The early detection of cervical cancer requires the implementation of molecular screening programmes for human papillomavirus (HPV). However, there are discrepancies in the optimization of screening protocols. The performance of 10 primary screening strategies based on molecular, cytological or combined techniques is now evaluated.
Material and MethodsA blind, prospective, and interventional study was designed in 1.977 35-year-old women. The molecular determination was carried out by the Cobas 4800 HPV platform. Cytological analysis were performed on the same samples without knowledge of the result of the molecular assay. All women in whom HPV-16/HPV-18 was detected or presented cytological alteration together with detection of other high-risk genotypes (HPVhr) were referred to colposcopy.
ResultsThe molecular assay detected the presence of HPVhr genotypes in 12.5% of the women, while only 8.1% of the cytologies were pathological. Among the patients referred to colposcopy, in 19.5% high-grade lesions were observed, being HPV-16 present in 65.3% of them. In six of these high-grade lesions (associated with HPV-16 in all cases), cytology was reported as normal. The follow-up one year later, of women with normal cytology and HPVhr detection a HSIL/CIN2+ lesion was detected (associated to HPV-33). In the comparative study with other strategies, the protocol called CRYGEN 16/18 yielded the best balance of sensitivity and specificity with the least referral to colposcopy.
ConclusionsPerforming molecular detection of HPVhr with partial first-line genotyping of at least HPV-16, with direct referral to colposcopy, increases the detection rate of HSIL/CIN2+ lesions.
La detección precoz del cáncer de cérvix requiere la implementación de programas de cribado del virus del papiloma humano (VPH). Sin embargo, existen discrepancias en la optimización de esas estrategias. Se evalúa el rendimiento de 10 protocolos basados en técnicas moleculares, citológicas o combinadas en cribado primario.
Material y MétodosSe diseña un estudio ciego, prospectivo e intervencionista en 1.977 mujeres de 35 años. La determinación molecular se realizó por la plataforma Cobas 4800 HPV. Los análisis citológicos se realizaron en las mismas muestras sin conocimiento del resultado molecular. Todas las mujeres en las que se detectaba VPH-16/VPH-18 o presentaban alteración citológica y detección de otros genotipos de alto riesgo (VPHar) eran derivadas a colposcopia.
ResultadosEl ensayo molecular detectó presencia de VPHar en 12,5% de las mujeres, mientras solo 8,1% de las citologías fueron patológicas. En 19,5% de las pacientes derivadas a colposcopia revelaron lesiones de alto grado, estando VPH-16 presente en el 65,3% de ellas. En seis de esas ocasiones (VPH-16 siempre presente), la citología había sido informada como normal. El seguimiento al año de las mujeres con citología normal y detección de VPHar, detectó una lesión HSIL/CIN2+ (asociada a VPH-33). En el estudio comparativo con otras estrategias, el protocolo denominado CRYGEN 16/18 rindió el mejor equilibrio de sensibilidad y especificidad con la menor derivación a colposcopia.
ConclusionesLa realización de detección molecular de VPH con genotipado parcial en primera línea, al menos VPH-16, con derivación directa a colposcopia, aumenta la tasa de detección de lesiones HSIL/CIN2+.
For several years, the World Health Organization (WHO) has been recommending the implementation of screening programmes for different types of cancer, such as breast, colorectal and cervical cancer. In 2013, the WHO identified cervical cancer as a priority action in its Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases1. Cervical cancer (CC) is caused by persistent infection with the so-called high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) genotypes. Four large randomised cohort studies indicate that screening based on molecular testing for HPV detection provides 60%–70% more protection against CC than cytological screening and also allows screening intervals to be safely extended2. For this reason, the USA, Australian and European guidelines3 recommend the implementation of the molecular detection of HPV for uterine CC screening4. In 2019, the Spanish Ministry of Health modified the portfolio of services related to CC screening, incorporating molecular detection as a first-line strategy (https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2019/04/27/pdfs/BOE-A-2019-6277.pdf).
Although HPV tests generally detect a set of 14 hrHPV genotypes, only 2 of them, the HPV-16 and HPV-18 genotypes, are recognised as being responsible for 70% of cases of uterine CC5. hrHPV6 tests with separate detection of HPV-16 and HPV-18 would be a more sensitive and efficient strategy for the detection of uterine CC than methods based solely on cytology2. This multicentre, prospective, blinded, interventional study sets out to demonstrate the advantages of a new protocol for CC screening in Spain based on the molecular detection of HPV with first-line genotyping for HPV-16/18 instead of cytology and to compare its performance against other screening strategies.
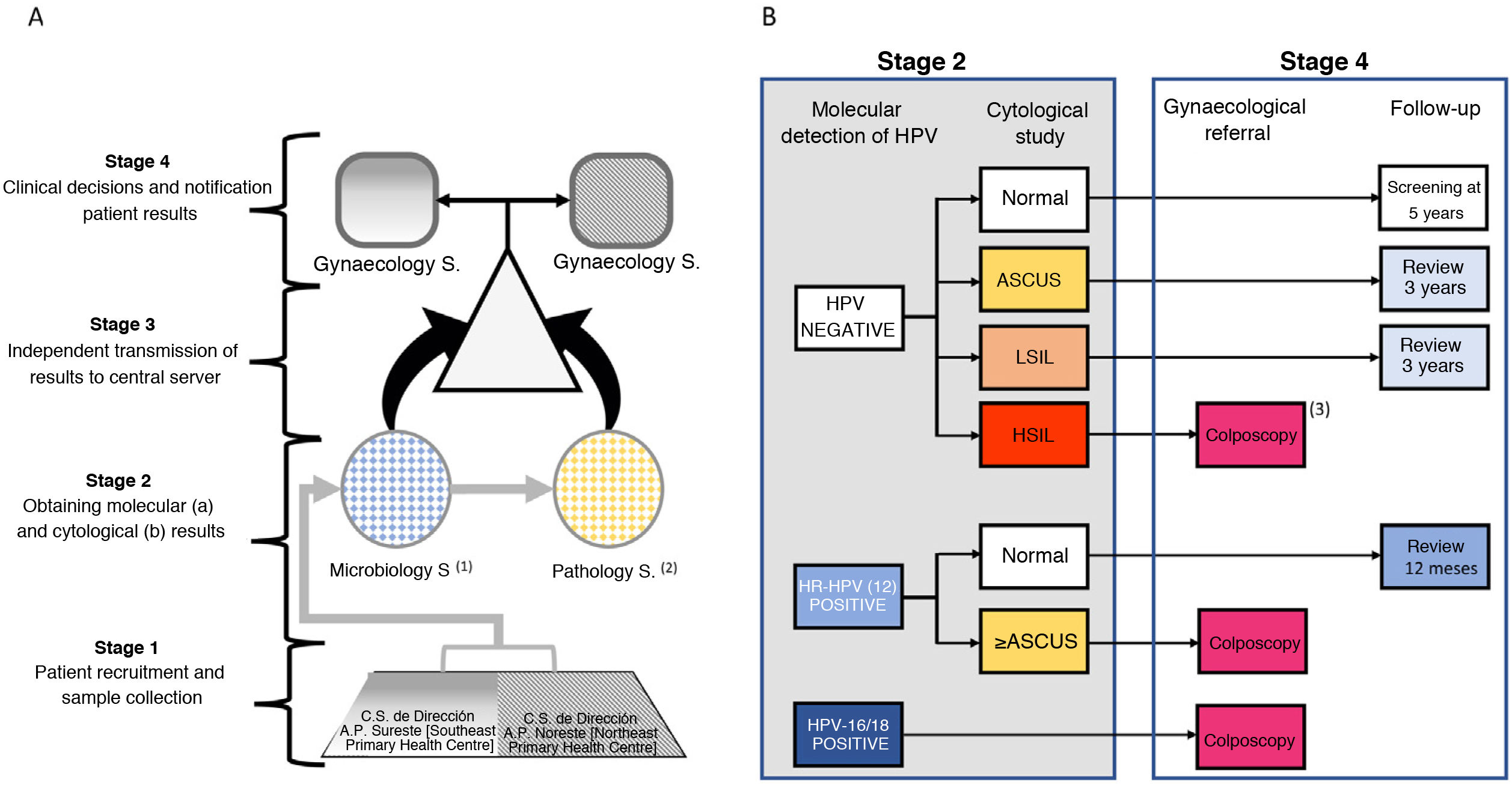
Materials and methodsWorkflow and study populationAccording to the census extracted from the official Community of Madrid CIBELES database, the target population of 35-year-old women residing in 2 health areas of the Community of Madrid during the study period was 11.864 women. The selection of this age group was conditioned by the fact that it was the first age group for which primary HPV screening by molecular detection was recommended in most international guidelines. All the women were invited to participate by means of a letter accompanied by an informative pamphlet on HPV infection and were subsequently contacted by telephone for an appointment. Those who decided to participate, after signing an informed consent, had a single sample taken for HPV molecular detection and the corresponding cytological study, which was collected by obstetricians using a Rovers Medical Devices BV cervical brush. The sample was placed in ThinPrep liquid fixative medium (Hologic, Bedford, MA) for storage, transport and analysis. The encrypted samples were sent to the Microbiology Service of the Hospital Ramón y Cajal. After the study for the molecular detection of the virus had been completed, the samples were sent to the Pathology Service of the Hospital Clínico de Madrid. Both laboratories independently sent the results to a central server without having access to the results obtained by each laboratory. The gynaecology services at the Hospital Clínico and the Hospital Infanta Leonor reported the results and clinical decisions regarding immediate action or scheduled follow-up for positive cases to the participants. The workflow is presented in Fig. 1A. The study was conducted between June 2017 and September 2018. The reference protocol in this study, CRYGEN 16/18, is a screening strategy based on molecular detection with partial genotyping in the primary screening of HPV. The protocol proposes a colposcopy referral for all women with: 1) positive HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 regardless of cytological result; 2) negative hrHPV with HSIL (high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion) cytology; 3) positive hrHPV not 16/18, with cytology≥atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS). If in the cytology is normal in the last two, follow-up after one year is indicated (Fig. 1B).
A) Proposed workflow. B) Reference protocol algorithm for this study, CRYGEN 16/18, for primary HPV screening in cervical cancer.
a The molecular analysis was performed at the Microbiology Service of the Hospital Ramón y Cajal.
b The cytological study was carried out at the Pathology Service of the Hospital Clínico San Carlos.
c The analysis of the biopsies of the patients referred for colposcopy was carried out at the Pathology Services of the Hospital Clínico San Carlos and the Hospital Infanta Leonor.
The protocol was approved by the ethics committees of the Hospital Clínico San Carlos and the Hospital Ramón y Cajal.
Molecular detection of human papillomavirus and cytological study of biological samples. Description of other strategiesThe presence of viral DNA was evaluated using the Roche cobas 4800 Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Test® (Roche Molecular Diagnostics), following the manufacturer's recommendations. This is a qualitative molecular method for the detection of 14 genotypes of hrHPV, permitting the specific differentiation of the HPV-16 and HPV-18 genotypes from the other 12 hrHPV genotypes (HPV-31, -33, -35, -39, -45, -51, -52, -56, -58, -59, -66 and -68) which are detected but not differentiated. Once the molecular study had been carried out, the samples were stored at 4°C until use for the cytological study in ThinPrep® medium. The reading was conducted using the Bethesda 2001 nomenclature7. The presence of ≥ASCUS was considered pathological. In a subsequent phase, the biopsies, performed on patients referred for colposcopy, were studied in the pathology services of the Hospital Clínico San Carlos and the Hospital Infanta Leonor. After formalin fixation and paraffin embedding, sections of 4μm were cut and stained with haematoxylin and eosin for study using Richart's CIN terminology and the LAST terminology8 (Fig. 1). Finally, for the follow-up of women in whom any of the 12 high-risk HPV genotypes (not-16/not-18) were detected with normal cytology, the women were invited to repeat the molecular test at 12 months, following the same pattern as at the first appointment. Similarly, women with a negative HPV test and ASCUS were referred for follow-up at 3 years. In women who presented hrHPV (not HPV-16, not HPV-18) after one year and high-grade lesions, the genotype would be identified using the Linear CLART HPV system (Genomica, SAU, Madrid, Spain).
The design of this protocol permits an a posteriori comparative analysis of the efficacy and optimisation of resources of the CRYGEN 16/18 strategy compared to 9 other strategies based on cytology (2 algorithms), cotest (3 algorithms) or molecular diagnosis (4 algorithms) in primary screening (a detailed description is provided further below). Strategy A. Cytology as primary screening: 1) referral to colposcopy of all pathological cytology (≥ASCUS); 2) referral to colposcopy for pathological cytology≥LSIL [low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions] or ASCUS+positive hrHPV reflex molecular detection. Strategy B. It groups the strategies based on cotest: 3) referral to colposcopy for any pathologic cytology (≥ASCUS) or positive hrHPV molecular detection; 4) referral to colposcopy for any pathological cytology (≥ASCUS) and positive hrHPVmolecular detection; 5) referral to colposcopy for any pathological cytology (≥LSIL) or positive HPV molecular detection for high-risk HPV-16/HPV-18 or ASCUS genotypes+positive HPV reflex molecular detection. Strategy C. Strategies based on molecular detection as primary screening: 6) referral to colposcopy for any molecular detection of HPV; 7) referral to colposcopy for any molecular detection of HPV with reflex pathological cytology (≥ASCUS); 8) referral to colposcopy for molecular detection of only HPV-16/HPV-18 genotypes: and 9) referral to colposcopy for molecular detection of only HPV-16/HPV-18 genotypes or molecular detection of other high-risk genotypes with pathological reflex cytology (>LSIL).
The variables analysed in the comparative study were, in addition to sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value, the number of patients referred for colposcopies, the number of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) detected or the number of cytologies or molecular detections avoided from each analysed algorithm.
Statistical analysisGiven the categorical nature of the variables, their description is conducted by counting the frequencies and converting them into percentages based on the valid n of each variable. The Chi square test of independence was used for the intersection between two categorical variables. The aforementioned test is used together with Cramér’s V as a measure of the association between the variables, whose squared value is equivalent to the effect size expressed in the classic R2 scale. Similarly, binary logistic regression was used as the best fit method to estimate OR. The SPSS program version 21 was used for all analyses.
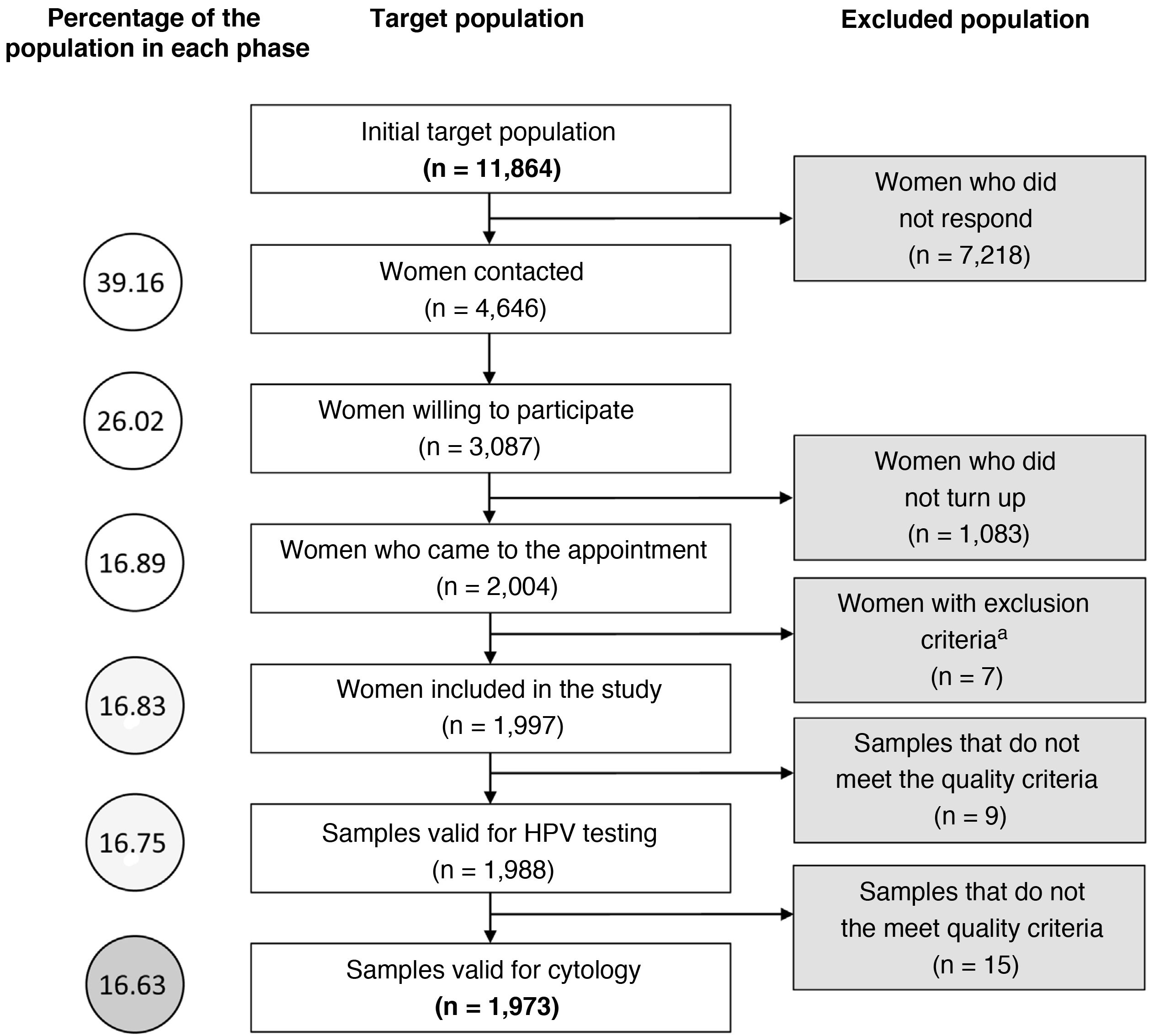
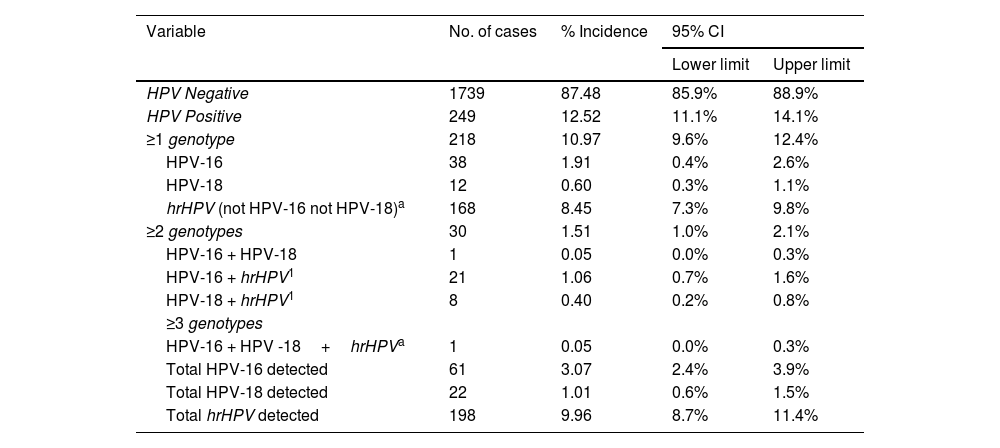
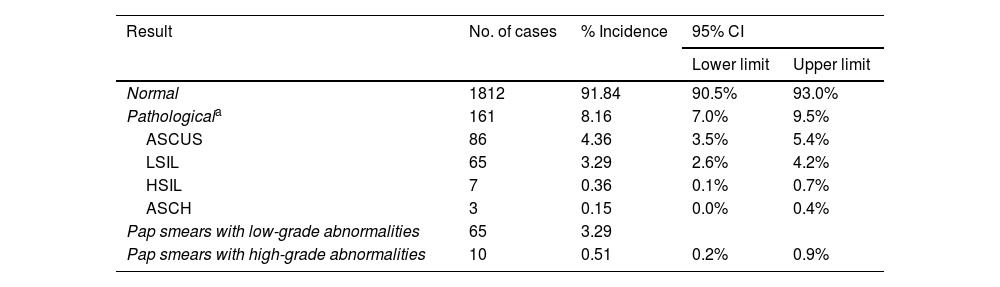
ResultsMolecular detection of human papillomavirus and cytological study. Correlation between both approachesThe initial population size was 11.864 women, although the study was successfully completed in only 16.6%. Fig. 2 describes the different stages of the process at which the population was lost. Of the 1988 valid samples, a positive amplification signal was detected for some hrHPV genotypes in 249 (12.5%) (CI 11.1 %–14.1 %). The HPV-16 genotype was detected in 61 samples (3.1%) and was the only genotype detected in 38 cases (1.9%). HPV-18 was identified in 22 samples (1.1%) and was the only agent on 12 occasions (0.60%). The distribution of cases in which hrHPV was detected, as well as whether they were mono- or coinfections, is shown in Table 1. Of the 1.973 samples finally included in the cytology study, 161 (8.1%, CI: 7%–9.5%) were reported as abnormal. HSIL was reported in 7 cases (0.36%) and ASCH in 3 (0.15%). The distribution of results of the cytological reading is shown in Table 2.
Molecular detection of high-risk HPV genotypes detected (n=1988).
| Variable | No. of cases | % Incidence | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower limit | Upper limit | |||
| HPV Negative | 1739 | 87.48 | 85.9% | 88.9% |
| HPV Positive | 249 | 12.52 | 11.1% | 14.1% |
| ≥1 genotype | 218 | 10.97 | 9.6% | 12.4% |
| HPV-16 | 38 | 1.91 | 0.4% | 2.6% |
| HPV-18 | 12 | 0.60 | 0.3% | 1.1% |
| hrHPV (not HPV-16 not HPV-18)a | 168 | 8.45 | 7.3% | 9.8% |
| ≥2 genotypes | 30 | 1.51 | 1.0% | 2.1% |
| HPV-16 + HPV-18 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.0% | 0.3% |
| HPV-16 + hrHPV1 | 21 | 1.06 | 0.7% | 1.6% |
| HPV-18 + hrHPV1 | 8 | 0.40 | 0.2% | 0.8% |
| ≥3 genotypes | ||||
| HPV-16 + HPV -18+hrHPVa | 1 | 0.05 | 0.0% | 0.3% |
| Total HPV-16 detected | 61 | 3.07 | 2.4% | 3.9% |
| Total HPV-18 detected | 22 | 1.01 | 0.6% | 1.5% |
| Total hrHPV detected | 198 | 9.96 | 8.7% | 11.4% |
CI: confidence interval; HPV: human papilloma virus.
Cytological evaluation of the samples included in the study (n=1973).
| Result | No. of cases | % Incidence | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower limit | Upper limit | |||
| Normal | 1812 | 91.84 | 90.5% | 93.0% |
| Pathologicala | 161 | 8.16 | 7.0% | 9.5% |
| ASCUS | 86 | 4.36 | 3.5% | 5.4% |
| LSIL | 65 | 3.29 | 2.6% | 4.2% |
| HSIL | 7 | 0.36 | 0.1% | 0.7% |
| ASCH | 3 | 0.15 | 0.0% | 0.4% |
| Pap smears with low-grade abnormalities | 65 | 3.29 | ||
| Pap smears with high-grade abnormalities | 10 | 0.51 | 0.2% | 0.9% |
ASCH: Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; HSIL: high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; CI: confidence interval; LSIL: low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.
In the correlation study between the positive/negative result of the HPV test and the normal/pathological cytological result, a significant relationship was observed (p<0.001) between the detection of HPV-16 and pathological cytology. The OR values in a univariate logistic regression show that the risk of presenting a high-grade cytology is 57 times more likely if the molecular study detects the presence of HPV-16. In contrast, no statistically significant association was observed between abnormal cytology and the presence of any other genotype (including HPV-18) (see Tables 1 and 2 in the Supplementary material).
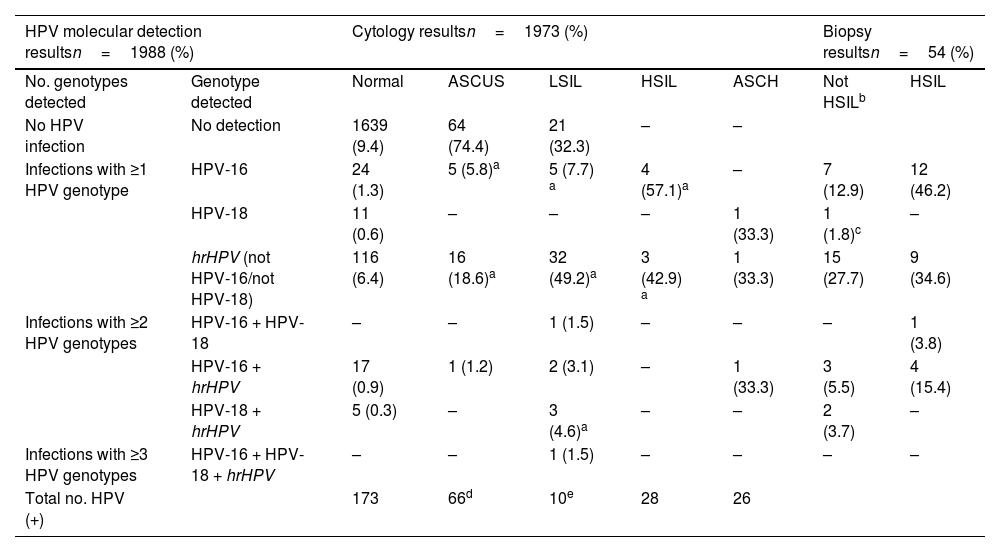
After the results obtained from molecular tests and cytological studies had been intersected, 133 women met the criteria to be referred for colposcopy following our algorithm (81 women for HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 detection and 52 women for hrHPV detection with cytological abnormalities [≥ASCUS]). There were no reports of HPV-negative high-grade cytology (Table 3). Of the 133 colposcopies performed, some degree of abnormality was observed in 54 patients (40.6% of referrals). These lesions were 26 HSIL/CIN2+ and 28 LSIL. One case was classified as micropapillary hyperplasia. In the 26 HSIL/CIN2+ lesions, HPV-16 was involved on 17 occasions, representing 65.4%. The remaining 9 high-grade lesions were related to abnormal cytology and the detection of other hrHPV genotypes (Table 3). One noteworthy finding is that 6 of these 26 patients with HSIL/CIN2+ lesions were referred for colposcopy due to HPV-16 molecular detection even although the cytological report was normal. This reveals that 23% of the high-grade lesions could not have been detected if primary cytological screening was considered or cytology as a triage of molecular detections of HPV-16. In addition, 12 of the 26 high-grade lesions had cytology reported as ASCUS or LSIL and were referred for colposcopy because hrHPV genotypes had been detected (see Table 3 in the Supplementary material).
Correlation of the molecular detection of HPV with partial genotyping, with the results observed by abnormal cytology, differentiating between the different grades of lesions and the results of the biopsies of patients referred to colposcopy.
| HPV molecular detection resultsn=1988 (%) | Cytology resultsn=1973 (%) | Biopsy resultsn=54 (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. genotypes detected | Genotype detected | Normal | ASCUS | LSIL | HSIL | ASCH | Not HSILb | HSIL |
| No HPV infection | No detection | 1639 (9.4) | 64 (74.4) | 21 (32.3) | – | – | ||
| Infections with ≥1 HPV genotype | HPV-16 | 24 (1.3) | 5 (5.8)a | 5 (7.7) a | 4 (57.1)a | – | 7 (12.9) | 12 (46.2) |
| HPV-18 | 11 (0.6) | – | – | – | 1 (33.3) | 1 (1.8)c | – | |
| hrHPV (not HPV-16/not HPV-18) | 116 (6.4) | 16 (18.6)a | 32 (49.2)a | 3 (42.9) a | 1 (33.3) | 15 (27.7) | 9 (34.6) | |
| Infections with ≥2 HPV genotypes | HPV-16 + HPV-18 | – | – | 1 (1.5) | – | – | – | 1 (3.8) |
| HPV-16 + hrHPV | 17 (0.9) | 1 (1.2) | 2 (3.1) | – | 1 (33.3) | 3 (5.5) | 4 (15.4) | |
| HPV-18 + hrHPV | 5 (0.3) | – | 3 (4.6)a | – | – | 2 (3.7) | – | |
| Infections with ≥3 HPV genotypes | HPV-16 + HPV-18 + hrHPV | – | – | 1 (1.5) | – | – | – | – |
| Total no. HPV (+) | 173 | 66d | 10e | 28 | 26 | |||
hrHPV: high-risk human papilloma virus.
The 116 women with molecular detection of any of the 12 hrHPV genotypes without HPV-16/18 with normal cytology were instructed to repeat the molecular and cytological studies at 12 months. A total of 83 women turned up (72%), meaning that 28% were lost to follow-up. In 37/83 women, a positive PCR continued to be detected for some of the 12 hrHPV genotypes (44.5%). The cytological study was performed for the 37 patients who maintained positive PCR: 22 of them presented normal cytology (59.4%), low-grade abnormalities were reported (ASCUS and LSIL) in 14 (38%) and a high-grade lesion (HSIL) was detected in 1 case (a pregnant woman), with the genotype involved being HPV-33. Thirty-seven (37) women were referred for colposcopy to complete the study. The colposcopy was normal in 33/37 cases (89.1%). In 3 cases, the diagnosis of LSIL/CIN1 was confirmed in the directed biopsy, as well as the only case of HSIL/CIN2+.
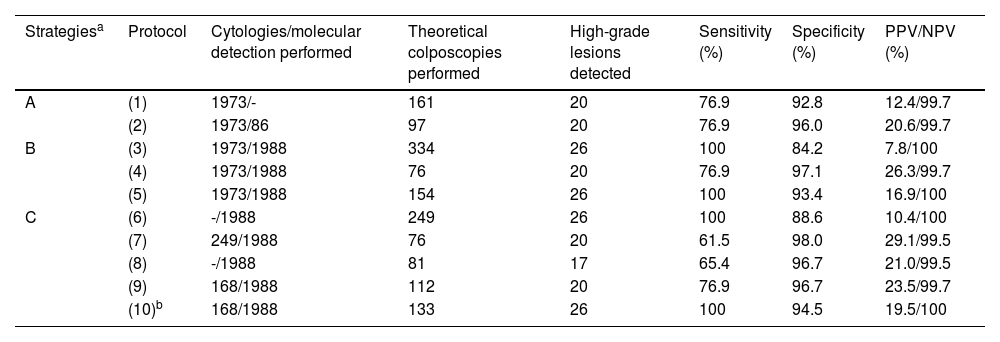
Comparative analysis of the CRYGEN 16/18 strategy with 9 other strategiesIn accordance with the criteria described in material and methods, of the 9 protocols compared with CRYGEN 16/18, only 3 turned out to be non-inferior when detecting the 26 high-grade lesions diagnosed by it. These protocols correspond to cotest strategies (protocols 3 and 5) and another to primary molecular screening (protocol 6) (see Table 4 for a more detailed description). However, these 3 protocols would do so with a higher rate of referral to colposcopy or the performance of a greater number of cytologies. Protocols based on cytology as primary screening would miss 23% of the high-grade lesions.
Comparative analysis of the different population screening strategies used for cervical cancer.
| Strategiesa | Protocol | Cytologies/molecular detection performed | Theoretical colposcopies performed | High-grade lesions detected | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV/NPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | (1) | 1973/- | 161 | 20 | 76.9 | 92.8 | 12.4/99.7 |
| (2) | 1973/86 | 97 | 20 | 76.9 | 96.0 | 20.6/99.7 | |
| B | (3) | 1973/1988 | 334 | 26 | 100 | 84.2 | 7.8/100 |
| (4) | 1973/1988 | 76 | 20 | 76.9 | 97.1 | 26.3/99.7 | |
| (5) | 1973/1988 | 154 | 26 | 100 | 93.4 | 16.9/100 | |
| C | (6) | -/1988 | 249 | 26 | 100 | 88.6 | 10.4/100 |
| (7) | 249/1988 | 76 | 20 | 61.5 | 98.0 | 29.1/99.5 | |
| (8) | -/1988 | 81 | 17 | 65.4 | 96.7 | 21.0/99.5 | |
| (9) | 168/1988 | 112 | 20 | 76.9 | 96.7 | 23.5/99.7 | |
| (10)b | 168/1988 | 133 | 26 | 100 | 94.5 | 19.5/100 |
The (–) symbol indicates “not relevant”, as it is not provided for in the strategy.
NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value.
aStrategy A: groups strategies based on cytology as primary screening. Strategy B: groups strategies based on cotesting (simultaneous and independent detection of cytology and molecular detection). Strategy C: strategies based on molecular detection as primary screening (see material and methods section where the description of each algorithm is detailed).
More than 5 years ago, the WHO9 and the European Guidelines for Quality Assurance in Cervical Cancer Screening3 proposed the molecular approach as the primary strategy for the early detection of precancerous cells. However, despite these evidence-based recommendations, implementation among the European Union member states is highly variable. The CRYGEN 16/18 algorithm has made it possible, albeit with certain limitations, to compare different population screening strategies proposed or implemented in neighbouring countries such as the Netherlands, Germany or Finland, which have implemented the different models compared in this work10.
In this study, only 16.63% of the target population completed the proposed screening protocol. In addition, 28% of the population was lost to follow-up at one year. These data reveal some of the social difficulties regarding the adequate implementation of these screening programmes. In this population, the prevalence of hrHPV infection in 35-year-old women was 12.5%, similar to the findings of the ATHENA study (11.6%)11, the CLEOPATRE study (12.8% in Madrid and 12.2% nationwide)12 and in the population study carried out in the Canary Islands (11.1%)13. When prevalence by genotypes is compared, similar prevalences were observed for HPV-16/HPV-18, 3.3% in ATHENA, 2.9%–0.5% in CLEOPATRE and 3.2%–1.1% in CRYGEN 16/18, respectively. However, in this study, which involved both an epidemiological and an intervention study, the detection of HPV-16 was seen to increase the risk of presenting a cytology with high-grade lesions 57-fold. Although such a strong association was not found between other genotypes, this was due to the non-discrimination of the screening system between the other 12 hrHPV genotypes. Therefore, the fact that another genotype could also have a significant association with high-grade lesions cannot be excluded.
On the other hand, the cytological results detected only 8.1% of pathological cytologies (≥ASCUS), with high-grade lesions representing 0.5% (0.36 HSIL and 0.15% ASCH), which coincides with other series14–16. In no case were high-grade lesions with a negative result in the molecular test observed. On the contrary, the incidence of low-grade lesions was 7.7%, similar to the percentages reported by the AEPCC [Asociación Española de Patología Cervical y Colposcopia (Spanish Association of Cervical Pathology and Colposcopy)], but higher than those reported in the Castile-León screening programme17. When the cytological data and molecular data were intersected, 83.1% of the results were negative for both techniques. If the techniques are compared, having any positive result, only in 30.5% of the cases did pathological cytology coincide with the detection of any hrHPV genotype (similar to the 29.7% reported in the ATHENA study). However, among the discrepant values, 6 cases of HPV-16 infections were detected, with a normal cytological report that resulted in high-grade lesions in the biopsy corresponding to the referral to colposcopy, which represented 23.07% of the total HSIL/CIN2+ lesions. This result confirms the greater sensitivity of the molecular techniques to be implemented as primary screening and even poses the question as to whether the cytological study in positive HPV samples should be replaced by other molecular biomarkers.
Among the 133 patients who were referred for colposcopy as per the protocol, 26 HSIL/CIN2+ lesions were detected, which means an incidence of 1.30% (26/1.988 women), values which are 10 times higher than the mean incidence estimated in Spain (0.13%)18, albeit without considering any age bracket. The HPV-16 genotype was detected in 17 of the 26 HSIL/CIN2+, which corresponds to 65.3% of all high-grade lesions, confirming that this genotype is by far the one with the highest risk, and therefore all screening protocols should at least include the specific identification of this genotype to increase the detection rate of high-grade lesions. This would guarantee a better risk stratification. In fact, the risk of HPV-16 was considerably higher than that of HPV-18, which was almost irrelevant in our series (one HSIL/CIN2+ case and associated with HPV-16). This finding is consistent with the reports by Monsonego et al.19
In the results of the 1-year follow-up of patients with infection by hrHPV not 16/18 with normal screening cytology, a high-grade lesion was detected histologically (2.7%), caused by HPV-33, coinciding with other similar studies in which high-grade lesions range between 2.5% and 3.9%, with HPV-33 being the most frequently identified genotype20. The results of this follow-up indicate that the proposed protocol strategy is safe, since only 1 out of 83 patients presented a high-grade lesion and there were no cases of invasive cancer.
The ideal strategy for CC screening would be the one that ensures maximum sensitivity combined with greater specificity to minimise false positives and thus avoid excessive referrals and overtreatment. When the different protocols are compared, the CRYGEN 16/18 protocol was the most balanced, since it detects the largest number of HSIL/CIN2+ lesions with a reasonable rate of referrals to colposcopy, acceptable in our setting, markedly reducing the number of cytological studies and yielding a very favourable ratio of tests necessary for each diagnosed lesion. This efficacy is consistent with the results reported by other groups21 and is an improvement upon the protocol proposed by the Ministry of Health, which does not provide for genotyping, as confirmed by our results, since 23% of HSIL/CIN2+ lesions were lost in the first round due to negative complementary screening cytology. The inclusion of a second round of molecular detection of hrHPV after one year in cases of hrHPV (not HPV-16, not HPV-18) with normal cytology may be a valid strategy, assuming a possible diagnostic delay of high-grade lesions (1/27 cases in our series), although the rate of referral to colposcopy is reduced22. It is also more efficient than strategies based on contesting23,24. The main limitation of the CRYGEN 16/18 study is the fact that a colposcopy was not performed systematically in all patients, an aspect that was included in the ATHENA study. Doing so would have made it possible to quantify the diagnostic rate for each proposed strategy accurately, as well as sensitivity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value. Since it was not performed, it can only be stated that the strategies that have detected the same number of HSIL/CIN2+ lesions as those found with CRYGEN 16/18 are not inferior, although it cannot be established whether they could be superior.
In conclusion, there are arguments that endorse the implementation of the HPV molecular detection test with partial genotyping in primary screening for CC screening due to its high clinical sensitivity and high negative predictive value, objectivity, low training requirements, reproducibility and high performance capacity. However, a risk stratification must be established to balance the population screening strategy (as established by the Ministry of Health and practically all screening guidelines) adequately. In this sense, the partial genotyping of at least HPV-16 increases the risk25, as was inferred from this work. In addition, the probability of clearance of the infection must be evaluated. Clearance is known to be high in young women26 (which is why molecular screening is not proposed in women <35 years), although even in our series, up to 55% of women with hrHPV (not HPV-16, not HPV-18) cleared the virus in one year, which will require this risk stratification to be progressively adjusted as new evidence emerges.
FundingThe CRYGEN 16/18 project was funded by Roche Diagnostics (Barcelona, Spain). The diagnostic company financed the consumable material, as well as grants for personnel other than the authors to carry out the work. It did not intervene in the analysis, interpretation or drafting of the data.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.