Excess weight is a major health problem. Aims of this study were to determine the prevalence rates of overweight and obesity, and to compare their associations with cardiometabolic and renal risk factors between obese and non-obese populations, and between overweight and non-overweight populations.
MethodsCross-sectional observational study conducted in Primary Care. Population-based random sample: 6588 study subjects between 18 and 102 years of age (response rate: 66%). Crude and sex- and age-adjusted prevalence rates of overweight and obesity were calculated, and their associations with cardiometabolic and renal variables were assessed by bivariate and multivariate analysis.
ResultsThe age- and sex-adjusted prevalence rates of overweight and obesity were 36.0% (42.1% in men; 33.1% in women) and 25.0% (26.2% in men; 24.5% in women), respectively. These prevalences increased with age, and were higher in men than in women. Fifty-two percent (95%CI: 50.0–53.9) of the overweight population and 62.3% (95%CI: 60.1–64.5) of the obese population had a high or very high cardiovascular risk. Abdominal obesity, physical inactivity, prediabetes, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, and low HDL-C were independently associated with both entities. Furthermore, diabetes was independently associated with overweight and hypercholesterolemia with obesity.
ConclusionsThe prevalence of overweight and obesity was 61.0% (68.4% in men and 59.0% in women). More than half of the overweight population and nearly two-thirds of the obese population had a high cardiovascular risk. Hyperglycemia, physical inactivity, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, low HDL-C, and hypertriglyceridemia were independently associated with overweight and obesity.
El exceso de peso constituye un importante problema de salud. Los objetivos del estudio fueron determinar las tasas de prevalencia de sobrepeso y obesidad, y comparar sus asociaciones con factores de riesgo cardiometabólicos y renales entre las poblaciones con y sin obesidad, y entre las poblaciones con y sin sobrepeso.
MétodosEstudio observacional transversal realizado en Atención Primaria. Muestra aleatoria de base poblacional: 6.588 sujetos de estudio entre 18 y 102 años (tasa de respuesta: 66%). Se calcularon las prevalencias crudas y ajustadas por edad y sexo de sobrepeso y obesidad, y se evaluaron sus asociaciones con variables cardiometabólicas y renales mediante análisis bivariado y multivariado.
ResultadosLas prevalencias ajustadas por edad y sexo de sobrepeso y obesidad fueron 36,0% (42,1% en hombres; 33,1% en mujeres) y 25,0% (26,2% en hombres; 24,5% en mujeres), respectivamente. Estas prevalencias se incrementaban con la edad, y eran más elevadas en hombres que en mujeres. El 52,0% (IC95%: 50,0–53,9) de la población con sobrepeso y el 62,3% (IC95%: 60,1–64,5) de la población con obesidad tenían un riesgo cardiovascular alto o muy alto. Obesidad abdominal, inactividad física, prediabetes, hipertensión, hipertrigliceridemia, y el c-HDL bajo se asociaban independientemente con ambas entidades. Además, la diabetes se asociaba independientemente con sobrepeso y la hipercolesterolemia con obesidad.
ConclusionesLa prevalencia de sobrepeso y obesidad era del 61,0% (68,4% en hombres y 59,0% en mujeres). Más de la mitad de la población con sobrepeso y casi dos tercios de la población con obesidad tenían un riesgo cardiovascular elevado. Hiperglucemia, sedentarismo, hipertensión, hipercolesterolemia, c-HDL bajo e hipertrigliceridemia se asociaban independientemente con sobrepeso y obesidad.
Excess weight is a global health problem with significant healthcare, cultural and socioeconomic consequences. In 2013 it was estimated that overweight and obesity caused 3.4 million deaths, 4% of lives lost and 4% of disability-adjusted life years.1
In 2016 the World health Organisation (WHO)2 estimated that the prevalence of obesity in the world was 13% in adults (11% in men and 15% in women), and had tripled since 1975. In China the prevalence of obesity in adults under 70 years of age tripled between 2004 and 2018.3 In Spain it was estimated that between 1987 and 2014, the prevalence of overweight and obesity increased by .28% every year and that direct medical cost overruns amounted to almost 2 billion euros per year (2% of the 2016 healthcare budget), and that it could rise to 3 billion per year in 2030 if this surge was not reversed.4 The WHO set a target of halting the rise in obesity for 2025,5 and recommended regular monitoring of the prevalence of overweight and obesity in all population groups.6
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by an abnormal or excessive accumulation of body fat, manifested by increased weight,6 and which constitutes a major risk factor of cardiometabolic disorders.7–10 Obesity is associated with osteoarthritis, obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome, several cancers and above all, with the main predictors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure (HBP) and dyslipidaemia.7,9,10 it also predisposes to chronic kidney disease, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, sudden cardiac death and stroke which are major causes of cardiovascular hospitalisation and mortality.8,10
The most commonly used tool for measuring obesity is the body mass index (BMI),6,11–13 although the American associations of endocrinology11 and the Spanish Society for the Study of Obesity12,13 also recommend the use of other anthropometric indicators to better assess the level of body fat distribution, such as the abdominal circumference, waist-height ratio (WHR) and the Clínica Universitaria de Navarra index, the Body Adiposity Estimator (CUN-BAE),14 especially in people who are vigorous, older, short, with water retention or pregnant.15,16 The BMI is often chosen because it is a universal measurement which is easy for people to calculate and very useful for classifying excess weight in both sexes and for all adult ages.17
The SIMETAP-OB study objective were to determine the prevalence rates of overweight and obesity in the adult population and to compare their associations with cardiometabolic and renal factors.
Material and methodsSIMETAP-OB is a cross-sectional observational study approved by the Health Service of the Community of Madrid (SERMAS for its initials in Spanish), which 121 family doctors participated in, selected competitively to reach the necessary sample size, and who belonged to 64 Primary Care centres (25% of the SERMAS healthcare centres). The information on the material and methods of the SIMETAP study were previously detailed in this journal.18 Simple random sampling was made of 5.45% of the whole target population aged 18 years or above (194,073 adults) attended by the primary care physicians of the SERMAS who participated in the study, using random numbers extracted by the excel function ALEATORIO.ENTRE (below, above). By protocol, we excluded patients who were terminally ill, institutionalised, cognitively impaired, pregnant or subjects without information on biochemical variables, and informed consent was obtained from study subjects. After a response rate of 65.8%, 6588 study subjects were selected. The following variables were considered: overweight11,19,20: BMI = 25.0–29.9 kg/ m2; obesity11,19,20: BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2; adiposity or body fat index CUN-BAE14 obesity > 25% (men), > 35% (women); abdominal or central obesity: abdominal circumference ≥ 102 cm (men) or ≥ 88 cm (women)21; metabolic syndrome (MetS) according to harmonised IDF/NHLBI/AHA/WHF/IAS/IASO consensus21; increased WHT22: abdominal circumference/height ≥ .55; HBP: systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg; hypercholesterolaemia: total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL; hypertriglyceridaemia triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) low: <40 mg/dL (men), <50 mg/dL (women); diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA)23: fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 126 mg/dL or glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥ 6.5%, or plasma glucose determination ≥ 200 mg/dL at any time or with oral tolerance testing to glucose in individuals with no diabetes, defined as pre-diabetes according to the ADA23: FPG between 100 and 125 mg/dL or HbA1c between 5.7% and 6.4%, and pre-diabetes according to the Spanish Diabetes Society (SED):24 FPG between 110 and 125 mg/dL or HbA1 between 6.0% and 6.4%; low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) according to CKD-EPI25: <60 mL/min/1,73 m2; albuminuria25: urine albumin-creatinine ratio ≥ 30 mg/g; chronic kidney disease: low eGFR and/or albuminuria; cardiovascular risk (CVR) according to SCORE.26,27
Qualitative variables were analysed using percentages, the Chi-square test and odds ratios, with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Means and interquartile ranges (IQR) of age and anthropometric parameters were determined. Continuous variables were assessed using standard deviation (SD) mean and the Student’s t-test or by analysis of variance. Crude and age- and sex-adjusted prevalences were determined and calculated by direct method, using standardised ten-year age groups and with the information of the Spanish population as of January 2015 according to the National Institute of Statistics.28 To assess the individual effect of comorbidities and cardiovascular risk factors (CVRF) on obesity and overweight dependent variables multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed using the backward stepwise method, initially introducing into the model all the variables that showed an association in the univariate analysis up to a value of p < .10, except for the CUN-BAE obesity variables,14 because BMI is included as part of the dependent variables. Increased WHR because height is included in the dependent variables; atherogenic dyslipidaemia and metabolic syndrome,21 because the criteria defining these were already included in the analysis; and erectile dysfunction, because it affects only men. Subsequently, the variable that contributed least to the fit of the analysis was eliminated at each step. All tests were considered statistically significant if the 2-tailed p-value was less than .05. A literature search was performed in PubMed, Medline, Embase, Google Scholar and Web of Science to compare the prevalence rates of the present study with similar studies from the previous 2 decades.
ResultsStudy populationThe study population was 6588 adults aged 18.0–102.8 years, whose mean (SD) age was 55.1 (17.5) years, and Mean (IQR) was 54.69 (41.68–68.09) years. The percentage difference between males (44.1% [95% CI 42.9–45.3]) and females (55.9% [95% CI 54.7–57.1]) was significant (p < .001). The Mean (IQR) ages of the male and female populations were 55.0 (42.4–67.5) years and 54.5 (41.0–68.8) years, respectively, with the difference in mean (SD) ages between males (55.3 [16.9] years) and females (55.0 [18.0] years) being non-significant (p = .634).
The Means (IQR) of the weight of the male and female populations were 80.0 kg (72.0–90.0) and 66.0 kg (58.5–76.0), respectively, with the difference in the means (SD) of weight between males (81.8 kg [14.5]) and females (68.3 kg [13.8]) being significant (p < .001). The Means (RIC) of the height of the male and female populations were 1.71 m (1.66–1.76) and 1.59 m (1.54–1.64), respectively, with the difference in the means (SD) of the height between males (1.71 m [0.08]) and females (1.59 m [0.07]) being significant (p < .001). The Means (IQR) of BMI of the male and female populations were 27.5 kg/m2 (24.8–30.5) and 26.4 kg/m2 (23.1–30.5), respectively, with the difference in the means (SD) of BMI between males (27.9 kg/m2 [4.5]) and females (27.2 kg/m2 [5.6]) being significant (p < .001). The Mean (IQR) abdominal circumference of the male and female populations were 98.0 cm (90.0–105.0) and 87.5 cm (79.0–99.0), respectively, with the difference in mean (SD) abdominal circumferences between males (98.0 cm [12.6]) and females (89.7 cm [14.1]) being significant (p < .001).
Overweight and obesity prevalence ratesThe crude and adjusted prevalence rates of overweight categories according to the Spanish Society for the Study of Obesity are shown in Table 1. The crude prevalence of combined overweight and obesity was 66.01% (95%CI: 64.87–67.16), the difference between men (73.24% [95%CI: 71.63–74.85]) and women (60.31% [95%CI: 58.74–61.89]) being significant (p < .001), and its age- and sex-adjusted prevalence was 61.01% (68.35% in men; 59.00% in women).
Gross and adjusted prevalence ratios of excess weight and obesity according to SEEDO categories.
| Category | BMI limit values (kg/m2) | Gross prevalence (% [95% CI]) | Gross prevalence men (% [95% CI]) | Gross prevalence women (% [95% CI]) | Adjusted prevalence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight | <18.5 | 1.68 [1.37−2.00] | 0.69 [0.39−0.99] | 2.47 [1,97−2,97] | 2.19 |
| Normal weight | 18.5−24.9 | 32.30 [31,17–33,43] | 26.07 [24,47–27,66] | 37.21 [35,65–38,78] | 36.80 |
| Overweight grade i | 25.0−26.9 | 16.21 [15,32–17,10] | 17.94 [16,55–19,34] | 14.85 [13,70–16,00] | 15.63 |
| Overweight grade ii (preobesity) | 27.0−29.9 | 21.98 [20,98–22,98] | 26.62 [25,01–28,23] | 18.32 [17,07–19,57] | 20.36 |
| Obesity type i (mild) | 30.0−34.9 | 19.52 [18,56–20,48] | 21.90 [20,40–23,41] | 17.64 [16,41–18,87] | 17.48 |
| Obesity type ii (moderate) | 35.0−39.9 | 6.22 [5,64–6,81] | 5.30 [4,49–6,12] | 6.95 [6,13–7,77] | 5.64 |
| Obesity type iii (morbid) | ≥40.0 | 2.08 [1,73–2,42] | 1.48 [1,04–1,92] | 2.55 [2,04−3,06] | 1.91 |
SEEDO: Spanish Society for the Study of Obesity.
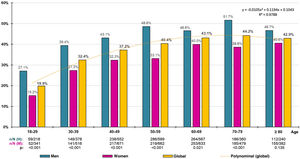
The crude prevalence of overweight was 38.19% (95%CI: 37.02–39.36), with a significant (p < .001) difference between males (44.56% [95%CI: 42.75–46.37]) and females (33.17% [95%CI: 31.65–34.69]), and its age- and sex-adjusted prevalence was 35.99% (42.12% in males; 33.15% in females). The distribution of overweight prevalence rates by decadal age groups increased overall until the 1970s, decreasing thereafter, with the difference between men and women being significant in all age groups except the ≥80 years (Fig. 1).
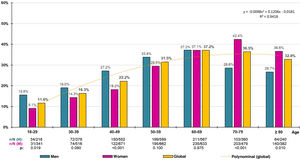
The crude prevalence of obesity was 27.82% (95%CI: 26.74–28.91), with no significant difference (p = .166) between men (28.68% [95%CI: 27.04−30.33]) and women (27.14% [95%CI: 25.71–28.58]), and its age- and sex-adjusted prevalence was 25.02% (26.22% in men; 24.46% in women). The prevalence of grade IV or extreme obesity was .07% (95% CI .05–.23). The distribution of obesity prevalence rates by decadal age groups increased overall until the 1960s, decreasing thereafter, except in women, where the increase in prevalence persisted until the 1970s (Fig. 2).
Comparison between populations with excess weight and without any excess weight or obesityThe proportion of men in the overweight population (51.43% [95%CI 49.48–53.38]) was significantly higher (p < .001) than in the non-overweight-obese population (34.70% [95%CI 32.73–36.67]). In the overweight population, the proportion of central obesity (abdominal girth ≥ 102 cm [men]; ≥88 cm [women]) was significantly higher (p < .001) in women (39.83% [95%CI 37.58–42.13]) than in men (34.21% [95%CI 31.41–37.10]).
The Mean (IQR) ages of the overweight and non-overweight-obese populations were 57.9 years (45.3–70.1) and 45.5 years (34.6–59.5), respectively. The Mean (IQR) anthropometric parameters of the overweight and non-overweight-obese populations were, respectively: weight: 74.0 kg (67.2, 80.8) and 60.4 kg (55.0–67.0); height: 1.65 m (1.57–1.71) and 1.64 m (1.59–1.71); BMI: 27.4 kg/m2 (26.2–28.6) and 22.8 kg/m2 (21.2–24.0); abdominal circumference: 94.0 cm (88.0–100.0) and 80.0 cm (76.0–87.0); ICT: .57 (.54–.61) and .49 (.46–.53).
The means of all clinical variables assessed were significantly higher in the overweight population than in the non-overweight-obese population, except for height, eGFR and HDL-C concentration, which were lower in the overweight population, and aspartate aminotransferase concentration, whose difference was not significant (Table 2).
Clinical characteristics of overweight and obese population groups and non-overweight and obese groups.
| Overweight | Not overweight or obese | p | Obese | Not obese | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean (SD) | N | Mean (SD) | N | Mean (SD) | N | Mean (SD) | |||
| Age (years) | 2.516 | 57.86 (16.51) | 2.239 | 48.10 (17.92) | <.001 | 1.833 | 60.01 (15.60) | 4.755 | 53.26 (17.87) | <.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 2.516 | 74.32 (9.39) | 2.239 | 61.09 (8.97) | <.001 | 1.833 | 90.13 (14.03) | 4.755 | 68.09 (11.31) | <.001 |
| Height (cm) | 2.516 | 164.48 (9.69) | 2.239 | 165.02 (9.14) | .047 | 1.833 | 162.71 (10.41) | 4.755 | 164.73 (9.44) | <.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 2.516 | 27.39 (1.41) | 2.239 | 22.35 (1.99) | <.001 | 1.833 | 33.97 (3.67) | 4.755 | 25.02 (3.04) | <.001 |
| Abdominal circumference (cm) | 2.516 | 93.95 (9.14) | 2.239 | 81.03 (8.87) | <.001 | 1.833 | 107.60 (10.67) | 4.755 | 87.86 (11.08) | <.001 |
| Waist-height ratio | 2.516 | .57 (.06) | 2.239 | .49 (.05) | <.001 | 1.833 | .66 (.07) | 4.755 | .53 (.07) | <.001 |
| Adiposity (%) | 2.516 | 34.63 (6.52) | 2.239 | 28.51 (6.77) | <.001 | 1.833 | 42.50 (6.92) | 4.755 | 31.75 (7.31) | <.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 2.516 | 123.44 (14.14) | 2.239 | 115.36 (14.95) | <.001 | 1.833 | 127.85 (14.82) | 4.755 | 119.63 (15.07) | <.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 2.516 | 74.19 (9.24) | 2.239 | 69.43 (9.53) | <.001 | 1.833 | 76.93 (9.08) | 4.755 | 71.95 (9.70) | <.001 |
| FPG (mg/dL)a | 2.516 | 97.13 (25.72) | 2.239 | 88.56 (19.34) | <.001 | 1.833 | 103.61 (30.48) | 4.755 | 93.10 (23.33) | <.001 |
| HbA1c (%)b | 2.003 | 5.69 (.90) | 1.688 | 5.35 (.73) | <.001 | 1.542 | 5.88 (.98) | 3.691 | 5.54 (.84) | <.001 |
| T&G index | 2.516 | 8.55 (.59) | 2.239 | 8.23 (.53) | <.001 | 1.833 | 8.73 (.59) | 4.755 | 8.40 (.58) | <.001 |
| TC (mg/dL)c | 2.516 | 194.58 (39.15) | 2.239 | 190.49 (38.62) | <.001 | 1.833 | 193.07 (40.34) | 4.755 | 192.66 (38.95) | .705 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL)c | 2.516 | 53.53 (13.96) | 2.239 | 59.52 (15.38) | <.001 | 1.833 | 50.90 (13.21) | 4.755 | 56.35 (14.95) | <.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL)c | 2.481 | 116.40 (34.08) | 2.231 | 111.40 (34.40) | <.001 | 1.814 | 114.48 (35.32) | 4.712 | 114.04 (34.19) | .638 |
| VLDL-C (mg/dL)c | 2.481 | 23.44 (12.22) | 2.231 | 19.18 (10.35) | <.001 | 1.814 | 26.83 (13.34) | 4.712 | 21.43 (11.58) | <.001 |
| non-HDL-C (mg/dL)c | 2.516 | 141.05 (37,94) | 2.239 | 130,98 (37,57) | <.001 | 1.833 | 142,17 (38,94) | 4.755 | 136,31 (38,10) | <.001 |
| TG (mg/dL)d | 2.516 | 126,53 (97,94) | 2.239 | 97,88 (58,77) | <.001 | 1.833 | 139,92 (80,27) | 4.755 | 113,04 (83,09) | <.001 |
| TC/HDL-C | 2.516 | 3,83 (1,13) | 2.239 | 3,38 (1,05) | <.001 | 1.833 | 3,99 (1,13) | 4.755 | 3,62 (1,12) | <.001 |
| Non-HDL-C/HDL-C | 2.516 | 2,83 (1,13) | 2.239 | 2.38 (1.05) | <.001 | 1.833 | 2.99 (1.13) | 4.755 | 2.62 (1.12) | <.001 |
| TG/HDL-C | 2.516 | 2.72 (3.15) | 2.239 | 1.86 (1.61) | <.001 | 1.833 | 3.09 (2.39) | 4.755 | 2.31 (2.58) | <.001 |
| LDL-C/HDL-C | 2.481 | 2.30 (.88) | 2.231 | 2.00 (.86) | <.001 | 1.814 | 2.37 (.88) | 4.712 | 2.16 (.88) | <.001 |
| PAI | 2.516 | −0.04 (.29) | 2.239 | −0.18 (.27) | <.001 | 1.833 | 0.04 (.28) | 4.755 | −0.11 (.29) | <.001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 2.355 | 5.10 (1.48) | 2.095 | 4.39 (1.31) | <.001 | 1.718 | 5.47 (1.47) | 4.450 | 4.77 (1.44) | <.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 1.851 | 22.61 (12.44) | 1.636 | 22.89 (70.48) | .866 | 1.325 | 23.94 (20.58) | 3.487 | 22.74 (49.11) | .387 |
| ALT (U/L) | 2.459 | 25.47 (16.43) | 2.183 | 21.78 (14.38) | <.001 | 1.771 | 27.85 (19.71) | 4.642 | 23.74 (15.61) | <.001 |
| GGT (U/L) | 2.333 | 35.61 (61.51) | 2.079 | 25.26 (30.97) | <.001 | 1.663 | 40.33 (52.92) | 4.412 | 30.73 (49.79) | <.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.516 | .86 (.28) | 2.239 | .81 (.30) | <.001 | 1.833 | .85 (.29) | 4.755 | .83 (.29) | .005 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 2.516 | 88.42 (20.07) | 2.239 | 96.54 (19.95) | <.001 | 1.833 | 86.17 (20.19) | 4.755 | 92.24 (20.41) | <.001 |
| UCAR (mg/g) | 2.516 | 17.28 (59.91) | 2.239 | 11.92 (42.55) | <.001 | 1.833 | 20.75 (77.12) | 4.755 | 14.75 (52.52) | <.001 |
Overweight: BMI = 25.0–29.9 kg/m2. Obesity: BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. Adiposity: CUN-BAE (Clínica Universitaria de Navarra-Body Adiposity Estimator) body fat index.
ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; BMI: body mass index; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate according to CKD-EPI; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transferase; FPG: fasting plasmatic; HbA1c: glycated haemoglobin; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; N: sample size; non-HDL-C: cholesterol not bound to high-density lipoprotein; p: p-value of the means difference; PAI: plasma atherogenic indexT&G index: triglyceride and glucose index; SBP: systolic blood pressure; SD: standard deviation; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; UCAR: urinary albumin/creatinine ratio; VLDL-C: very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and its remnants.
The proportion of men in the obese population (45.44% [95% CI 43.17–47.72]) was similar (p < .166) to that in the non-obese population (43.55% [95% CI 42.14–44.96]). In the obese population, the proportion of central obesity was significantly higher (p < .001) in men (64.79% [95%CI 61.89–67.61]) than in women (52.80% [95%CI 50.48–55.12]).
The Mean (IQR) ages of the obese and non-obese populations were 61.2 years (49.3–71.4) and 52.0 years (39.5–66.5), respectively. The Mean (IQR) anthropometric parameters of the populations with and without obesity were, respectively: weight: 89.0 kg (80.0–98.0) and 67.5 kg (60.0–76.0); height: 1.62 m (1.55–1.70) and 1.65 m (1.58–1.71); BMI: 32.9 kg/m2 (31.3–35.6) and 25.3 kg/m2 (22.9–27.5); abdominal circumference: 107.0 cm (101.0–114.0) and 87.5 cm (79.5–96.0); WHR: 0.66 (0.62−0.70) and 0.53 (0.49−0.58).
The means of all clinical variables assessed were significantly higher in the obese population than in the non-obese population, except for height, LDL-C and eGFR concentrations, which were lower in the obese population, and total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and aspartate aminotransferase concentrations, whose differences were not significant (Table 2).
Associations of cardiometabolic factors with excess weight and obesityTable 3 shows the univariate analysis to assess associations and compare comorbidities and CVRFs between overweight and non-overweight-obese populations, and between obese and non-obese populations. Differences in the percentages of individuals with high and very high CVRFs between obese (62.3% [95%CI: 60.1–64.5]) and non-obese (40.4% [95%CI: 39.0–41.8]) populations, and between overweight (52.0% [95%CI: 50.0–53.9]) and non-overweight-obese (27.4% [95%CI: 25.6–29.3]) populations were significant (p < .001).
Comorbidities and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese population groups and non overweight and obese population groups.
| Overweight (N = 2516) | Not overweight or obese (N = 2239) | OR [95% CI] | p | Obese (N = 1833) | Not obese (N = 4755) | OR [95% CI] | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||||
| Tobacco habit | 542 (21.5) | 553 (24.7) | .8 [0,7−1,0] | .010 | 331 (18.1) | 1095 (23.0) | .7 [0,6–0,8] | <.001 |
| Sedentary lifestyle | 1194 (47.5) | 855 (38.2) | 1.5 [1,3–1,6] | <.001 | 1030 (56.2) | 2049 (43.1) | 1.7 [1,5−1.9] | <.001 |
| CUN-BAE obesity | 2391 (95.0) | 608 (27.2) | 51,3 [41,9–62,8] | <.001 | 1833 (100.0) | 2999 (63.1) | NA | <.001 |
| Abdominal obesity | 1102 (43.8) | 145 (6.5) | 11.3 [9,4–13,6] | <.001 | 1675 (91.4) | 1247 (26.2) | 29.8 [25,0–35,5] | <.001 |
| Increased WHR | 1642 (65.3) | 270 (12.1) | 13.7 [11,8–15,9] | <.001 | 1784 (97.3) | 1912 (40.2) | 54.1 [40,5–72,3] | <.001 |
| SED prediabetes | 208 (8.3) | 88 (3.9) | 2.2 [1,7–2,9] | <.001 | 227 (12.4) | 296 (6.2) | 2.1 [1,8−2.6] | <.001 |
| ADA prediabetes | 612 (24.3) | 290 (13.0) | 2.2 [1,9–2,5] | <.001 | 547 (29.8) | 902 (19.0) | 1.8 [1,6–2,1] | <.001 |
| Diabetes | 426 (16.9) | 156 (7.0) | 2.7 [2,2–3,3] | <.001 | 453 (24.7) | 582 (12.2) | 2.4 [2,1–2,7] | <.001 |
| High blood pressure | 1053 (41.9) | 390 (17.4) | 3.4 [3,0–3,9] | <.001 | 1.104 (60.2) | 1443 (30.3) | 3.5 [3,1–3,9] | <.001 |
| Hypercholesterolaemia | 1666 (66.2) | 1.129 (50.4) | 1.9 [1,7–2,2] | <.001 | 1.306 (71.2) | 2795 (58.8) | 1.7 [1,6−2,0] | <.001 |
| Low HDL-c | 707 (28.1) | 395 (17.6) | 1.8 [1,6–2,1] | <.001 | 717 (39.1) | 1102 (23.2) | 2.1 [1,9–2,4] | <.001 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 815 (32.4) | 366 (16.3) | 2.5 [2,1–2,8] | <.001 | 766 (41.8) | 1181 (24.8) | 2.2 [1,9–2,4] | <.001 |
| Atherogenic dyslipidaemia | 382 (15.2) | 142 (6.3) | 2.6 [2,2–3,2] | <.001 | 417 (22.7) | 524 (11.0) | 2.4 [2,1–2,7] | <.001 |
| Metabolic syndrome | 1165 (46.3) | 364 (16.3) | 4.4 [3,9–5,1] | <.001 | 1.322 (72.1) | 1529 (32.2) | 5.5 [4,9–6,2] | <.001 |
| ACVD | 244 (9.7) | 126 (5.6) | 1.8 [1,4–2,3] | <.001 | 245 (13.4) | 370 (7.8) | 1.8 [1,5–2,2] | <.001 |
| Heart disease | 124 (4.9) | 61 (2.7) | 1.9 [1,4–2,5] | <.001 | 136 (7.4) | 185 (3.9) | 2.0 [1,6–2,5] | <.001 |
| Stroke | 95 (3.8) | 54 (2.7) | 1.4 [1,0–1,9] | .007 | 101 (5.5) | 149 (3.1) | 1.8 [1,4–2,3] | <.001 |
| PAD | 62 (2.5) | 30 (1.3) | 1.9 [1,2–2,9] | .005 | 58 (3.2) | 92 (1.9) | 1.7 [1,2–2,3] | .003 |
| Heart failure | 67 (2.7) | 41 (1.8) | 1.5 [1,0–2,2] | .055 | 76 (4.1) | 108 (2.3) | 1.9 [1,4–2,5] | <.001 |
| Auricular fibrillation | 90 (3.6) | 53 (2.4) | 1.5 [1,1–2,2] | .015 | 107 (5.8) | 143 (3.0) | 2.0 [1,6–2,6] | <.001 |
| Erectile dysfunction | 233 (18.0) | 106 (13.6) | 1.4 [1,1–1,8] | .009 | 165 (19.8) | 339 (16.4) | 1.2 [1,0–1,4] | .027 |
| Albuminuria | 164 (6.5) | 76 (3.4) | 2.0 [1,5–2,6] | <.001 | 145 (11.2) | 230 (7.3) | 1.5 [1,3–1,9] | <.001 |
| Low eGFR | 221 (8.8) | 100 (4.7) | 2.1 [1,6–2,6] | <.001 | 202 (11.0) | 322 (6.8) | 1.6 [1,4–1,9] | <.001 |
| CKD | 313 (12.4) | 139 (6.2) | 2.2 [1,7–2,6] | <.001 | 304 (16.6) | 452 (9.5) | 1.7 [1,5−2,0] | <.001 |
| Low CVR | 657 (26.1) | 1.251 (55.9) | .3 [0,2–0,3] | <.001 | 237 (12.9) | 1908 (40.1) | .2 [0,2–0,3] | <.001 |
| Moderate CVR | 551 (21.9) | 374 (16.7) | 1.4 [1,2–1,6] | <.001 | 454 (24.8) | 925 (19.5) | 1.4 [1,2–1,6] | <.001 |
| High CVR | 448 (17.8) | 228 (10.2) | 1.9 [1,6–2,3] | <.001 | 347 (18.9) | 676 (14.2) | 1.4 [1,2–1,6] | <.001 |
| Very high CVR | 860 (34.2) | 386 (17.2) | 2.5 [2,2–2,9] | <.001 | 795 (43.4) | 1246 (26.2) | 2.2 [1,9–2,4] | <.001 |
Overweight: BMI = 25.0–29.9 kg/m2. Obesity: BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. Abdominal obesity: abdominal circumference ≥ 102 cm (men) and ≥ 88 cm (women). SED Prediabetes: fasting plasmatic glucose (FPG): 110−125 mg/dL or glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c): 6.0%–6.4%). ADA Prediabetes: DPG: 100−125 mg/dL o HbA1c: 5.7%–6.4%). Tobacco habit: consumption of any cigarettes or tobacco during the last month. Physical inactivity: < 150 min/week. CUN-BAE Adiposity: CUN-BAE (Clínica Universitaria de Navarra-Body Adiposity Estimator) body fat index) > 25% (men) and > 35% (women). Central obesity: abdominal circumference ≥ 102 cm (men); ≥88 cm (women). Increased WHR: ≥.55. Hypercholesterolaemia: total cholesterol total ≥ 200 mg/dL. Low HDL-c: <40 mg/dL (men) and <50 mg/dL (women). Hypertriglyceridaemia: triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL. Atherogenic dyslipidaemia: hypertriglyceridaemia and low HDL-c. Albuminuria: albumin-creatinine ratio ≥ 30 mg/g. Low eGFR: <60 mL/min/1,73 m2 (estimated according to CKD-EPI).
ADA: American Diabetes Association; ACVD: artheroslerotic cardiovascular disease; BMI: body mass index; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; CKD: chronic kidney disease; CVR: cardiovascular risk; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; N: sample size; NA: not applicable; OR: odds ratio; p: p-value of percentage differences; PAD: peripheral arterial disease; SED: Spanish Society of Diabetes; WHR: waist-height ratio.
The effect of comorbidities and CVRFs on overweight and obesity is shown in Table 4, with the results of multivariate analyses of all variables (except the complex variables listed above in the material and methods section) that showed association with overweight or obesity in the univariate analysis. The cardiometabolic variables of abdominal obesity; AHT; hypertriglyceridaemia; pre-diabetes defined according to ADA criteria23; diabetes; physical inactivity and low HDL-C concentrations were independently associated with overweight, and the variables of abdominal obesity; HBP; pre-diabetes defined according to SED criteria SED24; low HDL-C concentrations; hypertriglyceridaemia and physical inactivity were independently associated with obesity.
Multivariate analysis of the effect of comorbidities and cardiovascular risk factor son overweight and obesity.
| Overweight | βa | OR Exp(β)b | pc | Obesity | βa | OR Exp(β)b | pc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal obesity | 2.25 (.10) | 9.48 (7.83−11.48) | <.001 | Abdominal obesity | 3.18 (.09) | 24.15 (20.18−28.89) | <.001 |
| Hypertension | .85 (.08) | 2.35 (2.00−2.75) | <.001 | Hypertension | .65 (.07) | 1.92 (1.66−2.22) | <.001 |
| Hipertriglyceridaemia | .60 (.08) | 1.81 (1.54−2.14) | <.001 | SED Prediabetes | .34 (.12) | 1.41 (1.12−1.78) | .004 |
| ADA Prediabetes | .56 (.09) | 1.75 (1.46−2.09) | <.001 | Low HDL-c | .29 (.08) | 1.33 (1.15−1.55) | <.001 |
| Diabetes | .52 (.12) | 1.68 (1.33−2.12) | <.001 | Hypertriglyceridaemia | .35 (.08) | 1.42 (1.12−1.78) | <.001 |
| Sedentary lifestyle | .30 (.07) | 1.35 (1.18−1.54) | <.001 | Sedentary lifestyle | .25 (.07) | 1.29 (1.12−1.48) | <.001 |
| Low HDL-c | .25 (.09) | 1.29 (1.09−1.52) | .003 | eGFR | −.23 (.12) | .80 (.63−1.00) | .054 |
| Auricular fibrillation | −.57 (.21) | 1.35 (.38−.85) | .006 | Hypercholesterolaemia | −.15 (.08) | .86 (.74−1.01) | .068 |
Overweight: body mass index (BMI) = 25.0–29.9 kg/m2. Obesity: BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. Abdominal obesity: abdominal circumference ≥ 102 cm (men) and ≥ 88 cm (women). Hypertriglyceridemia: triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL. SED Prediabetes: prediabetes according to the Spanish Society of Diabetes (fasting plasmatic glucose [FPG]: 110−125 mg/dL or glycosylated haemoglobin [HbA1c]: 6.0%–6.4%). ADA prediabetes: prediabetes according to the American Diabetes Association (FPG: 100−125 mg/dL or HbA1c: 5.7%–6.4%). Low HDL-c: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol < 40 mg/dL (men) and < 50 mg/dL (women). Sedentary lifestyle: physical activity < 150 min/week. Low eGFR: glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (estimated according to CKD-EPI). Hypercholesterolaemia: total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL.
The 1995 WHO report29 initially classified excess weight into 3 grades based on the association between BMI and mortality, with cut-off points of the BMI at 25, 30 and 40 kg/m2. Its later 1997 report19 defined preobesity with a BMI between 25.0 and 29.9 kg/m2, and classified obesity into 3 grades (i, ii and iii), the cut-off points of which were 30, 35 and 40 kg/m2. This SIMETAP-OB study took into account the WHO recommendations,19 the European Association for the Study of Obesity11 and the Spanish Society for the Study of Obesity12,13 on the use of the latter classification to estimate the prevalence of overweight and obesity and their associated risks. This led to the evaluation of their results, the comparison of groups at increased risk of morbidity and mortality between or within populations, and the setting of priorities for intervention in individuals or communities.
There has been a steady increase in the prevalence of overweight and obesity worldwide.2,3,30 The latest US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES)30 in adults, whose mean age was 47.9 years, showed that the mean BMI was 29.8 kg/m2 and that the prevalence of obesity was 42.4%, much higher than in European countries.31,32 The European Social Survey31 in European adults with an average age of 50.8 years showed a mean BMI of 25.8 kg/m2 and prevalences of overweight and obesity of 37.2% and 15.9%, respectively. In Spain, the prevalence of obesity in adults aged 20–65 years also increased from 14.5% in 2000 to 21.6% in 2015.33,34 These figures contrast with those provided by the European Social Survey,31 whose prevalences of overweight and obesity in Spain were 36.8% and 17.1%, respectively, or with the more recent European Health Survey in Spain,32 which showed prevalences of overweight of 37.6% (44.9% in men; 30.6% in women) and obesity of 16.0% (16.5% in men; 15.5% in women). The present study shows overweight prevalences similar to European surveys31,32 and obesity prevalence rates lower than the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,30 which could be justified by different lifestyles, and higher than the European Social Survey31 and the European Health Survey in Spain,32 possibly due to the different types of sampling and the fact that the SIMETAP-OB study included a population with a higher mean age (55.1 years), as the prevalence of obesity increases with age.3,30,33,34
The SIMETAP-OB study shows prevalence rates that are also comparable with other studies carried out in Spain.34–37 While the ERICE study35 showed a lower prevalence of obesity (22.8%), the DARIOS study36 showed higher prevalences of overweight (51% in men; 36% in women) and obesity (29% in men and women). The ENRICA37 study showed a higher prevalence of overweight (39.4%) and a lower prevalence of obesity (22.9%), with slightly lower prevalences of type II and type III obesity than the present study (4.2% vs. 5.6% and 1.2% vs. 1.9%, respectively). The ENRICA37 and SIMETAP-OB studies confirmed that the frequency of overweight and obesity increased with age, with a similar prevalence of obesity in the population aged 65 years and older (35% vs. 35.9%). In the present study, prevalences of overweight were higher in men than in women in all age groups. However, prevalences of obesity were higher in men than in women up to the 50s and higher in women from the age of 70 onwards. Similarly, the ENRICA37 study showed that the prevalence of obesity was higher in men than in women up to the age of 65–69 years, and higher in women thereafter. The PREDIMERC38 study in the Community of Madrid showed higher prevalences of overweight (52% in men and 37% in women) than the present study, and similar prevalences of obesity in men (26%) and slightly lower in women (23%).
The SIMETAP-OB study shows significant differences in mean age between overweight and non-overweight populations (almost 10 years), and between obese and non-obese populations (almost 7 years), justified by the increase in prevalences with age.
The variables abdominal obesity, increased WHR and adiposity CUN-BAE obesity showed strong associations with overweight and obesity, which are justified by including anthropometric parameters closely related to BMI. It is relevant that while the proportion of women with increased abdominal circumference (≥88 cm) in the overweight population increases by only 13% in the obese population, the proportion of men with increased abdominal circumference (≥102 cm) in the overweight population increases by 30% in the obese population.
FPG and HbA1c levels were higher in obese than in overweight subjects, with significant differences between overweight and non-overweight/non-obese populations. Both prediabetes and diabetes were associated with overweight and obesity. Prediabetes according to SED24 criteria was independently related to obesity, whereas both diabetes and prediabetes according to ADA23 criteria were independently related to overweight, probably because the ADA23 sets broader diagnostic criteria for prediabetes.
The present study supports the existing evidence on the relationship between BMI and cardiovascular disease risk.7,39–41 Overweight is associated with increased risk of sudden cardiac death and coronary heart disease; increased BMI with increased risk of cardiovascular or all-cause mortality, HBP, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease and stroke; and obesity is also associated with pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism and aortic stenosis.40 Adults who are overweight or obese are at increased risk of developing HBP.41 The present study shows the strength of the association between HBP and obesity or overweight, being the first non-anthropometric factor independently associated with both conditions. The proportions of low eGFR, albuminuria or chronic kidney disease were higher in overweight or obese populations and higher in obese than overweight populations, although these variables were not independently associated with overweight or obesity.
All lipid variables were significantly higher (lower c-HDL) in overweight or obese subjects. Hypercholesterolaemia, low HDL-C, hypertriglyceridaemia and atherogenic dyslipidaemia showed strong associations with overweight and obesity, with low HDL-C and hypertriglyceridaemia being independent factors associated with both entities.
The proportion of individuals with high or very high CVR in the obese population is very high (62%). However, it is noteworthy that the proportion reaches more than half of the overweight population, so the importance of the cardiovascular burden of this entity should not be underestimated. The associations of all anthropometric, glycaemic, blood pressure and lipid variables with overweight and obesity explain why there is a high proportion of individuals with high or very high CVR, and why they are almost twice as likely to suffer from metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease, with odds ratios ranging between 1.4 and 1.9 for overweight and between 1.7 and 2.0 for obesity.
Limitations of the present cross-sectional design study were the inability to determine causality or estimate incidence rates, possible inter-interviewer variability, calibration or possible heterogeneity of measurement and laboratory apparatus, and that pregnant women, terminally ill, institutionalised or cognitively impaired patients were not included. The main strengths include the randomised selection with a broad population base, the objective determination of anthropometric measures and the assessment of the possible association of overweight and obesity with numerous cardiometabolic and renal variables. The SIMETAP-OB study stands out for its sample size, the second largest conducted in Spain after the ENRICA study,37 with a wider age range and higher response rate (66% vs. 51%). It also confirms that both overweight and obesity are strongly influenced by age, with peaks in the last decades of life. It is therefore recommended that epidemiological studies include these age groups and that prevalence should be documented with age-adjusted rates for comparison with other populations.
Assessing the magnitude of the epidemiological situation of overweight in the population is essential to plan interventions aimed at preventing or reducing the burden of this health problem, and to be able to implement coherent, effective and easily applied prevention strategies, such as the acquisition of healthy eating habits and regular exercise.
ConclusionsThe age- and sex-adjusted prevalence of overweight was 61%, with 36% overweight and 25% obese. The prevalences of overweight and obesity increased with age. While prevalences of overweight were higher in men in all age groups, prevalences of obesity were higher in men up to the 50 s and in women from the age of 70 onwards. The cardiovascular burden of excess weight is very high, with 52.0% of the overweight population and 62.3% of the obese population having a high or very high CVR.
In the SIMETAP-OB study population, the cardiometabolic factors of abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, hypertriglyceridaemia, physical inactivity and low HDL-C were independently associated with both overweight and obesity. In addition to these factors, diabetes and ADA prediabetes were independently associated with overweight, and hypercholesterolaemia and SED prediabetes were independently associated with obesity.
FundingFunding for the SIMETAP study (Grant Code: 05/2010RS) was approved in accordance with Order 472/2010, of 16 September, of the Regional Ministry of Health, approving the regulatory bases and the call for grants for 2010 from the Pedro Laín Entralgo Agency for Training, Research and Health Studies of the Community of Madrid, for the implementation of research projects in the field of health outcomes in primary care.
AuthorshipAntonio Ruiz-García and Ezequiel Arranz-Martínez were joint first author and provided equal contribution.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
We would like to thank the following physicians who participated in the SIMETAP study research group, for their efforts, dedication and collaboration: Abad Schilling C, Adrián Sanz M, Aguilera Reija P, Alcaraz Bethencourt A, Alonso Roca R, Álvarez Benedicto R, Arranz Martínez E, Arribas Álvaro P, Baltuille Aller MC, Barrios Rueda E, Benito Alonso E, Berbil Bautista ML, Blanco Canseco JM, Caballero Ramírez N, Cabello Igual P, Cabrera Vélez R, Calderín Morales MP, Capitán Caldas M, Casaseca Calvo TF, Cique Herráinz JA, Ciria de Pablo C, Chao Escuer P, Dávila Blázquez G, de la Peña Antón N, de Prado Prieto L, del Villar Redondo MJ, Delgado Rodríguez S, Díez Pérez MC, Durán Tejada MR, Escamilla Guijarro N, Escrivá Ferrairó RA, Fernández Vicente T, Fernández-Pacheco Vila D, Frías Vargas MJ, García Álvarez JC, García Fernández ME, García García Alcañiz MP, García Granado MD, García Pliego RA, García Redondo MR, García Villasur MP, Gómez Díaz E, Gómez Fernández O, González Escobar P, González-Posada Delgado JA, Gutiérrez Sánchez I, Hernández Beltrán MI, Hernández de Luna MC, Hernández López RM, Hidalgo Calleja Y, Holgado Catalán MS, Hombrados Gonzalo MP, Hueso Quesada R, Ibarra Sánchez AM, Iglesias Quintana JR, Íscar Valenzuela I, Iturmendi Martínez N, Javierre Miranda AP, López Uriarte B, Lorenzo Borda MS, Luna Ramírez S, Macho del Barrio AI, Magán Tapia P, Marañón Henrich N, Mariño Suárez JE, Martín Calle MC, Martín Fernández AI, Martínez Cid de Rivera E, Martínez Irazusta J, Migueláñez Valero A, Minguela Puras ME, Montero Costa A, Mora Casado C, Morales Cobos LE, Morales Chico MR, Moreno Fernández JC, Moreno Muñoz MS, Palacios Martínez D, Pascual Val T, Pérez Fernández M, Pérez Muñoz R, Plata Barajas MT, Pleite Raposo R, Prieto Marcos M, Quintana Gómez JL, Redondo de Pedro S, Redondo Sánchez M, Reguillo Díaz J, Remón Pérez B, Revilla Pascual E, Rey López AM, Ribot Catalá C, Rico Pérez MR, Rivera Teijido M, Rodríguez Cabanillas R, Rodríguez de Cossío A, Rodríguez de Mingo E, Rodríguez Rodríguez AO, Rosillo González A, Rubio Villar M, Ruiz Díaz L, Ruiz García A, Sánchez Calso A, Sánchez Herráiz M, Sánchez Ramos MC, Sanchidrián Fernández PL, Sandín de Vega E, Sanz Pozo B, Sanz Velasco C, Sarriá Sánchez MT, Simonaggio Stancampiano P, Tello Meco I, Vargas-Machuca Cabañero C, Velazco Zumarrán JL, Vieira Pascual MC, Zafra Urango C, Zamora Gómez MM, Zarzuelo Martín N.