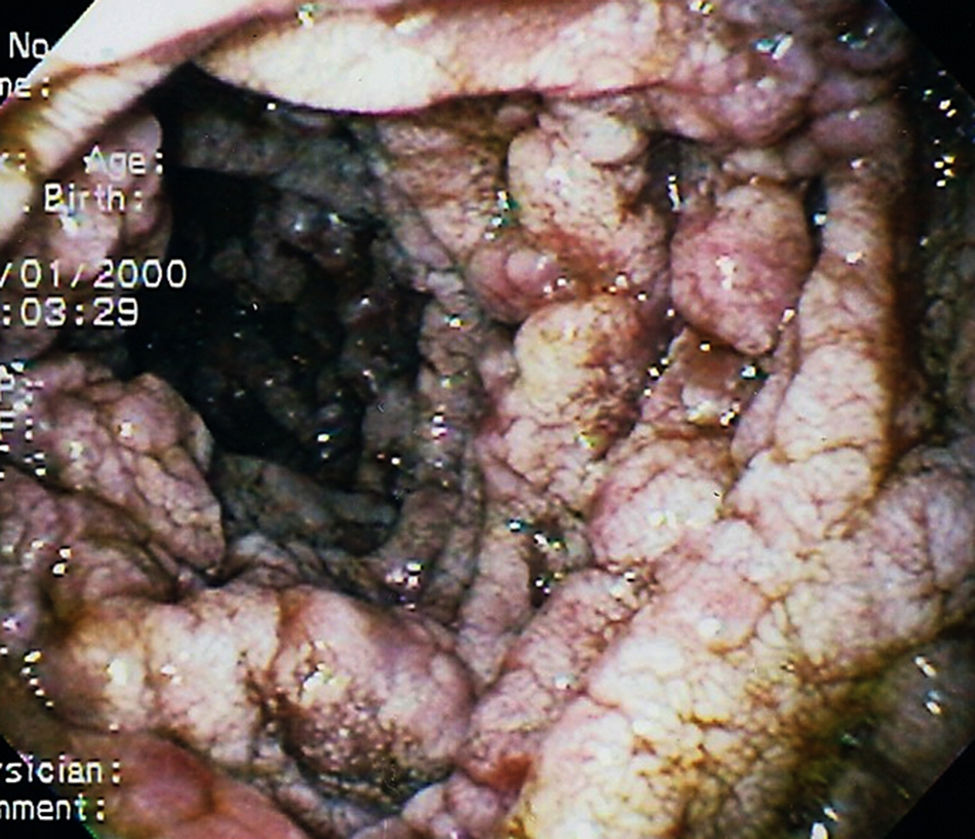
Male patient, 40-years old, previously healthy, smoker, with a past history of alcoholism, sought care due to fever, dysphagia, weight loss and cervical lymph node enlargement. Computed tomography showed multiple cystic lesions in cervical lymph nodes with peripheral contrast enhancement and thickening of duodenal and jejunal wall. Upper endoscopy was performed (Fig. 1), which shown oedema and white plaques. Lymph node and duodenal biopsies came back positive for PAS positive yeast, suggestive of Histoplasma capsulatum. Molecular diagnostics techniques were not available in our clinical practice to be performed. No immunosuppressive disease was found in work up. He was treated with intravenous amphotericin B for 14 days, followed by 6 months of oral itraconazole, with resolution of symptoms and duodenal lesions.
Disseminated histoplasmosis (DH) is a rare fungal infection more likely to be encountered in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients, and extremely rarely in immunocompetent patients. Intestinal involvement in DH can occur at any site along the gastrointestinal tract and it is also primarily found in immunocompromised patients.1 Cases of intestinal histoplasmosis (IH) in immunocompetent hosts have rarely been reported. Zhu et al. has published the largest case series of IH, consisting of 4 cases diagnosed with colonoscopy. The most common clinical finding was fever, weight loss and abdominal pain2. Diagnosis is made trough biopsy, which detect yeast-like pathogens positive for PAS and GMS stains but negative for Giemsa in the cytoplasm of the histiocytes, which is suggestive of Histoplasma capsulatum. Treatment is generally made with the administration of intravenous amphotericin B for 2–4 weeks, followed by itraconazole for 6 months.1,2