To analyze obesity, level of adherence to the Mediterranean diet, physical activity and body dissatisfaction in people aged 16–50 years in the Region of Murcia, Spain.
MethodDescriptive and cross-sectional study. A total of 85 people (58 men) aged 16–50 years (28.68 ± 8.846) from 3 sports centers with similar sociodemographic characteristics participated in the study. Anthropometric values were recorded. They were tested for adherence to the Mediterranean diet, International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) and test for dissatisfaction with their body (BSQ) and it was statistically related.
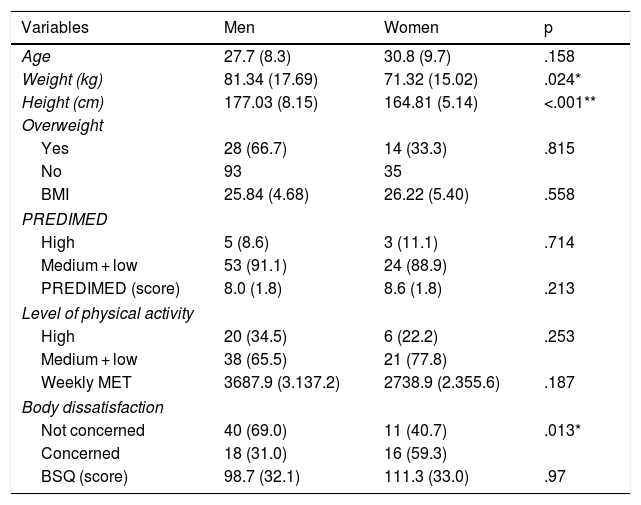
ResultsIt can be seen that the level of physical activity of both men and women is low, according to the IPAQ questionnaire, the men presented a METs/min per week of 3687.9 (DT = 3137.2) significantly higher than women’s.
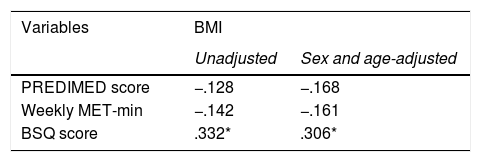
In body dissatisfaction we see that women’s concern with their bodies (59.3%) is greater than men’s (31%), with a statistically significant difference (p = 0.013). Eating habits and BMI do not have statistically significant differences according to sex.
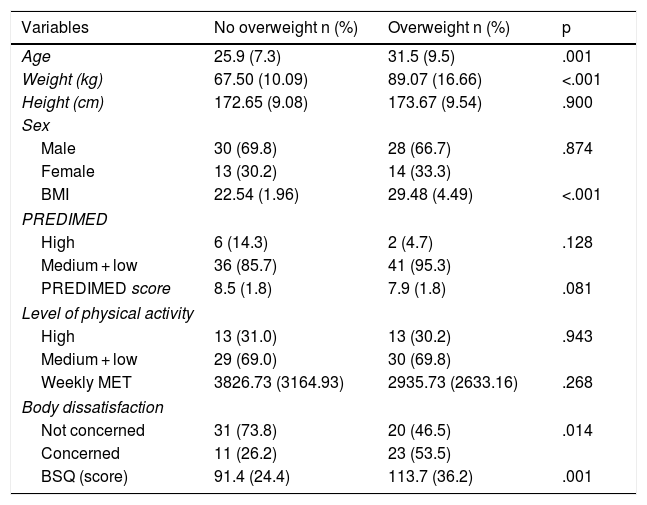
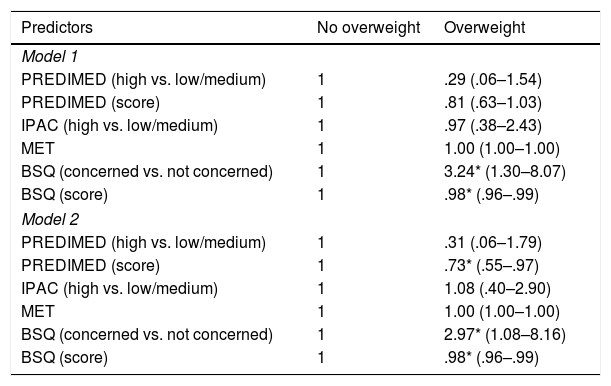
When applying the Mediterranean diet adherence test, it is observed that 95.3% of those with weight overload have a medium or low score, and only 4.7% have a discharge score (p = 0.128).
Those with weight overload have a score of 2935.73 MET/min per week (DT = 2633.16) and those without weight overload have a value of 3826.73 (DT = 3164.93, p = 0.268). There are significant differences regarding the values of body dissatisfaction. The level of concern of those with weight overload is 53.5%, compared to those without weight overload who have a level of concern of 26.2% (p = 0.014).
ConclusionsWeight overload is associated with body dissatisfaction and a low score in the test of adherence to the Mediterranean diet in people aged 16–50 years. The concern about body image in women was 59.3%.
Analizar la obesidad, adherencia a la dieta mediterránea, actividad física e insatisfacción corporal en personas de 16 a 50 años de la Región de Murcia.
MetodoEstudio descriptivo y transversal. Se incluyó a 85 personas (58 hombres) de 16 a 50 años de 3 centros deportivos con características sociodemográficas homogéneas. Se registraron los valores antropométricos. Posteriormente se les pasó un test de adherencia a la dieta mediterránea, el cuestionario internacional de actividad física (IPAQ) y el test de insatisfacción con su cuerpo (BSQ) y se relacionaron estadísticamente.
ResultadosSe puede observar que el nivel de actividad física tanto de hombres como de mujeres es bajo, según el cuestionario IPAQ. Los hombres presentaron un MET/min semanales de 3.687,9 (DE = 3.137,2) significativamente superior al de las mujeres.
En la insatisfacción corporal vemos que la preocupación de las mujeres con su cuerpo, 59,3%, es mayor que la que tienen los hombres, 31%, con diferencia estadísticamente significativa (p = 0,013). Los hábitos alimenticios y el IMC no tienen diferencias significativamente estadísticas en función del sexo.
Al aplicar el test de adherencia a la dieta mediterránea se observa que el 95,3% de los que tienen sobrecarga ponderal tiene una puntuación media/baja, y solo el 4,7% tiene una puntuación alta (p = 0,128). La puntuación de los que tienen sobrecarga ponderal tienen es de 2.935,73 MET/min semanales (DE = 2.633,16) y la de los que no tienen sobrecarga ponderal es de 3.826,73 (DE = 3.164,93; p = 0,268). Hay diferencias significativas con respecto a los valores de insatisfacción corporal. El nivel de preocupación de los que tienen sobrecarga ponderal es de 53,5%, respecto a los que no la tienen, cuyo nivel de preocupación es del 26,2% (p = 0,014).
ConclusionesLa sobrecarga ponderal se asocia con una insatisfacción corporal y una baja puntuación en el test de adherencia a la dieta mediterránea en personas de 16 a 50 años. La preocupación por la imagen corporal en las mujeres fue del 59,3%.