Both the standardised hospital mortality index (SHMI) and Care Quality Commission (CQC) ratings are used by the National Health Service (NHS) to monitor performance in English hospitals. We assessed if staff thriving, the concept of vitality and learning at work, through application of the surrogate measures engagement and research activity is associated with more favourable hospital performance outcomes.
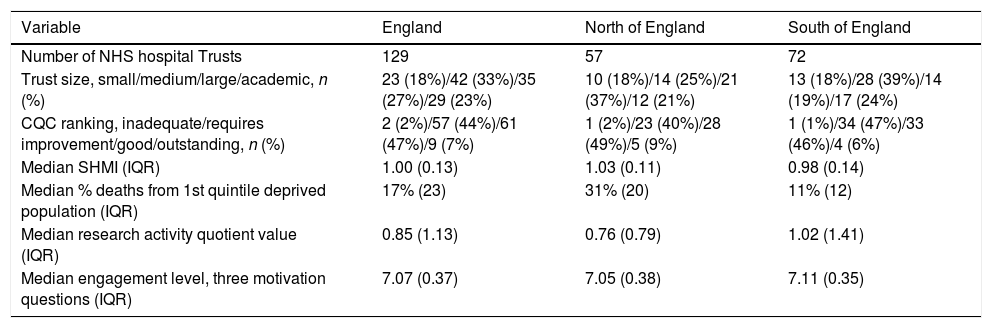
MethodsThis concerned a retrospective cross-sectional study using data for 129 English NHS hospital Trusts from the year 2019. Outcome measures were SHMI (linear regression, unstandardised coefficient beta) and CQC (binary logistic regression, odds ratio [OR]), whereas the independent variables considered were hospital location, degree of patient deprivation, research activity (drawn from National Institute for Health Research records and controlled for hospital size), and staff engagement scores (based on three survey questions corresponding to validated engagement factors).
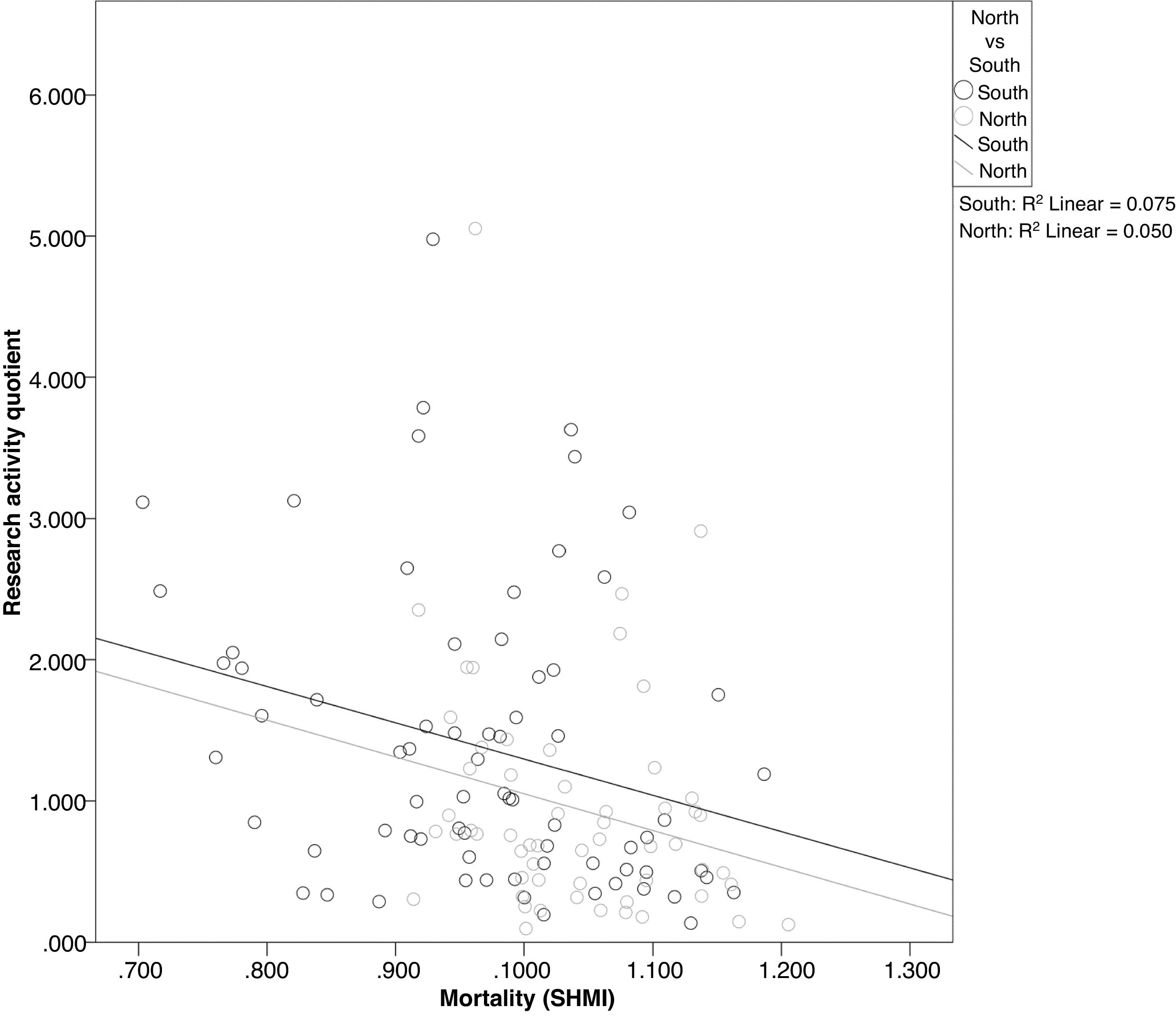
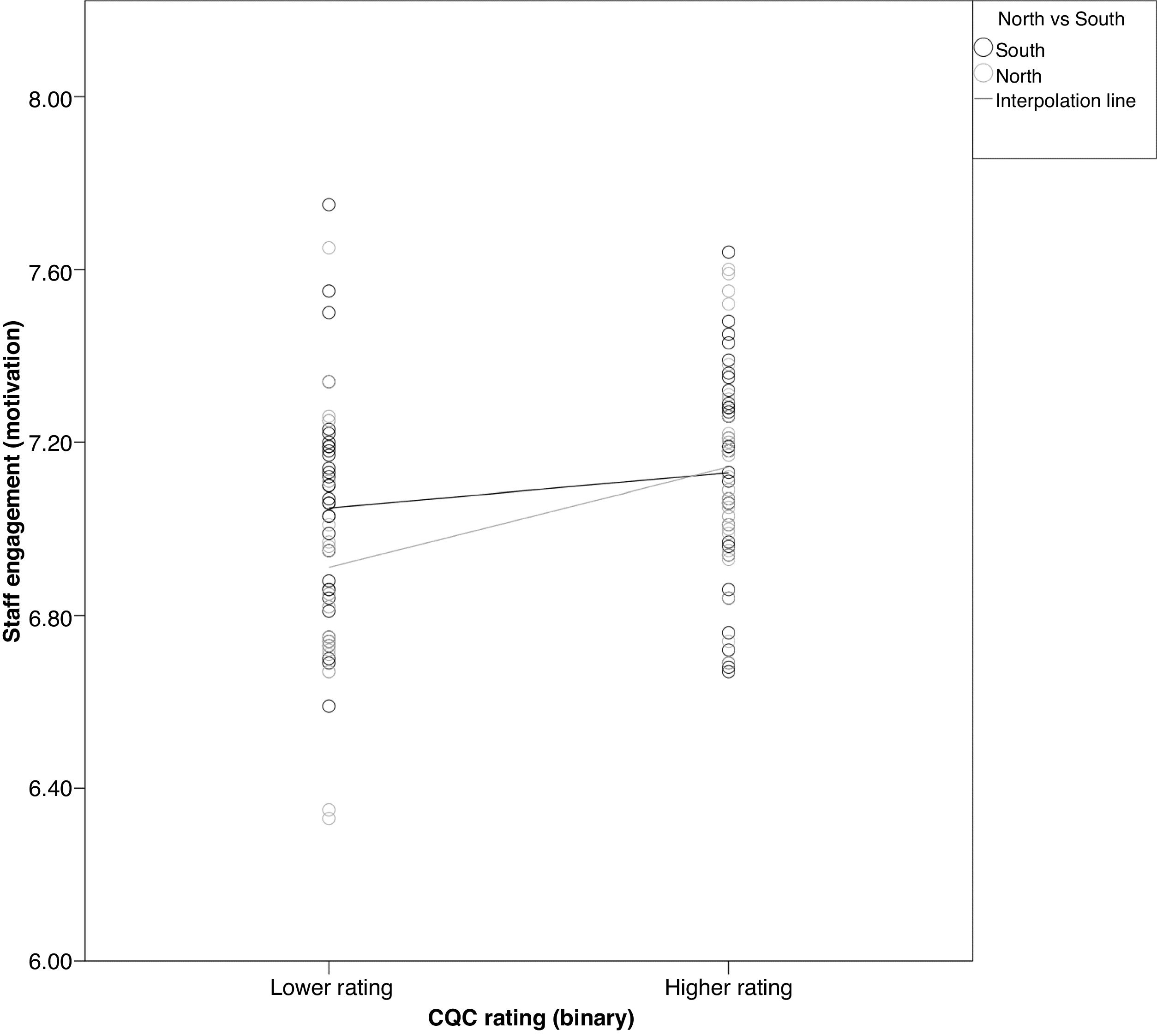
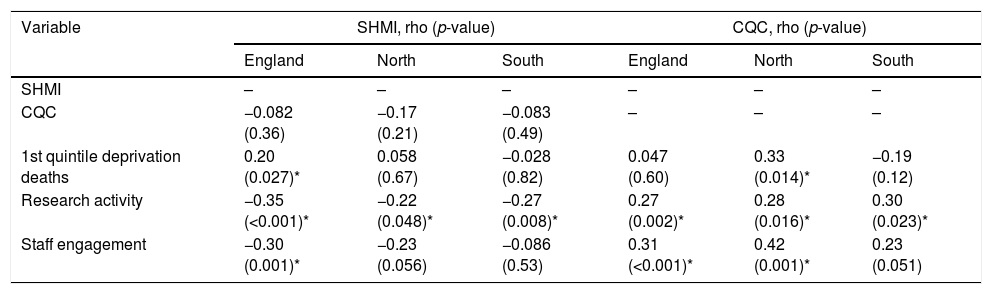
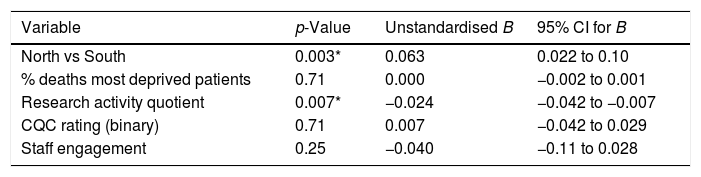
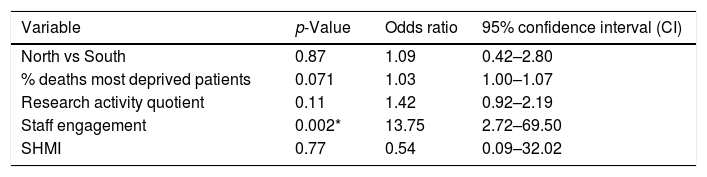
ResultsStaff engagement accounted for over half of the 13% variance R2 for the whole model related to improved CQC rating (OR 13.75, p-value 0.002). Increased research activity was associated with a lower SHMI score (unstandardized beta −0.024, p-value 0.007, R2 5% for each point change in research activity quotient), but independently from the higher SHMI seen for Northern hospital Trusts (beta 0.063, p-value 0.003, R2 11.6%). The degree of patient deprivation did not influence SHMI or CQC outcomes in the regression models.
ConclusionIncreased staff thriving exhibits a modest, yet significantly, association with improved hospital performance; this was observed despite an underlying regional dichotomy in mortality rates.