To establish the relationship between the use of home non-invasive ventilation (NIV) and inhospital mortality in people admitted due to exacerbation of their respiratory disease.
MethodsRetrospective cohort study with 191 cases of patients attended at the emergency department of the Reina Sofía General University Hospital in Murcia due to ARF of any cause and who required NIV as supportive treatment.
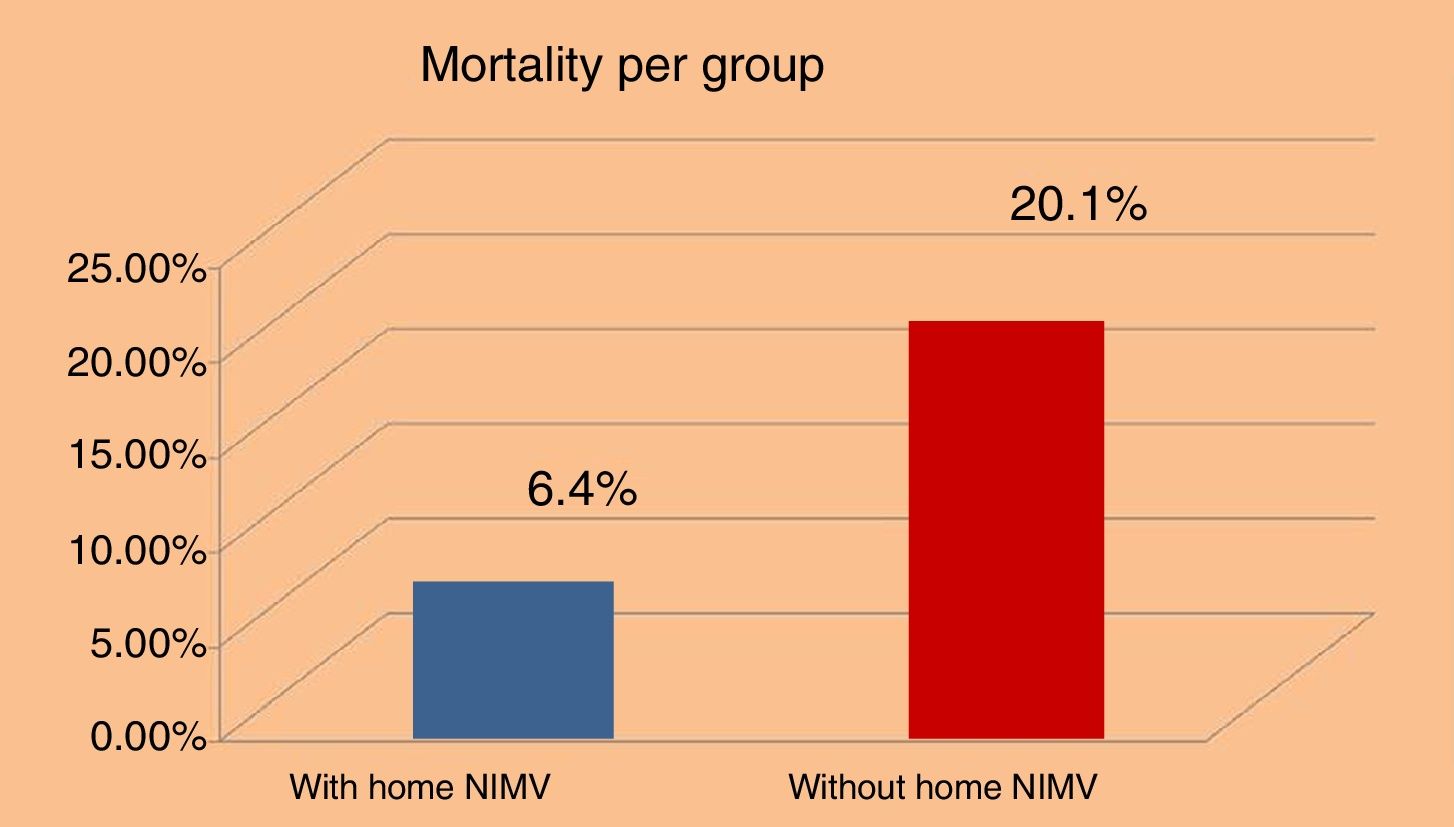
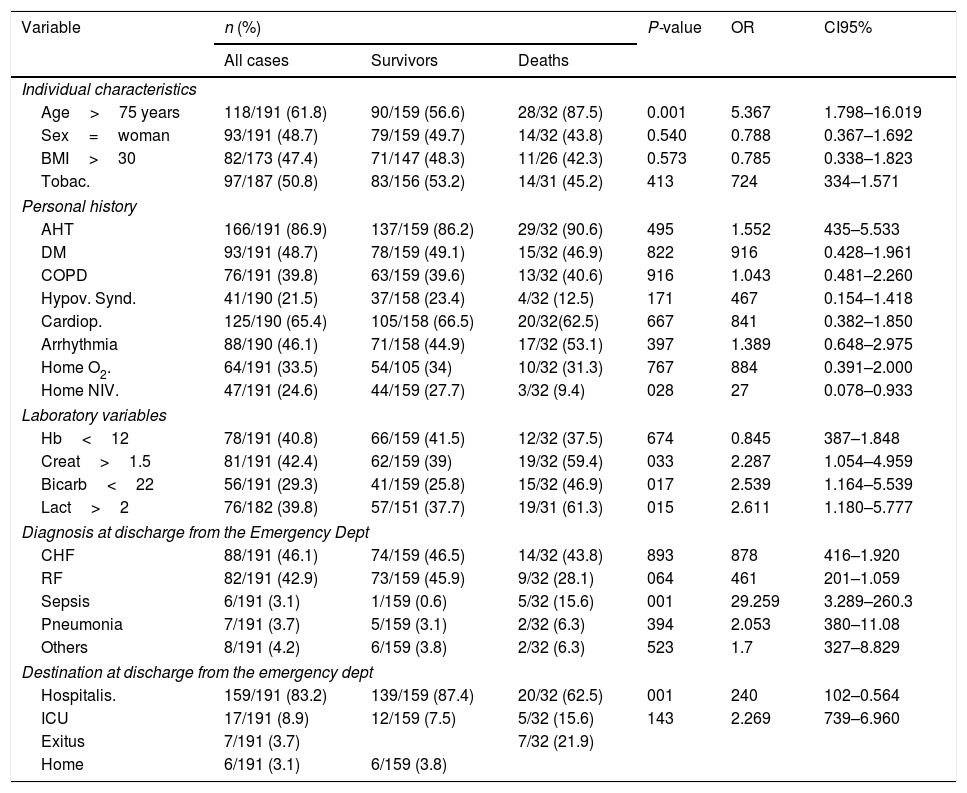
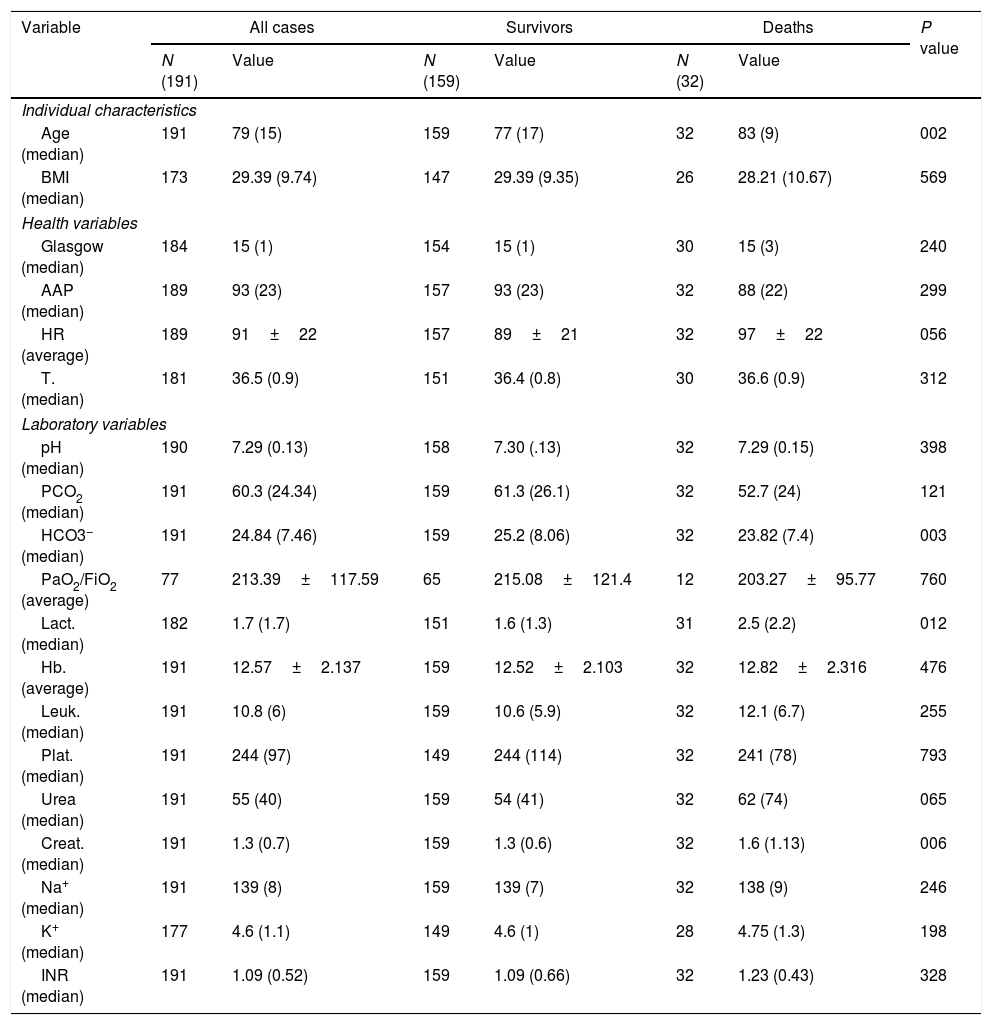
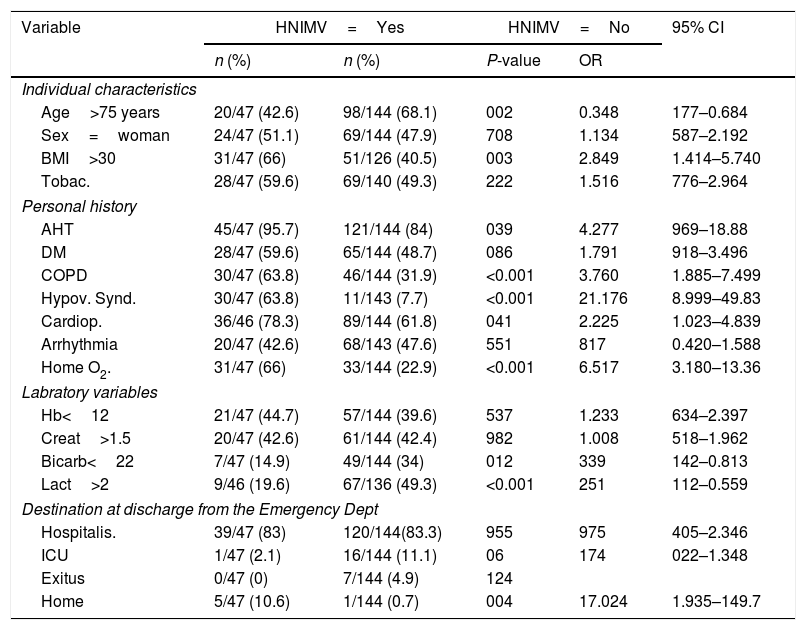
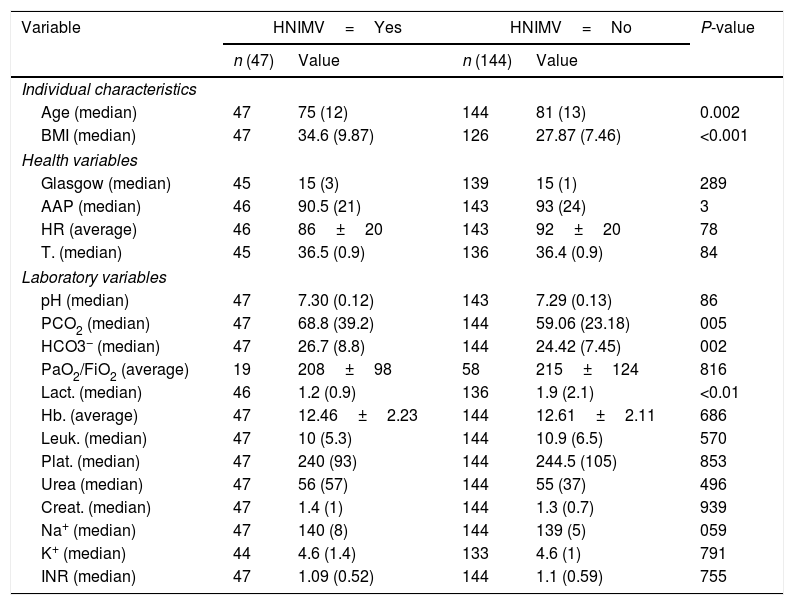
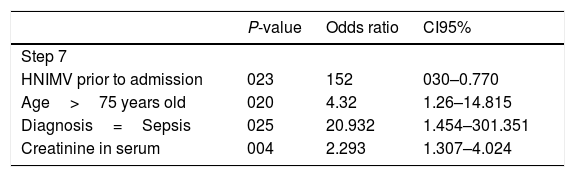
ResultsMortality among patients using NIV as routine home treatment was 6.45%, compared to 20.1% among those who did not use it (P<0.05).
ConclusionsRoutine domiciliary treatment with NIV has been shown to be a protective factor against inpatient hospital mortality for patients who underwent NIV during their admission, through the emergency department, for acute respiratory failure or acute chronic disease, regardless of the triggering pathology.
Conocer la relación entre el uso de ventilación mecánica no invasiva (VMNI) domiciliaria y la mortalidad intrahospitalaria en personas que ingresan por una agudización de su enfermedad respiratoria.
MétodoEstudio retrospectivo de cohortes con 191 casos de pacientes atendidos en el Servicio de Urgencias del Hospital General Universitario Reina Sofía de Murcia por padecer insuficiencia respiratoria aguda o crónica agudizada de cualquier causa y haber precisado VMNI como tratamiento de soporte durante su ingreso.
ResultadosLa mortalidad entre los pacientes que incluían la VMNI como tratamiento domiciliario fue del 6,45% frente al 20,1% entre aquellos que no la utilizaban (p<0,05).
ConclusionesEl tratamiento domiciliario habitual con VMNI ha mostrado comportarse como factor protector para la mortalidad intrahospitalaria de los pacientes sometidos a VMNI durante su ingreso, a través del servicio de urgencias, por insuficiencia respiratoria a aguda o crónica agudizada con independencia de la enfermedad desencadenante.