Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) treatment may increase the risk of infections. Vaccines are part of the comprehensive IBD patient care. The aim of this study was to describe indications and adherence of immunizations in IBD and identify possible associated factors.
MethodsA cross-sectional, analytic study was conducted in patients from an IBD Program of a tertiary center in Chile, between April – June 2019. Patients were asked to answer a vaccine survey and information also was obtained from the National Immunization Registry. Descriptive and association statistic were used (χ2; p < 0.05).
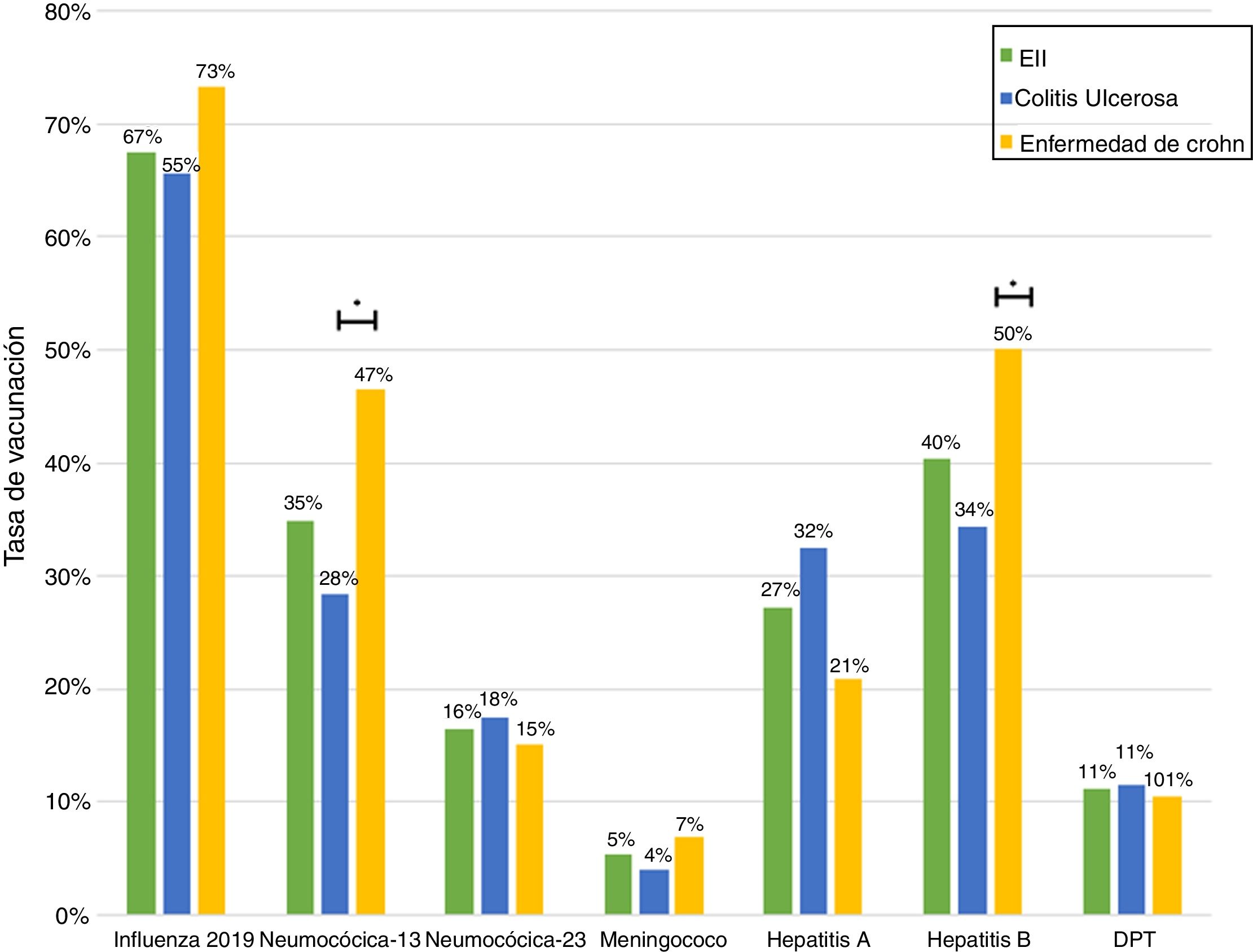
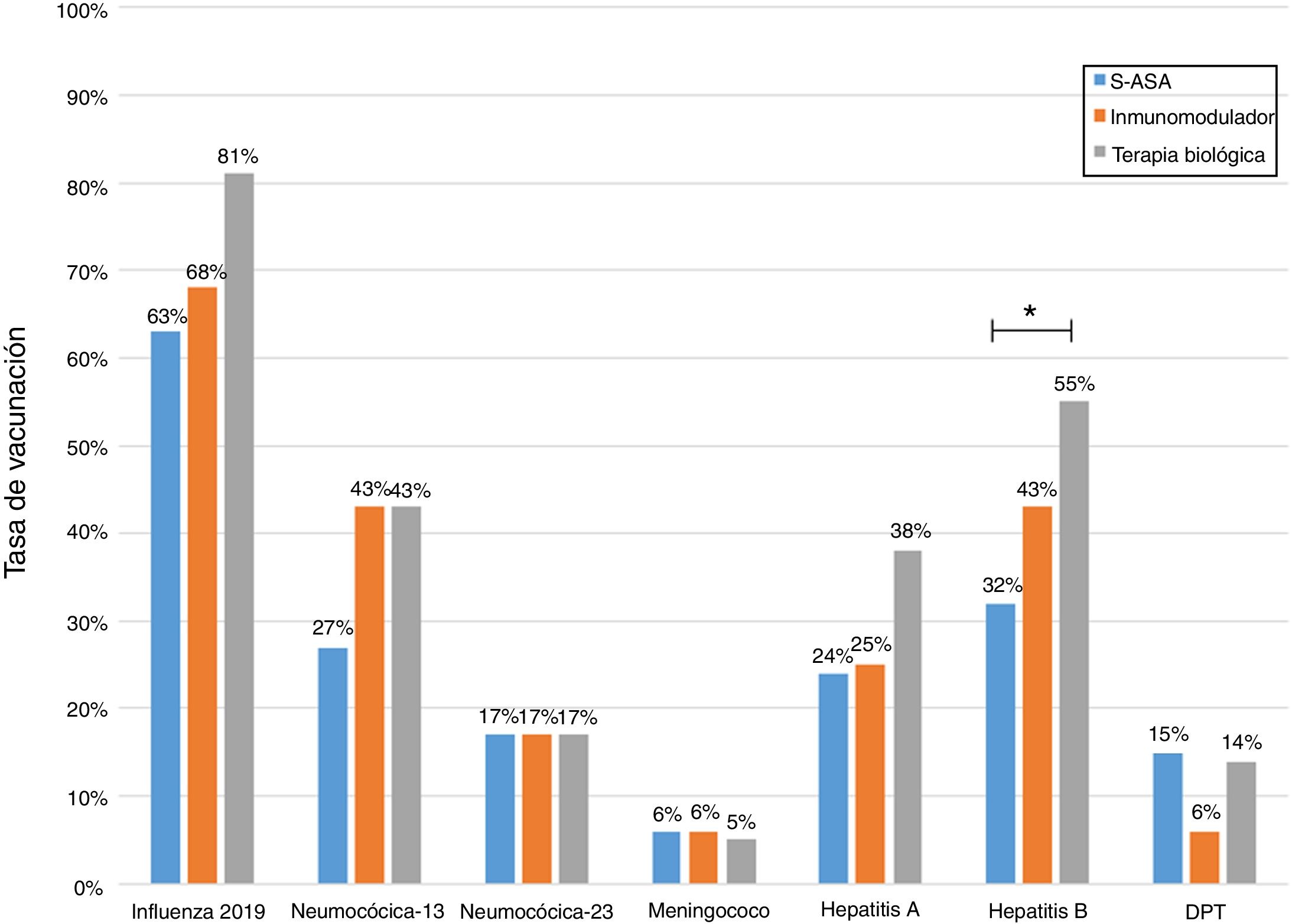
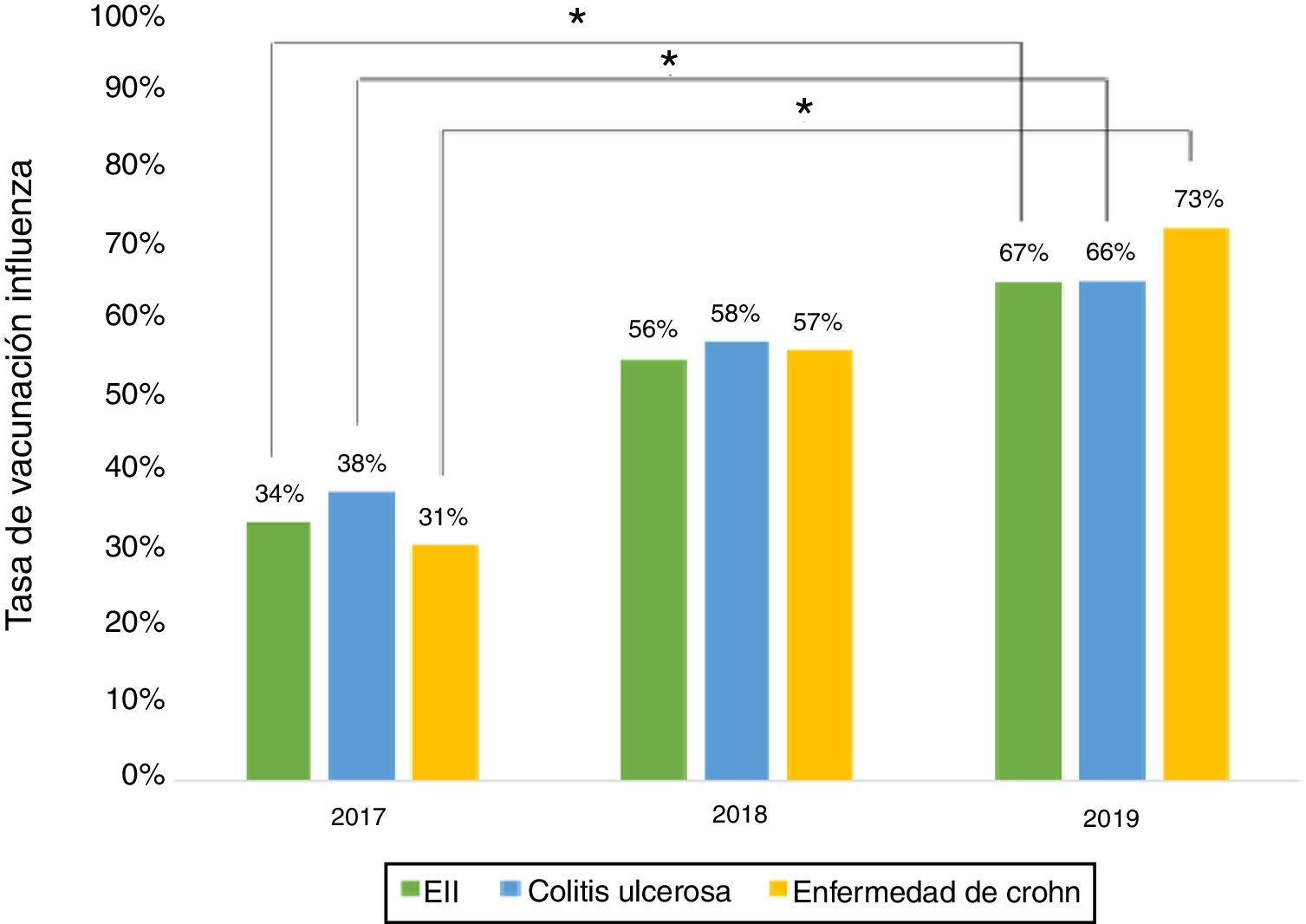
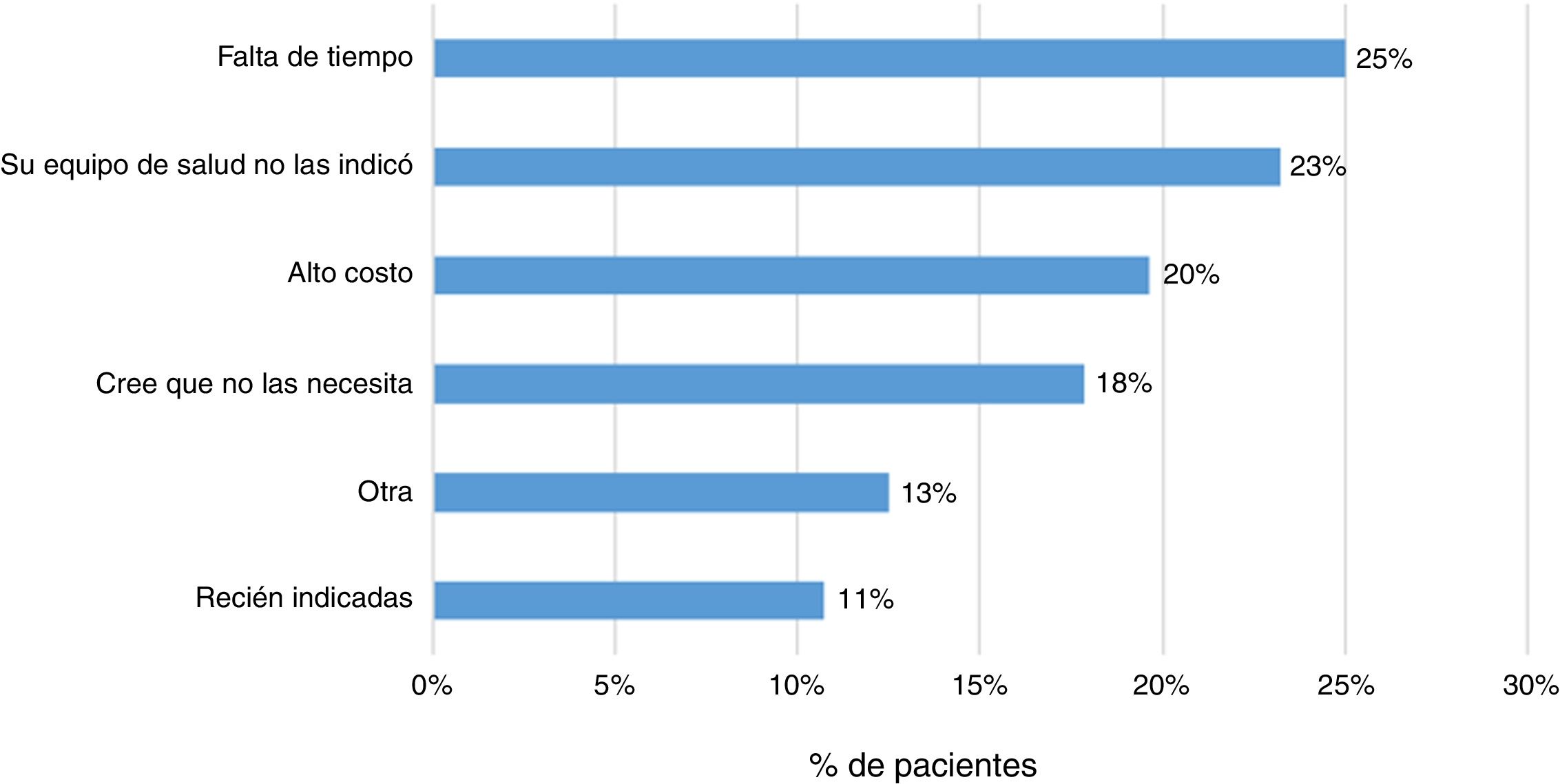
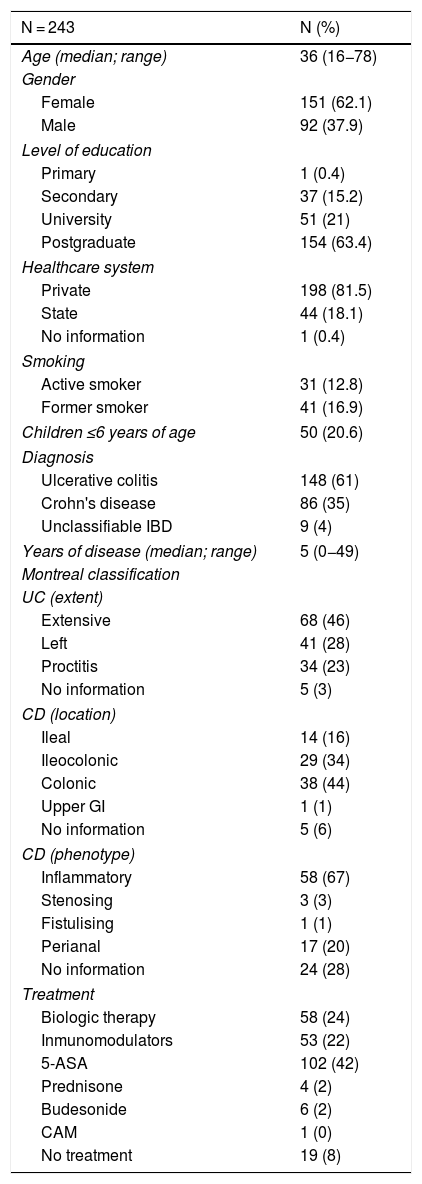
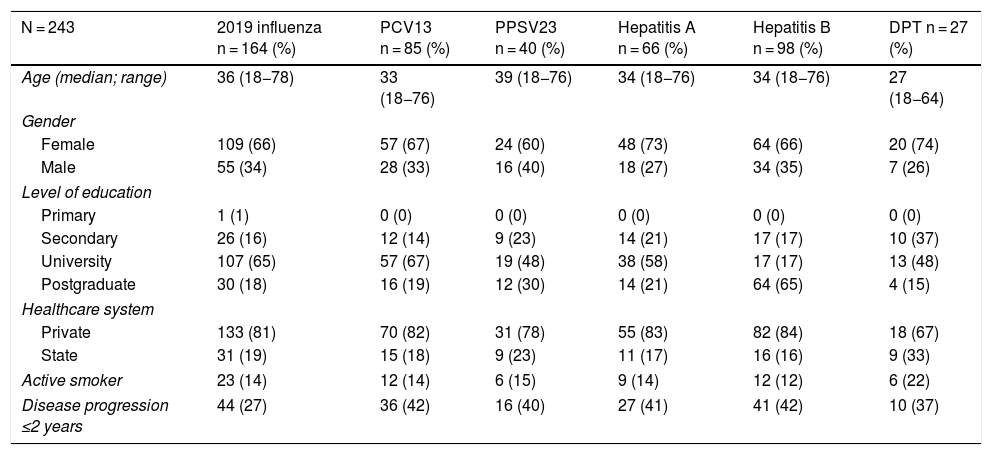
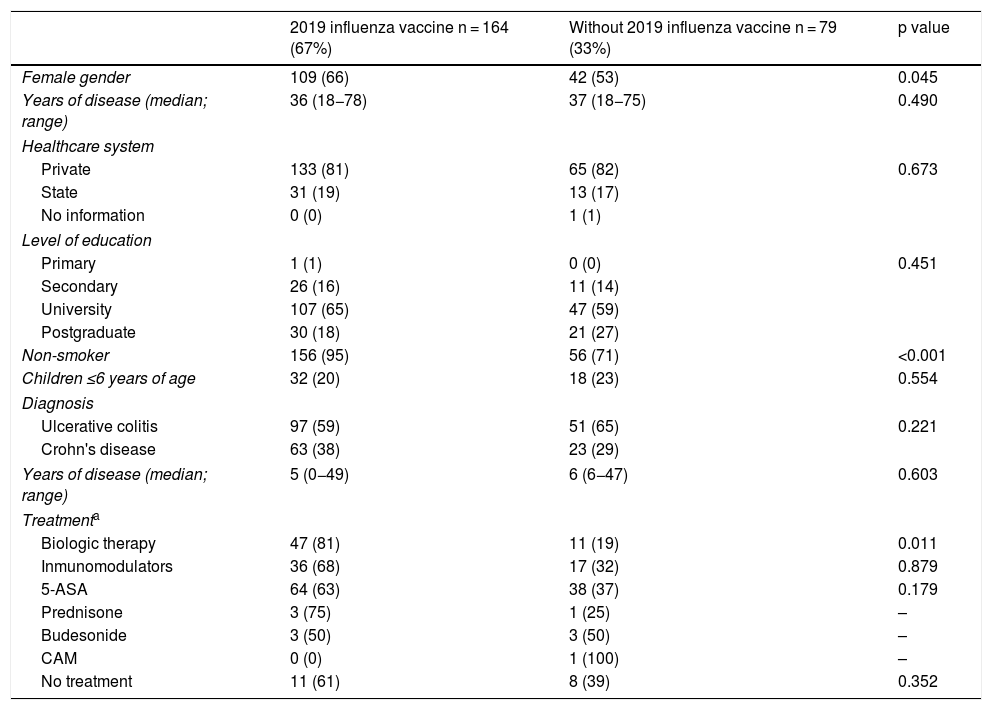
ResultsA total of 243 patients were included (148 ulcerative colitis (UC), 86 Crohn´s disease (CD) and 9 non-classifiable IBD). Only six patients (2%) of IBD patients received a complete immunization schedule. The highest vaccine rates were against influenza (67%), hepatitis B virus (40%), 13-valent pneumococcal (34%) and 23-polysaccharide pneumococcal (16%). The influenza vaccine rate has significantly increased, reaching 67% in 2019. The survey showed that 23% of patients have not been immunized with any vaccine, mainly due to lack of time, lack of medical prescription and high cost.
ConclusionIn this cohort, although vaccination rates are higher than previously reported, adherence to IBD immunization program would be improved, being considered since diagnosis by the multidisciplinary team.
El tratamiento de la Enfermedad Inflamatoria Intestinal (EII) puede aumentar el riesgo de infección. La inmunización es parte del manejo integral de la atención de estos pacientes. El objetivo de este estudio es describir la prescripción y adherencia a la vacunación en pacientes con EII e identificar los posibles factores asociados a ésta.
MétodosEstudio analítico, descriptivo, transversal en pacientes de un Programa de EII de Chile, entre abril-junio 2019. A los pacientes se les solicitó responder un cuestionario acerca de la adherencia a la vacunación. La información de las vacunas se obtuvo del Registro Nacional de Inmunizaciones. Se realizó análisis estadístico descriptivo y de asociación (χ2; p < 0.05).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 243 pacientes con EII (148 Colitis Ulcerosa (CU), 86 enfermedad de Crohn (EC) y 9 EII no-clasificable). Sólo 6 pacientes (2%) recibieron el esquema de inmunización completo. Las vacunas con los mayores porcentajes fueron contra la influenza (67%), virus hepatitis B (40%), neumocócica 13-valente (34%) y neumocócica 23-polisacárida (16%), siendo las dos primeras más frecuentes en EC vs CU (p: <0.05). La administración de la vacuna contra la influenza ha aumentado significativamente, alcanzando un 67% el 2019. La encuesta mostró que el 23% no ha sido inmunizado con ninguna vacuna, principalmente por falta de tiempo, falta de prescripción médica y el alto costo económico.
ConclusionesEn esta cohorte, aunque las tasas de vacunación son más altas que las reportadas previamente, la adherencia al programa de inmunización debe mejorar. siendo consideradas desde el diagnóstico por el equipo multidisciplinario.