To confirm the effectiveness and safety of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors in daily clinical practice.
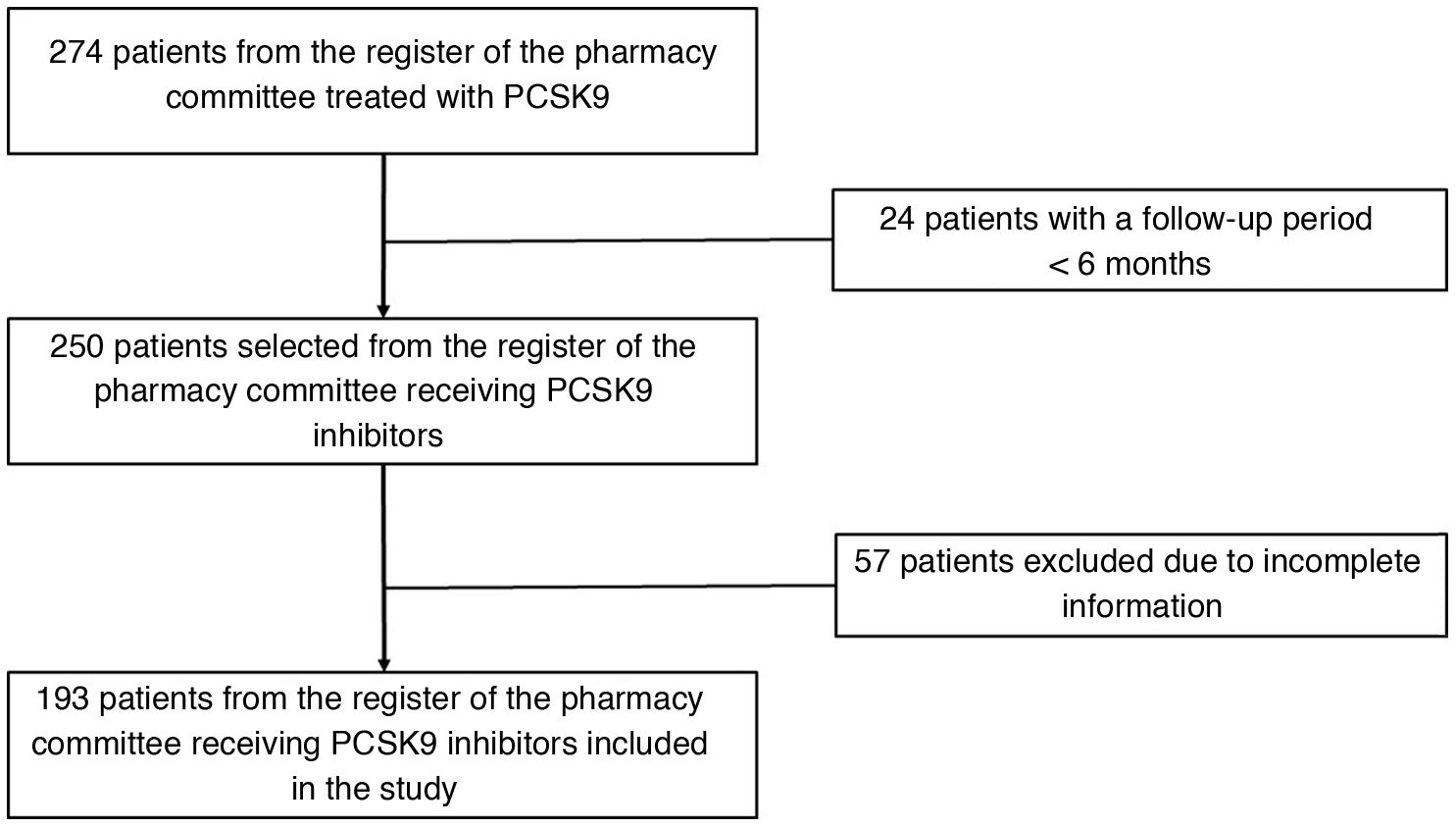
MethodsRetrospective observational study of patients from hospital registry of PCSK9 inhibitor treatment with a follow-up ≥6mo. The lipid-lowering effect and safety were evaluated.
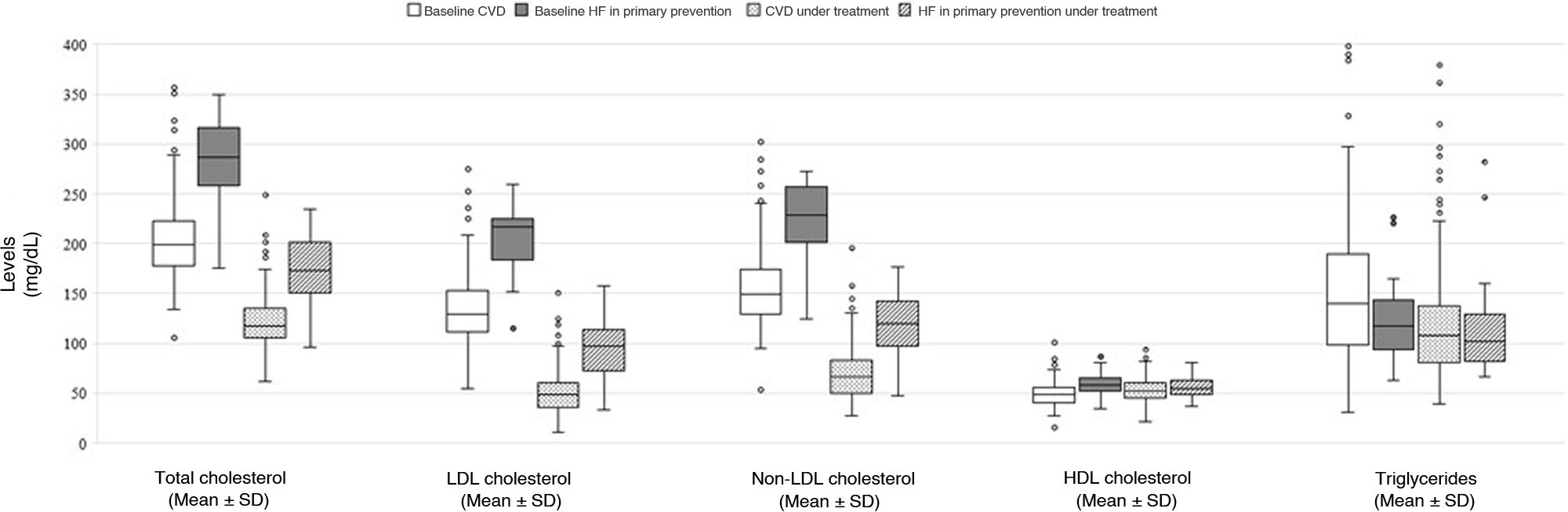
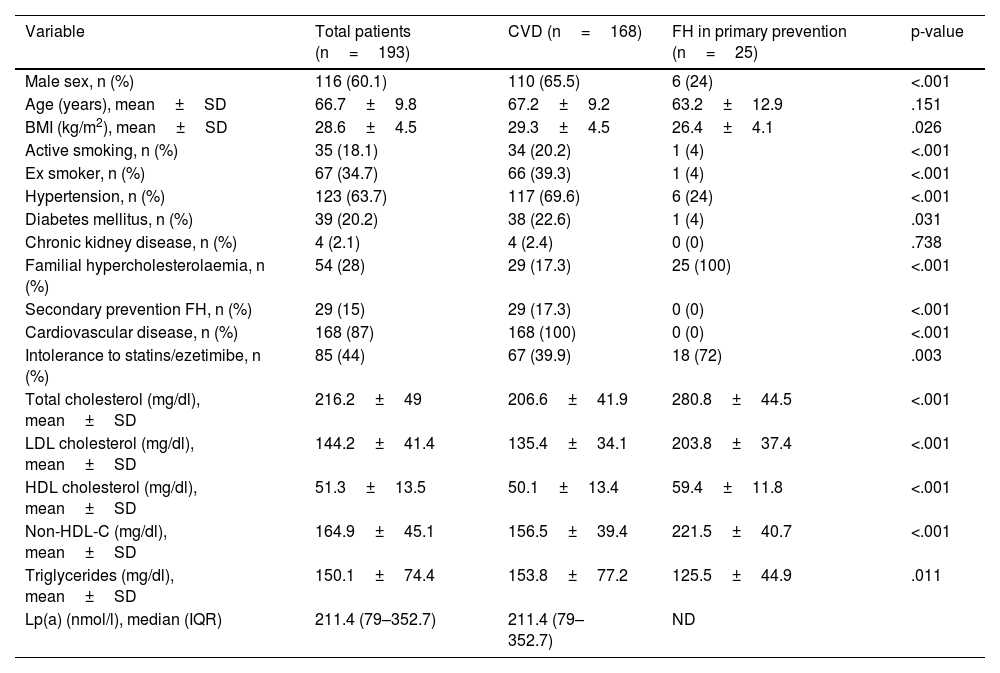
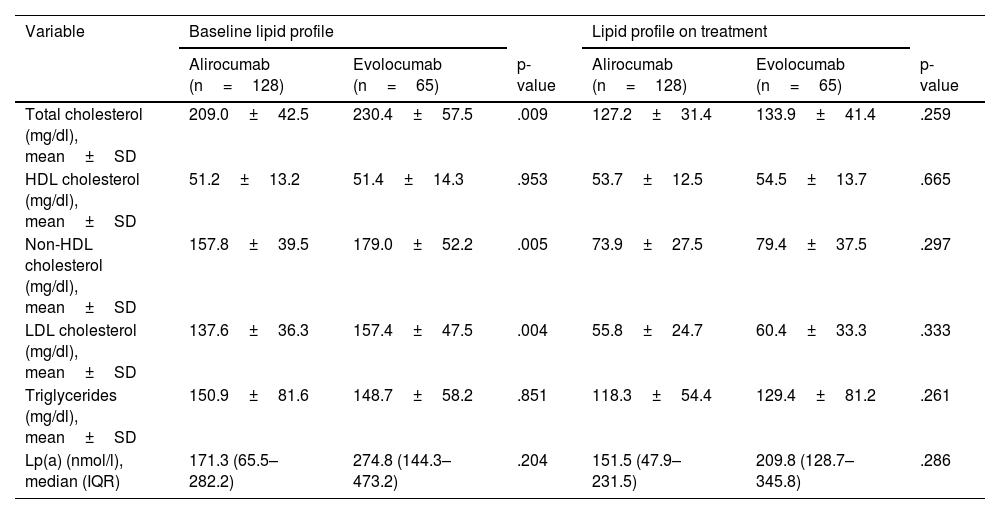
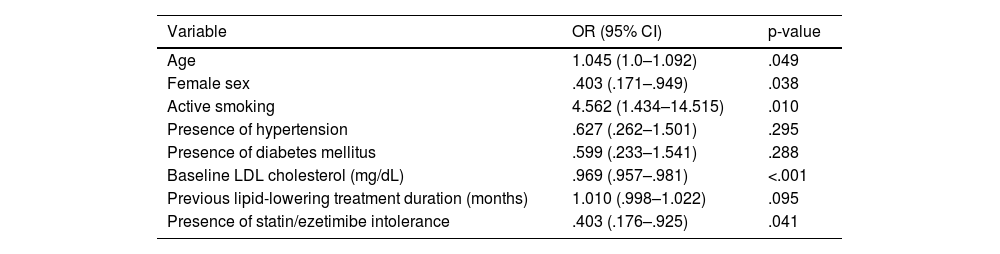
ResultsOf the 193 patients included in the study, 168 (87%) had cardiovascular disease, and 54 (28%) had familial hypercholesterolemia; 85 (44%) were intolerant to statins/ezetimibe. No differences between alirocumab and evolocumab groups regarding the rate of LDL-C reduction ≥50% (82.8% vs. 83.1%), achievement of the therapeutic target (60.9% vs. 65.5%), or complete remission (60.2% vs. 58.5%) were found. An erythema at the injection site in one patient treated with alirocumab and urticaria in one patient treated with evolocumab were recorded. According to the logistic regression analysis, complete remission of LDL-C in subjects treated with PCSK9 inhibitors was positively associated with increased age (OR 1.045; 95% CI 1.0–1.092; p=0.049) and active smoking (OR 4.562; 95% CI 1.434–14.515; p=0.010), and negatively associated with female gender (OR 0.403; 95% CI 0.171–0.949; p=0.038), baseline LDL-C levels (OR 0.969; 95% CI: 0.957–0.981; p<0.001)and statin/ezetimibe intolerance (OR 0.403; 95% CI 0.176–0.925; p=0.041).
ConclusionThis real-world practice study has confirmed that PCSK9 inhibitors are effective, safe and well tolerated, with lipid-lowering effects comparable to those described in randomized controlled trials, regardless of the monoclonal antibody used.
Confirmar la efectividad y seguridad de los inhibidores de la proproteína convertasa subtilisina/kexina tipo 9 (PCSK9) en la práctica clínica diaria.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo observacional de los pacientes del registro hospitalario de tratamiento con inhibidores de PCSK9 con un seguimiento ≥ 6 meses. Se valoró el efecto hipolipemiante y su seguridad.
ResultadosDe los 193 pacientes incluidos en el estudio, 168 (87%) presentaban enfermedad cardiovascular y 54 (28%) hipercolesterolemia familiar; 85 (44%) eran intolerantes a las estatinas/ezetimiba. No hubo diferencias en la tasa de reducción ≥ 50% de cLDL (82,8% vs 83,1%), consecución del objetivo terapéutico (60,9 vs 65,5%), ni de remisión completa (60,2 vs 58,5%) entre el grupo alirocumab y evolocumab. Se registró un eritema en el punto de inyección en un paciente tratado con alirocumab y urticaria en un paciente tratado con evolocumab. En el análisis de regresión logística la remisión completa del cLDL en los sujetos tratados con inhibidores de PCSK9 mostró una asociación positiva con el incremento de edad (OR 1,045, CI95%: 1,0- 1,092; p=0,049)) y el tabaquismo activo (OR 4,562; IC95% 1,434-14,515; p=0,010), y negativa con el sexo femenino (OR: 0,403; IC95% 0,171-0,949; p=0,038), los niveles basales de cLDL (OR 0,969, IC95% 0,957-0,981; p=0,041).
ConclusiónEste estudio de práctica real ha ratificado que los inhibidores de PCSK9 son eficaces, seguros y bien tolerados, con efectos hipolipemiantes comparables a los descritos en los ensayos controlados aleatorios, independientemente del anticuerpo monoclonal utilizado.