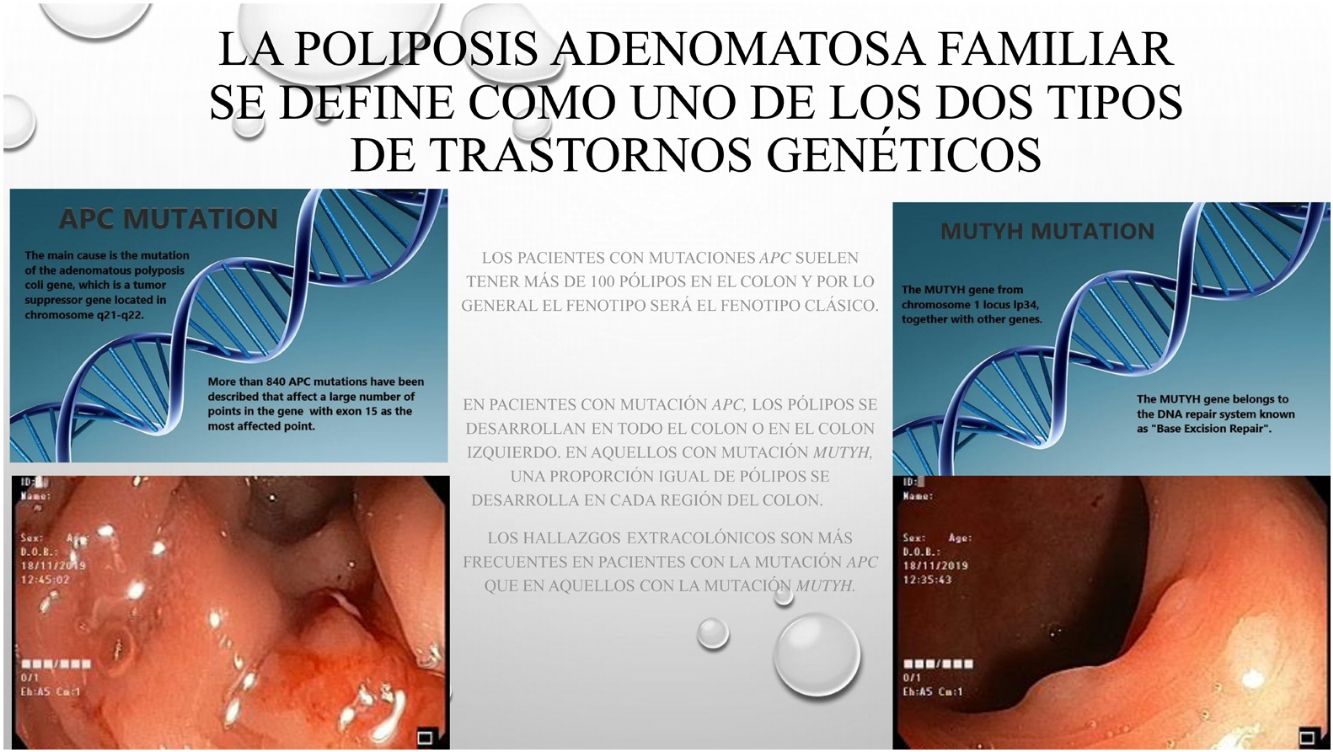
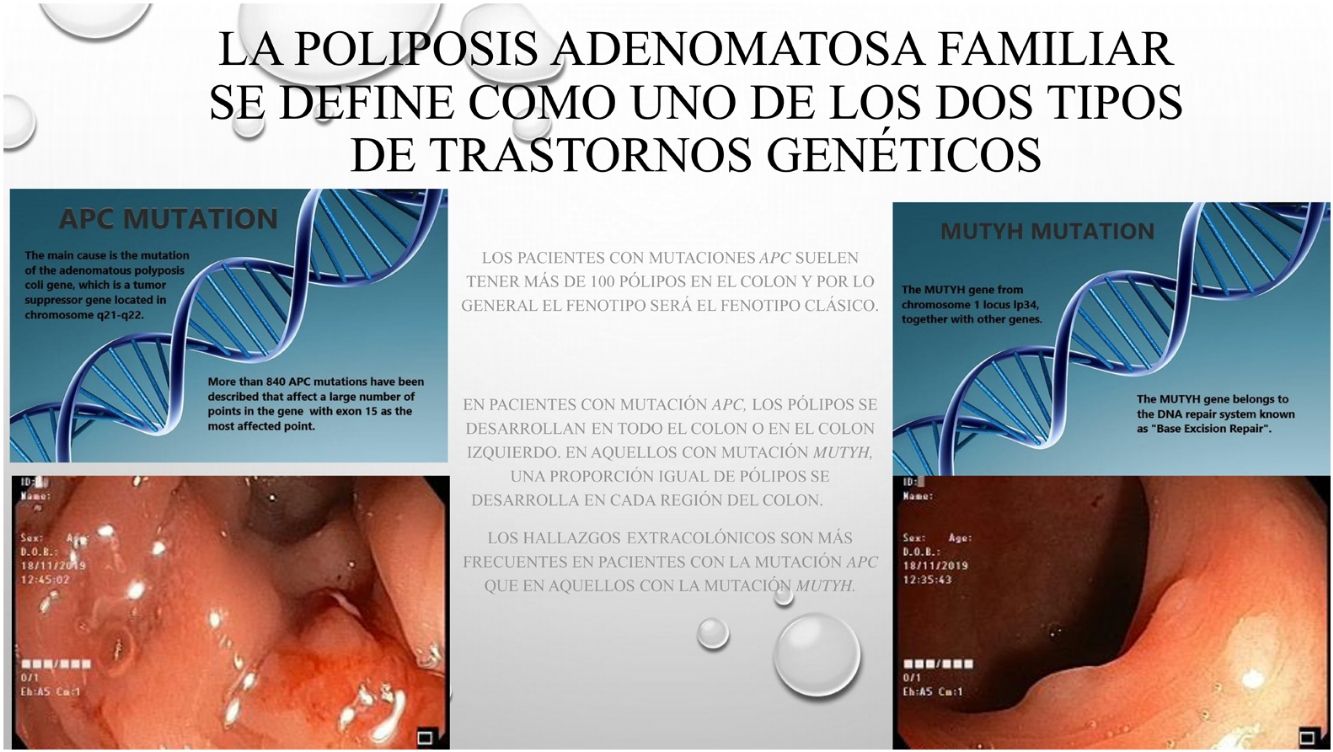
Familial adenomatous polyposis is described as one of the common two types of genetic disorders: APC and MUTYH gene associated polyposis syndrome and the clinical differences between the two can sometimes be unclear.
Materials and methodsA retrospective analysis and comparison was made of clinical, surgical, and histological criteria, mutation types and the long-term results of patients who underwent genetic analysis which resulted in the diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis between 1984 and 2018.
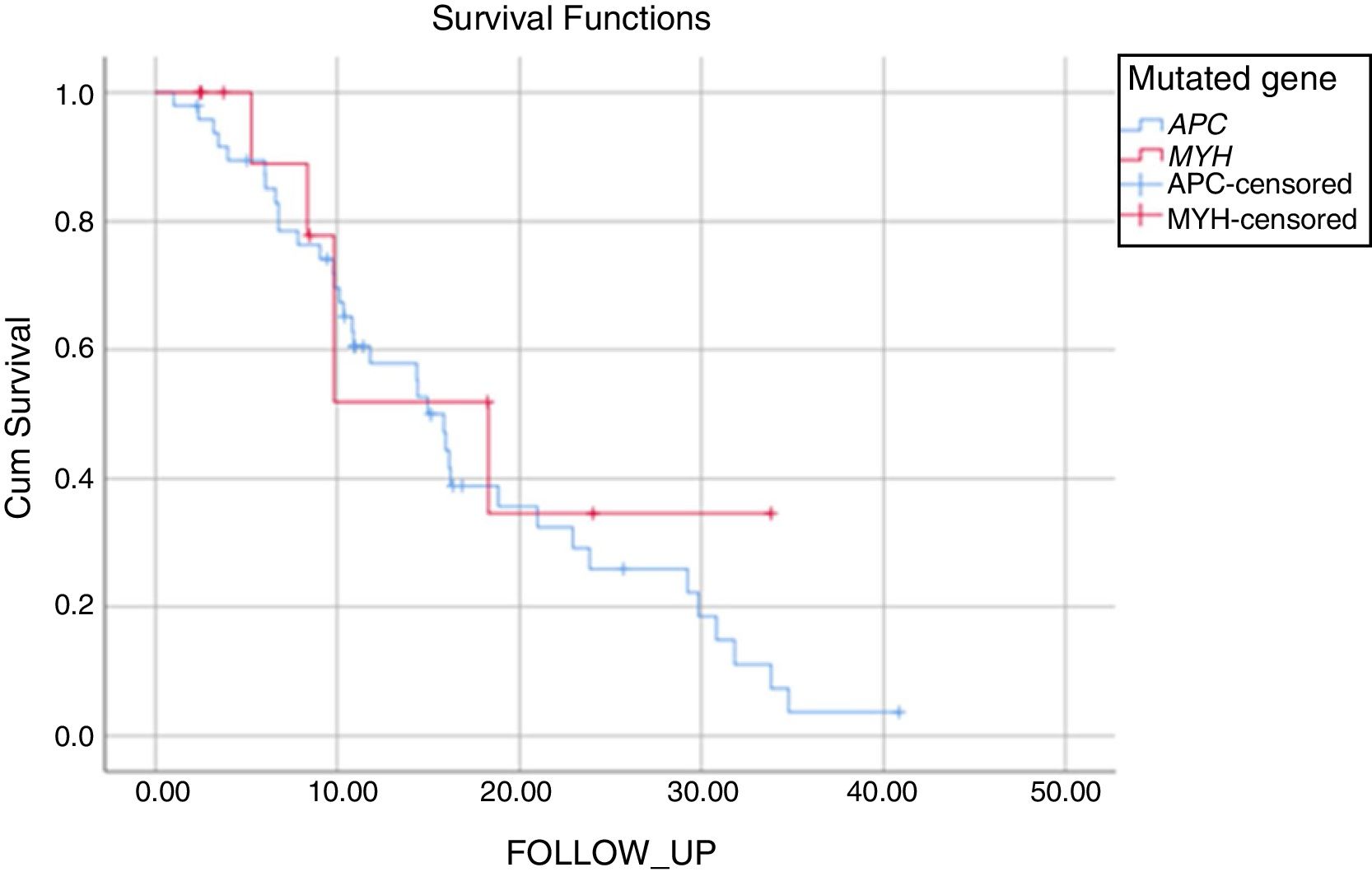
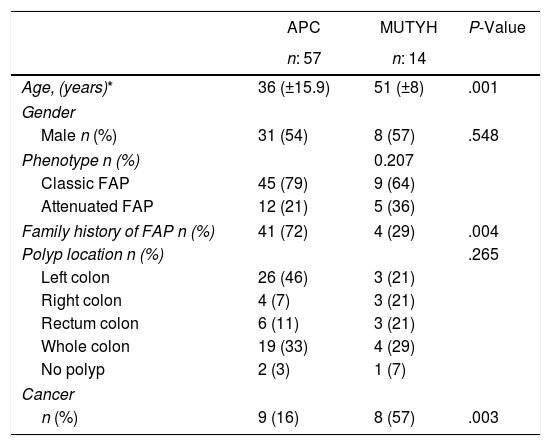
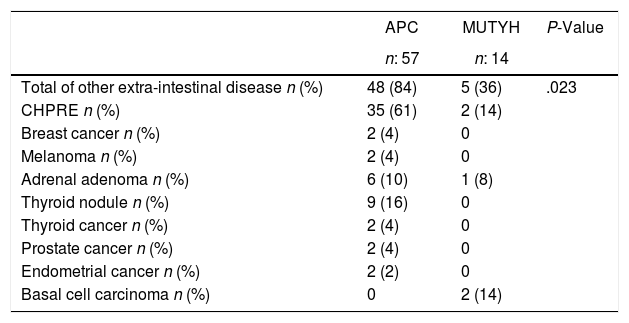
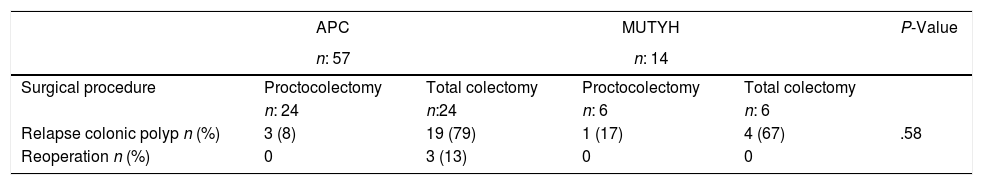
ResultsOf the total 71 patients included in the study, 14 were identified with the MUTYH gene, and 57 with the APC mutation. In patients with the APC mutation, 63% had duodenal adenoma, 61% gastric polyp and 54% had desmoid tumor. Of the patients with the MUTYH mutation, 21% had duodenal adenoma and 21% were diagnosed with gastric polyps. In 21% of the patients with APC mutation, the polyp count was <100, and 64% of those with the MUTYH mutation had >100 polyps in the colon No statistical difference was determined between the groups in respect of the proportion of patients with >100 polyps.
ConclusionThe pre-operative genetic testing of patients with polyposis coli will be useful in determining the future clinical outcome and helpful in guiding an informed decision as to whether to apply surgical treatment. It is useful to determine the colonic and extra-colonic involvement of genetic mutation diseases in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis.
La poliposis adenomatosa familiar (PAF) es una patología hereditaria, caracterizada por la existencia de pólipos y cáncer en el colon. La PAF se describe como uno de los dos tipos más frecuentes de trastornos genéticos: El gen adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) o el gen mutación Y homólogo (MUTYH), genes asociados con el síndrome polipoide. Muchas veces las diferencias clínicas y fenotipicas entre las dos alteraciones geneticas no estan claramente establecidas.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un analisis restrospectivo de las manifestaciones clinicas, criterios quirurgicos e caracteristicas histologicas, tipo de mutacion y resultados a largo plazo de pacientes diagnosticados mediante analisis genticos de poliposis adenomatosa familiar entre 1984 y 2018.
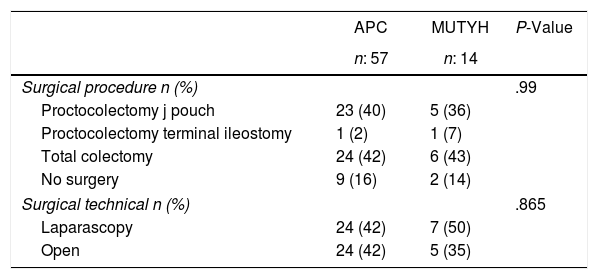
ResultadosDe un total de 71 pacientes incluidos en el estudio, en 14 de ellos se identificó mutación del gen MUTYH y en 57, mutación del gen APC. A 60 pacientes se les realizó tratamiento quirúrgico, a la mitad de ellos se les practicó proctocolectomía y a la otra mitad, colectomía total. En pacientes con la mutación APC, el 63% presentó; el 61%, y el 54%, tumor desmoide. De los pacientes con la mutación del gen MUTYH, el 21% presentó y al 21% se le diagnosticó pólipos gástricos. En el 21% de los pacientes con mutación del gen APC, el número de pólipos fue inferior a 100 y en el 64% de los pacientes que presentaron mutación del gen MUTYH se observaron más de 100 pólipos en el colon. No existió diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre lo grupos respecto a la proporción de pacientes con más de 100 pólipos.
ConclusiónEs importante valorar la afectación colónica y la extracolónica en pacientes con mutaciones genéticas asociadas a la PAF.