It has been proposed that non-invasive methods may replace liver biopsy for the diagnosis of tissue damage in patients with autoimmune liver disease (ALD). The aim of this study was to determine diagnostic performance and degree of concordance between the APRI index and liver biopsy for diagnosing cirrhosis in these patients.
Material and methodsIn a cohort of patients with ALD, the value of the APRI index and liver biopsy results were determined according to the METAVIR score. The AUC and the degree of concordance between an APRI value >2 and a METAVIR score of F4 were evaluated as markers of liver cirrhosis, through a kappa statistic.
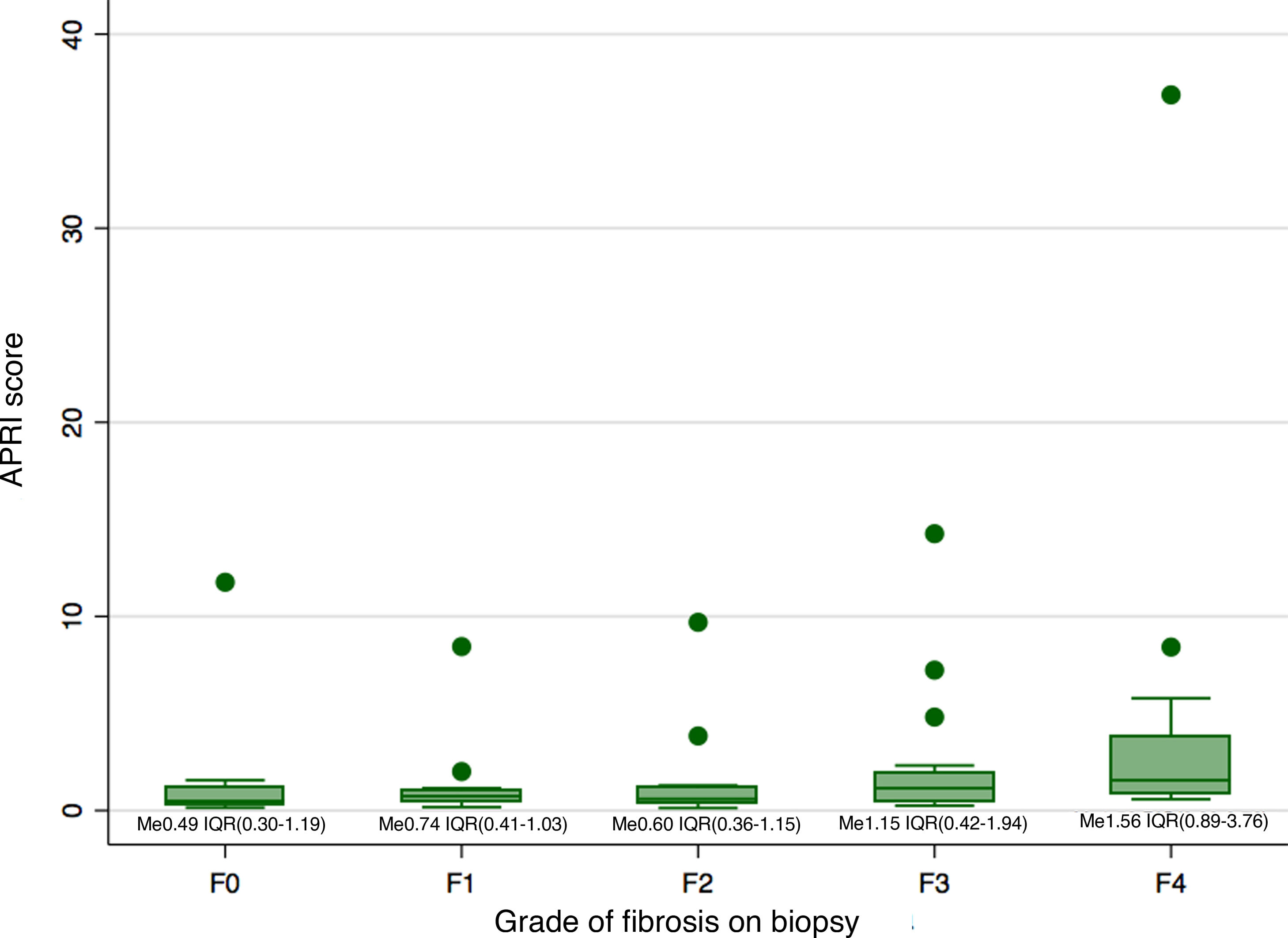
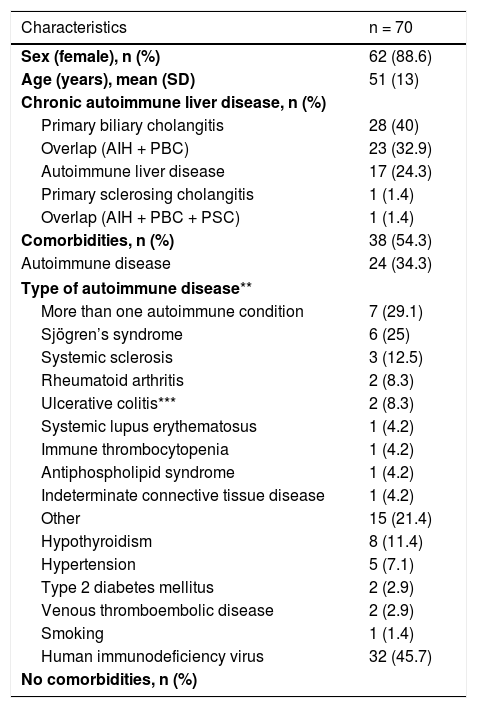
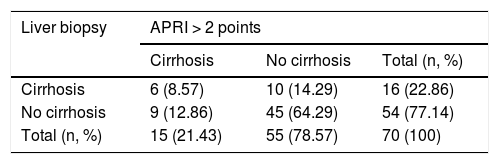
ResultsIn total, 70 patients (age 51 ± 13 years) were included. The most common autoimmune liver diseases were primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) (40%), autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) (24.3%) and AIH-PBC overlap syndrome (32.9%). Cirrhosis was confirmed by biopsy in 16 patients (22.9%). 15 patients (21.4%) had an APRI index >2 (Cirrhosis) and only six met both criteria. The AUC of the APRI was 0.77 (95% CI 0.65−0.88). The degree of concordance between the tests was low for an APRI cut-off point >2 (kappa 0.213; 95% CI 0.094−0.332), as well as for cut-off points >1.5, >1 and >0.5 (kappa 0.213, 0.255, 0.257, respectively)
ConclusionOur results suggest that there is little concordance between APRI and liver biopsy for the diagnosis of cirrhosis in patients with ALD. It should therefore not be used as a single diagnostic method to determine cirrhosis.
Se ha propuesto que métodos no invasivos pueden remplazar la biopsia hepática en el diagnóstico del daño tisular en pacientes con hepatopatía autoinmune (EHA). Este estudio evalúa el rendimiento diagnóstico y grado de concordancia entre el índice Ast to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) y la biopsia hepática en el diagnóstico de cirrosis en estos pacientes.
Material y métodosEn una cohorte de pacientes con EHA se determinó el valor del índice APRI y los resultados de la biopsia hepática según la escala METAVIR. Se evaluó el área bajo la curva (AUC) y la concordancia entre un valor de APRI > 2 y un puntaje METAVIR F4 como marcadores de la presencia de cirrosis hepática mediante un estadístico de kappa.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 70 pacientes (51 ± 13 años). Las hepatopatías autoinmunes más frecuentes fueron la cirrosis biliar primaria (CBP) (40%), Hepatitis autoinmune (HAI) (24,3%) y el síndrome de sobreposición HAI–CBP (32,9%). Se confirmó cirrosis por biopsia en 16 pacientes (22,9%); 15 pacientes (21,4%) presentaron índice APRI > 2 (cirrosis) y solo seis cumplieron ambos criterios. El AUC del APRI fue de 0,77 (IC 95% 0,65−0,88). La concordancia entre las pruebas fue baja para un punto de corte APRI > 2 (kappa 0,213; IC 95% 0,094−0,332), o para puntos de corte > 1,5, > 1 o > 0,5 (kappa 0,213, 0,255, 0,257, respectivamente).
ConclusionesNuestros resultados sugieren que existe un pobre acuerdo entre el resultado del APRI y la biopsia hepática en el diagnóstico de cirrosis en pacientes con EHA, por lo tanto, no se debe utilizar como método diagnóstico único para determinar la presencia de cirrosis.