Kidney transplantation from donors with expanded criteria has increased the pool of kidneys at the cost of a higher risk of short and long-term graft dysfunction. The main issue lies in determining which kidneys will offer acceptable function and survival compared with the risk represented by surgery and subsequent immunosuppression.
ObjectiveThe objective of our article is to review the current evidence on the tools for predicting the functionality of kidney transplantation from cadaveric donors with expanded criteria and determining the validity for their use in standard practice.
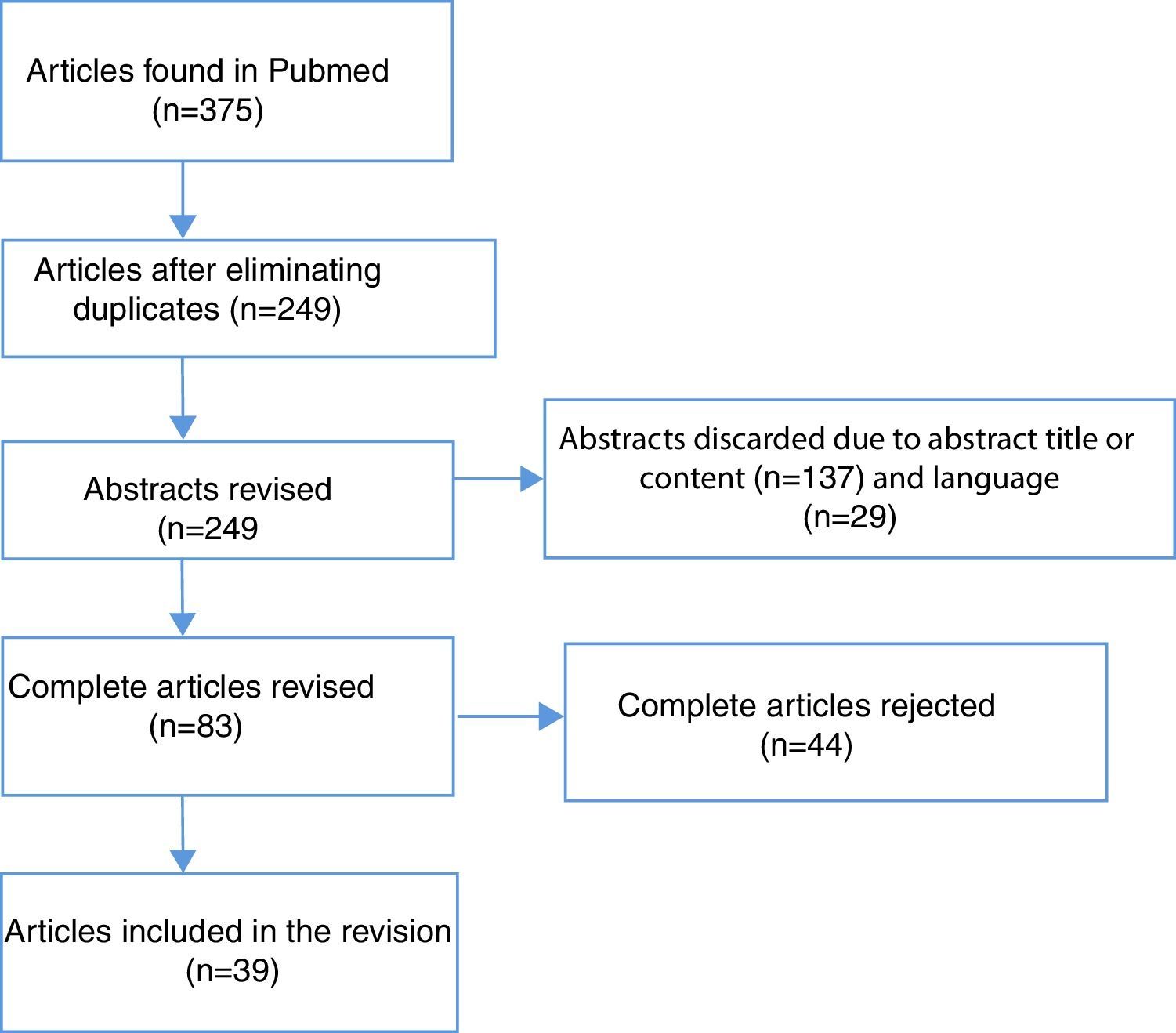
Acquisition of evidenceWe conducted a systematic literature review according to the PRISMA criteria, through Medline (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) and using the keywords (in isolation or in conjunction) “cadaveric renal transplantation; kidney graft function appraisal, graft function predictors”. We selected prospective and retrospective series and review articles. A total of 375 articles were analyzed, 39 of which were ultimately selected for review.
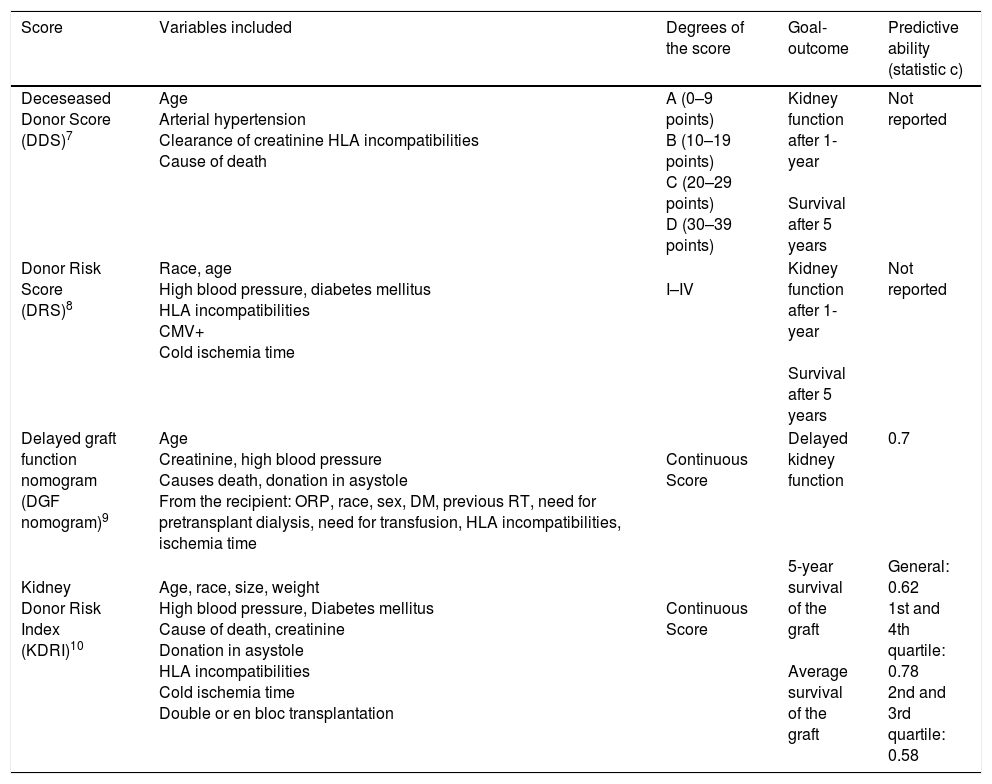
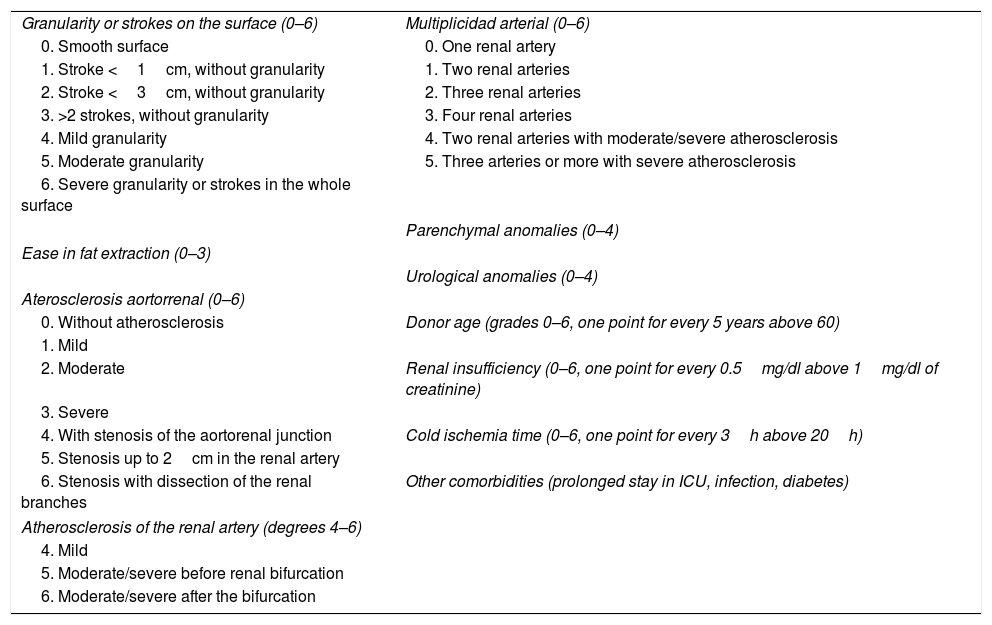
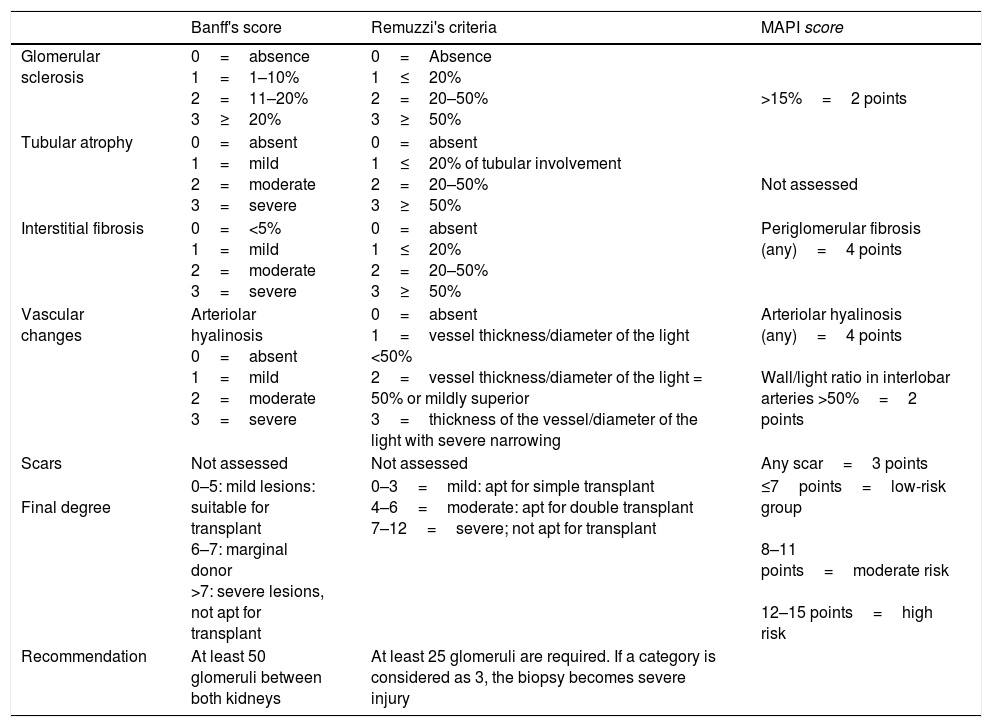
Summary of the evidenceThe predictors of functionality include the following: The donor risk indices; the calculation of the renal functional weight or the assessment of the nephronic mass; the measurement of vascular resistances during perfusion in hypothermia; the measurement of the donor's biomarkers in urine and in the perfusion liquid; the measurement of functional and reperfusion parameters in normothermia; and the measurement of morphological parameters (microscopic and macroscopic) of the target organ. In this article, we present an explanatory summary of each of these parameters, as well as their most recent evidence on this issue.
DiscussionNone of the reviewed parameters in isolation could reliably predict renal function and graft survival. There is a significant void in terms of the macroscopic assessment of kidney transplantation.
ConclusionsWe need to continue developing predictors of renal functionality to accurately define the distribution of each currently available donor kidney.
El trasplante renal de donantes con criterios expandidos ha aumentado el pool de riñones a costa de un riesgo superior de disfunción del injerto a corto y/o largo plazo. La cuestión principal reside en determinar qué riñones ofrecerán una función y supervivencia aceptables comparado con el riesgo que supone la cirugía y la posterior inmunosupresión.
ObjetivoEl objetivo de nuestro artículo es revisar la evidencia actual sobre las herramientas para predecir la funcionalidad del trasplante renal de donantes de cadáver con criterios expandidos y determinar la validez para su uso en la práctica habitual.
Adquisición de evidenciaHemos realizado una revisión sistemática de la literatura según los criterios PRISMA, a través de Medline (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), utilizando las palabras clave, aisladas o conjuntamente: cadaveric renal transplantation; kidney graft function appraisal; graft function predictors. Se seleccionaron series prospectivas y retrospectivas, así como artículos de revisión. Un total de 375 artículos fueron analizados, de los cuales 39 fueron finalmente seleccionados para revisión.
Síntesis de evidenciaEntre los predictores de la funcionalidad se encuentran: los índices de riesgo del donante; el cálculo del peso funcional renal o la valoración de la masa nefrónica; la medición de las resistencias vasculares durante la perfusión en hipotermia; la medición de biomarcadores en la orina del donante y en el líquido de perfusión; la medición de parámetros funcionales y de reperfusión en normotermia y la medición de los parámetros morfológicos, micro y macroscópicos, del órgano diana. En este artículo presentamos un resumen explicativo de cada uno de estos parámetros, así como su evidencia más reciente al respeto.
DiscusiónNingún parámetro de los revisados fue capaz de predecir por sí mismo, con fiabilidad, la función renal y la supervivencia del trasplante. Existe un importante vacío en cuanto a la valoración macroscópica del trasplante renal.
ConclusionesEs necesario continuar desarrollando los predictores de la funcionalidad renal para definir con precisión la distribución de cada uno de los riñones de los donantes que disponemos en la actualidad.