Prostate cancer (PC) is the malignant neoplasm with the highest incidence after lung cancer worldwide. The objective of this study is to review the literature on the methods that improve the efficacy of the current strategy for the early diagnosis of clinically significant PC (csPC), based on the performance of magnetic resonance imaging (RM) and targeted biopsies when suspicious lesions are detected, in addition to systematic biopsy.
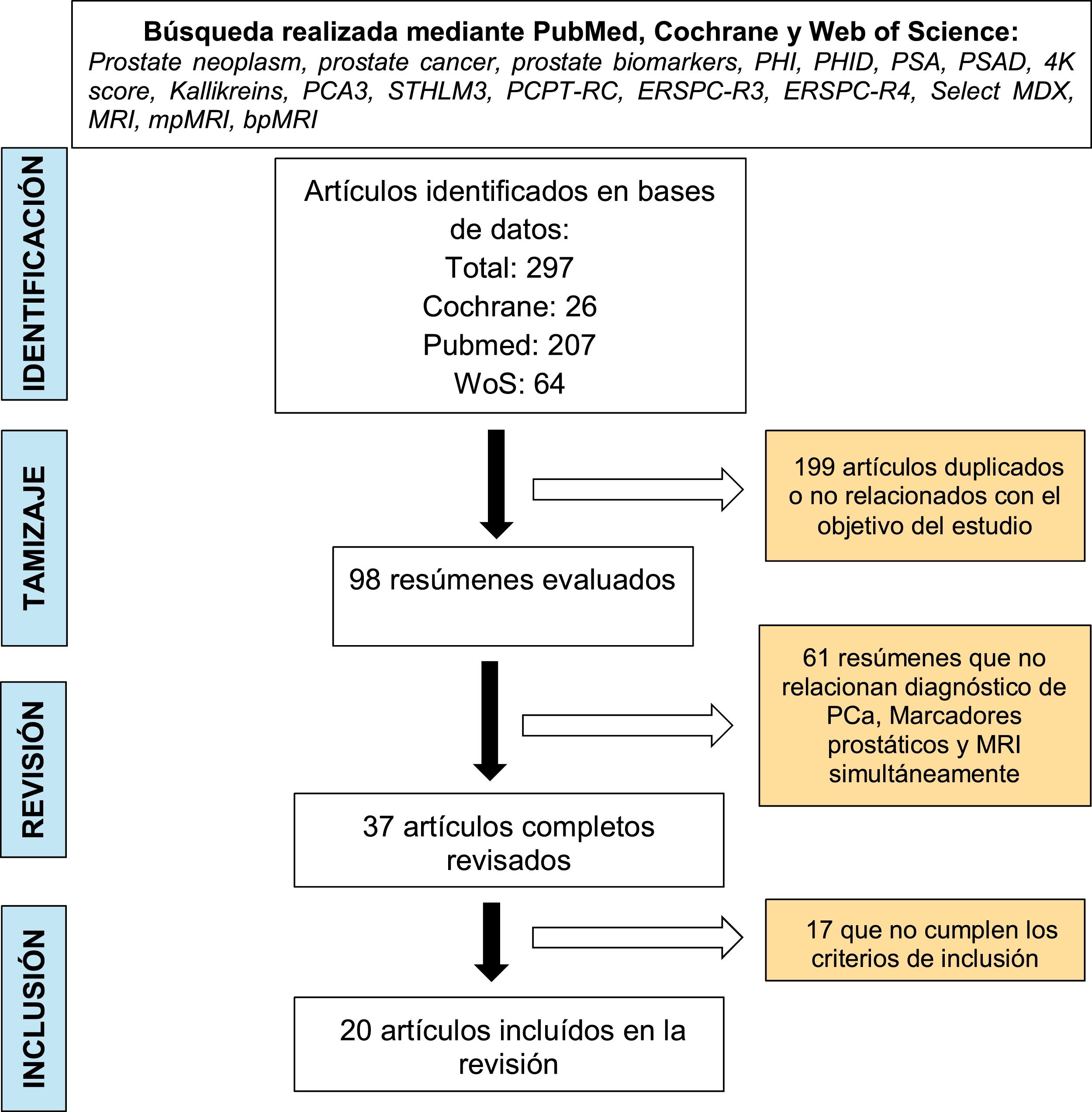
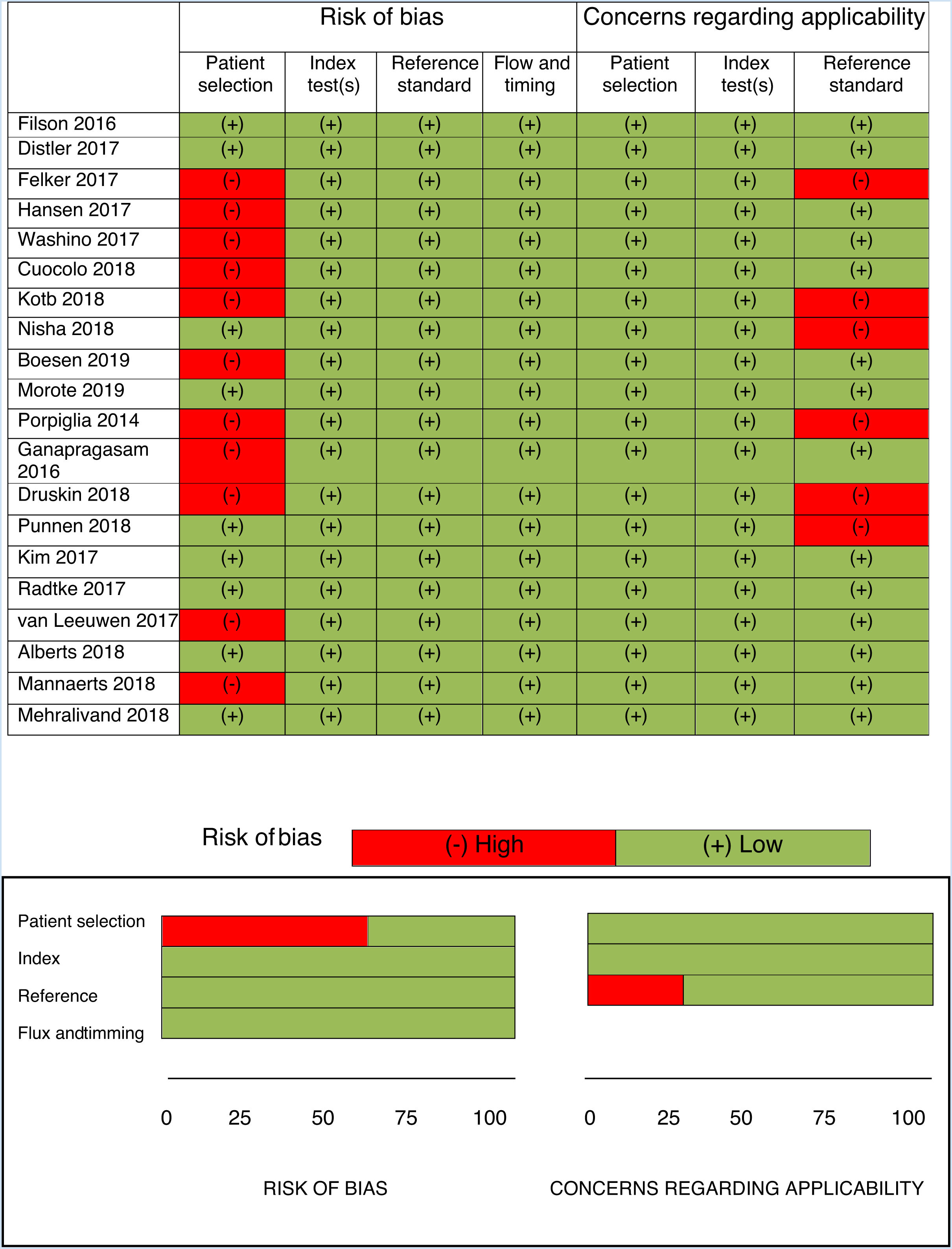
Evidence acquisitionA systematic literature review was performed in PubMed, Web of Science and Cochrane according to the PRISMA criteria (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses), using the search terms: multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging, biparametric magnetic resonance imaging, biomarkers in prostate cancer, prostate cancer y early diagnosis. A total of 297 references were identified and, using the PICO selection criteria, 21 publications were finally selected to synthesize the evidence.
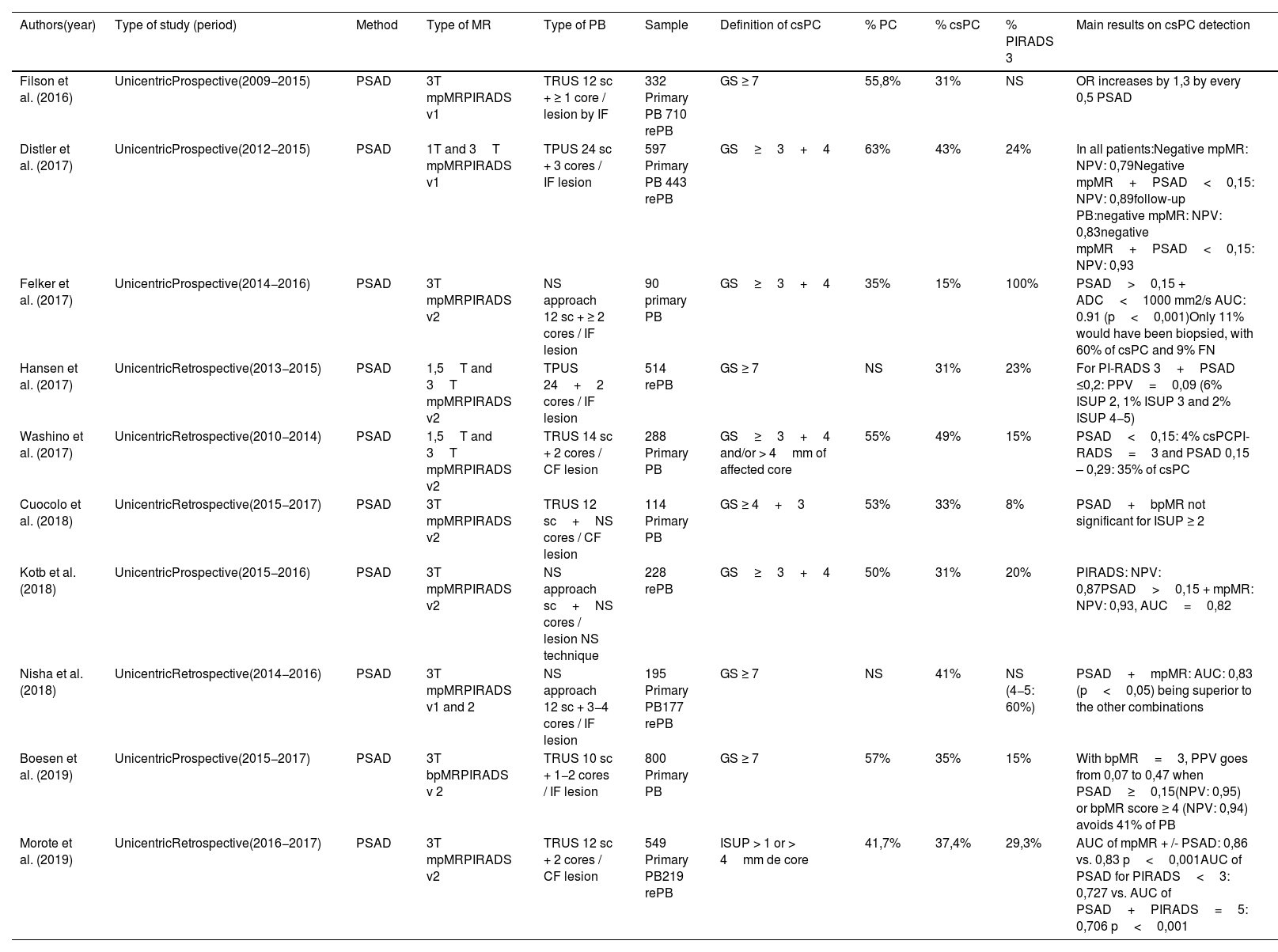
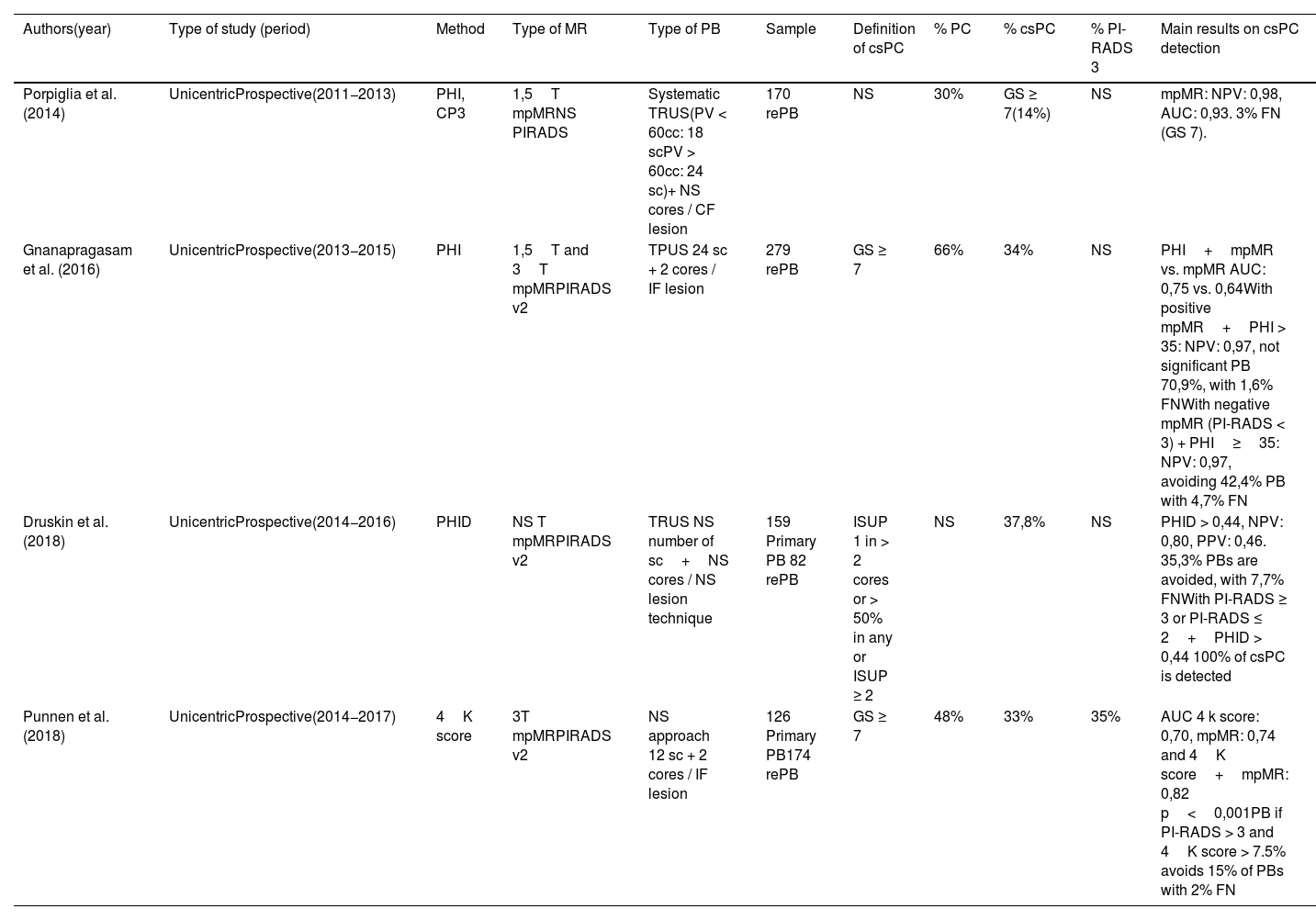
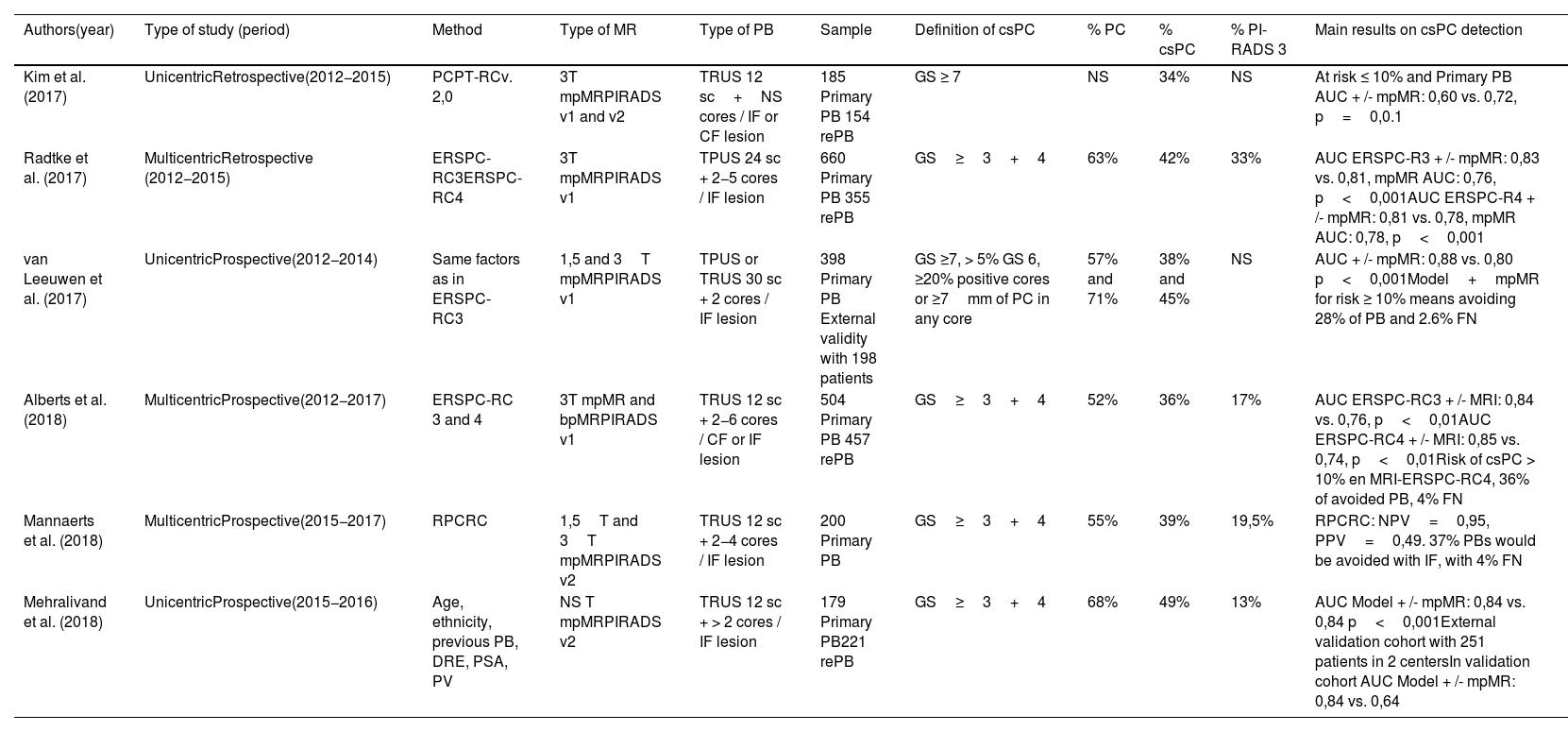
Evidence synthesisWith the consolidation of MRI as the test of choice for the diagnosis of prostate cancer, the role of PSA density (PSAD) becomes relevant as a predictive tool included in prediction nomograms, without added cost. PSAD and diagnostic markers, combined with MRI, offer a high diagnostic power with an area under curve (AUC) above 0.7. Only the SHTLM3 model integrates markers in the creation of a nomogram. Prediction models also offer consistent efficacy with an AUC greater than 0.8 when associating MRI.
ConclusionsThe efficacy of MRI in clinically significant prostate cancer detection can be improved with different parameters in order to generate predictive models that support decision making.
El cáncer de próstata (CP) es la neoplasia maligna con mayor incidencia a nivel mundial después del cáncer de pulmón. El objetivo de este estudio es revisar la literatura para conocer qué métodos permiten mejorar la eficacia de la estrategia actual de diagnóstico precoz del CP clínicamente significativo (csCP), basada en la realización de la resonancia magnética (RM) y biopsias dirigidas cuando se detectan lesiones sospechosas, además de la biopsia sistemática.
Adquisición de la evidenciaSe realizó una revisión sistemática de la literatura en PubMed, Web of Science y Cochrane según los criterios PRISMA (Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses), utilizando los términos de búsqueda: MRI multiparamétrica, MRI biparamétrica, densidad de PSA, PCA3, PHI, 4K score, cáncer de próstata, diagnóstico precoz. Se identificaron 297 referencias y, a través de los criterios de selección PICO, se seleccionaron 21 publicaciones para sintetizar la evidencia.
Síntesis de la evidenciaCon la consolidación de la MRI como prueba de elección el diagnóstico del PCa, la densidad de PSA (DPSA) es una herramienta de gran importancia incluyéndose en nomogramas predictores, sin coste añadido. La PSAD y los biomarcadores, asociando la MRI, ofrecen un poder diagnóstico elevado con un área bajo la curva (ABC) por encima del 0.7. Únicamente, el modelo SHTLM3 integra biomarcadores en la elaboración de un nomograma. Los modelos predictores ofrecen una eficacia constante en las diferentes series, con un AUC superior a 0.8 en asociación con la MRI.
ConclusionesLa eficacia de la MRI, para diagnosticar el csPCa, se puede mejorar con diferentes parámetros con el objetivo de generar modelos predictivos que apoyen la toma de decisiones.