This article presents an original conceptual framework for the strategic management of intellectual capital assets in software development companies. The framework is based on Lewin's Force Field Analysis. The framework makes it possible to assess software company managers’ opinions regarding the way driving and restraining forces affect the pillars of intellectual capital. The capacity to adapt to change is vital for companies in knowledge-intensive industries. Accordingly, this study examined a sample of 74 Romanian software development companies. The aim was to help companies benefit from managing the driving and restraining forces acting upon the pillars of intellectual capital (human, structural, and relational). The effects of the driving forces, quantified by PathMaker software's Force Field Tool, were observed to be greater than the restraining forces for each pillar of intellectual capital. This paper contributes by showing the explanatory power of this framework. The framework thus offers a tool that helps managers drive change in their organizations through effective intellectual capital management. Furthermore, this article describes how to encourage the implementation of changes that create value for software development companies.
El trabajo de investigación propone una esquema conceptual para el management estratégico de los activos de Capital Intelectual en el ámbito de las empresas del sector software, interrelacionado con el planteamiento analítico del modelo force field. El marco avanzado proporciona la evaluación de las opiniones de la dirección des empresas del sector software sobre el impacto percibido por los mismos, de las ambas fuerzas impulsores et impedidores repartidas entre los pilares del capital intelectual.
Considerando que la capacidad de adaptarse al cambiamiento es el desafío más pertinente para las empresas de las industrias intensivos en conocimiento, este trabajo de investigación está empleando una población de 74 empresas del sector informático localizadas en Rumania, para proporcionar valiosos revelaciones sobre las capacidades anticipativas, activando los beneficios del cambiamiento, a través manejar las fuerzas impulsores et impedidores a los niveles humano, estructural y relacional del Capital Intelectual. La análisis de los datos, a través del puntaje promedio por cada dimensión estructural dela esquema conceptual, nos está revelando que el efecto de las fuerzas impulsores, cuantificado por PathMaker Force Field Tool, es más significante que aquello de las fuerzas impedidores por cada nivel de los pilares del capital intelectual. La contribución original de este trabajo de investigación consiste de revelar el poder explicativo del marco conceptual propuesto, como respuesta a la demanda de los directivos de empresas, a la busca de soluciones de manejar el cambiamiento frente a los desafíos organizacionales, a través el management eficaz del Capital Intelectual. Además, el trabajo de investigación está describiendo como la validación de los resultados está animando la implementación del cambiamiento, con el propósito de la creación de valor en las empresas del sector informático.
The idea of writing this paper came from the relevance for the present business landscape of a statement made by Kurt Lewin long time ago (1943), according to which an organization is held in balance by the interaction of two opposing sets of forces – those seeking to promote change (driving forces) and those attempting to maintain the status quo (restraining forces). The need for change, due to high pressures of both external and internal environment, assumes the consideration on how to reduce resisting forces, while driving forces are stronger.
The intellectual capital (IC) was proved to be useful for promoting organizational change processes (Lönnqvist, Kianto, & Sillanpää, 2009), being recognized as a highly important resource that organizations need to develop to gain sustainable competitive advantages (Kong & Thomson, 2009).
Based on the experiences gained in previous researches focused on IC management and Strategic Intelligence within the particular context of software industry, the challenging opportunity to emphasize the role of Lewin's force field analysis in the process of IC strategic management arises. After a careful analysis of the body of knowledge related to IC management, this is the first research paper that addresses IC specific strategic issues through Lewin's force field analysis, in the attempt to calibrate the capability of change in the case of software development companies.
Sustainable advantage life cycle of each organization is relying upon managerial capacity to set up the change priorities based on intangibles assets – as future competence to train – in the attempt to develop its absorptive capacity. We advance that our conceptual construct is relevant both to reveal new knowledge by means of developing IC potential and to provide an adjusted methodology to employ as well, as response to strategic decision making need for external expertise.
The paper is structured as follows: in the first section, dedicated to literature review, the issues referring to the interconnections between IC, change management and force field analysis were highlighted; the second section describes the research methodology and tools; in the third section, we presented the main findings of the study, using Force Field Tool embedded into Path Maker software; in the last section, we presented the conclusions, the limitations of our study, its practical implications and the guidelines for the future research agenda.
Theoretical backgroundMost part of managers are not fully aware of the value of their own intellectual capital and they do not know if they have the people, resources or business processes in place to make a change in order to better perform on their markets. They do not understand what know-how, management potential or creativity they have access to with their employees and as they are devoid of such information, they are rightsizing, downsizing and reengineering in a vacuum (Bontis, 1999).
Intellectual capital can be defined as the sum of intangible resources (knowledge, information, intellectual property and experience) that have been formalized, captured and leveraged to create assets of higher value (Davenport & Prusak, 1998; Kannan & Aulbur, 2004).
Little attention has been given on how intellectual capital can be conceptualized and interpreted in a change management perspective. Through an extensive review of the literature focused on inter-related perspectives of IC and change management, we found a case study, which clearly identify the key-knowledge assets involved in a change management program (Schiuma, Lerro, & Sanitate, 2008).
IC and software development address particular attention to managers, as they are both intangible in nature and difficult to express in monetary terms (Barney, Aurum, & Wohlin, 2009). A significant challenge for software companies is to assess their competency needs and ensure that they get the best return from their IC while supporting change management processes.
The capability to adapt to change becomes crucial in the context of the lack of an extensive technological knowledge base, especially in software development companies from emerging economies, which makes knowledge spillovers particularly important (Pathak, Xavier-Oliveira, & Laplume, 2013). Agile practices proved their efficiency and respect the software industry's increasing needs for rapid development and coping with continuous change (Boehm & Turner, 2005).
Software developers exploit patents to shield key technological features of software from market competitors and outlying the IP rights in any change management program is compulsory (Suh & Oh, 2015).
A research conducted by Díaz-Fernández, González-Rodríguez, and Simonetti (2015) reveals the importance of IC management team's approach in order induce innovativeness and enhance competitive advantages through driving forces that is favorable to change.
A highly interesting approach for measuring the components of IC in software industry leads to institutionalization of standardized metrics for benchmarking purposes in software development companies (Seleim, Ashour, & Bontis, 2004). Moreover, changes that may occur require to software firms’ managers to develop customized key performance indicators that contribute to the process of establishing tailored IC measures for each software firm, based on their own vision and strategy.
Strengthening the organizational strategy through the development of its intangible assets and consulting different behavior profiles of intellectual capital components enable organizational success, according to a research conducted by Axtle-Ortiz (2013).
Based on a competitiveness factors framework, which enable the identification and comparison of the intellectual capital indicators from software industry, the results of a research undertaken at the level of Romanian software development companies (Capatina, Olaru, & Balan, 2012) reveals how they become more adaptable and flexible by capturing opportunities in a very dynamic market.
Based upon Lewinian force theory, the behavior of a software company is the result of a field of forces, each of which had direction and magnitude. Following his idea, software developers’ post-action expectancies and valences could be combined in a multiplicative way to predict their satisfaction and intention to continue participating in software projects (Wu, Gerlach, & Young, 2007).
A recent research emphasizes an original decision support frameworks capable to support managers in the assessment of ICAs’ benefits in a strategic perspective, validated by managers’ commitment to implement actions related to the recommended ICAs in the case of a knowledge-intensive company (Rossi, Cricelli, Grimaldi, & Greco, 2016).
Conceptual framework and research methodologyThis article proposes a decision-support framework that aims at improving the strategic IC management of knowledge-intensive software development companies using Force Field Tool provided by PathMaker software. The research methodology, envisaging five steps is following the conceptual framework requirements.
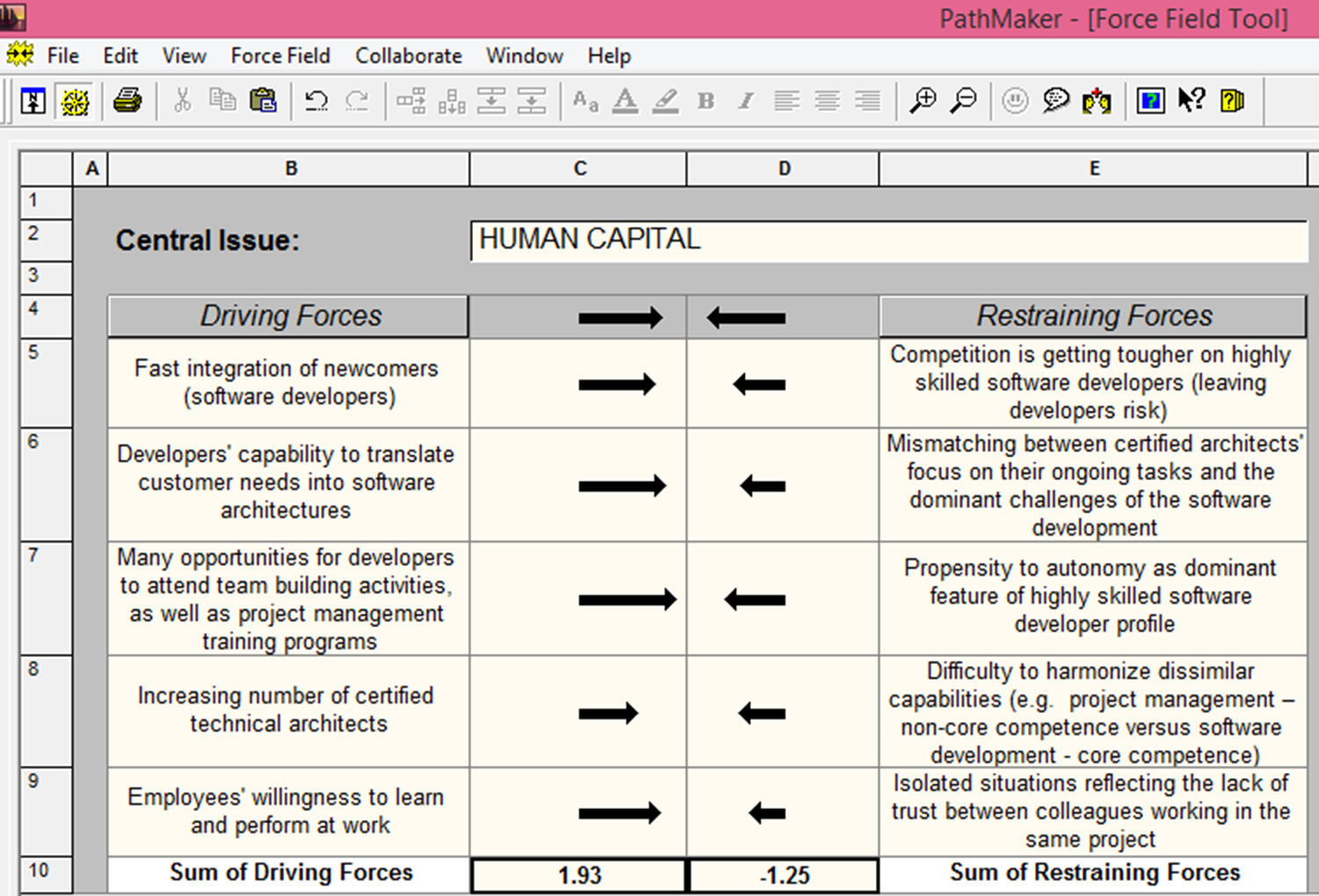
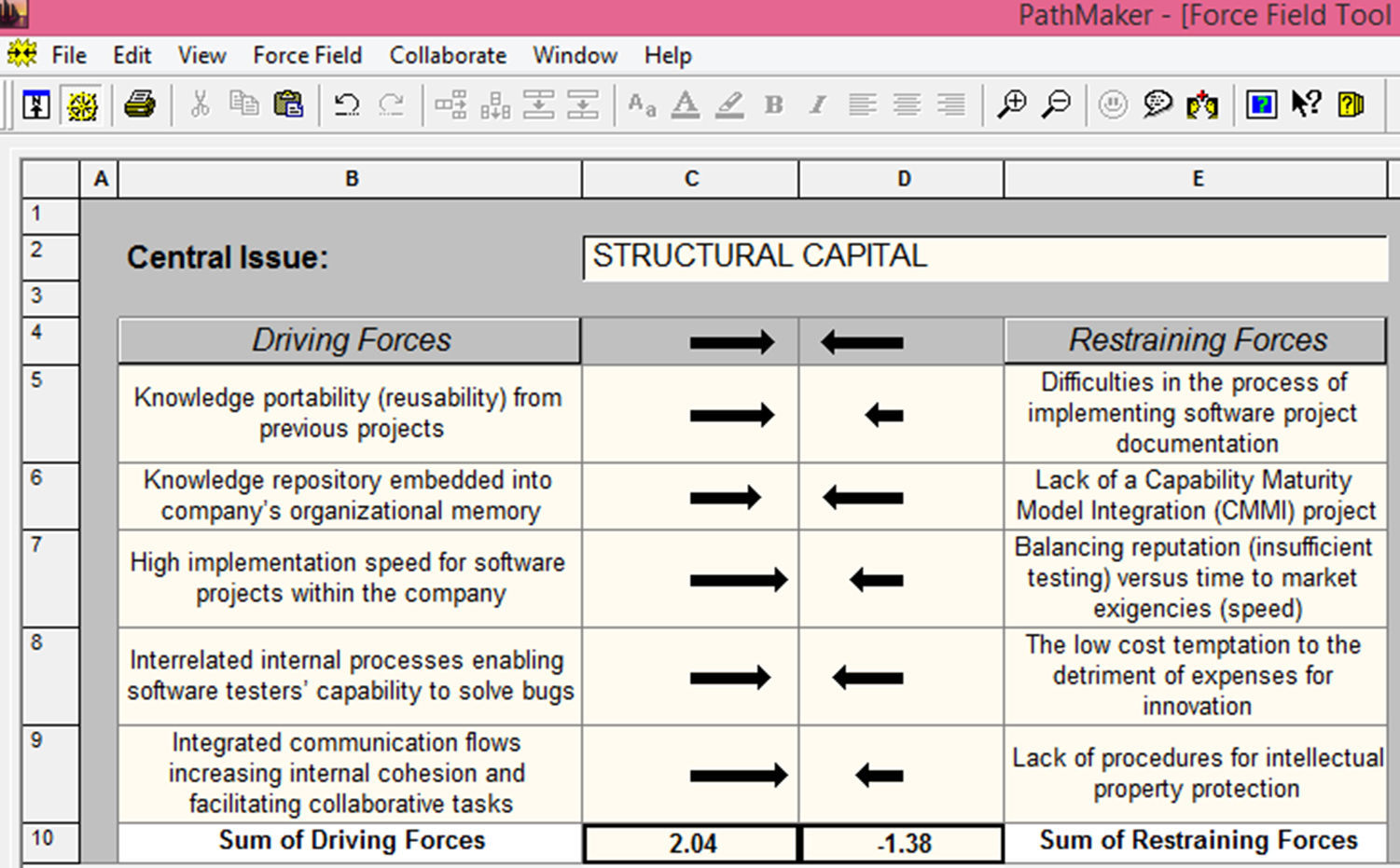
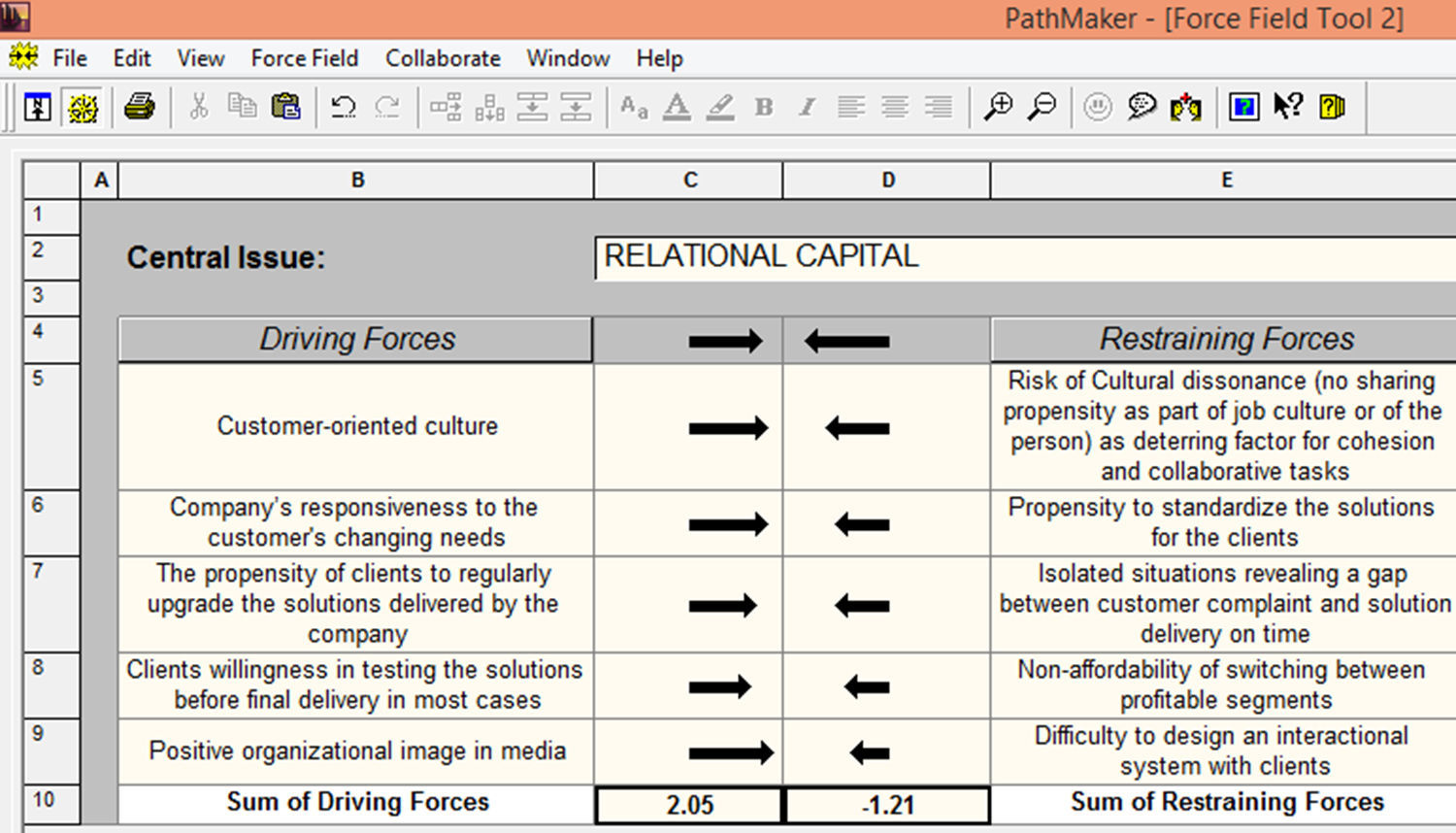
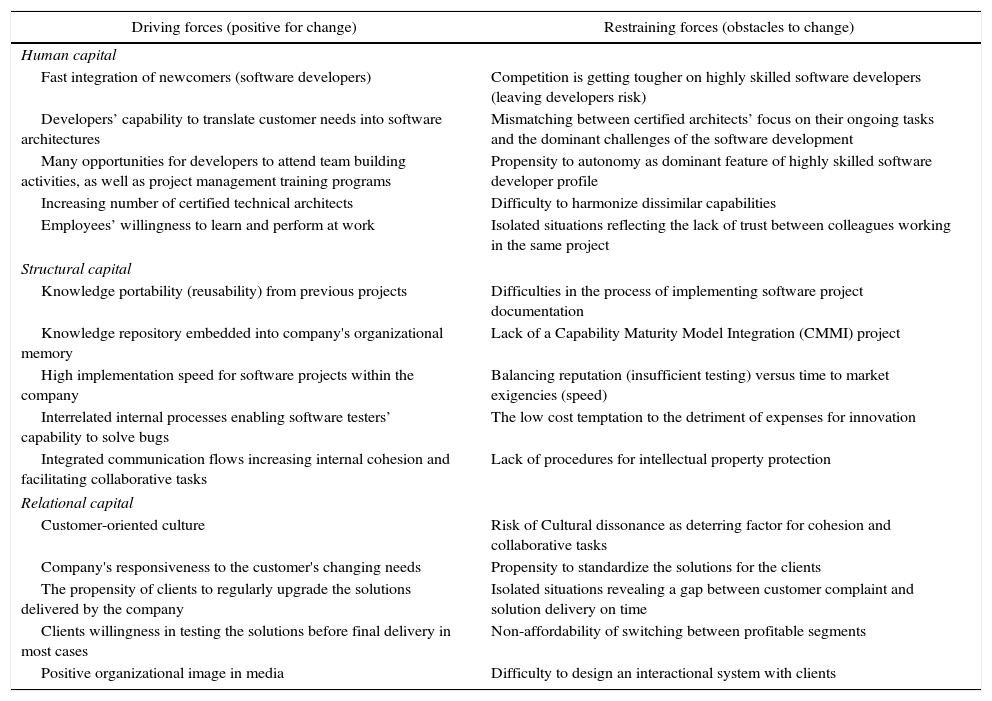
Step 1: definition of relevant IC pillars and their interrelationsFirst, the researchers identified within a focus-group the relevant items to be analyzed and designed the self-assessment questionnaire to be further addressed to the managers of software companies. The framework include 10 items per each IC pillar (human, structural and relational), considers 5 items for driving forces, respectively 5 items for restraining forces (Table 1).
Framework revealing driving and restraining forces on IC management of software companies.
| Driving forces (positive for change) | Restraining forces (obstacles to change) |
|---|---|
| Human capital | |
| Fast integration of newcomers (software developers) | Competition is getting tougher on highly skilled software developers (leaving developers risk) |
| Developers’ capability to translate customer needs into software architectures | Mismatching between certified architects’ focus on their ongoing tasks and the dominant challenges of the software development |
| Many opportunities for developers to attend team building activities, as well as project management training programs | Propensity to autonomy as dominant feature of highly skilled software developer profile |
| Increasing number of certified technical architects | Difficulty to harmonize dissimilar capabilities |
| Employees’ willingness to learn and perform at work | Isolated situations reflecting the lack of trust between colleagues working in the same project |
| Structural capital | |
| Knowledge portability (reusability) from previous projects | Difficulties in the process of implementing software project documentation |
| Knowledge repository embedded into company's organizational memory | Lack of a Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) project |
| High implementation speed for software projects within the company | Balancing reputation (insufficient testing) versus time to market exigencies (speed) |
| Interrelated internal processes enabling software testers’ capability to solve bugs | The low cost temptation to the detriment of expenses for innovation |
| Integrated communication flows increasing internal cohesion and facilitating collaborative tasks | Lack of procedures for intellectual property protection |
| Relational capital | |
| Customer-oriented culture | Risk of Cultural dissonance as deterring factor for cohesion and collaborative tasks |
| Company's responsiveness to the customer's changing needs | Propensity to standardize the solutions for the clients |
| The propensity of clients to regularly upgrade the solutions delivered by the company | Isolated situations revealing a gap between customer complaint and solution delivery on time |
| Clients willingness in testing the solutions before final delivery in most cases | Non-affordability of switching between profitable segments |
| Positive organizational image in media | Difficulty to design an interactional system with clients |
The analysis scale for driving and restraining forces items is the same, reflecting the following assignments: 0.5 – high impact on change; 0.3 – medium impact on change; 0.1 – low impact on change and 0 – no impact on change. The framework content was translated in a questionnaire, which was validated before submission by the eight managers who attended the focus-group.
Step 2: submission of questionnairesThe researchers submitted the self-assessment questionnaires to a convenience sample formed by 120 Romanian software companies. After careful analyses of inputs, the scores related to 74 questionnaires is validate and included into an Excel database for further exploitation.
Step 3: synthesis of average scores related to driving and restraining forces, in the case of each IC pillarThe outputs from Excel database, considered as inputs in Force Field Tool from PathMaker software, mark the average scores associated to the items embedded in each IC pillar, corresponding to both driving and restraining forces. The sum of average scores, in the particular case of human, structural and relational capital, determined the strength of driving, respectively restraining forces in Force Field Tool.
Step 4: translating average scores into strength arrows by means of Force Field ToolThe arrows outlining the strength of each force (driving vs. restraining) graphically represents the average scores inserted into Force Field Tool, for each central issue (represented by Human, Structural and Relational Capital).
Once we entered all the forces and set their strength arrows, the Force Field Tool added up all the forces in order to enabling comparative the total driving forces against the total restraining forces.
Step 5: discovery the meanings of associations between the components of IC through multidimensional scaling (MDS)In order to gain deeper insights from the information stored in the research database, we tried to discover the coherence of data with the components (human capital – H, relational capital – R and structural capital – S) of IC, by exploring (discovering) some latent variable that could be identified with H, R and S.
By using correlations and factor analysis, we observed that the respondents, for different reasons, have not understood very well the intended meaning of the questions and reacted to those items/stimuli according with the way data expresses it. In this context, it would be interesting to characterize the meanings of associations implicit in their answers. The most appropriate method to study these issues is multidimensional scaling (MDS) that provides a map (a topology) of the respondents’ reactions (mental proximities between meanings of concepts) to items embedded into the proposed framework. The study of the visual mapping of pairwise dissimilarities in Euclidean space, in the given context, can be useful to rephrase the sentences of questionnaire, to judge about the correction of some factors, to set up training of managers in future application of the self-assessment instrument.
ResultsOne of the central goals of this paper addresses the assessment of propensity to change through Force Field analysis. The organizational commitment for strategic change involves the superiority of driving forces to restraining ones. Thus, to determine the balance of power between driving and restraining forces emphasized in the proposed framework, we conducted analyses by means of PathMaker software.
Force field analysisFirst analysis was performed using the outputs provided by Force Field Tool from Path Maker software.
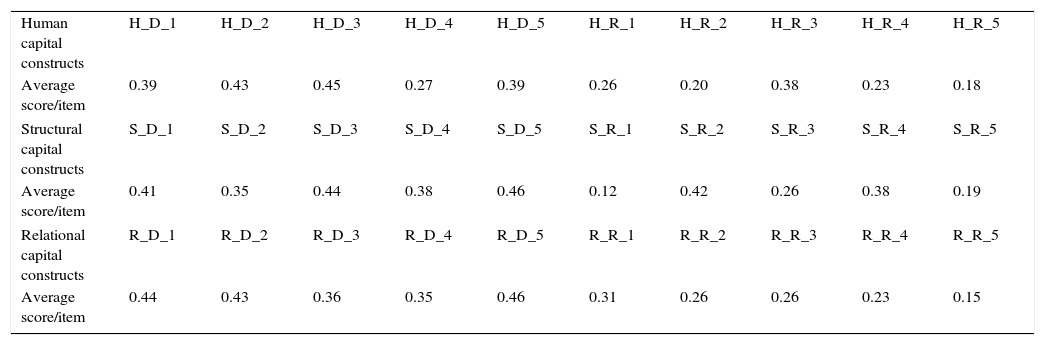
We codified the constructs related to IC pillars as follows: first letter: H, R, S for Human capital, R Relational, S-Structural; second letter – D for Driving forces or R for Restraining forces, while third symbol (1,2,3,4,5) refers to item number, according to the framework emphasized in Table 1.
The average scores related to the constructs were computed in Excel database (Table 2), transferred into PathMaker software and converted into strength arrows (Figs. 1–3).
Average scores related to constructs.
| Human capital constructs | H_D_1 | H_D_2 | H_D_3 | H_D_4 | H_D_5 | H_R_1 | H_R_2 | H_R_3 | H_R_4 | H_R_5 |
| Average score/item | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.23 | 0.18 |
| Structural capital constructs | S_D_1 | S_D_2 | S_D_3 | S_D_4 | S_D_5 | S_R_1 | S_R_2 | S_R_3 | S_R_4 | S_R_5 |
| Average score/item | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.12 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.19 |
| Relational capital constructs | R_D_1 | R_D_2 | R_D_3 | R_D_4 | R_D_5 | R_R_1 | R_R_2 | R_R_3 | R_R_4 | R_R_5 |
| Average score/item | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.15 |
We observe that the sum of average scores translated into strength arrows highlights higher values corresponding to Driving forces than the values reflecting Restraining forces, at the level of all IC pillars. This finding reveals a high degree of propensity to change in the sample of companies involved in this research, as forces seeking change are stronger than those seeking to maintain the status quo. If we analyze companies’ propensity to change case-by-case, we remark a single case where restraining forces are stronger than driving forces both for relational and structural capital and three cases with the same result at the level of relational capital.
At a glance, the Human Capital score (Driving forces strength=1.93/Restraining forces strength=−1.25) is exposing the difficulty to master driving forces and restraining forces as it is based on conflicting features of intellectual capital strategic management capability for coordinating organizational competence and individual competence. The level of human capital in terms of experience, knowledge, creativity and values is mediate by the collaborative, communicative and coordinative capability of an effective IC strategic management. The preliminary results offer promising insights of organizational internal environment prone to rapid individual/team integration and talent retaining as a deterrent for competence portability and knowledge waste.
Deeper analysis will assess the IC management propensity to improve the score of mastering driving/retaining forces, through refining mechanisms of individual versus organizational specific skills on software sector. Further research must recall competence and integrity approach of trust, as precursor of an effective IC strategic management based upon its fundamental pillar, Human Capital.
As regards Structural Capital score (Driving forces strength=2.04/Restraining forces strength=−1.38) we observe a moderate confidence based upon features of organizational process assets embedded in a mature propensity to design and develop intelligent routines embedded in organizational memory.
We also advance the necessity to analyze the observed consistency in associated items of specific features of Human and Structural Capital in terms of driving and restraining forces mastering.
The endeavor, if prove sustainable, could have an impact on the primary research conceptual framework and an improvement framing could insure a highest impact of IC strategic management efforts to compel against the exigencies of organizational maturity endowment in terms of IC assets.
The preliminary results of the Relational capital score (Driving forces strength=2.05/Restraining forces strength=−1.21) prove the highest level of management confidence in mastering driving forces to change and monitoring restraining forces, accordingly. At a first glance, this could be consistent with software sector's knowledge intensive features and easy to observe the firms’ self-confidence on its Relational Capital asset impact upon rivalry mechanisms dominance. The value derived from relationships with prospectors is a peculiar combination of knowledge and a valuable asset to employ through an effective IC strategic management.
Keeping in mind that relational capital component of intellectual capital is about knowledge value embedded on a myriad of stakeholder's partnerships (clients, media, agents and other prospectors), it is compelling to fully master the knowledge value chain of the sector by effective management of intellectual capital.
Deeper investigations will enable the assessment of the valuable promising alignment propensity, based upon organizational adjusting capability, in terms of specific metrics of profiling behavior impact: market leader versus market follower and market nicher versus market challenger.
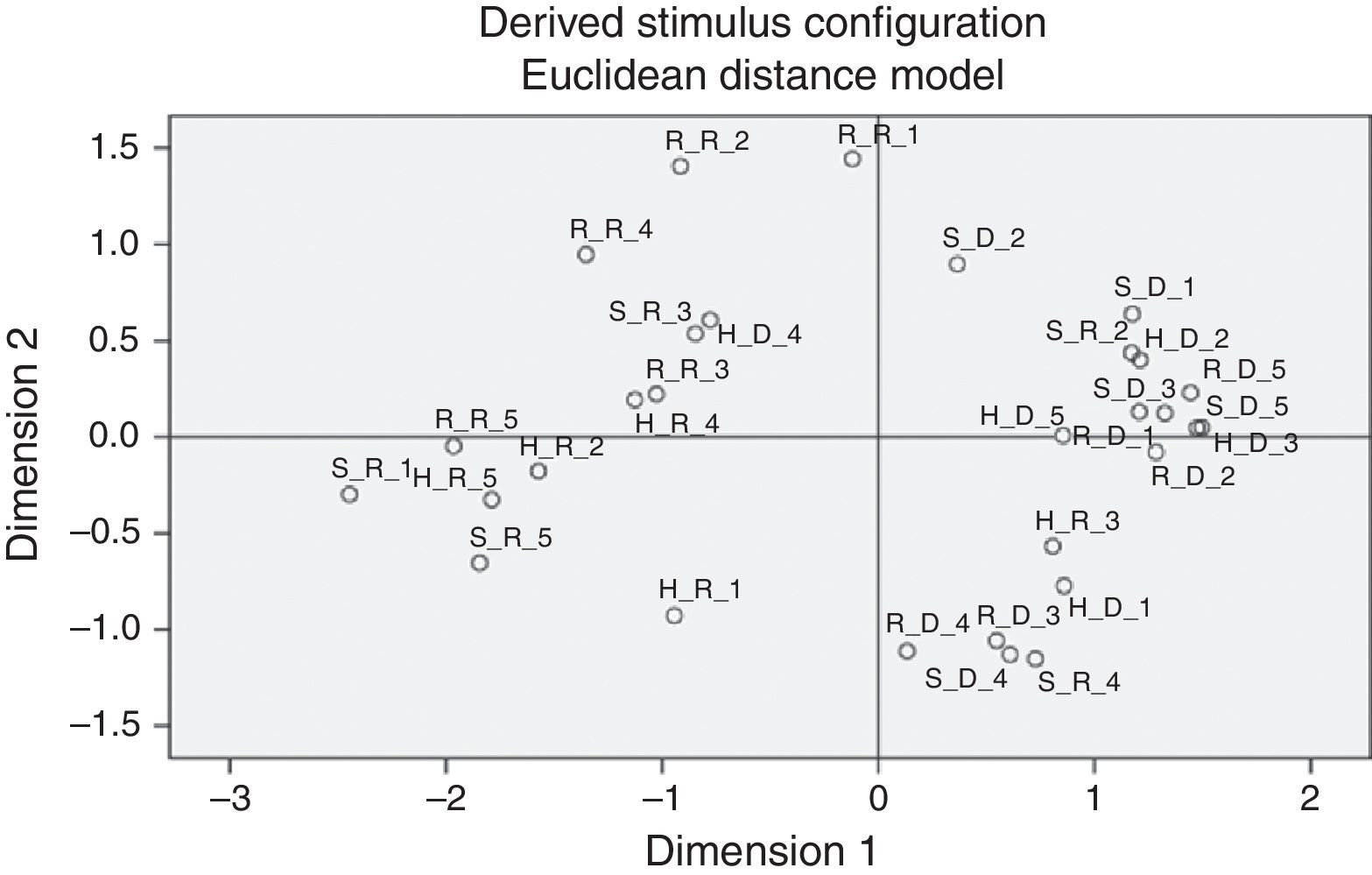
Multidimensional scale analysisIn the context of MDS, the points (Fig. 4) are defined by means of stimulus (items to which respondents react according with the meaning they attribute to those stimuli/items (interpretation). This means that, if two of those stimuli appear very near in the graph, they were interpreted nearly the same way by the set of 74 respondents. And the inverse: two stimulus far away in the graph mean that for the whole of respondents, its meaning was considered very distinct.
The plot separates – with some exceptions – the items related to D (Driving forces), positioned in the right side of the visual map, from those related to R (Restraining forces). This means that respondents interpreted very well this intended macroscopic distinction – with minor exceptions
The exceptions from this pattern are the following:
- •
H_D_4 – is positioned in the left side, meaning that respondents interpret this stimuli as an R (Restraining factor) instead as a D, Driving force, giving it practically the same meaning as S_R_3;
- •
S_R_2 – is interpreted as a driving force (in the right side), practically with the same meaning as H_D_2;
- •
H_R_3 – is interpreted as a Driving force instead as an R (restraining force, as intended)
- •
S_R_4 – is interpreted as a driving force instead of an R (restraining force, as intended)
Considering groups of stimuli (items) to which the respondents attribute similar meaning (interpret roughly the same way) we have the following groups (detected subjectively), such as follows:
G1={R_R_1; R_R_2; R_R_4} – This group is homogeneous in relation to IC and refers only to Relational Capital
G2={S_R_3; H_D_4: R_R_3; H_R_4}
G3={H_R_2; H_R_5; S_R_1; S_R_5; R_R_5}
G4 ={H_D_2; H_D_5; R_D_2, R_D_5; S_R_2; S_D_3; S_D_5; R_D_1}
G5={H_D_1; R_D_3; R_D_4; S_D_4; S_R_4}
One question that arise represents a challenging task of this research: since the respondents interpret the stimuli in the same group, roughly the same way (assigning to them similar meanings), can it happen that subjacent to these groups of items (that mixtures items from H, D, R – with the exception of G1) appear? The answer can be provided by studying each group using the Cronbach alfa.
In the case of G1 – Cronbach alfa (0.372) considerably higher than the one found for the predefined groups of items (H; R; S) but not large enough to allow the existence of a latent variable of high quality. This group is homogeneous in the sense that all correlations are positive and refers exclusively to the same type of IC.
For the other groups, the values of Cronbach alfa (Group 2: −0.214; Group 3: 0.103; Group 4:0.237; Group5: 0.405) are considerably higher than for the initial variables but for none we find values large enough to assume the existence of interesting latent variables subjacent to groups.
We think that the associations found comparing the intended meanings of wordings and the meanings assigned by respondents and expressed by these associations expressed by those groups can suggest some action relative to calibration of the self-assessment instrument.
By analyzing only the variables H_D (sum of H_D_1 to H_D_5), R_D and R_R; S_D and S_R, the new visual map obtained with MDS – Fig. 5 – seems interesting and has a structure as expected: the variables D's and R's are separated and opposed in distinct quadrants of graph. This finding corresponds to a clear understanding of the general meaning of D and R by the respondents.
Figs. 4 and 5 visualize the items reflecting restraining forces – R (with some exceptions in case of Fig. 4 and no exceptions in case of Fig. 5) in the left side of graphs, while the items relative to driving forces – D in the right side (with some exceptions in case of Fig. 4 and no exception in case of Fig. 5).
This suggests that respondents grasp correctly the intended meaning of opposition D-R. Given this fact, we could suggest that in both graphs the meaning of this distinction (R-D) is associated to the horizontal axis.
As a concluding remark, since respondents apparently interpret the items/stimuli in ways distinct to the intended meanings, MDS seems an adequate method to discover, out of collected data, what those real meanings are. This kind of value added information (knowledge) is employable as input to redesign the training of respondents.
Conclusions, managerial implications and future research agendaAs the outcomes of this research explore new recipes of conceptual association, while the managerial pertinence of solutions to the challenging endeavors of strategic decision is thoroughly addressed, the following final arguments seem compulsory.
Re-FramingThe advanced Intellectual Capital and Force Field (IC&FF) conceptual construct represents an innovative insight for channeling the debate around the strategic approach to intellectual capital assets. By employing Force Field framework to improve the IC management self-assessment is the main contribution of the paper, as relying upon organizational practices of discovering new knowledge, while training collective IC capability to reframe and prioritize the change enable organizational performance.
Beyond IC management awarenessThe real valuable distinction between new knowledge and really new knowledge resides on enabling the natural IC management approach to change by training its capacity to objectively construct, compare and select between feasible alternatives, in respect to each organizational perceived impact of its driving and restraining forces.
Our approach proposes a new recipe not only by exposing the DF/RF stimuli, but also for revealing a re-framed strategic decision process by refreshing the intuitive knowledge and expertise.
The pertinence of the construct is challenging the strategic management's trained capacity (without any appetite for change), usually framed as internal and external organizational factors, toward the untrained capacity approach. Advancing the IC&FF framework and its associated dimensions, the analysis is focusing on a changing approach recalibrating the above dubitative internal/external factors toward organizational environment renewal architecture of influences. The results of our research seem promising, as the conceptual construct and the methodology support the validity of the outcome: organizational behavior committed to change and the action-oriented propensity.
Leveraging IC&FF recipe through methodological argumentsThe methodological approach of the original conceptual framework for the strategic management of intellectual capital assets in software development companies, interconnected with force field analysis, is a preliminary attempt of an ambitious endeavor to foster the possibility to discover meta-integration approaches through Action-Design/implementation and Action-Learning.
The current preliminary analysis consists in advancing a framework to assess the opinions of the managers from software companies about the impact of both driving and restraining forces on the pillars of intellectual capital.
As regards the internal consistence reliability of the instrument to assess its acceptation and usefulness, we intended to employ it as self-assessment tool that means we anticipate and assume that it is about the specific perception of respondents (managers) as regard the same stimuli as belonging to restraining force instead as driving force, as it was perceived by the whole cohort, or vice versa.
The value of the exceptions: developing the self or assisted learning Practice of collective sense making from stimuli switching perspectives (Driving/Restraining Forces) emphasis the IC management role to leverage it as a force for discovering new knowledge. This argumentation is consistent with both recognitional versus analytical strategic decision-making and organizational propensity to face change, as we previously defined it as “ready to adjust” capability (Bleoju & Capatina, 2015).
Ready to adjust suppose in this case a type of organizational qualification in terms of superior factor endowment aspiration – maturity level – based on specific IC Management generated processes.
The score driving/restraining forces offers good insights for prioritizing and calibrating specific skills as compulsory for developing the capacity to adopt or to induce change in knowledge intensive industries. Furthermore, this is also consistent with the self-assessment character of the instrument, as opposed to any quantitative strategic planning framework, which trains to deliver only a prioritized list of strategies.
Further researchThis analysis proves useful to mobilize the experts to collaborate with respondents case by case, where significant, in order to explore and reveal common semantic but mostly identify commonalities of cognitive approach of sense making training, for further testing the portability of the instrument. As methodological approach, it seems natural to comply with following Action-Design/implementation and Action-Learning, as above prescribed, being more appropriate for design and implement actionable knowledge.
Nevertheless, caution is necessary to discriminate between the conceptual constructs of calibrating the change capacity of the proposed framework and thoroughly recalibrating the managerial instrument, due to the compulsory methodological validity assessment.
The conceptual construct, the methodology and the promising preliminary conclusions serve to the strategic management of intellectual capital approach, as new knowledge contribution to the debate and constitute a useful experimenting contribution to managerial practice in order to validate their pertinence, as well.