Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and traumatic brain injury (TBI) are associated with chronic inflammation, as inferred from increased, but variable, peripheral levels of cytokines. We sought proof of concept for the notion that peripheral cytokine binding proteins and/or soluble receptors can confound measures of cytokines in those with a history of physical and psychological traumatic exposures. Efforts were focused on one of the major cytokines involved in inflammation, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF- α).
MethodsWe examined blood plasma concentrations of TNF-α, its soluble receptors (TNF-soluble receptors (sR) I and TNFsRII), and C-reactive protein (CRP-1) in a cohort of US Veterans. In a previous study, CRP-1 was shown to be reduced by probiotic anti-inflammatory treatment in this patient cohort. All participants (n = 22) were diagnosed with PTSD and had a history of mild TBI with persistent post-concussive symptoms. Exclusion criteria included medications directly targeting inflammation.
ResultsMolar concentrations of soluble TNFsRI and II exceeded concentrations of the TNF-α ligand. TNFsRI, but not TNFsRII, was significantly associated with CRP-1 (Spearman Rho correlations = 0.518; p=.016 and 0.365; p = .104, respectively).
ConclusionsTNF soluble receptors may bind to and sequester free TNF-α, suggesting that only measuring ligand concentrations may not provide a fully comprehensive view of inflammation, and potentially lead to inaccurate conclusions. TNFsRI concentration may provide a better estimate of inflammation than TNF-α for those with PTSD and post-acute mTBI with post-concussive symptoms, a hypothesis that invites further testing in larger studies.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is often called a “signature injury” of the recent conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan. Studies show that approximately 11–23% of United States (US) Service Members from recent conflicts have a history of TBI, with most of these injuries being mild (mTBI).1-3 Mild TBI occurs when an injury to the brain is associated with loss of consciousness of less than 30 min and posttraumatic amnesia that is present for 24 h or less. It has been estimated that about 20% of individuals with mTBI continue to experience post-concussive symptoms following these events (e.g., insomnia, memory loss and other cognitive problems, irritability, anxiety, physical symptoms including headaches or dizziness). A diagnosis of post-concussive syndrome is appropriate when three or more symptoms persist for three or more months.4 Many of the symptoms of this disorder overlap with those of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and it has been estimated that significant numbers, up to half of all US service members with mTBI meet diagnostic criteria for PTSD.4-6 The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) defines PTSD as a psychiatric disorder arising from exposure to events such as severe injury, sexual violence, or witnessing death. Diagnosis includes four symptom clusters (1) re-experiencing phenomena, (2) avoidant behaviors, (3) cognitive distortions, memory deficits and negative emotional states, and (4) heightened arousal). We focused on a population of veterans diagnosed with both mTBI with persistent post-concussive symptoms and PTSD at the time of the study. Many studies report an association of PTSD and/or mTBI with chronic inflammation, as defined by an increase in peripheral levels of inflammatory cytokines.7-10 Systematic reviews of the PTSD or TBI studies point to heterogeneity in study design and between-study results.7,9 Potential confounding factors include comorbid depressive disorder, psychotropic medications, and differing measurement techniques.9 We propose that an additional critical issue, hitherto given insufficient attention, pertains to the potential interference of cytokine measures by specific interacting proteins. The current study was designed to seek proof of principle for this concept by focusing on tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).
TNF-α is a principal cytokine associated with inflammation. It is a key regulator of the innate and adaptive immune systems and contributes to the initiation and maintenance of inflammation. Thus, early reports of increased levels of TNF-α in patients with various autoimmune and degenerative diseases produced a wave of enthusiasm for the potential of anti-TNF therapies. This led to the development, testing, approval, and clinical use of several anti-TNF-α drugs (such as infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept; for reviews see11-13). While these therapies have been successfully used to treat several autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, their limitations in terms of restricted responsiveness and side effect profiles11,14 have led some investigators to consider other components of the TNF-α system, such as TNF-α receptors as potential alternative therapeutic targets.14,15 Importantly, the effect of TNF-α depends on the receptor to which it binds and activates. The TNF receptor type I (TNFRI) is often linked to pro-apoptotic and pro-inflammatory responses, while the type II receptor (TNFRIII) has been associated with immunoregulation and tissue regeneration.11,16 These primary roles and their regulation are supported by a growing body of evidence of the intracellular signaling cascades for each receptor, their modulators, and target nuclear signals (for reviews, see13,16), as well as by studies of transgenic mice carrying deletions of TNFRI or II genes.17 Excess levels of the TNF-α ligand are associated with proteolytic cleavage of the TNF receptors from the cell surfaces. The cleaved receptors are released from the cellular plasma membranes into peripheral circulation. This proteolytic process is believed to be a negative feedback mechanism which helps to curtail TNF activity by removing responsive cell bound receptors and producing soluble receptors that can bind and sequester bio-available TNF-α.18,19 The aims of the present study were to probe whether TNF-α and/or its soluble receptors: 1) can be accurately assessed in the peripheral circulation of a well-defined Veteran population with comorbid mTBI/PTSD; and 2) are associated with C-reactive protein-1 (CRP-1). CRP-1 is a potent marker of inflammation20,21 that bears relevance to this study cohort, since the parent investigation showed preliminary evidence that this protein is sensitive to anti-inflammatory probiotic treatments.22
MethodsParticipantsPlasma was collected prior to supplementation with probiotics from a subsample of 22 participants from the larger sample.22 Briefly, individuals were males that served in the recent conflicts that had a current PTSD diagnosis and history of mTBI with endorsement of persistent post-concussive symptoms. Participants were excluded if they had a history of moderate or severe TBI. Additional exclusions were current substance abuse or dependence, other mental disorders associated with peripheral inflammation such as bipolar, psychotic, or anxiety disorders and/or chronic unresolved medical disorders. Individuals on medications for pulmonary, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, hepatic, or renal functioning, immunosuppressive drugs and/or cytokines and their inhibitors were also excluded. The study was approved by the Colorado Multiple Institutional Review Board.
Procedures. Blood samples were collected, plasma was prepared, and samples from each participant distributed into separate aliquots, frozen on dry ice and stored at −80 °C. The participants that we included in the present study had a mean age of 36.5 ± 6.65 years and were mostly Caucasian (16 of 22 participants) with small proportions of Multicultural (4/22), Native American/Alaskan Native (1/22) and Black or African American (1/22) individuals.
MeasuresDiagnostic Criteria: Participants were included if they had a history of mTBI and concurrent PTSD. mTBI was assessed by the Ohio State University (OSU) TBI-ID,23 occurred at least 6 months prior to the study, and resulted in current symptoms in three or more post-concussive symptom categories as defined by the International Classification of Diseases (ICD)−10, and measured by the Rivermead Post-concussive Symptom Questionnaire 24; for additional details, please see22). Current PTSD was assessed by the Clinician Administered PTSD Scale-5 (CAPS-5).25,26 Other psychiatric disorders were assessed by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM Disorders (SCID) and medical conditions and treatments by medical chart review and interview.
TNF and CRP-1 Measures: CRP-1 levels were determined using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) following the instructions of the manufacturers (Cat No. DCRP00, R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). The present study used archival values from the parent study matching samples to those used for the current study.22 TNF-α levels were assessed by the Human TNF alpha (Total) ELISA kit (Cat No. BMS2034, Invitrogen/ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). This assay was reported by the company to be free of interference by the TNF-receptor and had a lower limit of detection of 23 pg/ml. However, this assay did not detect TNF-α in these samples, and thus archival values of TNF alpha measured by high sensitivity multiplex ELISA (Cat No. 85–0002, Quanterix, Billerica, MA, USA) which had a lower detection limit of 0.098 pg/ml were used. TNFsRI and TNFsRII were measured by quantikine ELISA kits (Cat No. DRT 100 and DRT 200 respectively, R&D Systems). Both assays had a lower limit of detection of 10 pg/ml, and were reported by the company to measure total levels of soluble receptors, as assessed by the insensitivity of the assays of standard samples to added levels of TNF-α. All soluble receptor assays were carried out using three replicates in the same ELISA plate and averages/sample calculated. Coefficients of variation over 10% between replicates were excluded from further analysis. Molar concentrations were calculated using molecular weights of 18 Kda, 55 Kda, and 75 Kda for the ligand and TNFsRI and II, respectively. SPSS software version 27 (SPSS 27) was used for all statistical analysis of results. Evaluations of the data normality for each variable were conducted prior to correlation analysis, including inspection of boxplots and histograms and evaluation of Shapiro Wilks criteria (SPSS 27).
Optimization of Measures: Plasma samples were diluted 1:10 and 1:30 for assays of TNFsRI and TNFsRII, respectively, as these dilutions reproducibly provided optical density readings centered at or around the mid-point of the standard curve. The effect of freeze-thawing samples was assessed by comparing freshly thawed and 2x thawed samples (stored at −80 °C for another 1–3 months after being thawed once and then re-frozen). There was no detectable loss of activity of either receptor after freeze/thawing of 4 samples (average recoveries ± standard deviation (SD) = 107% ± 12.6%). Thus, we used samples that had been freeze thawed once or twice for assays of TNFsRs. Archival values for TNF-α and CRP-1 from samples of the initial study were thawed only once.
ResultsTNF-α measures vs TNFsRI & IITNF-α protein was below the lower limit of detection of the Invitrogen ELISA at all dilutions tested (ranging from 1:20 to no dilution). Thus, data generated from the original pilot study using the ultra-sensitive Quanterix assay were used. These values were very low, with several samples having undetectable activity or values close to the lowest standard (mean = 22.67 pg/ml ± 45.81). By contrast, both soluble receptors were easily and reproducibly detected in the mid-portion of the standard curves for all samples.
Fig. 1 shows a contrast between measured levels of TNF-α ligand and each of the two soluble receptors, TNFsRI and TNFsRII, with levels of the latter being significantly higher than the ligand. Also, a remarkably consistent relationship is displayed between the soluble receptors, with TNFsRII always being present at ∼2-fold higher levels than TNFsRI, irrespective of inter-participant variation, and both receptors exceeding levels of the TNF-α ligand. Taken together, the data suggested that plasma contained sufficient levels of soluble receptors to bind and sequester any free, bio-available TNF-α (see Discussion) and suggested that the levels of soluble receptors were strongly correlated. To probe the reproducibility of these results, assays were repeated for each of the two soluble receptors on separate occasions. For TNFsRII, plasma samples for each of 22 participants were measured in triplicate, averaged, and the overall mean of three sets of separate assays and their standard deviations calculated: 2136.19 pg/ml ± 542.76. Similarly, duplicate assays conducted at separate times for TNFsRI (n = 22) resulted in a mean of 1037.71 pg/ml and an average standard deviation of 282.79. The corresponding average molar concentrations were as follows: (TNF-α = 1.21 picomolar (pM); TNFsRI = 8.87 pM (7-fold excess over TNF-α), and TNFsRII = 28.5 pM (24 molar excess over TNF-α).
Comparison of the concentrations of TNF-α, TNFsRI and TNFsRII in blood plasma
The assays for TNFsRI and TNFsRII were conducted in parallel on the same day (by two experimenters). Each point represents average of triplicates. The TNF-α values shown are from archival data. Concentrations are total concentrations per ml after correction for dilutions.
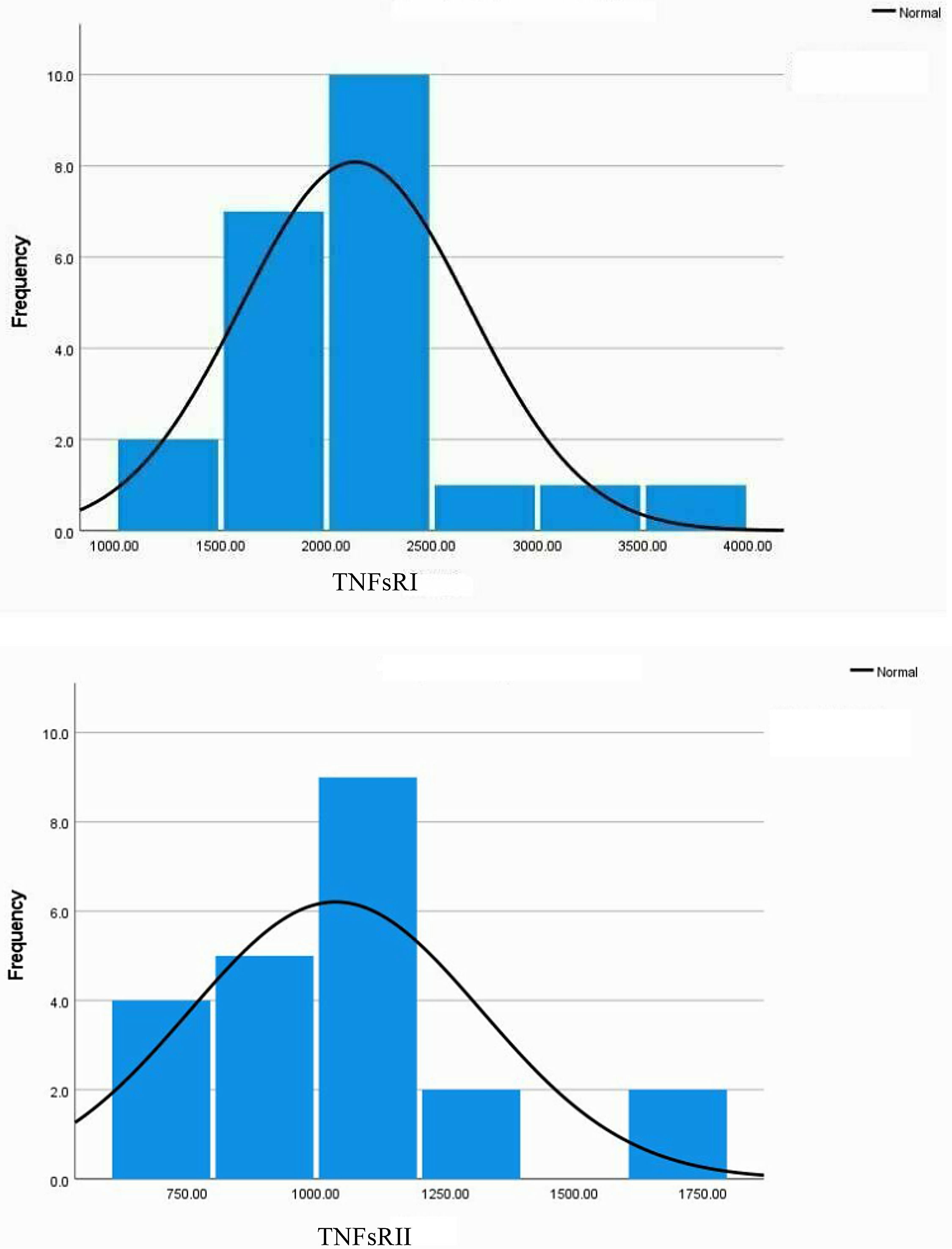
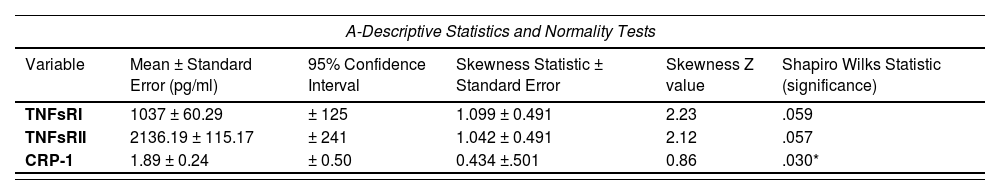
Key variables showed deviations from normality by histogram (Fig. 2) and boxplot inspection (not shown).
The histograms for the TNFsRI and TNFsRII inFig. 2 show the positive skewness of the distributions. Fig. 2 also visually confirms the initial suggestion that the two soluble receptors follow similar trends. Statistical analysis of the distributions is shown in Table 1A, which shows a mild but significant skewness for both receptors. Spearman's rho correlations are shown in Table 1B.
Statistical analysis of the distribution of key variables and their associations.
The mean and standard deviation values for the receptors were calculated as indicated in Methods. The same samples were repeatedly assayed (on different days) for TNFsRI and II and the results averaged. These means were used to assess the correlations shown in Table 1.
The two soluble receptors were strongly and significantly correlated (0.719, p < .01)). TNFsRI had a strong, significant correlation with CRP-1 (0.518, p = 0.016). On the other hand, the TNFsRII had a weaker, non-significant correlation with CRP-1 (0.365, p = .104). There were two outliers for each of the receptors by boxplot analysis (not shown), so the correlation data was also calculated after removal of these outliers, showing similar correlation trends for each of the receptors with CRP-1: significant for TNFsRI (0.511, p = .025) and non-significant for TNFsRII (0.275, p = .254). Pearson correlations were also calculated since the skewness of the sample distributions were not severe. These correlations ± outliers followed the same trends as the non-parametric correlations (not shown).
DiscussionIn the present study, concentrations of plasma TNF-α soluble receptors exceeded those of TNF-α. Consistent with this, Himmerick et al.,27 found that PTSD patients had serum concentrations of TNFsRI and TNFsRII 50-170 fold higher than TNF-α. Thus, there is mounting evidence that measures of TNF-α in blood serum or plasma be complemented by evaluation of the two soluble receptors - TNFsRI and TNFsRII. Similar complimentary measurement of ligand and receptors may apply to the interpretation of cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, and others produced downstream of TNF-α.28 This study provides evidence that the binding proteins/soluble receptors of TNF-α and likely other cytokines are contributing to variable interpretations of inflammatory activity in those with a history of trauma. The significant correlation of TNFsRI with CRP-1 is a novel finding for mTBI/PTSD cohorts. This finding is also consistent with the reports of bidirectional transcriptional regulation between these two proteins in certain systems.21 In addition, the temporal sequelae of TNF-α expression following injury in animal models of TBI were associated with an increase in the TNF-α ligand within hours of induction, and with deleterious effects, followed by a more delayed effect wherein TNF-α signaling was associated with anti-inflammatory repair-related activities.29 Our finding support other studies promoting the concept of bifunctional and complementary activities of TNF-α following TBI, with an important temporal expression timeline (reviewed in30,31). This suggests that TNF-α initiates and orchestrates activities needed to remove damaged brain tissue prior to tissue reconstruction, and it may be hypothesized that in a well-regulated system, cells might respond by producing TNFsRI to block pro-inflammatory activity when injured tissue has been removed. On the other hand, TNFsRII may be down regulated in certain anti-inflammatory cells such as astrocytes to promote repair signaling. According to this simplified schema, it may be further proposed that in humans, stressful stimuli from traumatic and/or other situations post-injury contribute to the production of additional inflammatory episodes that lead to dysregulation of the homeostatic activities of TNF-α. In this scenario, cells may respond to TNF-α signaling by indiscriminately increasing the release of both soluble receptors, meaning that our observations of increased release of the “reparative” TNFsRII alongside the release of TNFsRI, may partly reflect this failure of the normal sequence of events and feedback mechanisms. Future analysis of the receptors in circulatory inflammatory cells, as well as the relative levels of the two soluble receptors at various times following TBI may provide information regarding the inflammatory stage (destruction vs. repair or their transition) of the disease, a possibility that deserves future scrutiny. Overall, these mechanisms are likely to be highly complex and to include alarmin signaling as well as anti-inflammatory mediators and their regulators.
The present study is limited by a small number of participants. On the other hand, the present study also opens a number of significant possibilities for key future studies. Studies should consider whether other members of the TNF superfamily (i.e., lymphotoxins), might contribute to binding the soluble receptors. The present study conducted at least 6 months post-TBI is in agreement with and extends a previous study,32 which reported increases in plasma TNFsRI and TNFsRII during the first 10 days following TBI. Larger longitudinal studies would shed more insight into mechanistic changes. For example, explorations of how: 1) TNF (and other cytokine) parameters change starting immediately post-injury to several years thereafter including history of social stressors in the interim; and 2) PTSD onset and severity, would likely provide further insight. It is also worth noting that the present work has implications for the experimental design and interpretation of the role and staging of inflammatory conditions in related neuropsychiatric fields. These areas include Chronic Traumatic Encelopathy (CTE); suicidal behavior; depression; and Sars-CoV-2,33-36 all of which are strongly associated with neuroinflammation. Further, a TNF-α polymorphism (TNF-alpha-308G/A) is associated with suicide attempts in those with major depressive disorder.37 Another study reported an association of Interleukin-8 with suicide risk in Mexican American families.38 These initial genetic studies support the notion that neuroinflammation is not just a response to various disorders, but that there may be a biological predisposition playing an important role in their etiopathogenesis. In addition, the relevancy, specificity, and outcome of the exciting ongoing and future studies will largely depend on longitudinal analysis of the cell lineages involved in each disorder and of the appropriate inflammatory cytokines as well as their regulatory proteins. One of the strengths of the current paper is that it addresses an important topic amidst the current impetus of vigorous inflammation studies in key neuropsychiatric disorders; thus, we showed how soluble receptor proteins for TNF-α are key examples of the importance of including regulatory proteins in studies of inflammation. The measures and relationships of TNF-α system, its soluble receptors, and CRP-1 also provide defined experimental anchors to examine the current general hypothesis that, at least in other disorders, neuroinflammation increases neurotoxicity via increased serotonergic and glutamatergic activity in the brain (discussed in35). Associations of these effector alongside - TNF-α, its soluble receptors, and CRP-1 in the circulation would probe this presumed correlation in patients with PTSD/mTBI with and with/without suicidal behavior.
In conclusion, we show that in this population of US Veterans with comorbid PTSD and mild TBI with persistent post-concussive symptoms that concentrations of plasma TNF-α receptors exceed those of TNF-α, raising the question of the bioavailability and significance of measured TNF-α concentrations. Further, the soluble TNFsRI correlated with levels of the acute inflammatory protein CRP-1, which agrees with the notion that this receptor reflects the inflammatory activity. These findings open the possibility that in some cases TNFsRI may be a more sensitive biomarker of inflammation than TNF-α.
Ethical considerationsInformed consent was obtained from human subjects and their privacy rights were observed. The study was approved by the Colorado Multiple Institutional Review Board. Funding. This work was supported by the VA Office of Academic Affiliations, Advanced Fellowship Program in Mental Illness Research and Treatment, Department of Veterans Affairs, and the VA Rocky Mountain Mental Illness Research Education and Clinical Center.
We are grateful for the graciousness of Dr. Christopher Lowry, Ph.D., (University of Colorado) in sharing these samples with us, for his continuing support of the work, and his critical review of the data. We are also grateful to Alexander Fessler for his highly competent technical work.
Author Notes
Disclaimers: The views, opinions and/or findings contained in this article are those of the author(s) and should not be construed as an official Department of Defense or Veterans Affairs position, policy, or decision unless so designated by other documentation.