To explore the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with Aspergillus spp. isolation from respiratory samples, and to identify which factors may help us to distinguish between colonisation and infection.
MethodsA retrospective cohort study was performed. All patients with COPD and respiratory isolation of Aspergillus spp. over a 12-year period were included. Patients were assigned to 2 categories: colonisation and pulmonary aspergillosis (PA), which includes the different clinical forms of aspergillosis. A binary logistic regression model was performed to identify the predictive factors of PA.
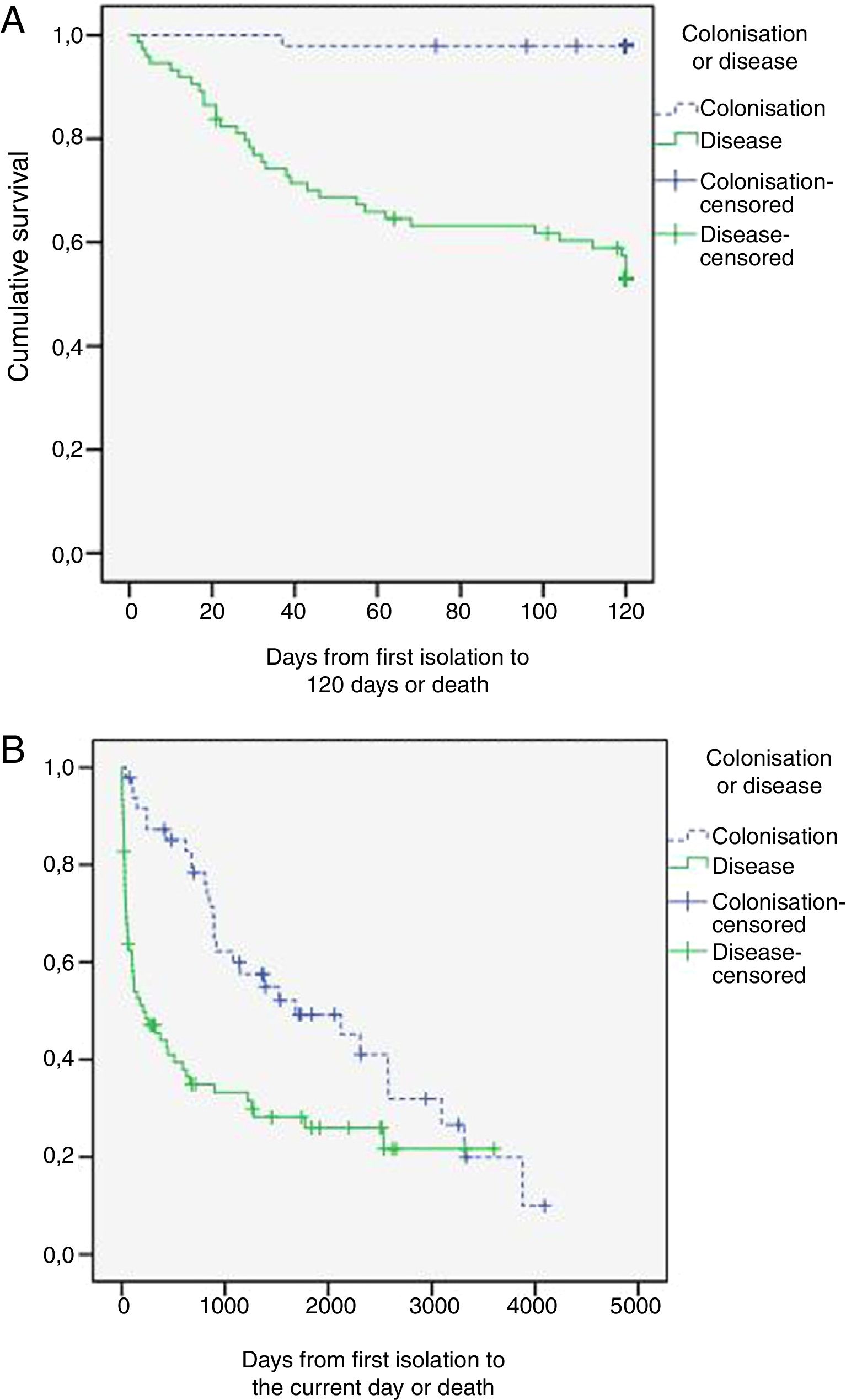
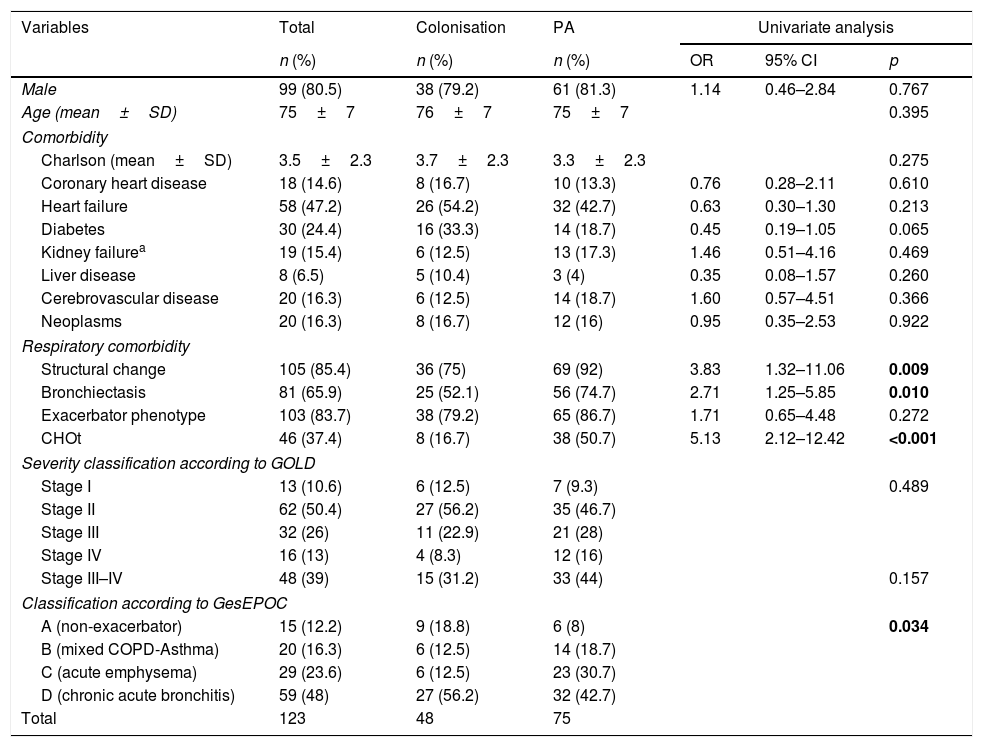
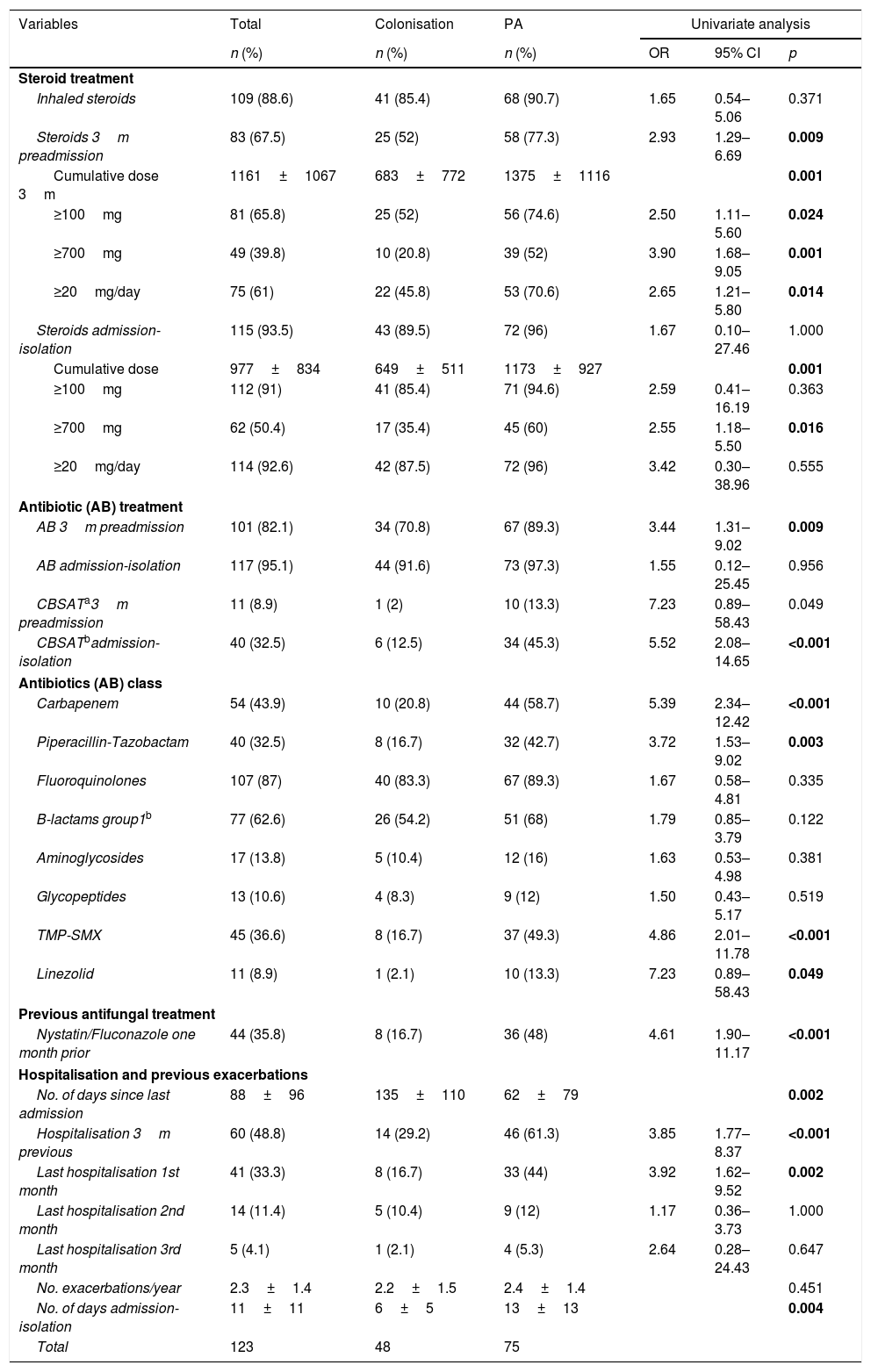
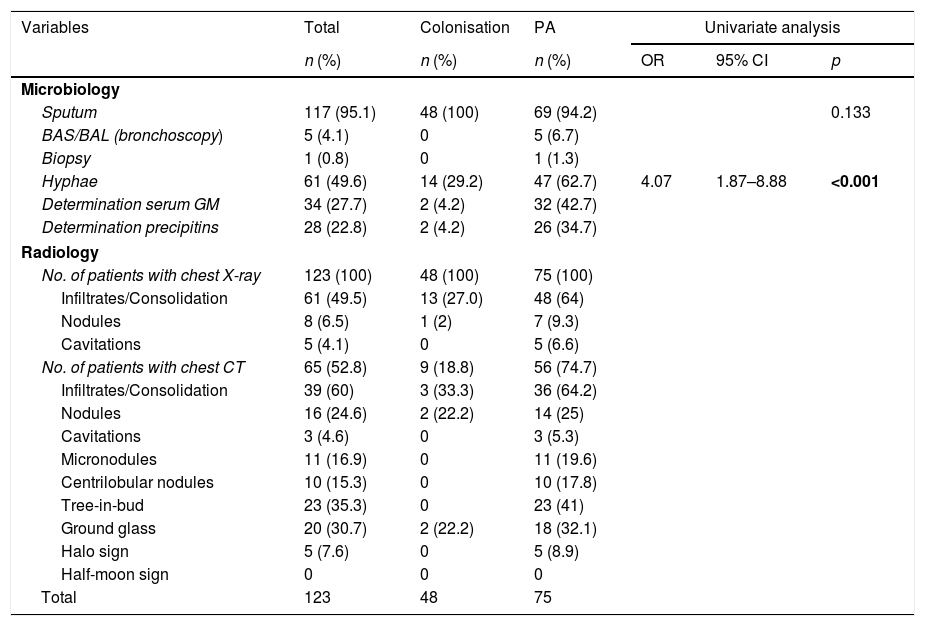
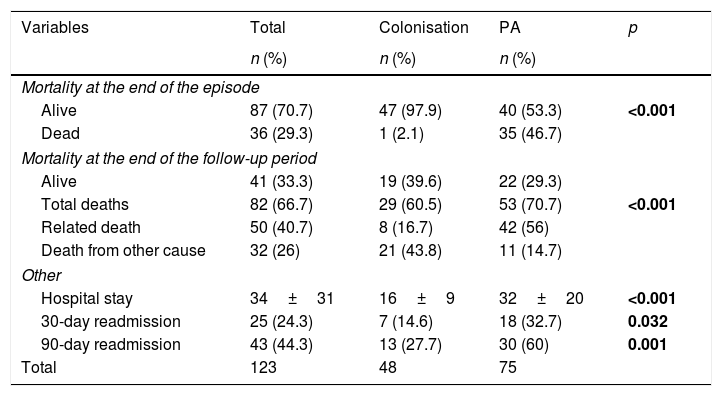
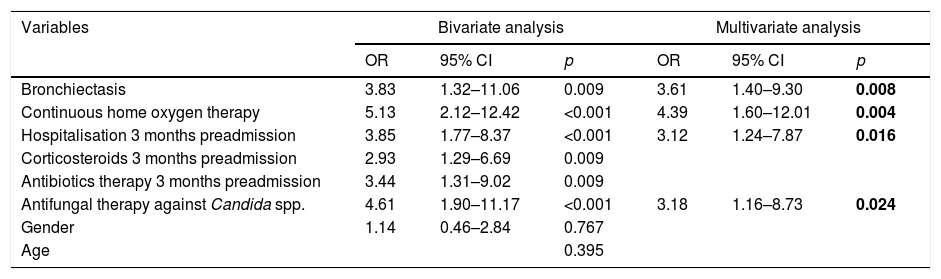
ResultsA total of 123 patients were included in the study: 48 (39.0%) with colonisation and 75 (61.0%) with PA: 68 with probable invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and 7 with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Spirometric stages of the GOLD classification were not correlated with a higher risk of PA. Four independent predictive factors of PA in COPD patients were identified: home oxygen therapy (OR: 4.39; 95% CI: 1.60–12.01; p=0.004), bronchiectasis (OR: 3.61; 95% CI: 1.40–9.30; p=0.008), hospital admission in the previous three months (OR: 3.12; 95% CI: 1.24–7.87; p=0.016) and antifungal therapy against Candida spp. in the previous month (OR: 3.18; 95% CI: 1.16–8.73; p=0.024).
ConclusionsContinuous home oxygen therapy, bronchiectasis, hospital admission in the previous three months and administration of antifungal medication against Candida spp. in the previous month were associated with a higher risk of pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with COPD.
Conocer las características clínicas y epidemiológicas de los pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) y aislamiento de especies de Aspergillus en muestra respiratoria e identificar factores que nos ayuden a diferenciar entre colonización e infección.
MétodosEstudio de cohortes retrospectivo en el que se incluyeron todos los pacientes con EPOC y aislamiento de Aspergillus spp. en muestra respiratoria durante un periodo de 12 años. Se asignaron los pacientes a 2 categorías: colonización y aspergilosis pulmonar (AP), que incluye las diferentes formas de presentación clínica. Se aplicó un modelo de regresión logística binaria para identificar los factores predictores de desarrollo de AP.
ResultadosUn total de 123 pacientes fueron incluidos en el estudio: 48 (39%) colonizados y 75 (61%) con AP: 68 con AP invasiva probable y 7 con AP crónica. No hubo correlación entre el riesgo de AP y los estadios espirométricos de la clasificación GOLD. Se identificaron como factores predictores independientes de AP en pacientes con EPOC la oxigenoterapia domiciliaria (OR: 4,39; IC 95%: 1,60-12,01; p=0,004), las bronquiectasias (OR: 3,61; IC 95%: 1,40-9,30; p=0,008), la hospitalización en los 3 meses previos al ingreso (OR: 3,12; IC 95%: 1,24-7,87; p=0,016) y la terapia antifúngica frente a Candida spp. en el mes previo (OR: 3,18; IC 95%: 1,16-8,73; p=0,024).
ConclusionesLa oxigenoterapia continua domiciliaria, las bronquiectasias, la hospitalización en los 3 meses previos al ingreso y la utilización de terapia antifúngica frente a Candida spp. en el mes previo se asocian a mayor riesgo de AP en pacientes con EPOC.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí
Para realizar los cursos formativos
La actividad estará abierta para socios de la SEIMC. IMPORTANTE, recuerde que requiere registro previo gratuito. Empezar aquí