El accidente cerebrovascular supone una de las primeras causas de discapacidad física de la población adulta. Los afectados pueden presentar alteraciones motoras y sensitivas, así como alteración del control postural o equilibrio y, consecuentemente, un elevado riesgo de caída. Conociendo la relación entre el control postural y los sistemas sensoriales somatosensorial, vestibular y visual, este estudio se centra en la influencia del sistema visual. El objetivo es averiguar la efectividad del entrenamiento visual en la rehabilitación del equilibrio en pacientes con accidente cerebrovascular crónico.
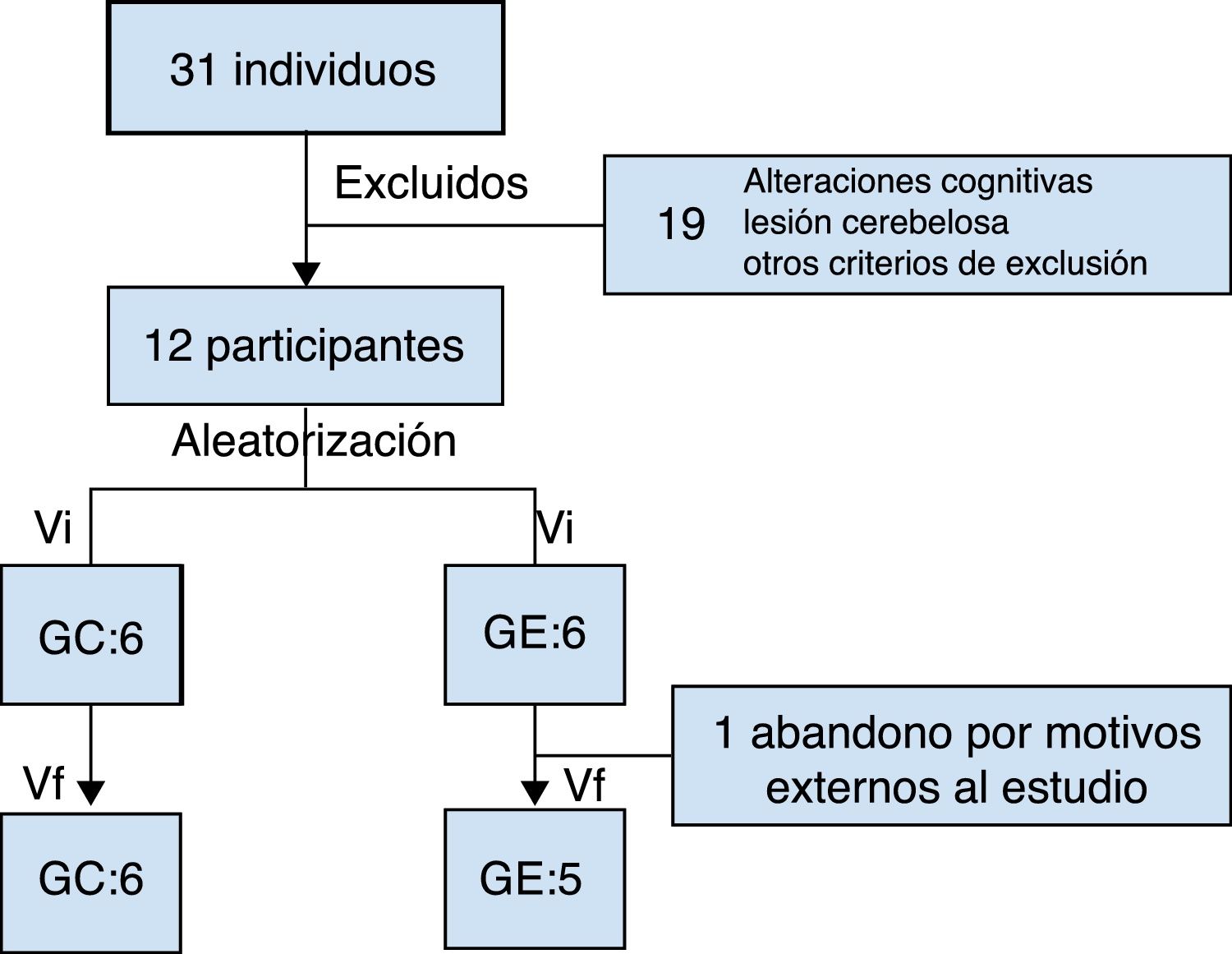
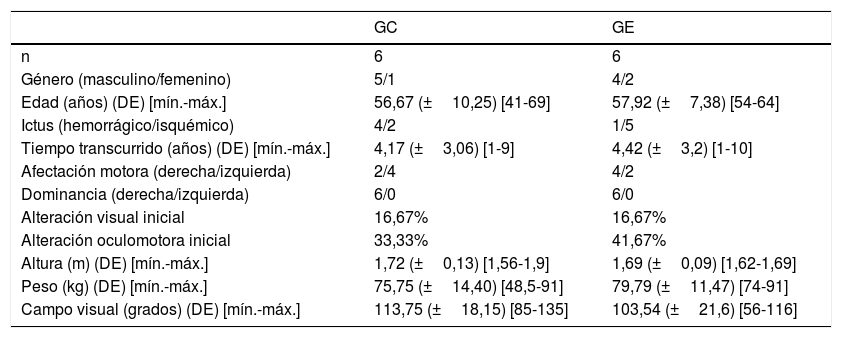
Material y métodosSe ha realizado un estudio piloto aleatorizado simple ciego (estudio experimental, longitudinal y prospectivo). El total de participantes fue de 12 (accidente cerebrovascular>1 año), aleatoriamente distribuidos en 2 grupos. Los grupos realizaron terapia del equilibrio orientada a tarea (30min) y, adicionalmente, el grupo experimental realizó entrenamiento visual (15min). Ambos grupos completaron 5 sesiones en 3 semanas. El control postural se ha valorado con la Escala de Equilibrio de Berg, prueba Timed Up and Go y monitorización del centro de presión.
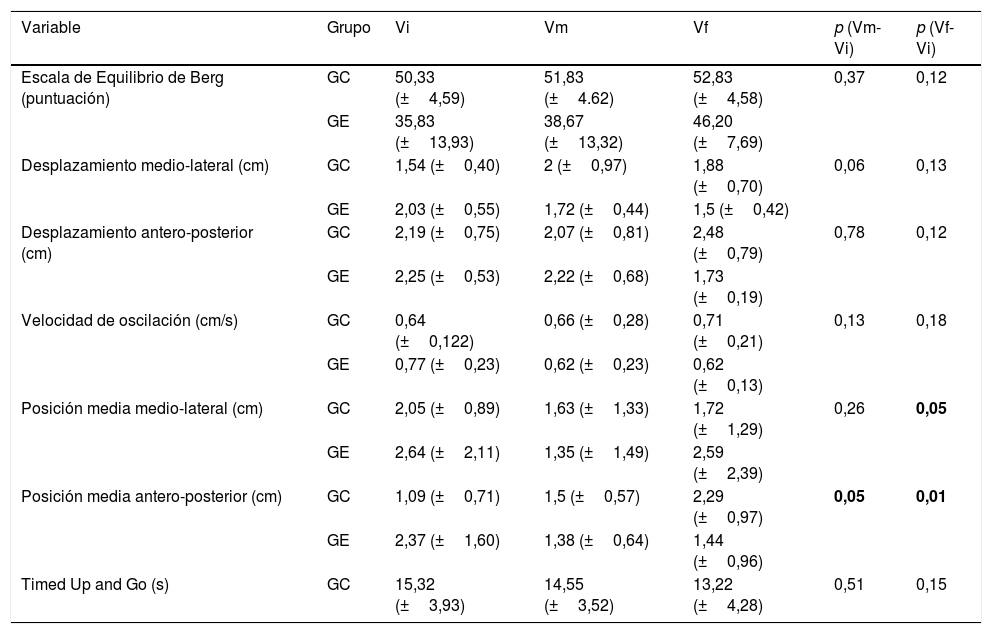
ResultadosRelativo a todas las variables, se ha observado mayor rango de evolución positiva en el grupo experimental en comparación con el grupo de control. Sin embargo, los únicos resultados estadísticamente significativos fueron relativos a la simetría del centro de presión corporal (p=0,05 y p=0,01).
ConclusionesEl entrenamiento visual parece ser útil en la rehabilitación del control postural de individuos con accidente cerebrovascular crónico. Son necesarias futuras investigaciones para confirmar su efectividad.
Stroke is one of the first causes of physical disability in the adult population. Those affected may have motor and sensory disturbances, as well as altered postural control, and consequently high risk of falls. Knowing the relationship between postural control and somatosensory, vestibular and visual systems, this study focuses on the influence of the visual system. The aim of this study is to determine whether visual training increases the effectiveness of balance rehabilitation in patients with chronic stroke.
Material and methodsA single blind randomised pilot study (prospective longitudinal experimental study) was conducted on a total of 12 participants (Stroke>1 year) randomly distributed into two groups. The groups performed task-oriented balance therapy (30minutes), in addition the experimental group performed visual training (15minutes) in the same session. Both groups completed 5 sessions in 3 weeks. Postural control was assessed using the Berg Balance Scale, Timed Up and Go test, and pressure centre monitoring.
ResultsA greater range of positive progress was observed in all variables in the experimental group compared to the control group. However, the only statistically significant results were related to the symmetry of the centre of body pressure (P=.05 and P=.01).
ConclusionsVisual training seems to be useful in postural control rehabilitation of individuals with chronic stroke. Further research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".