To describe the factors related to the situation of SARS-CoV-2 transmission identified by health professionals in Spain and to propose prevention strategies.
MethodCross-sectional descriptive study. The population were healthcare professionals working in institutions caring for COVID-19 patients and also confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection. A questionnaire with sociodemographic, occupational and epidemiological variables was used. Descriptive and bivariate analysis was performed according to the nature of the variables.
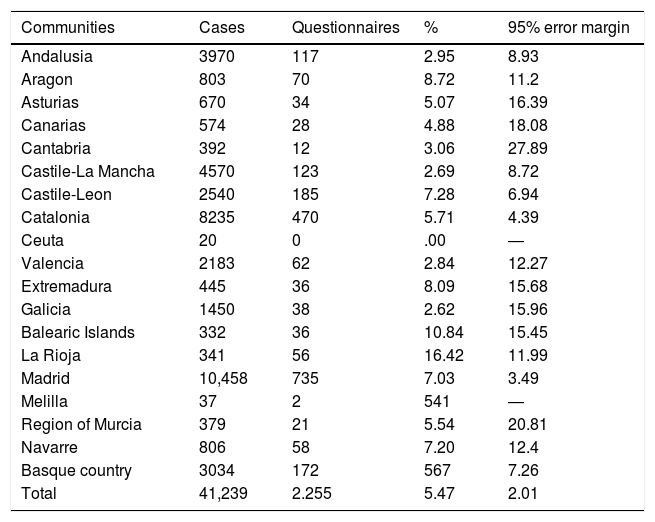
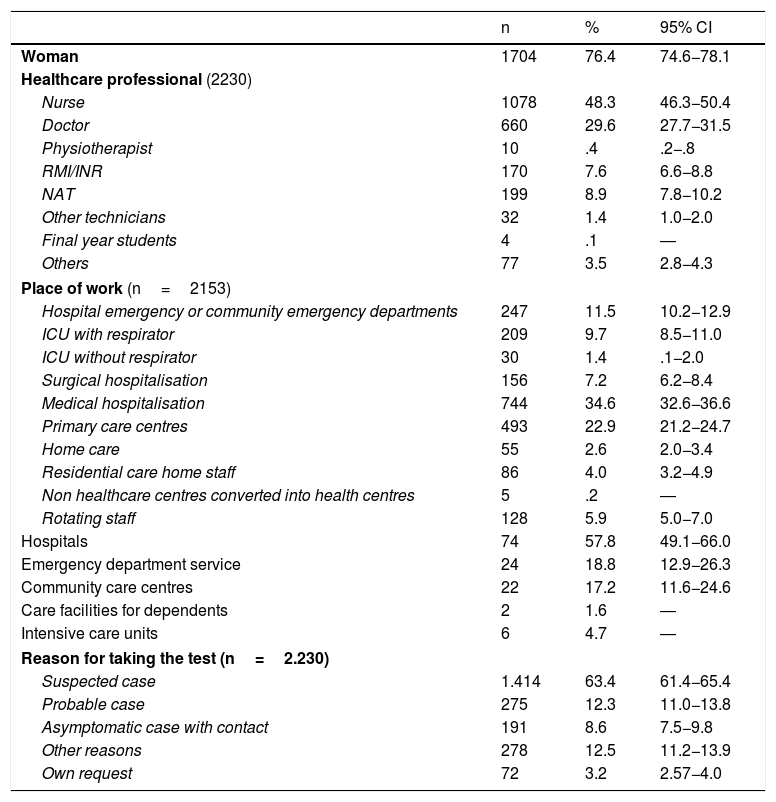
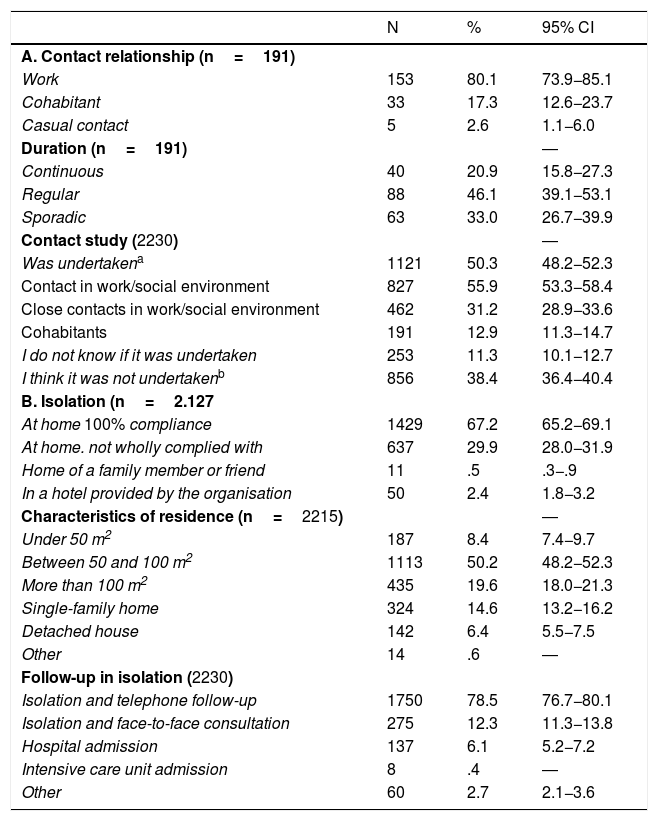
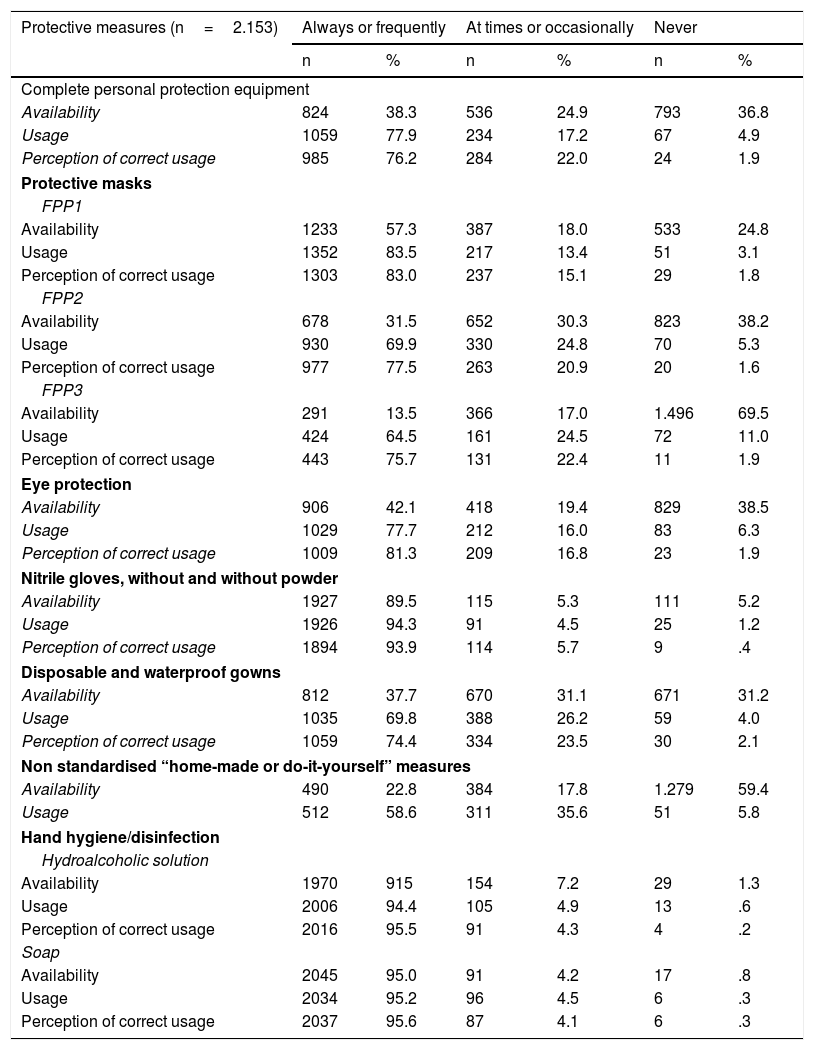
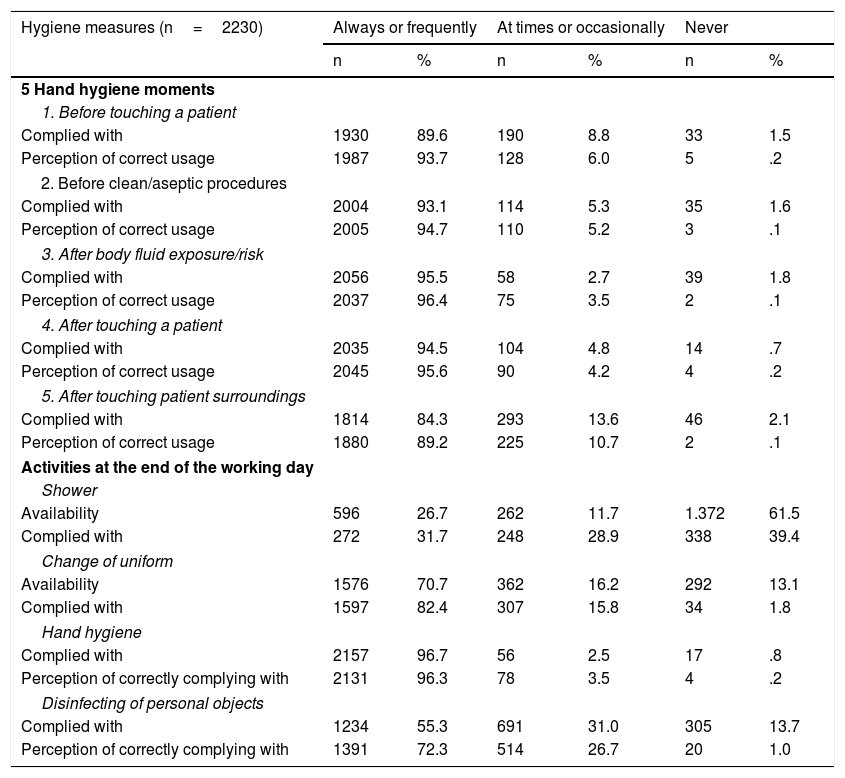
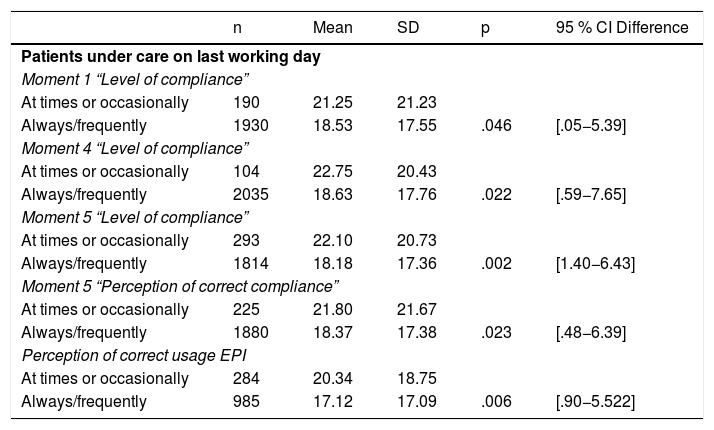
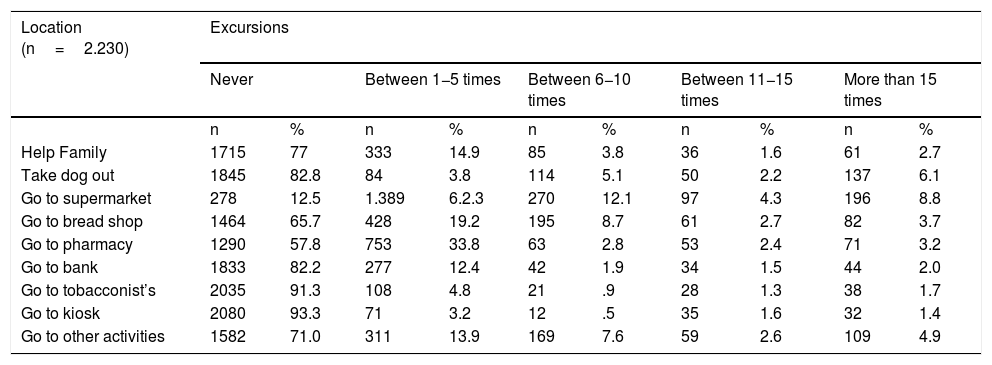
ResultsTwenty-two hundred and thirty questionnaires were analysed on a potential population of 41,239 (5.47%). The diagnosis was made based on a suspicious case (63.4%) and a probable case (12.3%). A study of contacts was carried out at 50.3%. The perception about the availability of protective measures as "always/frequently" were: FPP1 mask 57.3%, gloves 89.5%, soap 95% and hydroalcoholic solution 91.5%. In PPE, FPP2, FPP3 mask, goggles and disposable gowns at around 50%. The availability of protective measures, by field of work, presented significant differences. The average number of patients attended related to the performance of hand hygiene at moment 4 and the perception of performing it correctly at moments 4 and 5.
ConclusionsPreliminary data are presented, with variability in the response rate by Autonomous Region. Healthcare professionals infected by SARS-CoV-2 identified the management of the chain of infection transmission, the use and adequacy of protective equipment, as well as the effectiveness of handwashing as factors related to the transmission of the virus among professionals.
Describir los factores relacionados con la situación de contagio del SARS-CoV-2 identificados por los profesionales de la salud en España y proponer estrategias de prevención.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo transversal. La población fueron profesionales de la salud trabajando en instituciones con atención a pacientes con COVID-19 y caso confirmado de infección por SARS-CoV-2. Se utilizó un cuestionario con variables sociodemográficas, laborales y epidemiológicas. Se realizó análisis descriptivo y bivariado según la naturaleza de las variables.
ResultadosSe analizan 2230 cuestionarios sobre una población potencial de 41,239 (5,47%). El motivo para realizar el diagnóstico fue: caso sospechoso (63,4%) y caso probable (12,3%). Se hizo estudio de contactos al 50,3%. La percepción sobre la disponibilidad de medidas de protección como “siempre/frecuentemente” fueron: mascarilla FPP1 57,3%, guantes 89,5%, jabón 95% y solución hidroalcohólica 91,5% y en EPIs, mascarillas FPP2, FPP3, gafas y batas desechables alrededor del 50%. La disponibilidad de medidas protectoras, por ámbito de trabajo, presentó diferencias significativas. La media de pacientes atendidos se relacionó con la realización de higiene de manos del momento 4 y en la percepción de realizarla correctamente en momentos 4 y 5.
ConclusionesSe presentan datos con carácter preliminar y con variabilidad en la tasa de respuesta por Comunidad Autónoma. Los profesionales de la salud contagiados por SARS-CoV-2 identifican la gestión de la cadena de contagios, el uso y adecuación en la disponibilidad de equipos de protección, así como la efectividad en la realización del lavado de manos, como factores relacionados con el contagio de los profesionales.