We estimate that more tan 63,000 prostate biopsies are performed in our country each year. There are no functional status data of those patients and if there is a relationship between biopsy result and functional status. In order to solve that question we have performed this study.
Material and method1128 prostate biopsies were included. Patients fill in the IPSS, IIEF-5 and ICIQ-SF questionnaires before the prostate biopsy was performed. A prospective data collection of clinical, pathological and questionnaires results was done. A descriptive analysis was carried out. IPSS and IIEF-5 results were categorized. Results were compared depending on the biopsy result. In the subgroup of patients with prostate cancer, questionnaires results were stratify according to the clinical risk group.
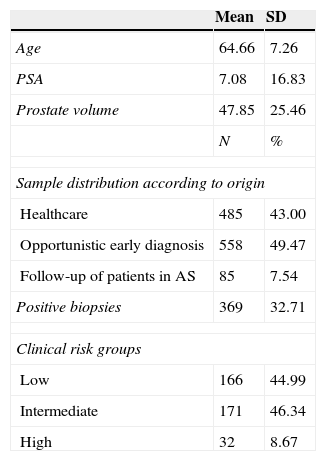
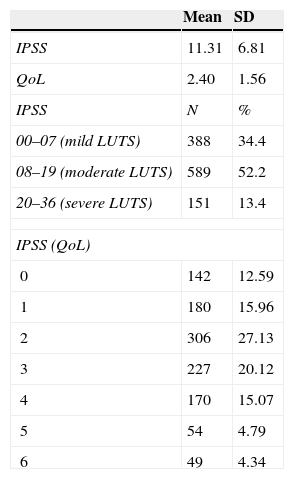
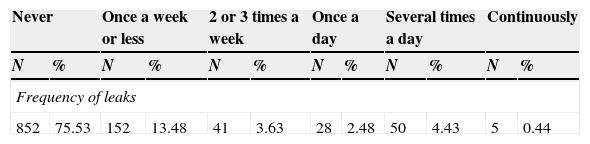
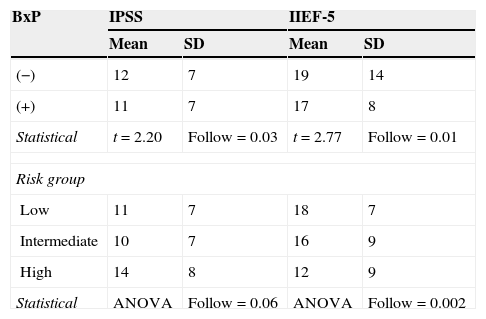
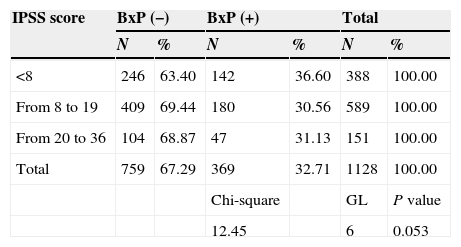
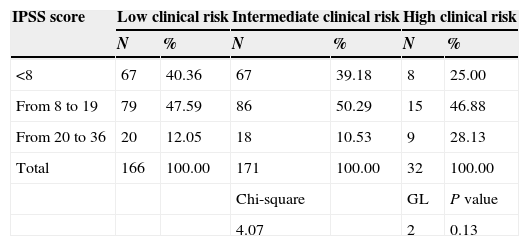
ResultsThe mean age of the sample was 65. Prostate cancer detection rate was 32.71%, 52.2% of the sample had mild lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and 13.4% had severe LUTS at the time of the biopsy. Regarding the impact of LUTS on quality of life (QOL), only 12.6% showed a perfect QOL. More than 50 percent of patients suffered from some degree of erectile dysfunction at the time of the biopsy. According to ICIQ-SF, 24% of the sample experienced some kind of urinary incontinence, although it is true that most of them classified it as small amount. Patients with a positive biopsy had a lower IPSS and IIEF-5 average score. There were no differences in the prostate cancer detection rate stratified by the severity of LUTS.
ConclusionsPatients undergoing prostate biopsy have, with a high probability, LUTS. Approximately 50% suffer from some degree of erectile dysfunction and 24% had some kind of urinary leakage.
Estimamos que en España se llevan a acabo alrededor de 63.000 biopsias de próstata. No hay datos al respecto del estado funcional de los pacientes que acuden a realizarse dicha prueba, ni de si el resultado de la biopsia responde a un patrón funcional concreto. Planteamos un estudio que resuelva el anterior planteamiento.
Material y métodoSe incluyeron 1.128 biopsias. Los pacientes cumplimentaban, antes de la biopsia, los cuestionarios: IPSS, IIEF-5 y ICIQ-SF. Se recopilaron de forma prospectiva las variables clínicas, patológicas y los resultados de los cuestionarios. Se procedió a un análisis descriptivo de la muestra a estudio, incluyendo el resultado de los cuestionarios. Se comparó el resultado medio de los cuestionarios en función de la presencia de cáncer en la biopsia. Los síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI) y de disfunción eréctil se categorizaron en grados de severidad, y se calculó la distribución de los mismos en función del resultado de la biopsia y, cuando la biopsia era positiva, del grupo de riesgo clínico.
ResultadosLa edad media de los pacientes era de 65 años. La tasa de biopsias positivas fue del 32.71%. El 52.2% refirió padecer síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI) moderados y el 13.4% severos. En cuanto a la influencia de los STUI en la CV de los pacientes solo un 12.6% refería que su vida no estaba influenciada por los STUI. El 50.76% padecía algún grado de disfunción eréctil. Según los resultados del ICIQ-SF un 24% de la muestra refería padecer algún tipo de incontinencia urinaria, si bien es cierto que la mayor parte de ellos lo etiquetaba como escapes de escasa cuantía. Los pacientes con cáncer de próstata tenían un IPSS y un IIEF-5 medio menor. No se encontraron diferencias de la tasa diagnóstica de cáncer en función de la seriedad de los síntomas del tracto urinario.
ConclusionesLos pacientes a quienes indicamos una biopsia de próstata padecen con una alta probabilidad STUI, aproximadamente un 50% tiene cierto grado de disfunción eréctil y un 24% problemas de escapes urinarios.