A 19-year-old male presented with abdominal distention and constipation for 3 days and vomiting for one day. There was no similar history in the past. There were no other co-morbidities. On examination, patient had abdominal distension. Routine lab investigations were within normal limits.
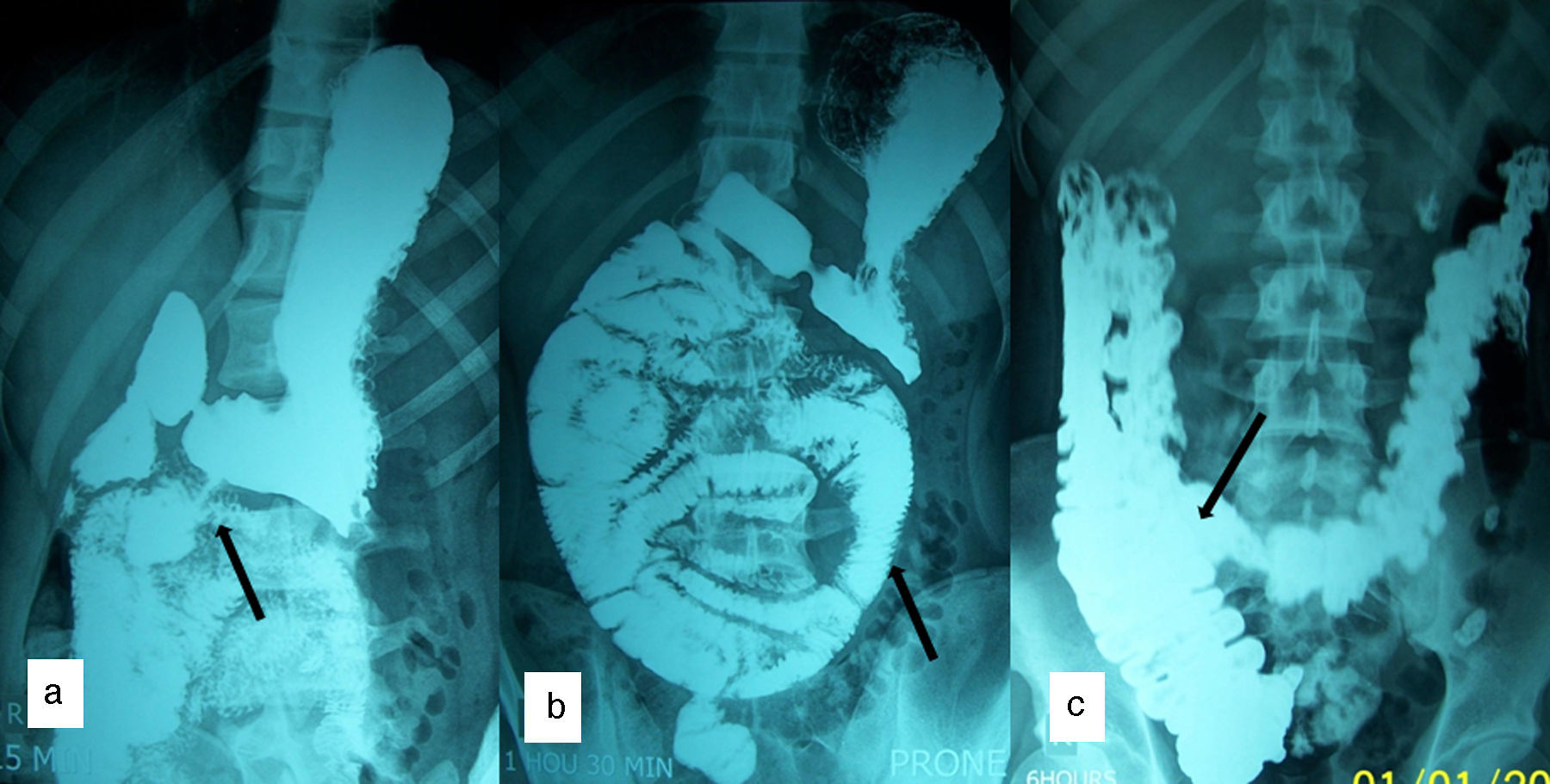
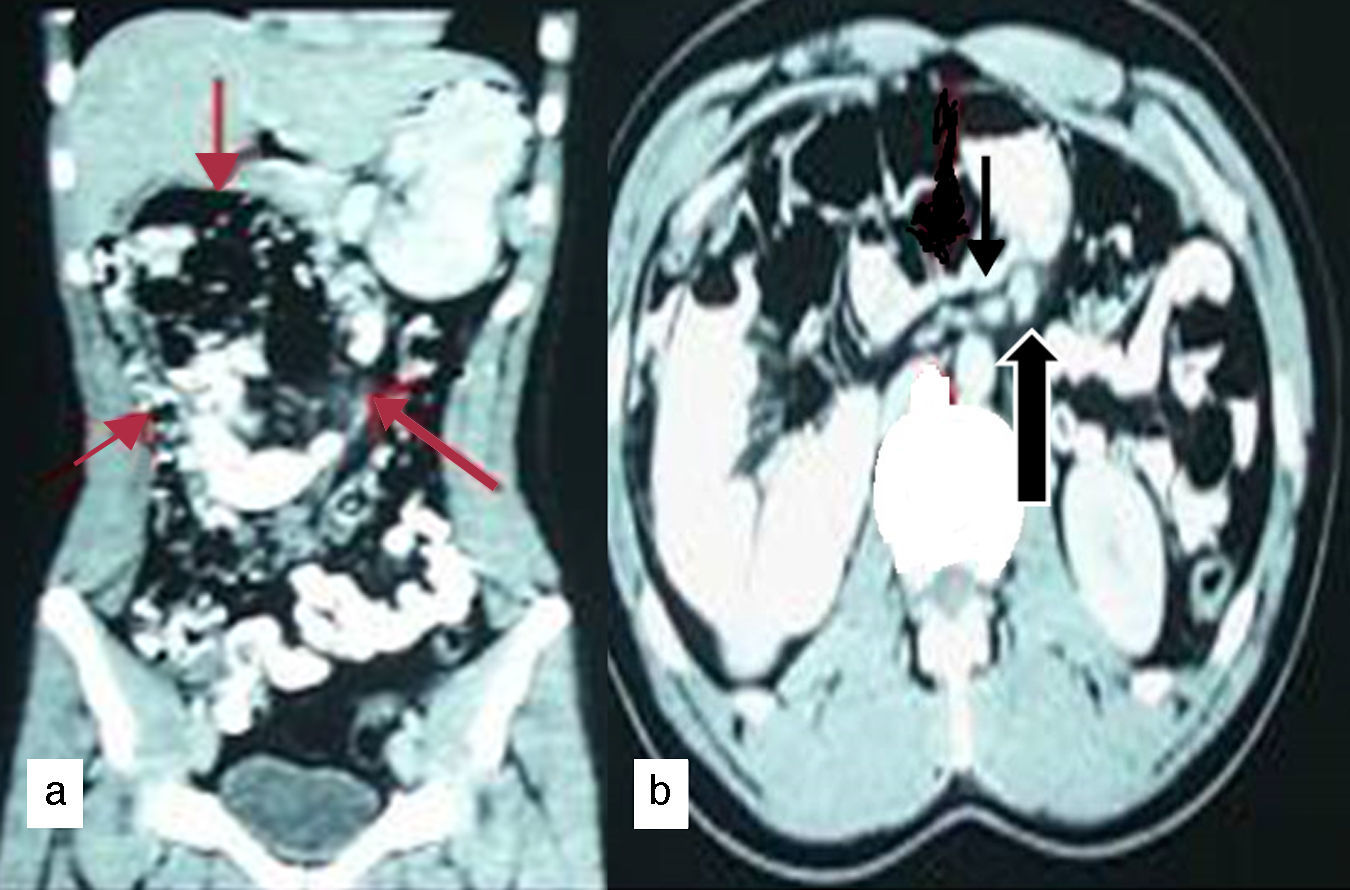
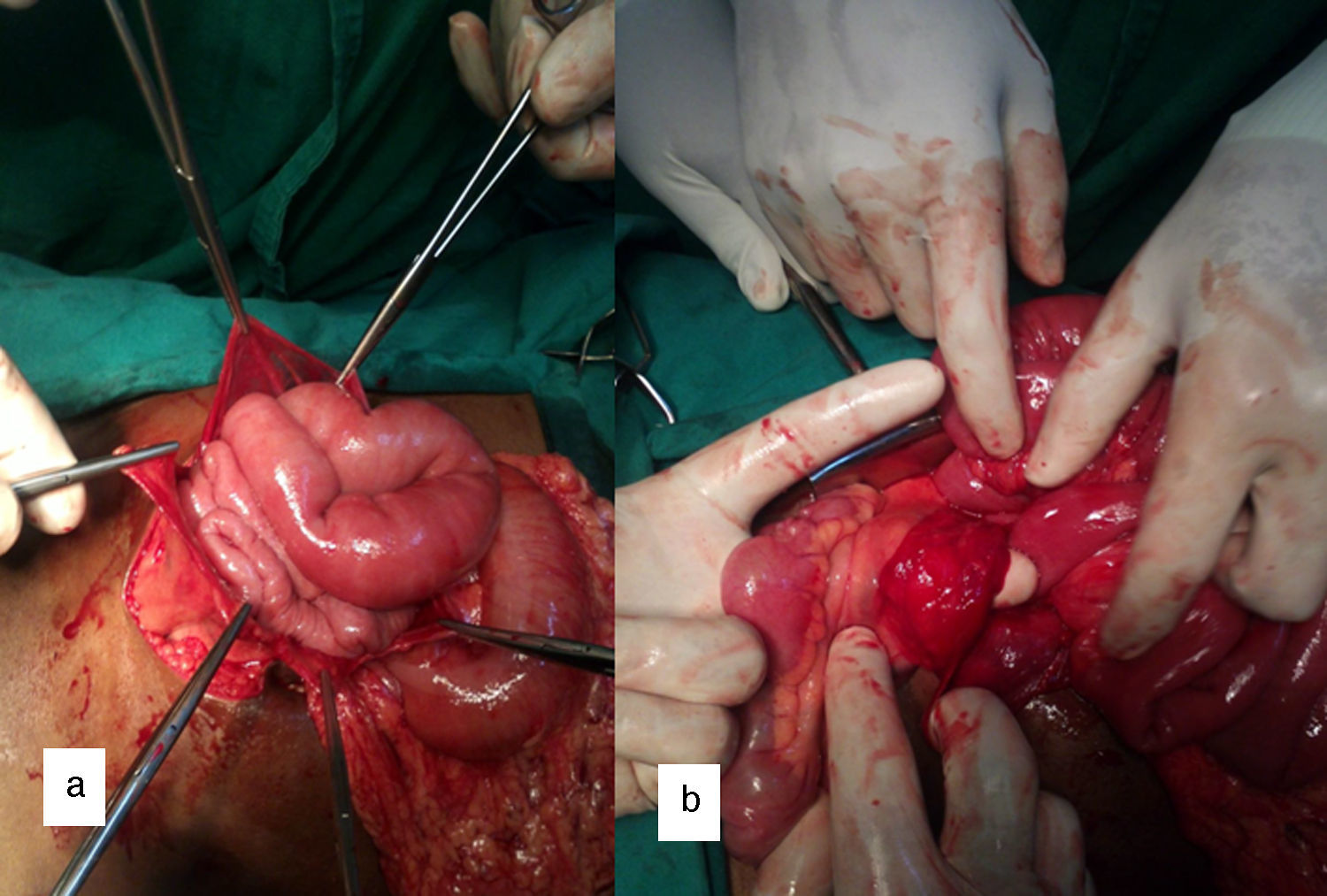
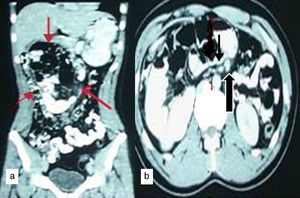
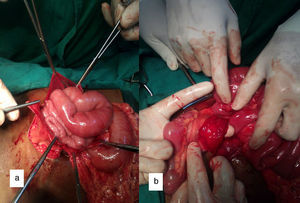
Barium meal showed the duodeno-jejunal (DJ) flexure on the right side of abdomen and clustered proximal jejunal loops lying in the right half of abdominal cavity. Large intestine and cecum were in normal position (Fig. 1). Contrast enhanced CT abdomen showed a cluster of dilated small bowel loops encapsulated in the right half of abdomen (Fig. 2a). DJ flexure was not seen in the normal location. Mesenteric vessels and bowel loops were seen converging toward a point at the medial aspect of the encapsulated sac. Superior mesenteric vein was seen ventral and to the left of superior mesenteric artery (Fig. 2b). At laparotomy, entire jejunum was found to be herniating from the left side through a defect in the mesentery and seen within a sac in right side of the abdomen (Fig. 3). The DJ flexure was found on the right side of the midline. There were no congenital bands. Large bowel was in normal location. Patient underwent Ladd's procedure and did not have any complaints during follow up.
Contrast enhanced CT abdomen (a) coronal reformat shows clustered dilated jejunal loops in the central and right half of abdomen (red arrows). (b) Axial section shows abnormal orientation of superior mesenteric vein (bold black arrow) was seen ventral and to the left of superior mesenteric artery (thin black arrow).
Congenital malrotation of the midgut classically presents within the first month of life.1 Lack of complete rotation of midgut during the embryonal period, is the cause of intestinal malrotation. In adults, malrotation may be asymptomatic or present as complications like midgut volvulus/internal hernia with obstruction. Adult presentation of intestinal malrotation is rare and its association with internal hernia is even rarer and difficult to diagnose.2 These patients often present with chronic abdominal pain and vomiting with or without signs of intestinal obstruction. Paraduodenal hernia, also known as mesocolic hernia is the most common type of congenital internal hernia. Seventy five percent of mesocolic hernias occur on the left side and 25% on the right side with middle mesocolic hernia being very rare.3 Right paraduodenal hernia occurs when the prearterial limb of the gut fails to rotate around the superior mesenteric artery causing a portion of the small bowel to remain to the right of the superior mesenteric artery. Diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion. The diagnosis of malrotation with or without associated internal hernia should be kept in mind when evaluating adult patients with atypical abdominal symptoms. Surgical intervention is mandatory to avoid complications of obstruction and ischemia. Ladd's procedure involves mobilization of duodenum and right colon, section of the Ladd's bands along with possible adhesions near the superior mesenteric vessels and appendectomy. Ladd's procedure, done either by laparotomy or laparoscopy, remains the accepted procedure.4,5
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.