Sunlight exposure is the main source of vitaminD. Our aim was to describe both sun exposure and sun protection behaviour in a series of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and to study their potential association with vitaminD concentration.
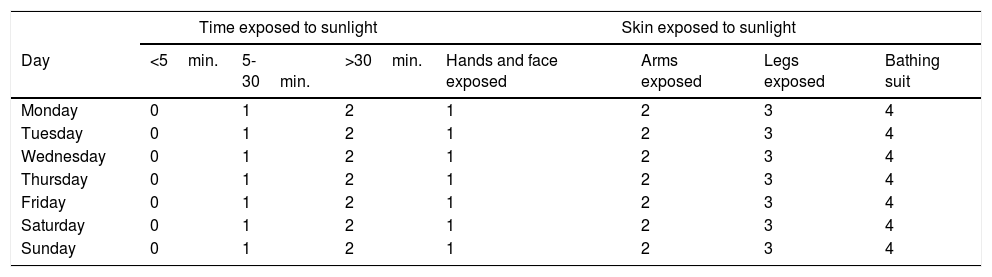
Patients and methodsA cross sectional, observational study. The clinical-demographic variables were obtained via clinical interviews and medical history review. The sunlight exposure assessment was carried out using the Sun Exposure Questionnaire and the concentration of 25-hydroxy vitaminD (25OHD) was measured by an electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay. Questionnaires were conducted on quality of life, physical activity, weekly vitaminD intake and sun protection behaviour.
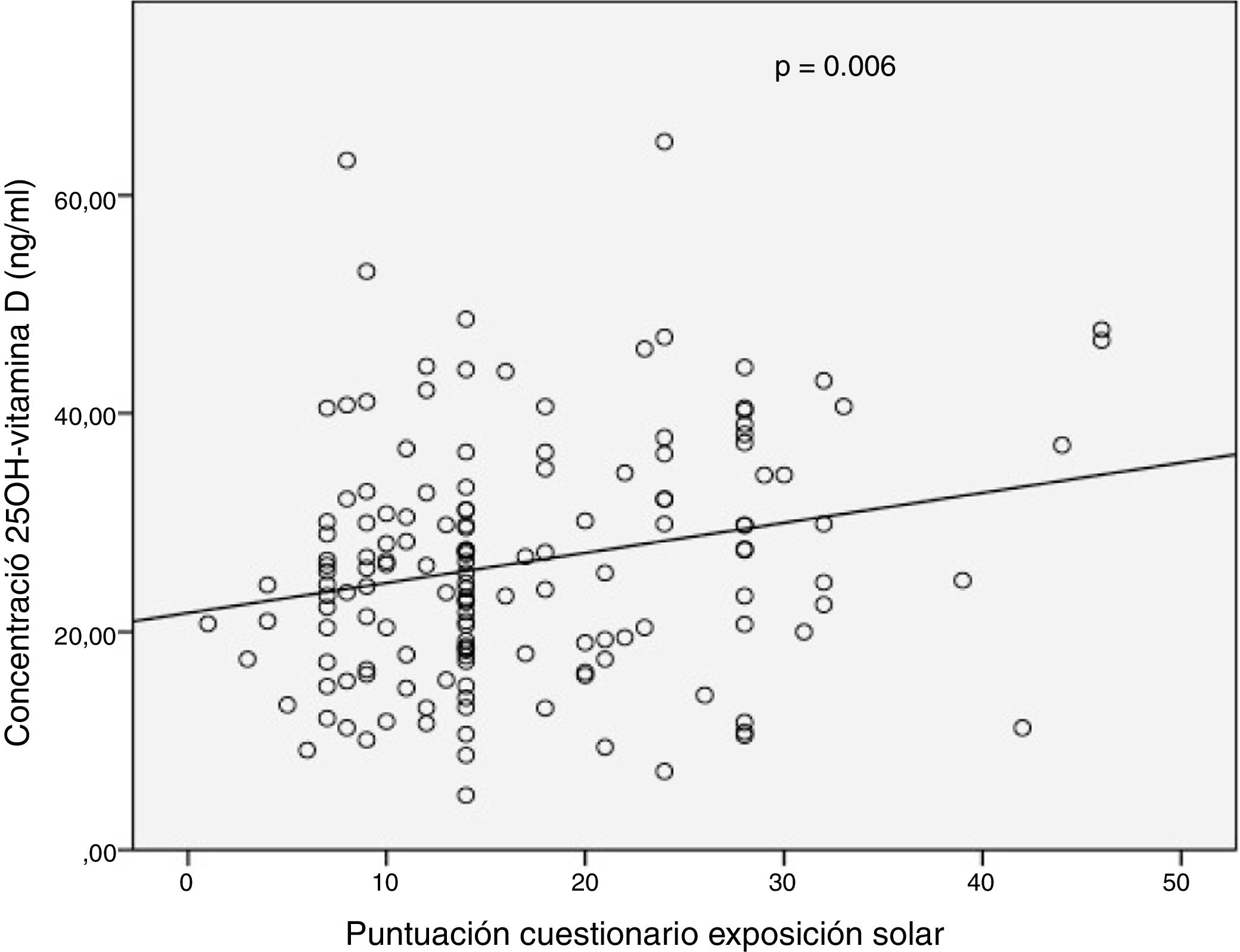
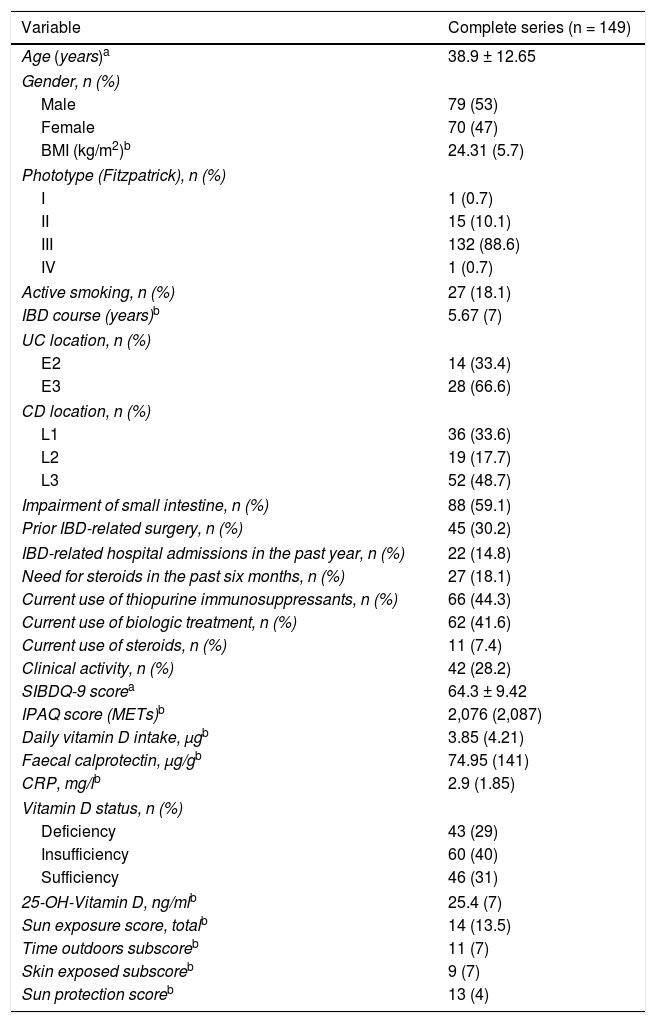
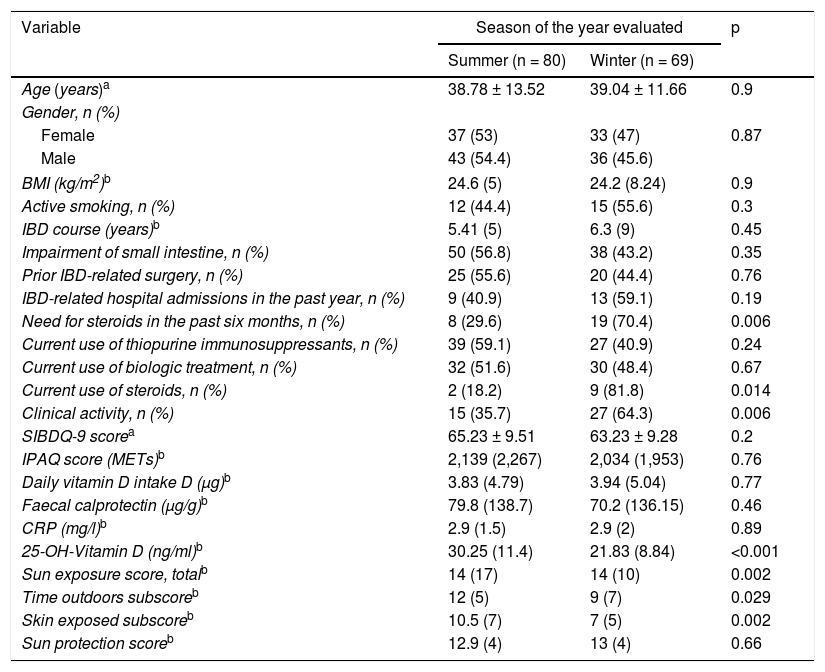
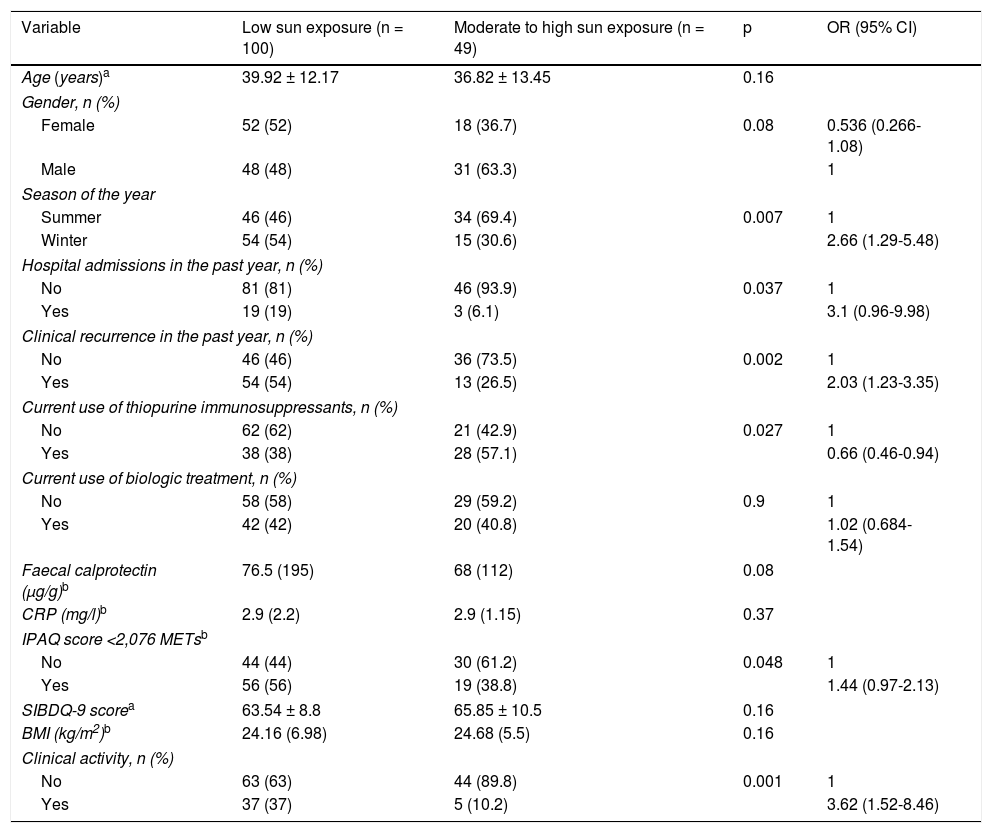
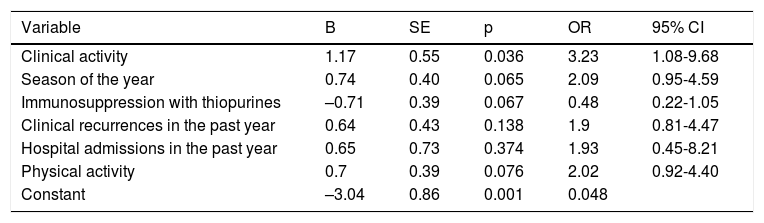
Results149 patients were included. In 69% of patients, deficient or insufficient 25OHD values were recorded. 67% showed low sun exposure. A modest significant correlation was observed between the total score of the solar exposure questionnaire and the 25OHD concentration in the complete series (r=0.226, P=.006) and in the summer (r=0.274, P=.01). The sun protection behaviour questionnaire score did not influence the 25OHD concentration. In the multivariate analysis, only the presence of clinical activity was associated with low sun exposure (OR=3.23).
DiscussionSun exposure according to the questionnaire used was low, was associated with the presence of clinical activity and was weakly correlated with serum 25OHD concentration. More studies are needed to explore the use of individual questionnaires for sun exposure and its relationship with vitaminD in patients with IBD.
La exposición solar es el principal determinante del estado de vitaminaD. Nuestro objetivo fue describir las prácticas de exposición y protección solar de una serie de pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII) y evaluar su influencia en la concentración sérica de vitaminaD.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional de tipo transversal. Las variables clínico-demográficas se obtuvieron mediante entrevista clínica y revisión de la historia. La evaluación de la exposición solar se realizó mediante el Sun Exposure Questionnaire. La concentración de 25-hidroxivitaminaD (25OHD) se determinó por electroquimioluminiscencia. Se realizaron cuestionarios de calidad de vida, actividad física, ingesta semanal de vitaminaD y hábitos de protección solar.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 149 pacientes. En el 69% de los pacientes se registraron valores deficientes o insuficientes de 25OHD. El 67% presentaron una baja exposición solar. Se observó una modesta correlación significativa entre la puntuación total del cuestionario de exposición solar y la concentración de 25OHD en la serie completa (r=0,226; p=0,006) y en verano (r=0,274; p=0,01). La puntuación del cuestionario de protección solar no influyó en la concentración de 25OHD. En el análisis multivariado solo la presencia de actividad clínica se asoció a una exposición solar baja (OR=3,23).
DiscusiónLa exposición solar de acuerdo con el cuestionario empleado fue baja, se asoció a la presencia de actividad clínica y se correlacionó débilmente con la concentración de 25OHD sérica. Se necesitan más estudios que exploren el uso de cuestionarios individuales de exposición solar y su correlación con la vitaminaD sérica en la EII.