The increase in penicillin susceptibility among Staphylococcus aureus (SA-PenS) might have therapeutic relevance. We aimed to study the current situation in our environment.
Material and methodsOver a 2.5 years period, all SA isolates from bacteraemia were analysed. For all isolates, antimicrobial susceptibility profile, beta-lactam resistance genes (blaZ, mecA) and Panton-Valentine leucocidine encoding-genes were studied. For SA-PenS-blaZnegative isolates, spa-type, MLST and the presence of other resistance genes were studied.
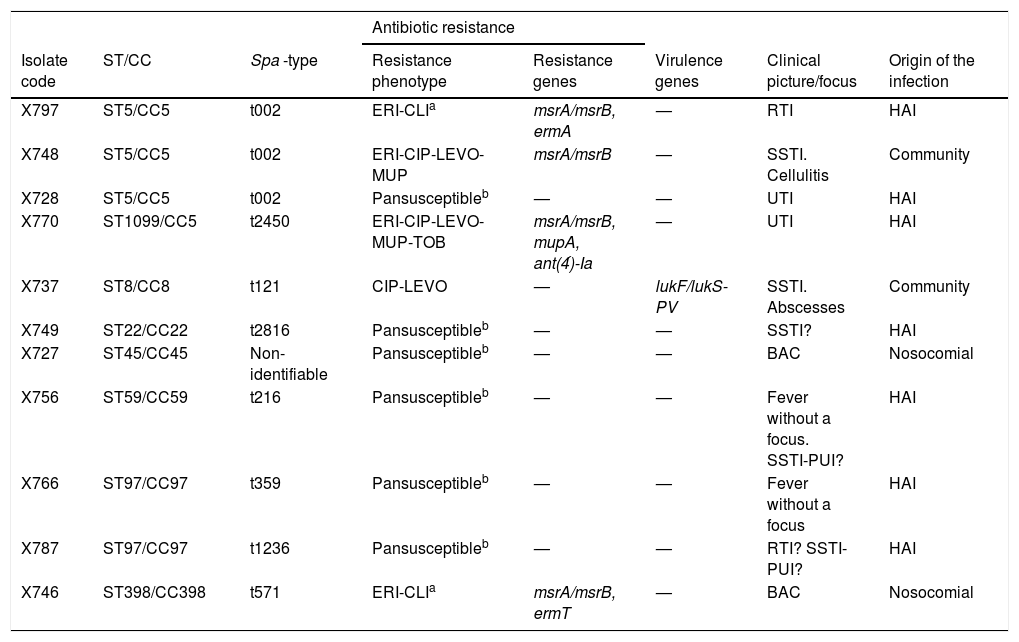
ResultsAmong 84 patients with SA bacteraemia (35.7% MRSA and 64.3% MSSA), 77 were analysed; 22.2% of MSSA isolates were PenS and blaZnegative (Pen-MIC ≤0.03 µg/mL) corresponding to 14.3% of the total SA. In MSSA-PenS-blaZnegative isolates, eight spa-types corresponding to seven clonal complexes were detected.
ConclusionA high prevalence of MRSA/SA and MSSA-PenS-blaZnegative/MSSA was detected in blood cultures. Pen-MIC ≤0,3 µg/mL corresponded to MSSA-PenS-blaZnegative. This situation raises therapeutic options which should be further evaluated in larger studies and clinical trials.
El aumento de la sensibilidad a penicilina en Staphylococcus aureus (SA-PenS) podría tener relevancia terapéutica. Pretendemos conocer esta situación en nuestro medio.
Material y métodosSe analizaron bacteriemias por SA durante 2,5 años (2015–2017). Estudiamos la sensibilidad a antimicrobianos, genes de resistencia a beta-lactámicos (blaZ, mecA) y presencia de leucocidina de Panton-Valentine. En aislados SA-PenS-blaZnegativo se determinó el tipo de spa, MLST y genes de resistencia a antimicrobianos no-beta-lactámicos.
ResultadosHubo 84 pacientes con bacteriemia por SA (35,7% SARM y 64,3% SASM), se analizaron 77. El 22% de los SASM estudiados (n = 11) fueron PenS- blaZnegativo (CMI-Pen ≤0,3 µg/mL), correspondiendo a 14,3% del total de SA. En SASM-PenS-blaZnegativo se detectaron ocho tipos de spa asociados a siete complejos clonales.
ConclusiónDetectamos alta prevalencia de SARM/SA y de SASM-PenS-blaZnegativo/SASM en hemocultivos. Una CMI-Pen ≤0,3 µg/mL se correspondió con SASM-PenS-blaZnegativo. Esta situación plantea opciones terapéuticas que deberán reevaluarse con estudios más amplios y ensayos clínicos.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí
Para realizar los cursos formativos
La actividad estará abierta para socios de la SEIMC. IMPORTANTE, recuerde que requiere registro previo gratuito. Empezar aquí