Las recomendaciones del Ministerio de Sanidad español sobre vacunación en grupos de riesgo incluyen a la mesalazina entre los tratamientos con un posible efecto negativo en su efectividad. Sin embargo, esta no es la recomendación de la mayoría de los expertos. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar el efecto de la mesalazina en la respuesta humoral a la vacuna contra el SARS-CoV-2 en los pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII).
MétodosVACOVEII es un estudio español, prospectivo y multicéntrico promovido por GETECCU, que evalúa la efectividad de la vacuna contra el SARS-CoV-2 en los pacientes con EII. En él se incluyen pacientes con EII con vacunación completa y sin infección previa por COVID-19. La seroconversión se fijó en 260 BAU/mL (determinación centralizada) y se evaluó a los seis meses después de la vacunación completa. En este subanálisis se comparan los resultados entre pacientes tratados con mesalazina y sin tratamiento.
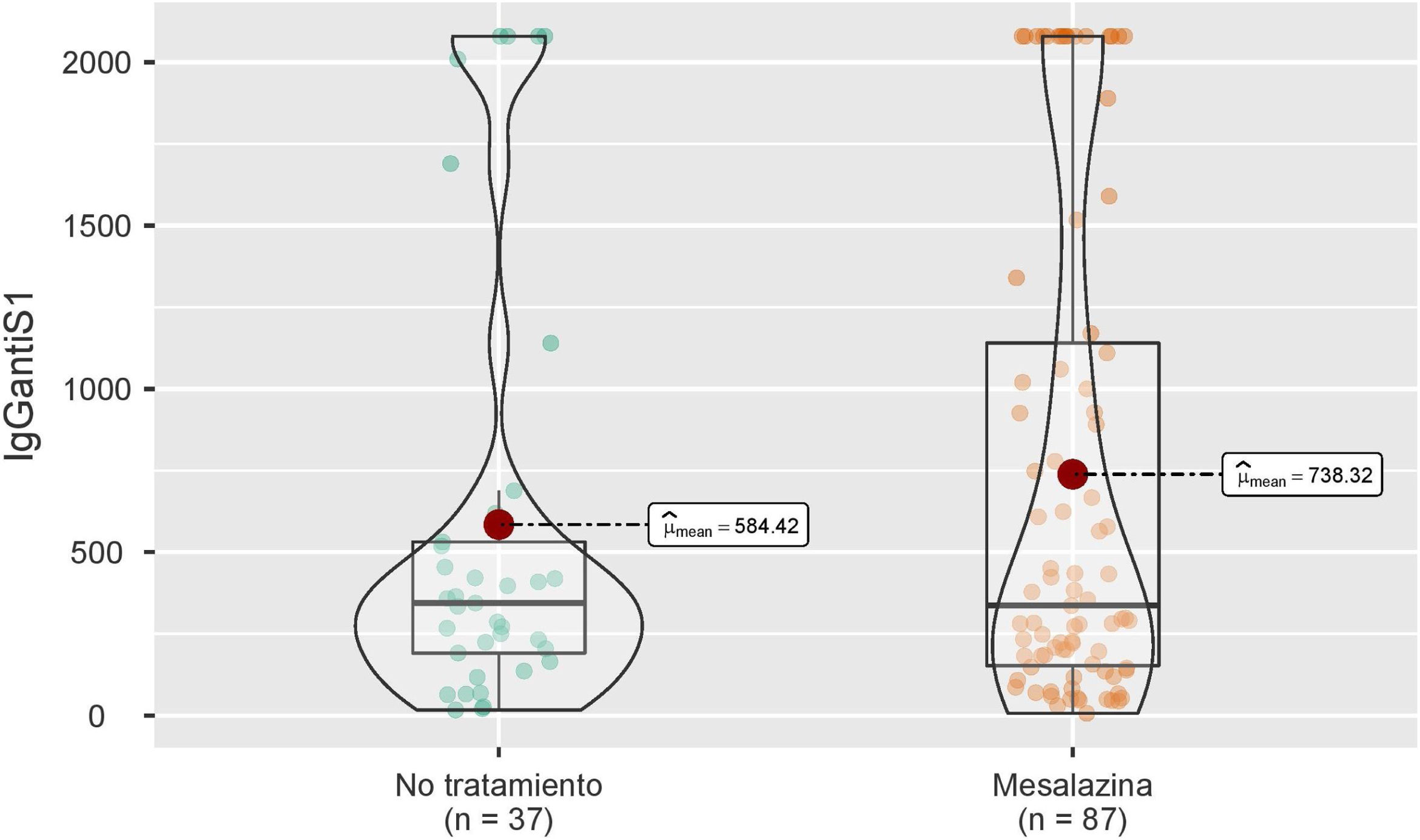
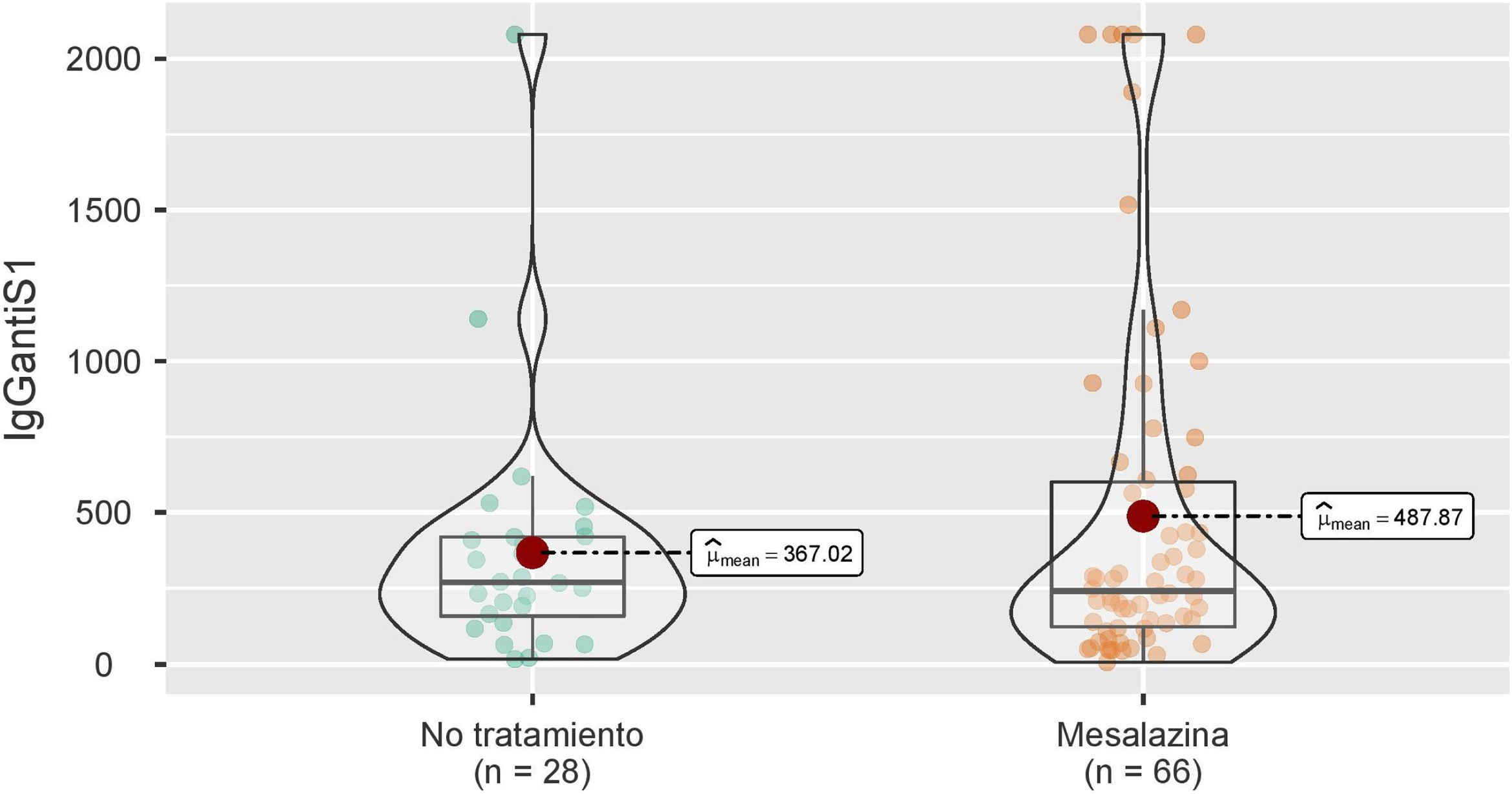
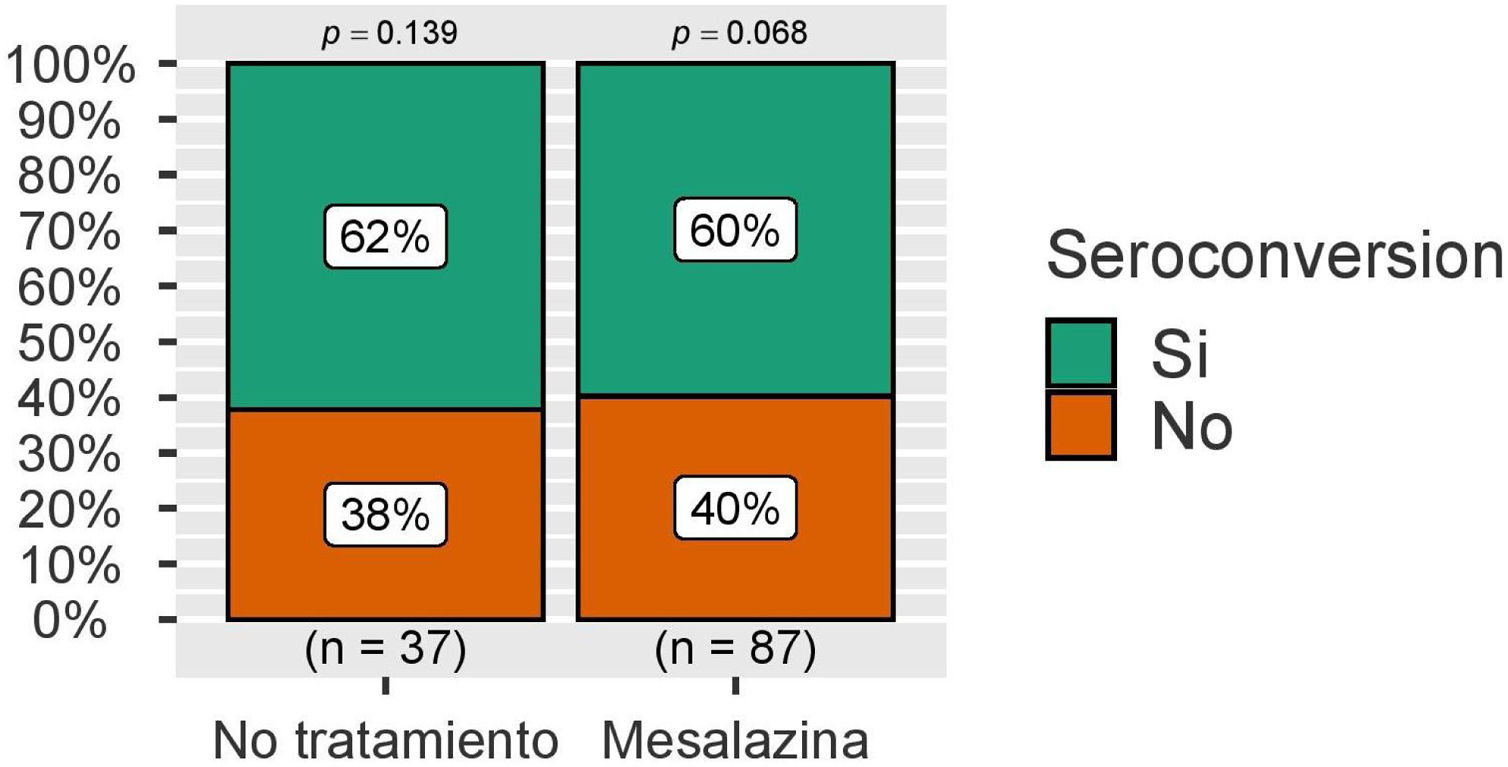
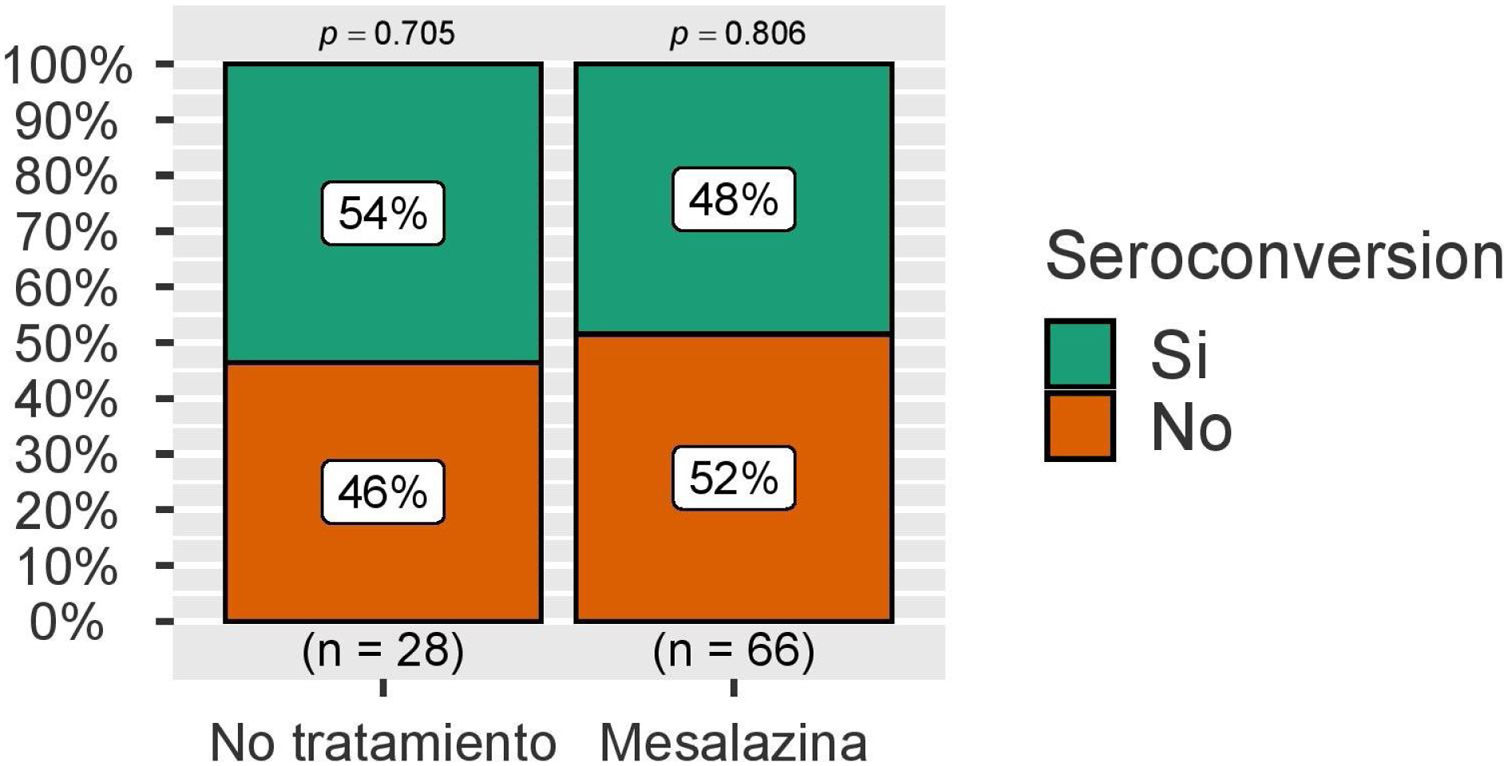
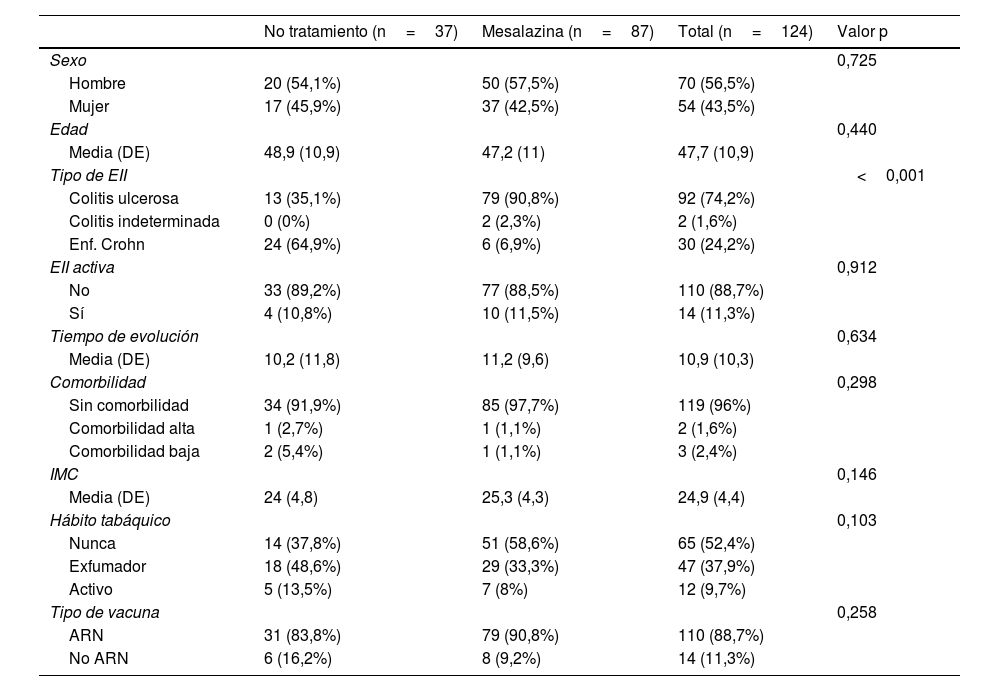
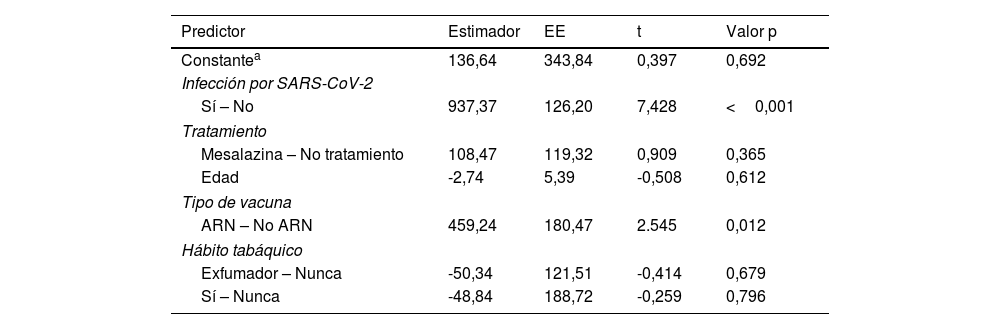
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 124 pacientes sin terapia inmunosupresora, de los cuales 32 no recibían ningún tratamiento y 92 mesalazina únicamente. Seis meses después de la vacunación completa, no se observan diferencias significativas en las concentraciones medias de IgG anti-S entre ambos grupos. En el análisis multivariable los títulos de anticuerpos se asociaron de forma independiente con el uso de vacunas ARNm y con la infección por SARS-CoV-2.
ConclusiónLa mesalazina no tiene un efecto negativo sobre la respuesta a las vacunas contra el SARS-CoV-2 en los pacientes con EII.
The recommendations of the Spanish Ministry of Health on vaccination in risk groups include mesalazine among the treatments with a possible negative effect on its effectiveness. However, this is not the recommendation of most experts. Our objective was to evaluate the effect of mesalazine on the humoral response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
MethodsVACOVEII is a Spanish, prospective, multicenter study promoted by GETECCU, which evaluates the effectiveness of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with IBD. This study includes IBD patients who have recieved the full vaccination schedule and without previous COVID-19 infection. Seroconversion was set at 260BAU/mL (centralized determination) and was assessed 6 months after full vaccination. In this subanalysis of the study, we compare the effectiveness of the vaccine between patients treated with mesalazine and patients without treatment.
ResultsA total of 124 patients without immunosuppressive therapy were included, of which 32 did not receive any treatment and 92 received only mesalazine. Six months after full vaccination, no significant differences are observed in the mean concentrations of IgG anti-S between both groups. In the multivariate analysis, antibody titers were independently associated with the use of mRNA vaccines and with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
ConclusionMesalazine does not have a negative effect on the response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in IBD patients.