To study the effects on the renal system in a porcine model of intraabdominal hypertension, and to determine the indirect technique of choice for determination of the intraabdominal pressure.
Materials and methods30 pigs were used and divided into two groups according to increased intraabdominal pressure values (20mm Hg and 30mm Hg). In both groups pressures were registered 8 times, summing up to 3h, with a CO2 insufflator. Three different measures of the intraabdominal pressure were taken: a direct transperitoneal measure, using a catheter of Jackson-Pratt connected to a pressure transducer, and two indirect measures, a transvesical by means of a Foley to manometer system, and a transgastric by introducing in the stomach a catheter connected to a pressure monitor with electronic hardware. Mean arterial pressure was calculated, along with the cardiac index, production of urine and serum creatinine.
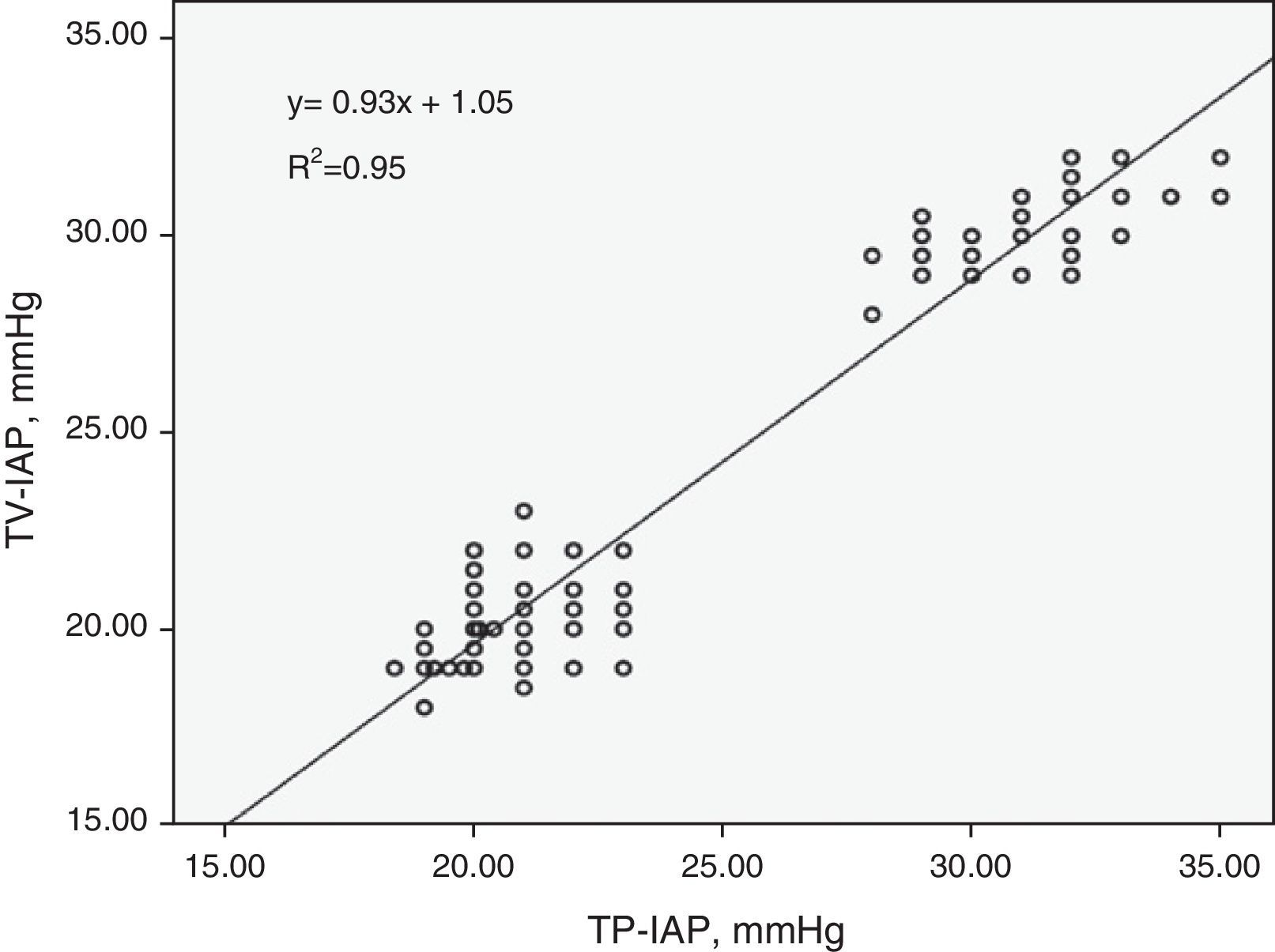
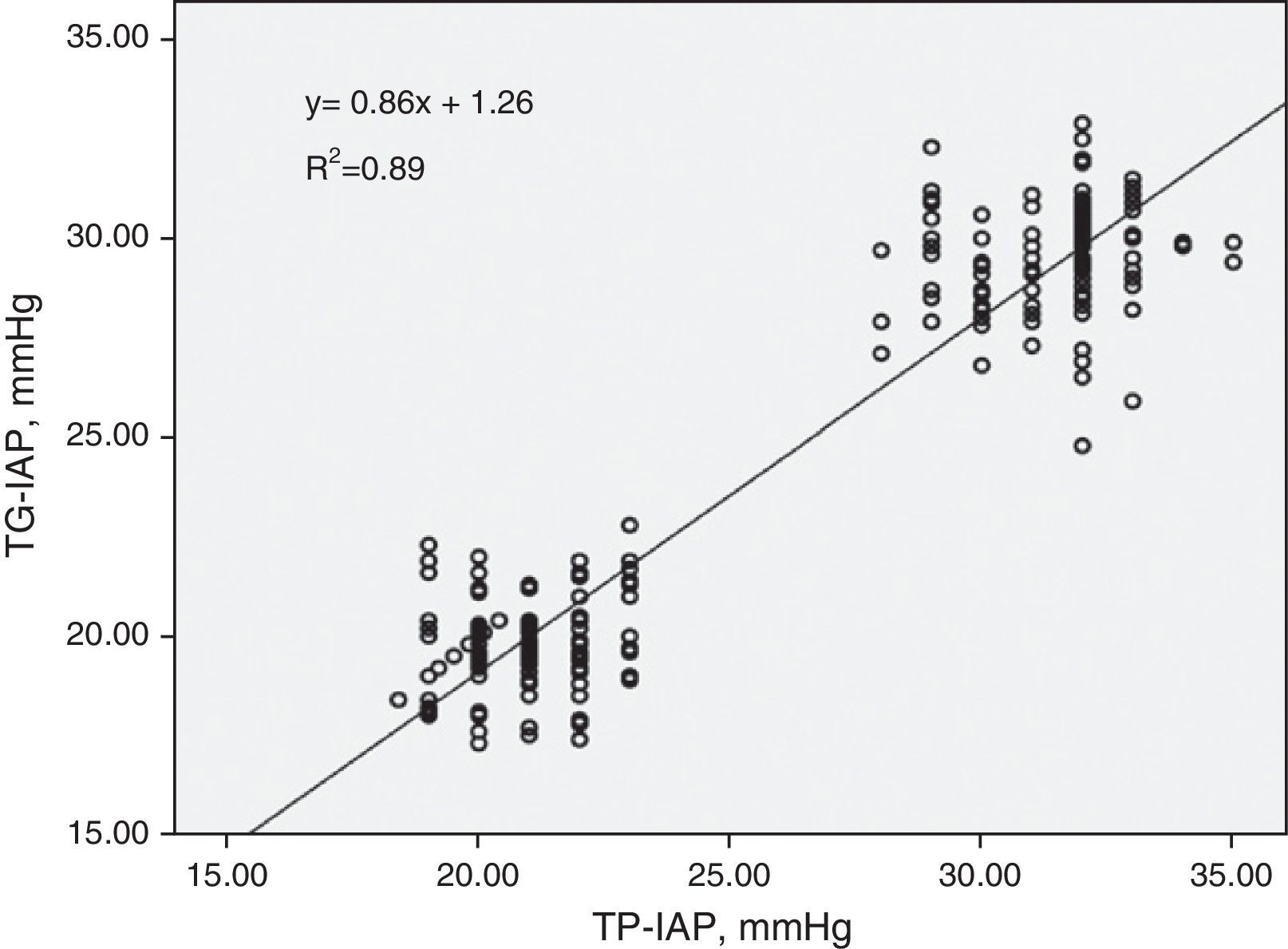
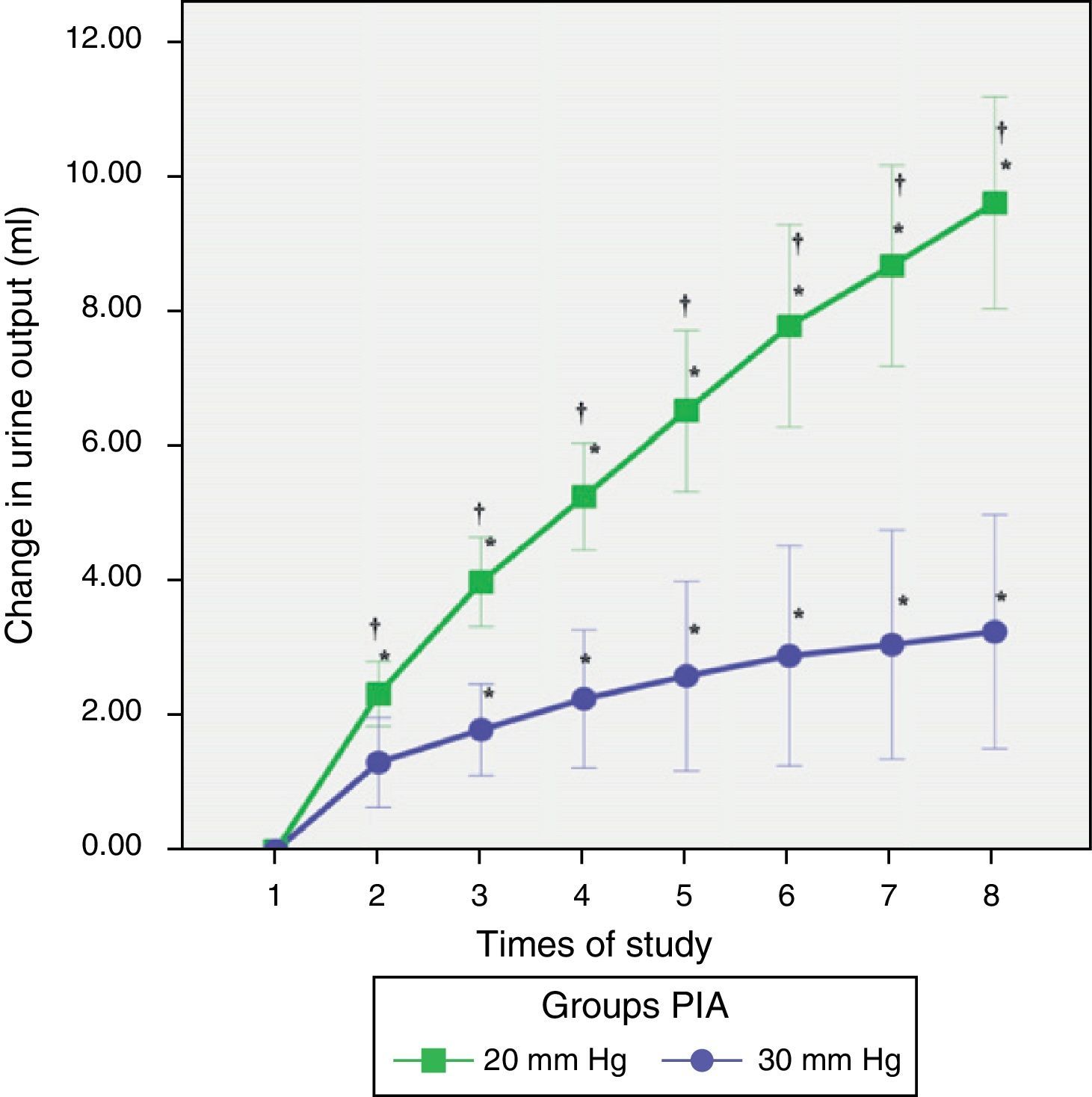
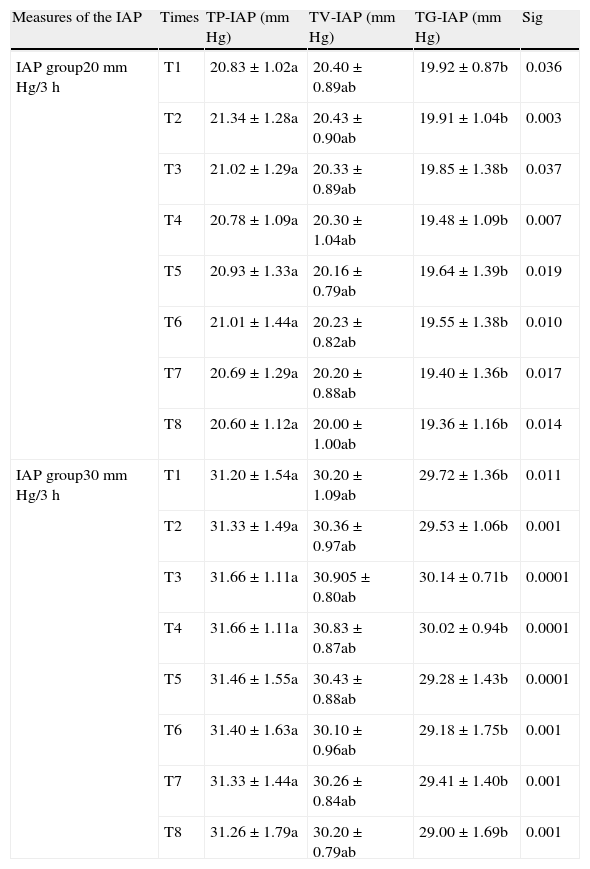
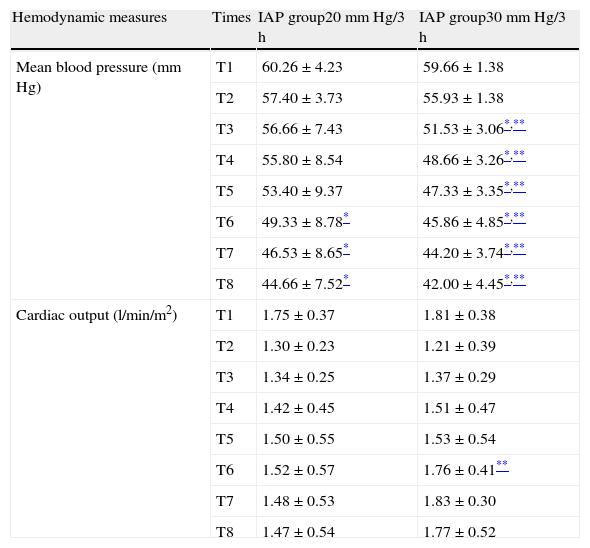
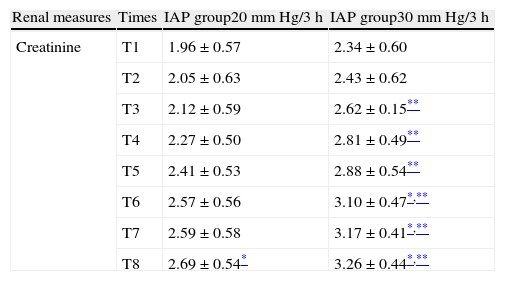
ResultsThere was a greater correlation between the transvesical and the transperitoneal intraabdominal pressures (R2=0.95). Average transgastric intraabdominal pressure was inferior to the transperitoneal indicator in all taken measurements. The average arterial pressure descended in both groups, with earlier significant differences observed at 30mm Hg (p<0.020). Urine production was lower at 30mm Hg compared with the 20mm Hg group (9.63±1.57ml versus 3.26±1.73ml). Serum creatinine increased in both groups being pathological at 30mm Hg after 1h 20min, with existing differences between early pressures (p<0.027).
ConclusionsThis study revealed marked renal affectation with higher severity at 30mm Hg pressures. The transvesical technique showed a greater correlation with the direct measurement technique used, defining this as the method of choice for determination of intraabdominal pressure.
Estudiar las consecuencias renales en un modelo porcino de hipertensión intraabdominal y determinar de la técnica indirecta de elección para la medida de la presión intraabdominal.
Material y métodosSe utilizaron 30 cerdos divididos en dos grupos, presión intraabdominal incrementada en 20mm Hg y en 30mm Hg. En ambos, las presiones se registraron en 8 tiempos hasta 3 horas con un insuflador de CO2. Se realizaron tres medidas de la presión intraabdominal, una directa trasperitoneal, empleando un catéter de Jackson-Prat conectado a un traductor de presión, y dos indirectas, una transvesical mediante un sistema de la foley manometer y otra transgástrica introduciendo en el estómago un catéter conectado a un monitor de presión con hardware electrónico. Se calculó la presión arterial media, el gasto cardiaco, la producción de orina y la creatinina sérica.
ResultadosHubo una mayor correlación entre la presión intraabdominal transvesical y la transperitoneal (R2=0,95). La media de la presión intraabdominal transgástrica fue menor que la trasperitoneal en todos los tiempos. La presión arterial media descendió en ambos grupos observando diferencias significativas más precoces a 30mm Hg (p<0,020). La producción de orina fue menor a 30mm Hg (9,63±1,57) vs (3,26ml±1,73). La creatinina aumentó en ambos grupos siendo patológica a 30mm Hg a partir de 1h 20min existiendo diferencias entre presiones precoces (p<0,027).
ConclusionesHubo afectación renal más marcada a presiones de 30mm Hg. La técnica trasvesical mostró una mayor correlación con la técnica directa empleada, por lo que consideramos ésta como la de elección.