To analyze the likelihood of undetectable PSA (<0.01 ng/mL) after extended (ePLND) versus standard pelvic lymph-nodes dissection (sPLND) in pN+ patients.
Materials and MethodsThe institutional prospectively maintained Prostate Cancer Database was queried for patients who underwent radical prostatectomy with PLND and were found with three or less lymph-nodal metastases between 2007 and 2017. The extension of the PLND was defined according to the number of lymph-nodes (LN) removed. Patients in the 75th or higher percentile of lymph-nodes removed were considered as the ePLND group; patients in the 25th or lower percentile in the sPLND group. Groups were compared in clinical and pathological variables. Student t-test was used for comparing continuous variables; chi-square test was used for categorical variables. Multivariable logistic regression assessed the probability of undetectable PSA at 3rd month postoperatively. Kaplan–Meier method estimated the probability of biochemical recurrence. Differences between the groups were compared by Log-rank test.
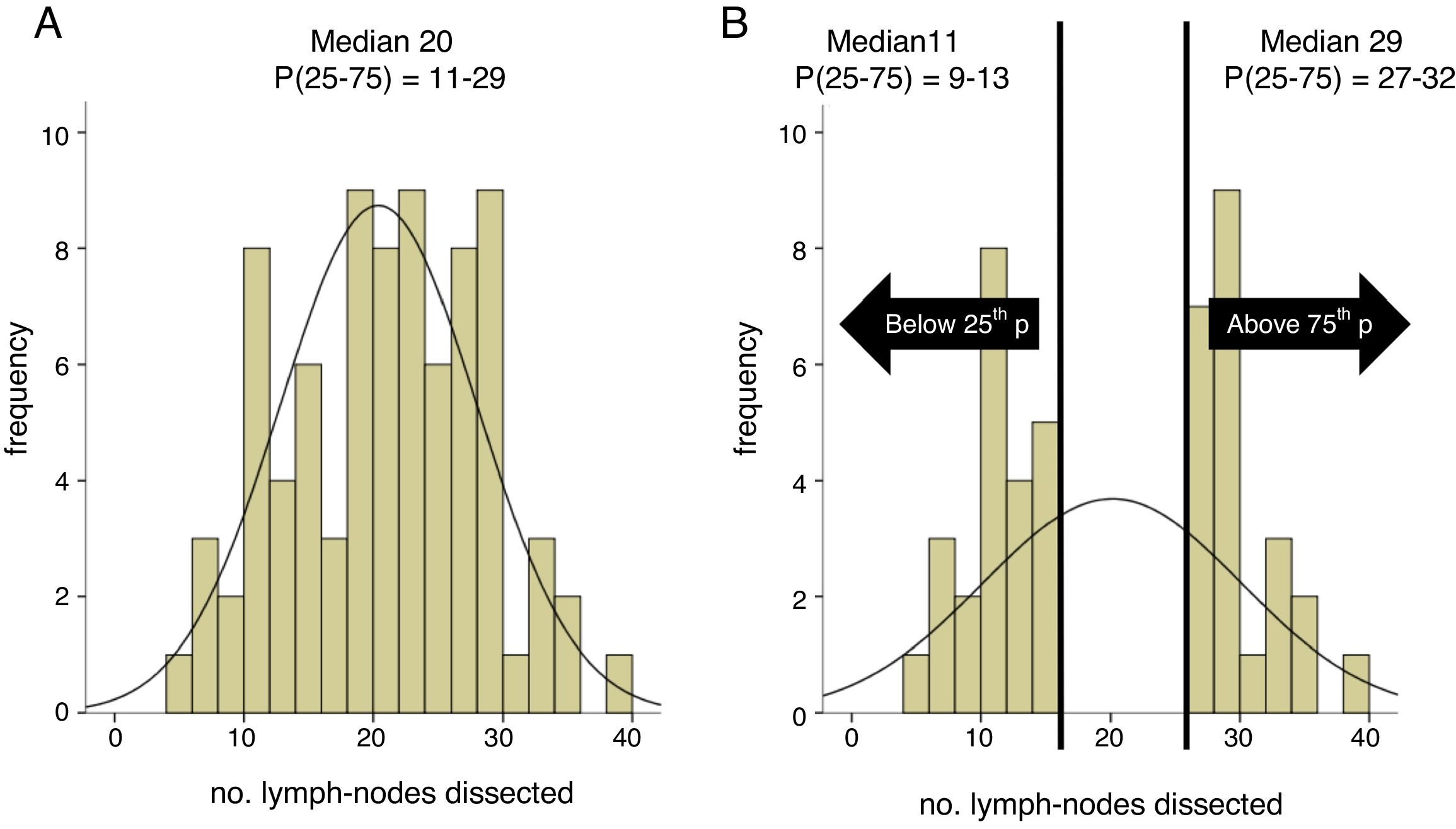
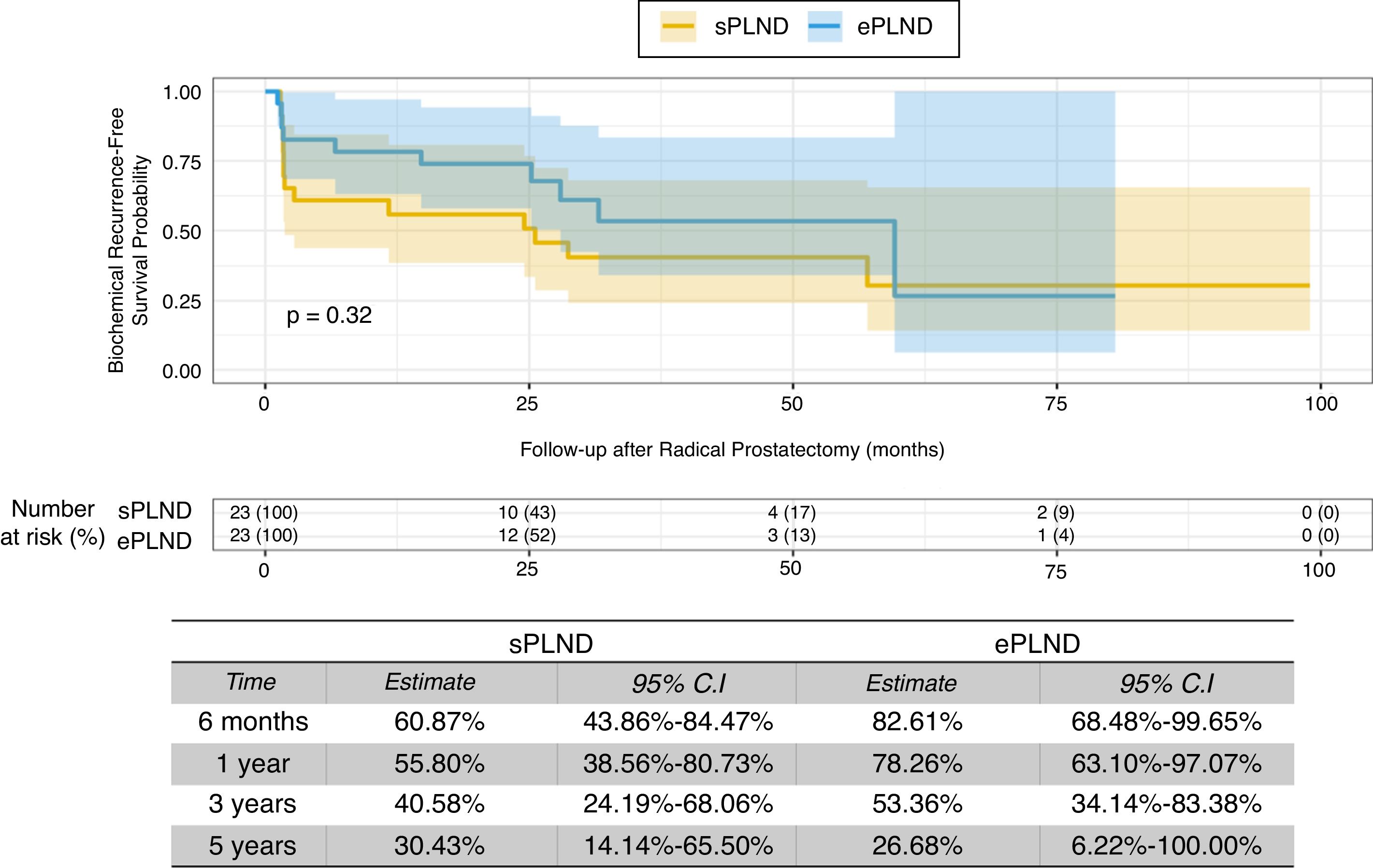
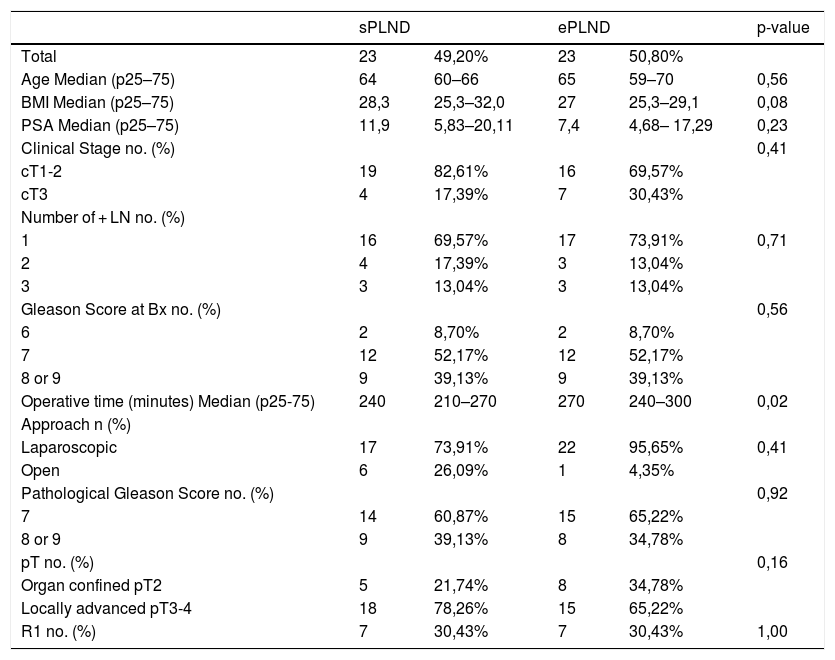
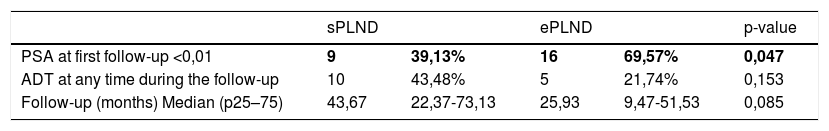
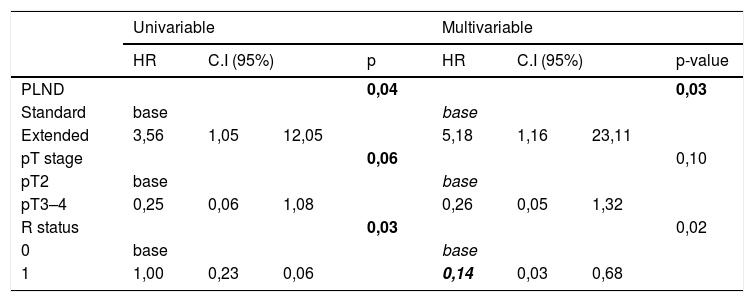
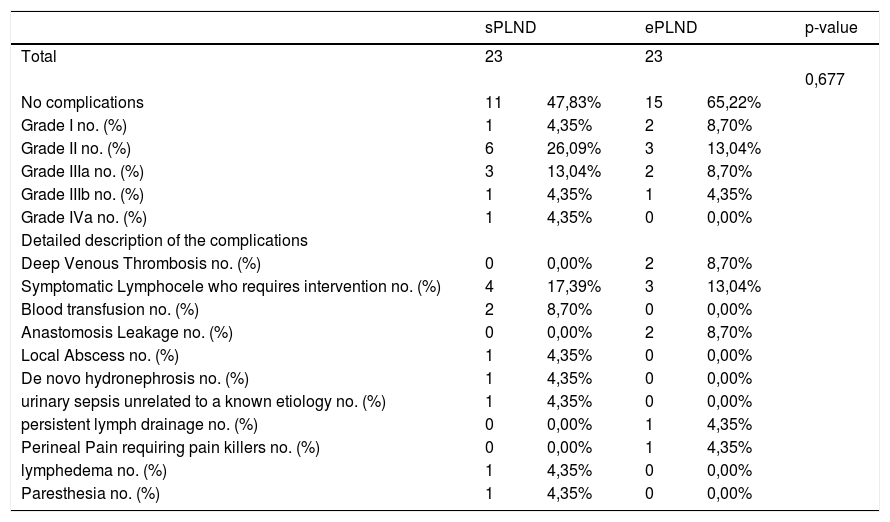
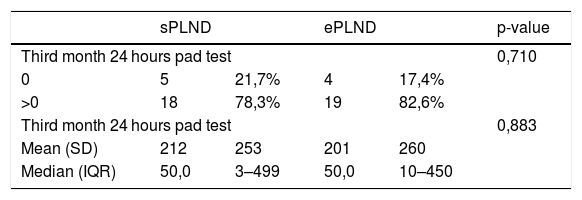
Results1478 patients were treated within the time span considered. 95 with 1–3 lymph-nodal metastases were extracted. After accounting for inclusion criteria, 23 patients with a median of 11 L N removed were included in the sPLND group (25th percentile); 23 patients with >27 L N were included in ePLND group (75th percentile). Surgical time was longer for ePLND. Sixteen patients (69.6%) who underwent ePLND had undetectable PSA postoperatively. At multivariable analysis, the probability of undetectable PSA at 3rd month was higher in patients who received an ePLND (HR = 5.18; IC95% = 1.16–23.11; p = 0.03).
ConclusionsePLND is more likely to predict undetectable PSA at third month after radical prostatectomy, irrespective of disease characteristics.
Analizar la probabilidad de PSA indetectable (<0.01 ng/mL) tras
(DGLP-ampliada) versus disección estándar de los ganglios linfáticos pélvicos (DGLP-estándar) en pacientes pN+.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó investigación en la base de datos institucional de cáncer de próstata para obtener información sobre pacientes que se sometieron a PR con DGLP con hallazgos de 3 o menos metástasis ganglionares entre 2007 y 2017.
La DGLP ampliada se definió de acuerdo al número de ganglios linfáticos (GL). Los pacientes con un percentil 75 o superior de ganglios linfáticos extraídos conformaron el grupo DGLPa; los pacientes con un percentil 25 o inferior se adjudicaron al grupo DGLPe (DGLP estándar). Se compararon las variables clínicas y patológicas entre ambos grupos. Se utilizó la prueba T de Student para comparar las variables continuas; la prueba de Chi-cuadrado para las variables categóricas. La regresión logística multivariable evaluó la probabilidad de PSA indetectable al tercer mes desde la operación. El método de Kaplan-Meier estimó la probabilidad de recurrencia bioquímica. Las diferencias entre los grupos se compararon mediante la prueba de log-rank.
ResultadosDe1478 pacientes tratados en el periodo de tiempo considerado, se seleccionaron 95 con 3 o menos metástasis en los ganglios linfáticos. Tras aplicar los criterios de inclusión, 23 pacientes con una mediana de 11 G L extraídos se incluyeron en el grupo PGLPe (percentil 25) y 23 pacientes con >27 G L se incluyeron en el grupo PGLPa (percentil 75). El tiempo quirúrgico fue más largo para el grupo de DGLPa. Dieciséis pacientes (69.6%) tratados con DGLPa presentaron PSA indetectable tras la operación. En el análisis multivariable, la probabilidad de PSA indetectable a los 3 meses fue mayor en los pacientes tratados con DGLPa (HR = 5,18; IC 95% = 1.16–23.11; p = 0.03).
ConclusionesIndependientemente de las características de la enfermedad, la DGLPa tiene más probabilidades de predecir un PSA indetectable al tercer mes tras la prostatectomía radical.