To describe the impact of a standard hospital educational intervention including active physical exercises on personal well-being, functional capacity and knowledge of the benefits of prescribed physical activity for patients undergoing haemodialysis.
MethodAn uncontrolled, quasi-experimental, before-and-after study with repeated measures of response variables at 4, 8 and 12 weeks after participating in an educational and physical exercise hospital intervention. It was performed at the Nephrology Unit at the Hospital Complex in Vic within September and December 2014. The patients’ well-being, functional capacity and knowledge were assessed. Assessment tools: NOC nursing indicators, Barthel index scale, FAC Holden, Timed Get Up and Go test and Daniels scale.
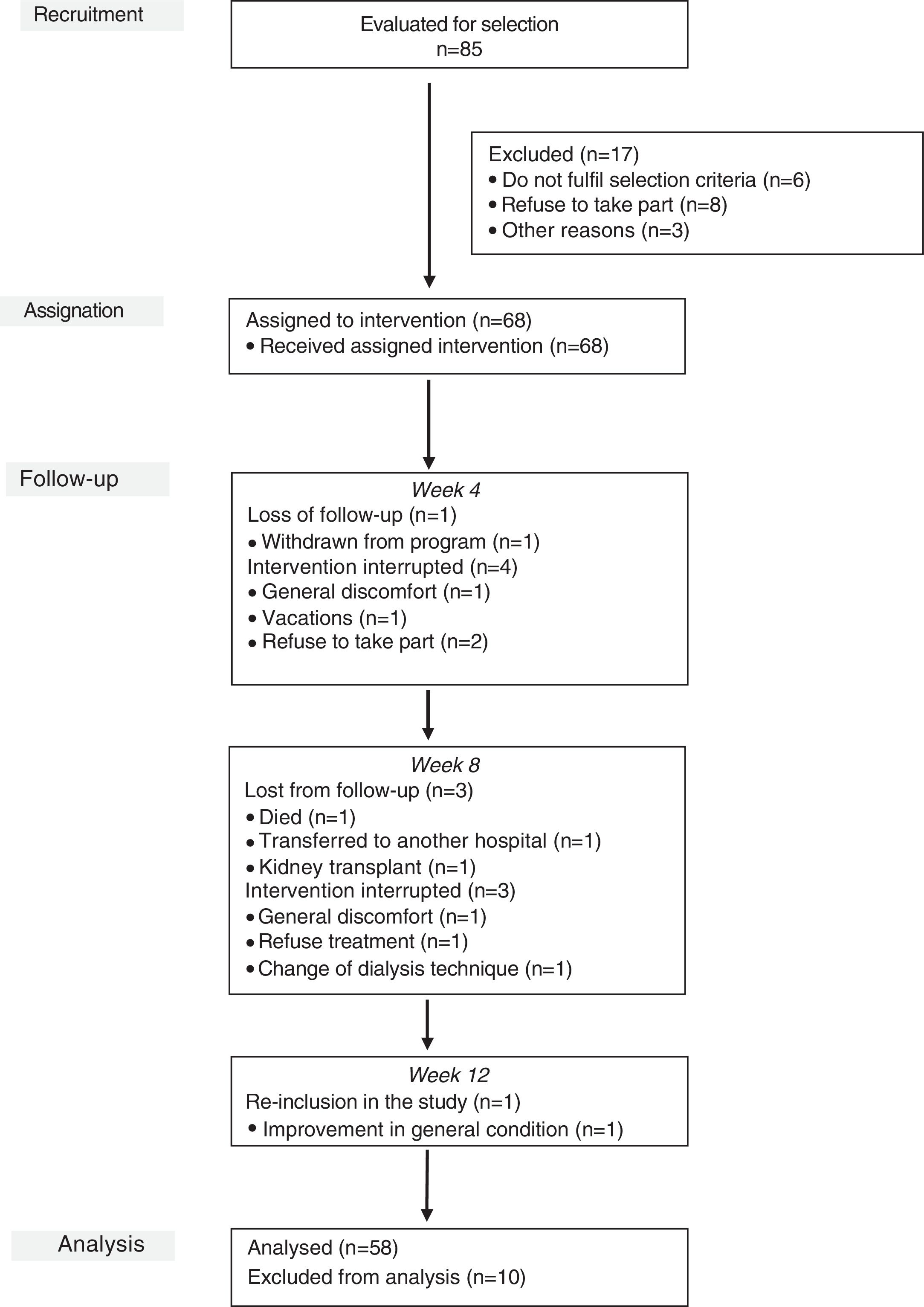
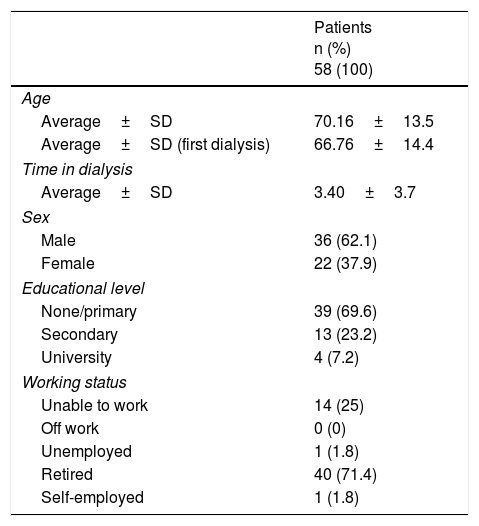
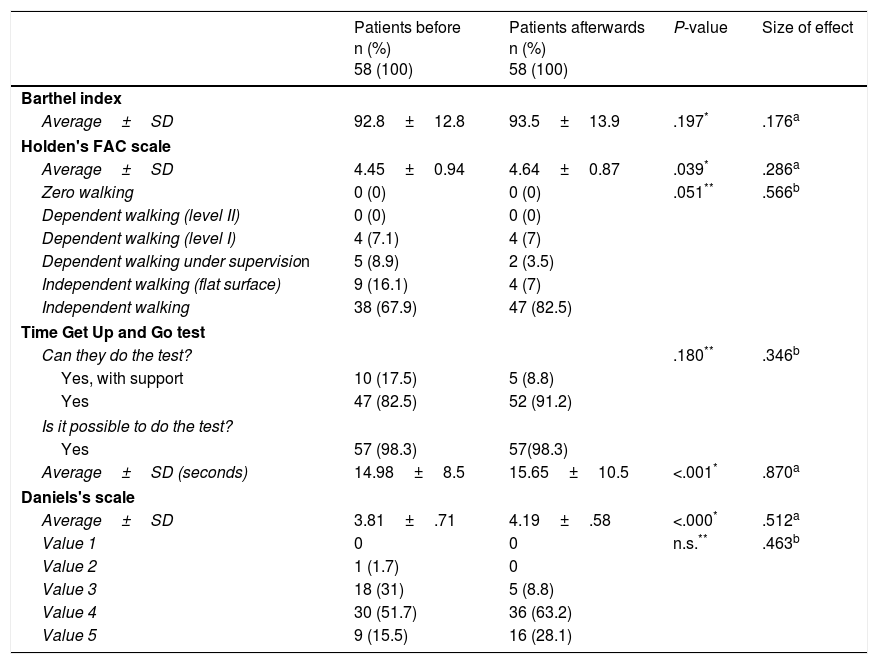
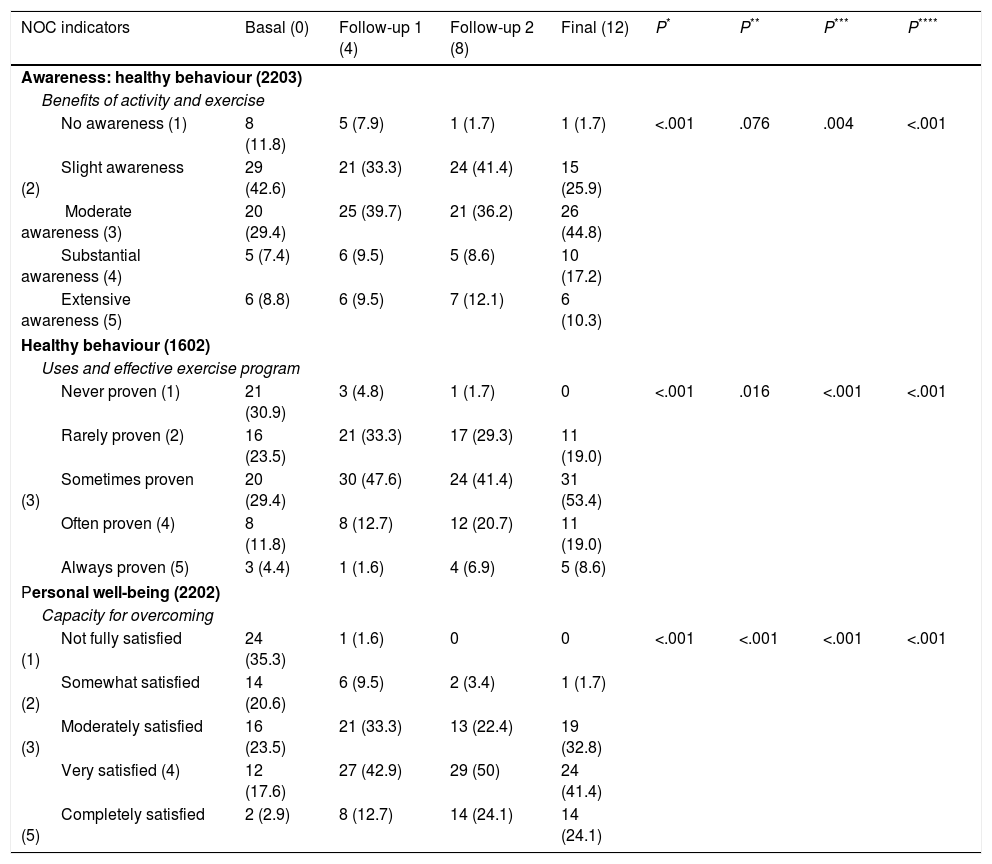
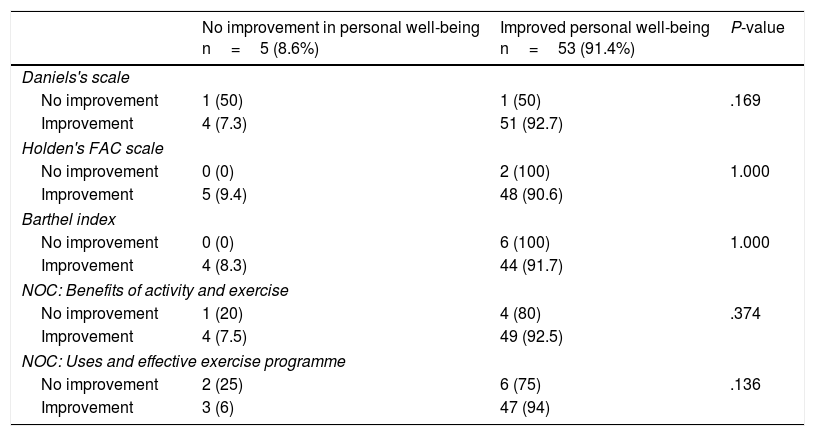
ResultsWe included 68 (80.0%) patients and 58 (85.3%) completed, with a mean age of 70.16±13.5 years; 62.1% were males. After 12 weeks, the patients had better scores of personal well-being (2.33±1.2, 3.88±0.8), more autonomy to perform activities of daily living (Barthel: 92.8±12.8; 93.5±13.9), more muscle strength (Daniels Scale: 3.81±0.7, 4.19±0.6) and walked more briskly (Get Up and Go test: 14.98±8.5; 15.65±10.5). All of the score differences were statistically significant (P<.05) except the Barthel Index.
ConclusionsThe standard educational intervention and active exercise performed at hospital level improved the personal well-being, knowledge and functional capacity of patients on haemodialysis.
Describir el impacto de una intervención educativa hospitalaria estandarizada incluyendo la realización de ejercicios físicos activos, en el bienestar personal, capacidad funcional y nivel de conocimiento de los pacientes en hemodiálisis.
MétodoEstudio cuasiexperimental, no controlado, antes y después, con medidas repetidas de las variables respuesta a las 4, 8 y 12 semanas, después de participar en una intervención educativa a nivel hospitalario y de ejercicio físico intradiálisis. Se desarrolló en la Unidad de Nefrología del Consorcio.
Hospitalario de Vic, entre setiembre y diciembre de 2014. Se evaluó el bienestar de los pacientes, capacidad funcional y conocimientos. Instrumentos de valoración: indicadores de resultados de enfermería NOC, índice de Barthel, escala FAC de Holden, Timed Get Up and Go test y escala de Daniels.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 68 (80%) pacientes y finalizaron 58 (85,3%) de los cuales el 62,1% eran hombres y una media de edad de 70,16±13,5 años. Después de 12 semanas, los pacientes presentaron mejores puntuaciones de bienestar personal (2,33±1,2; 3,88±0,8), más autonomía para realizar las actividades de la vida diaria (Barthel: 92,8±12,8; 93,5±13,9), más fuerza muscular (escala de Daniels: 3,81±0,7; 4,19±0,6) y andaban más ligeros (Get Up and Go test: 14,98±8,5; 15,65±10,5). Todas las diferencias de las puntuaciones fueron estadísticamente significativas (p<0,05), excepto el índice de Barthel.
ConclusionesLa intervención educativa y de ejercicios físicos activos desarrollada en el ámbito hospitalario mejora el bienestar personal, el grado de conocimiento y la capacidad funcional de los pacientes en hemodiálisis.