The aim of this study was to analyze the impact of surgical site infections (SSI) in patients who underwent radical cystectomy, in terms of excess hospital mortality, stay prolongation and cost overruns.
Material and methodsA retrospective observational study was conducted on a sample of patients who underwent radical cystectomy as recorded in the basic minimum data sets of 87 Spanish hospitals from 2008 to 2010.
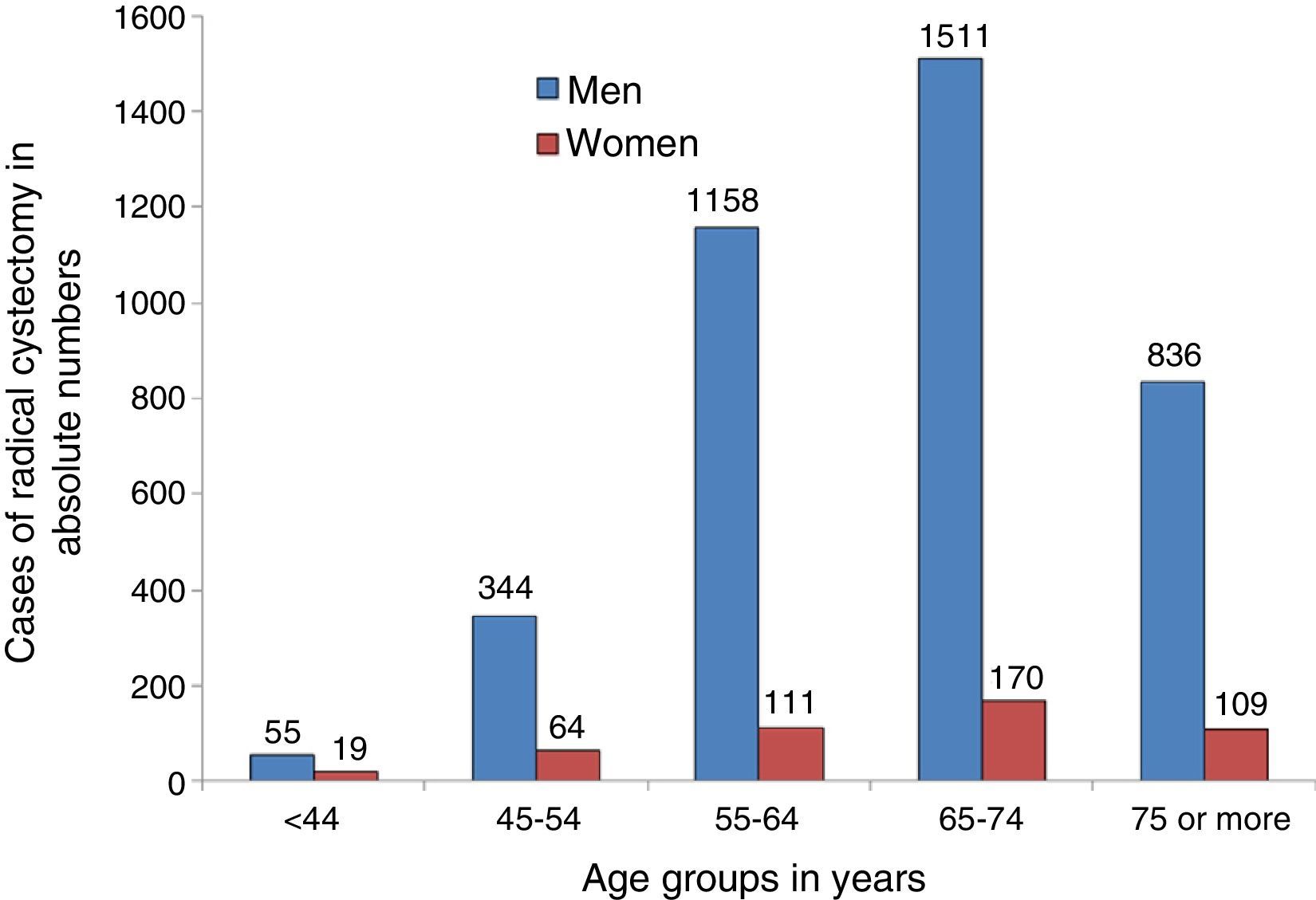
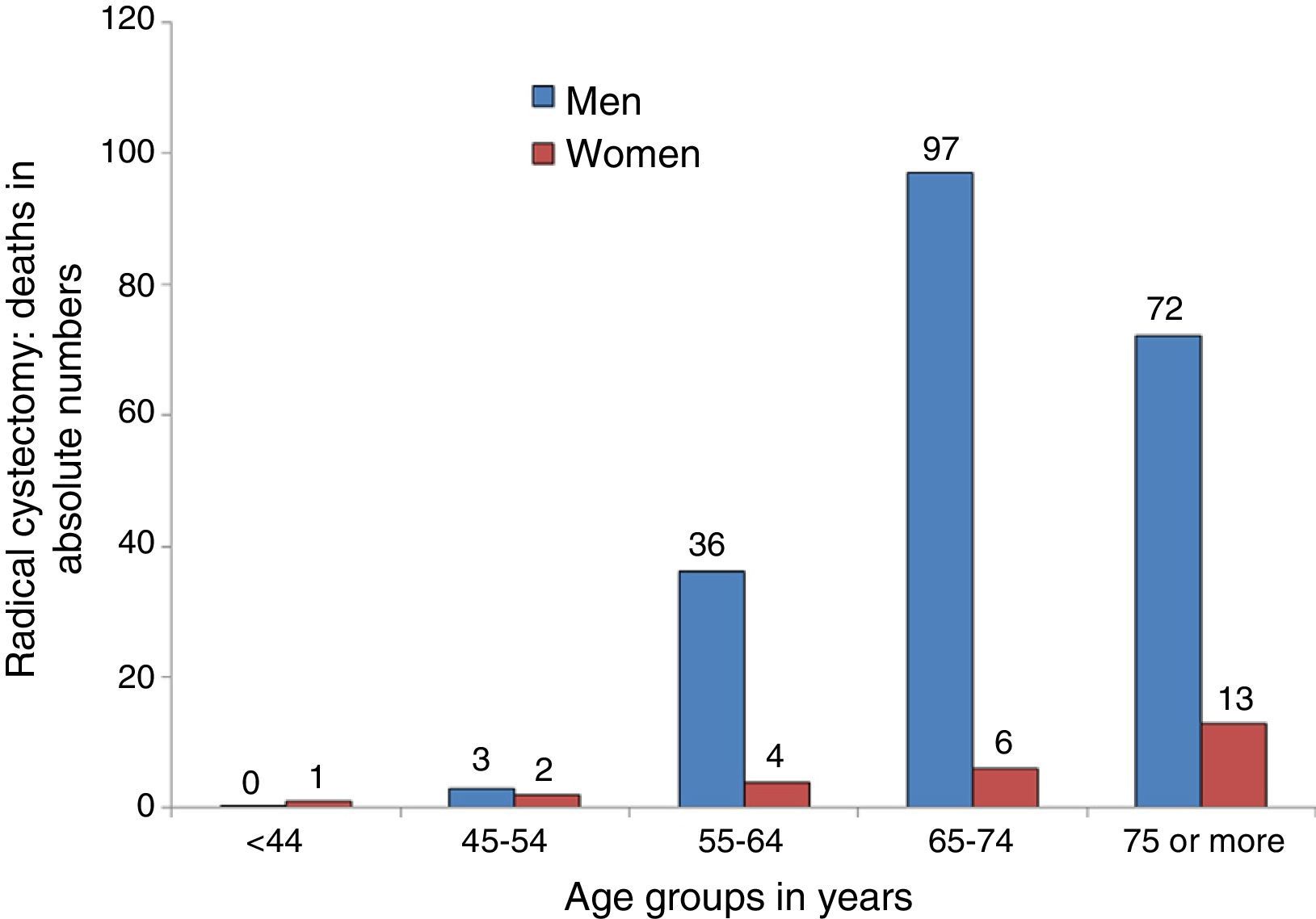
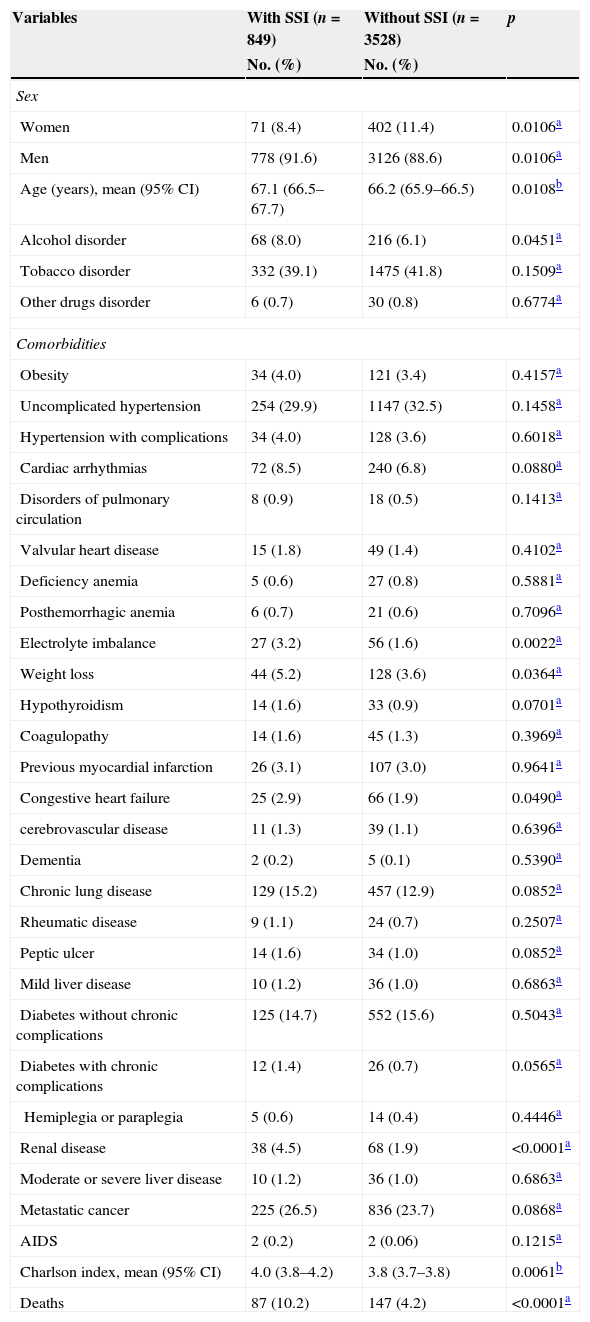
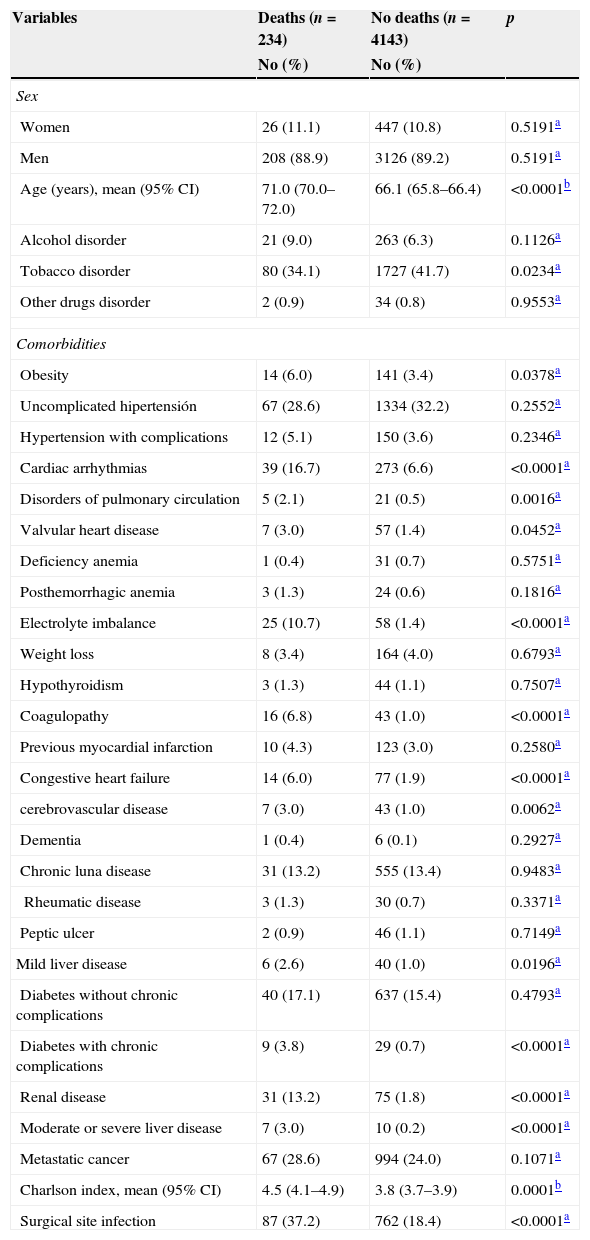
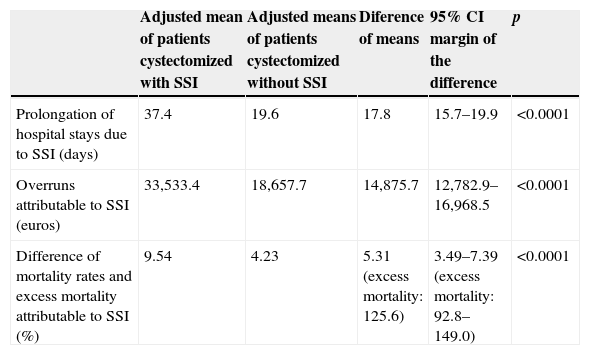
ResultsWe studied 4377 patients who underwent radical cystectomy (3904 men and 473 women) of whom 849 (19.4%) experienced a SSI. The patients with SSI were predominantly men, elderly and had a higher prevalence of alcohol-related disorders and more number of comorbidities. The patients with SSI had significant excess mortality (125.6%), undue stay prolongation (17.8 days) and cost overruns (14,875.70 euros).
ConclusionsAfter controlling for demographic variables, hospital type, addiction disorders and comorbidities using multivariate pairing, the onset of SSI in patients who underwent radical cystectomy significantly increased the mortality, stay and cost. Certain preventive measures already established in previous studies could reduce the incidence of SSI and its healthcare and financial impact.
El objetivo de este estudio es el análisis del impacto de las infecciones de localización quirúrgica (ILQ) en los pacientes tratados con cistectomía radical, en términos de exceso de mortalidad intrahospitalaria, prolongación de estancias y sobrecostes.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de una muestra de pacientes tratados con cistectomía radical recogidos en los conjuntos mínimos básicos de datos de 87 hospitales españoles durante el periodo 2008-2010.
ResultadosSe estudió a 4.377 pacientes tratados con cistectomía radical, 3.904 varones y 473 mujeres, de los cuales 849 (19.4%) experimentaron una ILQ. Los pacientes con ILQ fueron predominantemente varones, de mayor edad, con mayor prevalencia de trastornos asociados al consumo de alcohol y con más comorbilidades. Los pacientes con ILQ presentaron importantes excesos de mortalidad (125,6%), prolongación indebida de estancias (17,8 días) y sobrecostes (14.875,7 euros).
ConclusionesControlando mediante el emparejamiento multivariado las variables demográficas, el tipo de hospital, los trastornos adictivos y las comorbilidades, la aparición de ILQ en pacientes tratados con cistectomía radical aumenta significativamente la mortalidad, la duración de la estancia y su coste. Ciertas medidas preventivas ya consagradas en estudios previos podrían disminuir su incidencia y su impacto sanitario y económico.