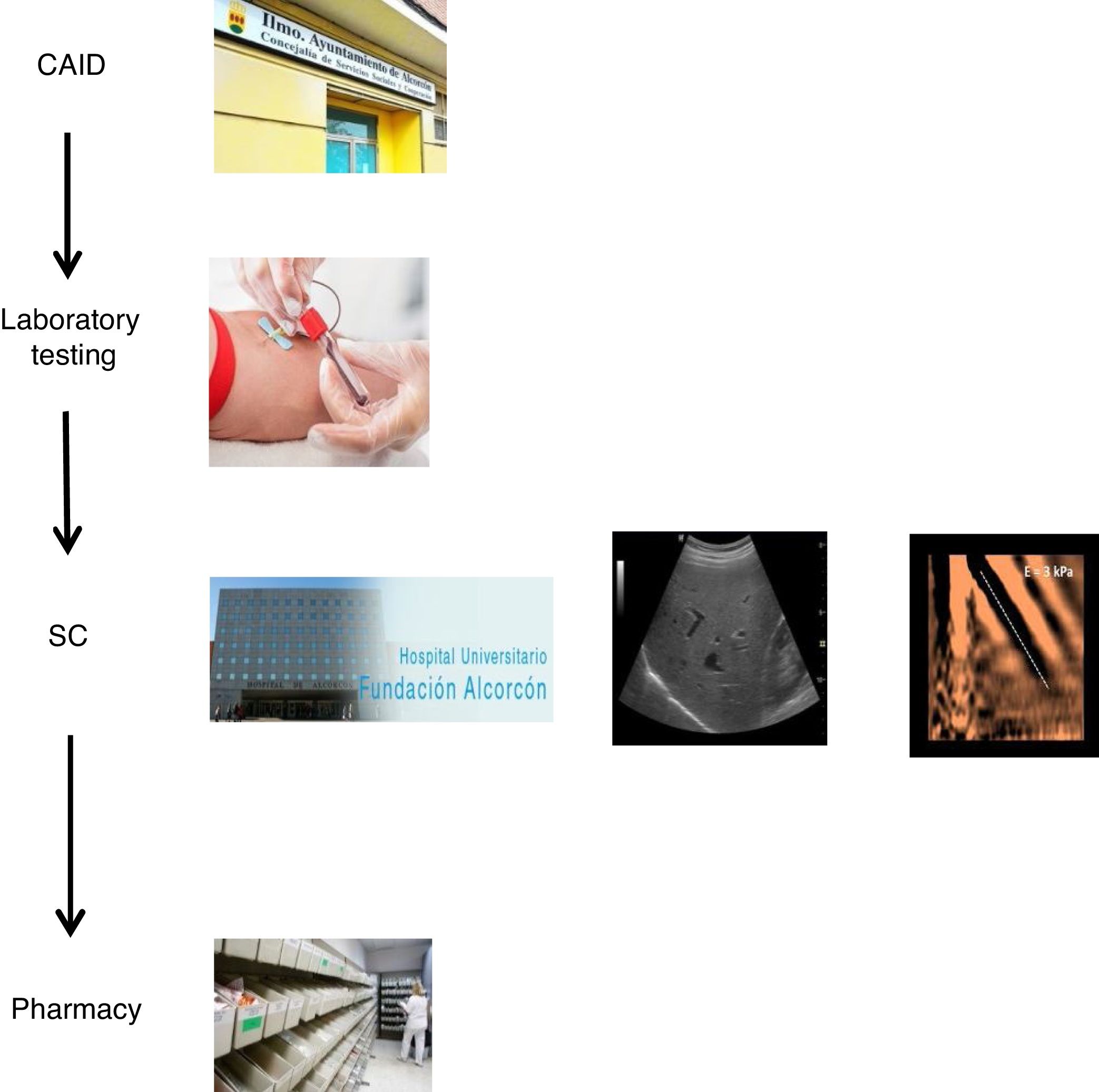
The drug-injecting population has a high prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and high risk of transmission. It is a priority to establish an agile diagnostic and treatment plan.
Objectives1) Assess the effectiveness of a new coordinated care plan of referral from the Comprehensive Care Centre for Drug Addicts (CAID) to specialised care and 2) Determine the prevalence of HCV, clinical characteristics, effectiveness and safety of treatment in this population.
Methods1300 serologies requested by the CAID between 1998 and 2018 were retrospectively analysed, the seroprevalence of HCV was calculated and the efficiency of the traditional CAID-specialised care referral system was evaluated. A care plan was designed and coordinated among specialists involved in diagnosis and treatment. Since October 2018, 11 patients have been included in the new plan and the performance of both referral systems was compared.
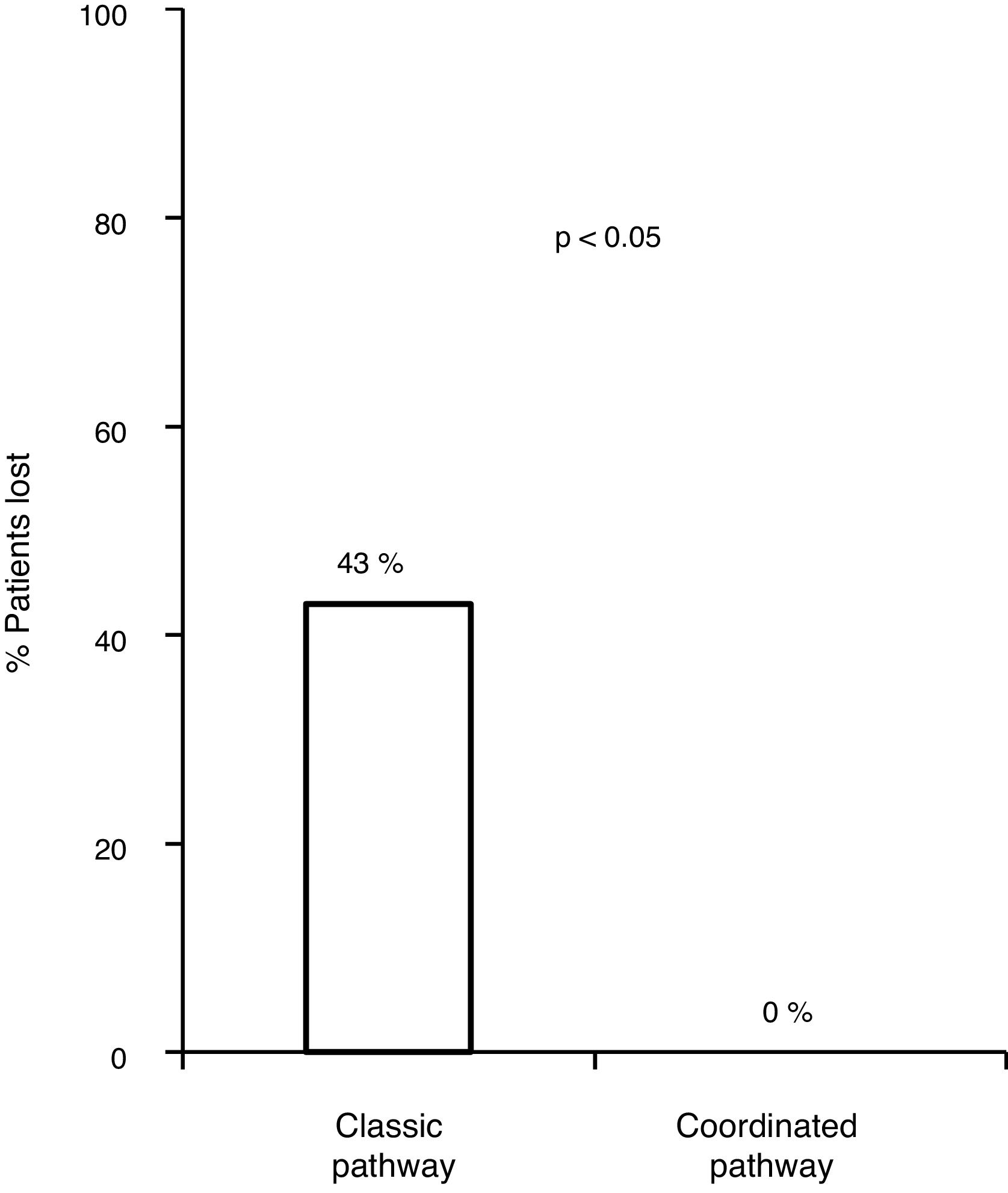
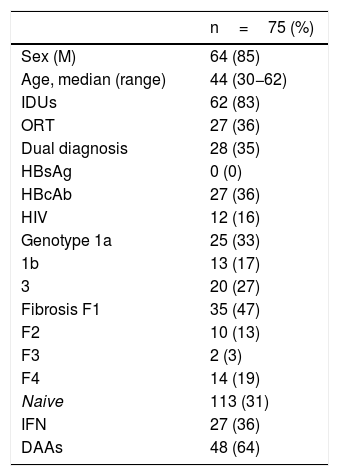
ResultsWith the traditional system, 48.2% (83/172) of the patients were lost. 14.5% (172/1300) presented positive HCV serology, compared to the general population OR=19; 95% CI 14.3−25. The prevalence of active infection was 80.3% (90/112). The prevalence of active infection was 80.3% (90/112). Of the 11 patients referred by the new plan, 76.9% (8/11) had active infection and 100% (8/8) were treated with Direct Antiviral Agents successfully.
ConclusionsThe new coordinated CAID-specialised care plan presents high effectiveness in comparison with the traditional referral system. The seroprevalence and prevalence of active infection in the CAID population is very high. Treatments with Direct Antiviral Agents are effective and safe.
La población que se inyecta droga presenta una alta prevalencia de VHC y elevado riesgo de transmisión. Es prioritario establecer un plan ágil de diagnóstico y tratamiento.
Objetivos1) Valorar la efectividad de un nuevo plan asistencial coordinado de derivación desde el Centro Atención Integral al Drogodependiente (CAID) a atención especializada y 2) Conocer la prevalencia del VHC, características clínicas, efectividad y seguridad del tratamiento en esta población.
MetodosSe analizaron retrospectivamente 1300 serologías solicitadas por el CAID entre 1998–2018, se calculó la seroprevalencia de VHC y se valoró la eficiencia del circuito clásico de derivación CAID-atención especializada. Se diseñó un plan asistencial coordinado entre especialistas implicados en el diagnóstico y tratamiento. Desde octubre de 2018 se incluyeron 11 pacientes en el nuevo plan y se comparó el rendimiento de ambos circuitos de derivación.
ResultadosCon el circuito clásico, se perdió un 48,2% (83/172) de los pacientes. Un 14,5% (172/1300) presentaron serología VHC positiva, en comparación con población general OR=19; IC 95% 14,3-25. La prevalencia de infección activa fue del 80,3% (90/112). Con el nuevo circuito acudieron el 100% (11/11) (p=0,0003). De los 11 pacientes derivados mediante el nuevo plan, 76,9% (8/11) tenían infección activa y el 100% (8/8) fueron tratados con Agentes Antivirales Directos con éxito.
ConclusionesEl nuevo plan asistencial coordinado CAID-atención especializada presenta alta efectividad en comparación con el circuito clásico de derivación. La seroprevalencia y prevalencia de infección activa en la población del CAID es muy elevada. Los tratamientos con Agentes Antivirales Directos son efectivos y seguros.