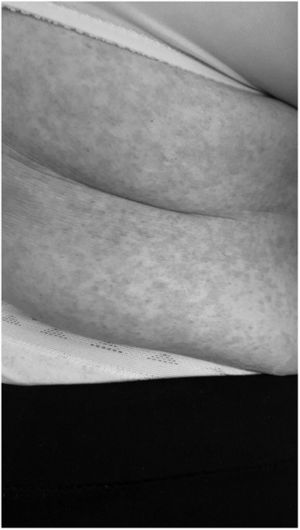
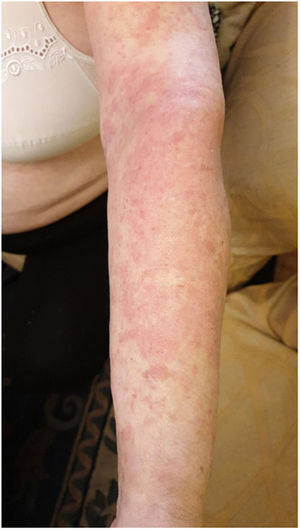
There is little data on cutaneous manifestations in people with COVID-19.6 We report the case of a patient diagnosed with COVID-19 infection who developed cutaneous manifestations after hospitalization (five days after discharge and 20 days after the onset of symptoms).
The cutaneous manifestation was an erythematous rash. The trunk was the main site involved. These were slightly itchy lesions, which generally healed within a few days. Apparently, there was no correlation with the severity of the disease, nor with the treatments prescribed during admission.
We can conclude that the cutaneous manifestations are similar to the cutaneous involvement that occurs during common viral infections (Figs. 1 and 2).
FundingNone.
Conflicts of interestNone.
Please cite this article as: Obaya Rebollar JC. Manifestaciones cutáneas de la infección por COVID-19. A propósito de un caso. Med Clin (Barc). 2020;155:50.