To compare two therapeutic regimes in terms of bacterial eradication of post-menopausal with uncomplicated acute cystitis who complete antibiotic treatment.
Materials and methodsA multicenter, randomized, prospective and controlled study between two short antibiotic regimes: fosfomycin trometamol (FMT) 3g, 2 doses separated by 72h and ciprofloxacin 250mg every 12h for 3 days. A total of 118 post-menopausal women were enrolled in the study. They underwent an initial urine culture to know the responsible microorganism and susceptibility to treatment. This was repeated 5–7 days and 4 weeks after the treatment to evaluate bacterial eradication. Clinical symptoms and treatment safety were also evaluated.
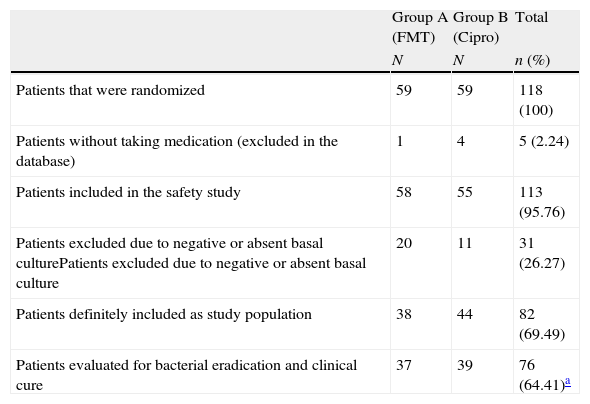
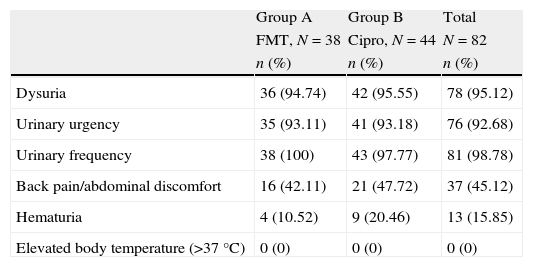
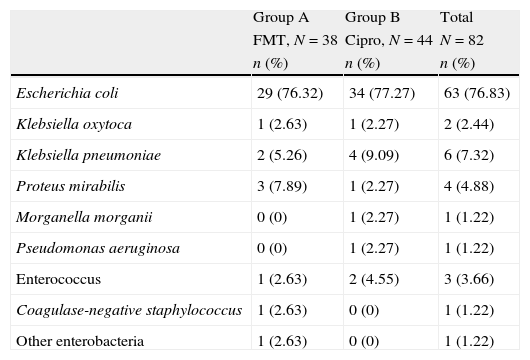
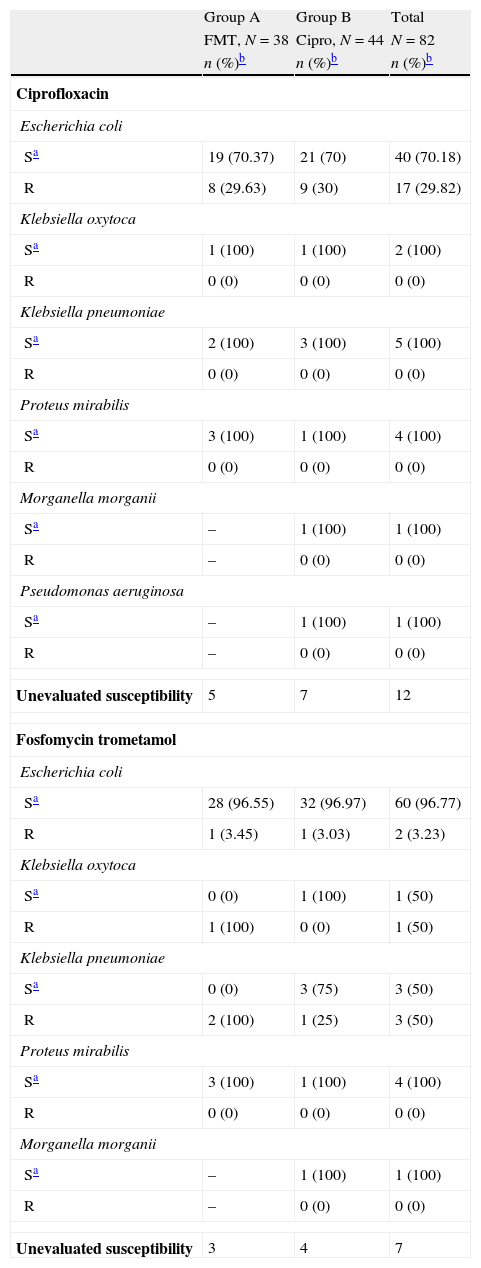
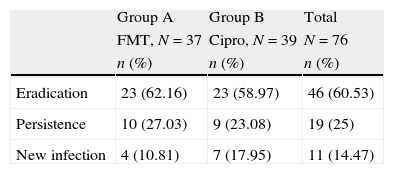
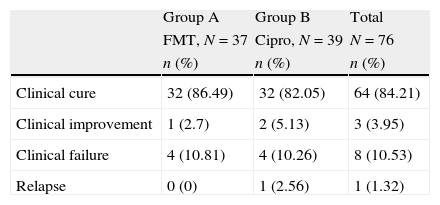
ResultsThere were microbiological data at the onset of the treatment in 82 women (69.49%). Of these, 27 did not have positive culture at the first visit (30.51%), 76 (64.41%) fulfilled all the protocol requirements and adverse effects from the treatment were collected in 113 (95.76%) of the patients enrolled in the study. The germs isolated most frequently were Escherichia coli (E. coli) (76.83%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) (7.32%), Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis) (4.89%) and Enterococo sp. (3.66%). In terms of efficacy, no differences were detected in the proportion of patients who achieved bacterial eradication between the two study arms: 62.16% of the patients who received FMT and 58.97% of those treated with ciprofloxacin (Chi-square, p=0.78). The proportion of patients who achieved clinical cure was also similar (86.49% for FMT and 82.05% for ciprofloxacin; square, p=0.59). These results indicate similar efficacy of both antibiotics in the treatment of uncomplicated lower tract urinary infection in post-menopausal women. In regards to safety data, the proportion of global adverse effects associated to the treatments was 3.45% for FMT and 9.09% for ciprofloxacin. Treatment compliance was 100% for FMT and 83.64% for ciprofloxacin.
ConclusionsThe FMT administered at a dose of 3g every 72h (2 total doses) and ciprofloxacin at a dose of 250mg every 12h during 3 days (6 total doses) have a comparable efficacy profile in lower tract urinary infection in post-menopausal women who adequately comply with the treatment, also having comparable safety. The FMT has a better antimicrobial susceptibility profile and better rate of treatment compliance.
Comparación de 2 regímenes terapéuticos en términos de erradicación bacteriana para mujeres posmenopáusicas con cistitis aguda no complicada, que completan el tratamiento antibiótico.
Material y métodoEstudio multicéntrico prospectivo aleatorizado y controlado entre 2 pautas de antibioterapia corta: fosfomicina trometamol (FMT) 3g, 2 dosis cada 72h y ciprofloxacino 250mg cada 12h durante 3 días. Se incluyeron 118 mujeres posmenopáusicas en el estudio. Se practicó cultivo de orina inicial para conocer el microorganismo responsable y la sensibilidad al tratamiento, y se repitió 5–7 días y 4 semanas después del tratamiento, para evaluar erradicación bacteriana. También se evaluaron los síntomas clínicos y la seguridad del tratamiento.
ResultadosExisten datos microbiológicos al inicio del tratamiento en 82 mujeres (69,49%), 27 no presentaron cultivo positivo en la primera visita (30,51%), completaron todos los requisitos del protocolo 76 (64,41%) y se recogieron los efectos adversos del tratamiento en 113 (95,76%) de los pacientes inicialmente incluidos en el estudio. Los gérmenes aislados con mayor frecuencia fueron Escherichia coli (E. coli) (76,83%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) (7,32%), Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis) (4,89%) y Enterococo sp. (3,66%). En términos de eficacia no se detectaron diferencias en la proporción de pacientes que consiguieron erradicación bacteriana entre los 2 brazos del estudio: 62,16% de los pacientes que recibieron FMT y 58,97% de los tratados con ciprofloxacino (Chi-cuadrado, p=0,78). La proporción de pacientes que consiguieron curación clínica fue también parecido (86,49% para FMT y 82,05% para ciprofloxacino; Chi-cuadrado, p=0,59). Estos resultados indican una eficacia parecida de ambos antibióticos en el tratamiento de la infección urinaria de vías bajas no complicada en mujeres posmenopáusicas. En lo que respecta a los datos de seguridad la proporción de efectos adversos globales asociados a los tratamientos fueron 3,45% para FMT y 9,09% para ciprofloxacino. La adherencia al tratamiento fue del 100% para FMT y del 83,64% para ciprofloxacino.
ConclusionesLa FMT administrada en dosis de 3g cada 72h (2 dosis total) y ciprofloxacino en dosis de 250mg cada 12h durante 3 días (6 dosis total) tienen un perfil de eficacia equiparable en la infección del tracto urinario inferior de la mujer posmenopáusica que completa apropiadamente el tratamiento, con una seguridad también equiparable, la FMT presenta un mejor perfil de sensibilidad antimicrobiana y mejor tasa de adherencia terapéutica.